Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chloroplast
Chloroplast
Uploaded by
Jerome Gamit0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
18 views8 pagesChloroplasts are organelles found in plant cells and algae that capture sunlight to produce sugars through photosynthesis. They contain chlorophyll which absorbs sunlight and uses the energy to convert carbon dioxide and water into glucose through light-dependent and light-independent reactions. Specifically, the light-dependent reactions use sunlight to produce ATP and NADPH, while the light-independent Calvin cycle uses these products to fix carbon dioxide into carbohydrates.
Original Description:
This shows what's inside in the chloroplast.
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentChloroplasts are organelles found in plant cells and algae that capture sunlight to produce sugars through photosynthesis. They contain chlorophyll which absorbs sunlight and uses the energy to convert carbon dioxide and water into glucose through light-dependent and light-independent reactions. Specifically, the light-dependent reactions use sunlight to produce ATP and NADPH, while the light-independent Calvin cycle uses these products to fix carbon dioxide into carbohydrates.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
18 views8 pagesChloroplast
Chloroplast
Uploaded by
Jerome GamitChloroplasts are organelles found in plant cells and algae that capture sunlight to produce sugars through photosynthesis. They contain chlorophyll which absorbs sunlight and uses the energy to convert carbon dioxide and water into glucose through light-dependent and light-independent reactions. Specifically, the light-dependent reactions use sunlight to produce ATP and NADPH, while the light-independent Calvin cycle uses these products to fix carbon dioxide into carbohydrates.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 8
Chloroplast
Chloroplast
Chloroplasts are the food
producers of the cell. The
organelles are only found
in plant cells and some protists
such as algae. Only plant cells
do have chloroplast.
Chloroplasts are one of the many unique
organelles in the body, and are generally
considered to have originated as
endosymbiotic cyanobacteria.
Photosynthetic cyanobacteria are free-
living close relatives of chloroplasts;
endosymbiotic theory posits that
chloroplasts and mitochondria(energy-
producing organelles in eukaryotic cells)
are descended from such organisms.
Function of Chloroplast
Chloroplasts capture light
energy from the sun to
convert it into sugars that can
be used by cells. The entire
process is called
photosynthesis and it all
depends on the little green
chlorophyll molecules in each
chloroplast.
The Two Stages of
Photosynthesis
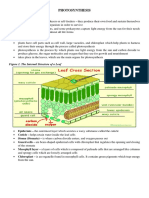
Light Dependent Reaction
Just as the name implies, light-dependent
reactions require sunlight. In the light-
dependent reactions, energy from
sunlight is absorbed by chlorophyll and
converted into stored chemical energy,
in the form of the electron carrier
molecule NADPH (nicotinamide adenine
dinucleotide phosphate) and the energy
currency molecule ATP (adenosine
triphosphate). The light-dependent
reactions take place in the thylakoid
membranes in the granum (stack of
thylakoids), within the chloroplast.
Calvin Cycle
In the light-independent reactions
or Calvin cycle, the energized
electrons from the light-
dependent reactions provide the
energy to form carbohydrates
from carbon dioxide molecules.
The light-independent reactions
are sometimes called the Calvin
cycle because of the cyclical
nature of the process.
THANK YOU FOR
LISTENING!
You might also like
- Flow of Energy and Matter in Ecosystems: Prepared By: Mr. Joselito Christian Paulus M. VillanuevaDocument9 pagesFlow of Energy and Matter in Ecosystems: Prepared By: Mr. Joselito Christian Paulus M. VillanuevaPaulus VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis ReviewerDocument4 pagesPhotosynthesis ReviewerLJ RacadioNo ratings yet
- Photosyntheis and RespirationDocument37 pagesPhotosyntheis and Respirationfelisilda.136571140273No ratings yet
- Notes Chloroplast: Characteristics of ChloroplastsDocument2 pagesNotes Chloroplast: Characteristics of ChloroplastsSamantha JerezNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis and CRDocument5 pagesPhotosynthesis and CRKhyla Grace DijenoNo ratings yet
- 2 8 PhotosynthesisDocument27 pages2 8 Photosynthesisıamnıkolaı 4No ratings yet
- Topic I: Cell: The Basic Unit of LifeDocument70 pagesTopic I: Cell: The Basic Unit of LifeJai CataluñaNo ratings yet
- Energy and The Cell: Photosynthesis and Cellular RespirationDocument45 pagesEnergy and The Cell: Photosynthesis and Cellular RespirationlovepugsNo ratings yet
- Mateo Aquiso Planas - Photosynthesis-DINBDocument6 pagesMateo Aquiso Planas - Photosynthesis-DINBMateo Aquiso PlanasNo ratings yet
- G4 BIOENERGETICS and EVIDENCE OF EVOLUTIION 2Document6 pagesG4 BIOENERGETICS and EVIDENCE OF EVOLUTIION 2niru098No ratings yet
- Integrated ScienceDocument12 pagesIntegrated ScienceMalinda GreeneNo ratings yet
- Energy TransformationDocument14 pagesEnergy TransformationJoaquine ArateaNo ratings yet
- ELS HardDocument3 pagesELS HardmppsregistrarNo ratings yet
- Differences Between Mitochondria and ChloroplastDocument10 pagesDifferences Between Mitochondria and ChloroplastAsma Adawiyah Idris100% (1)
- Write Ups Chapter 7Document12 pagesWrite Ups Chapter 7Joel CabañasNo ratings yet
- Introduction To PhotosynthesisDocument11 pagesIntroduction To PhotosynthesisSohmNo ratings yet
- Biology - Photosynthesis - Chap 7 NotesDocument14 pagesBiology - Photosynthesis - Chap 7 NotessarayoshicaNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis: 6CO2+6H2O+light Energy C6H12O6 + 6O2Document3 pagesPhotosynthesis: 6CO2+6H2O+light Energy C6H12O6 + 6O2louNo ratings yet
- Cellular Enegy CH 4 and 5Document71 pagesCellular Enegy CH 4 and 5G TeenaNo ratings yet
- PhotosynthesisDocument1 pagePhotosynthesisHatdog Ka BaNo ratings yet
- CHLOROPLASTDocument4 pagesCHLOROPLASTjyotirmoy choudhuryNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis and RespirationDocument46 pagesPhotosynthesis and RespirationCarmsNo ratings yet
- Earth and Life Science: Humss Grade 11Document22 pagesEarth and Life Science: Humss Grade 11Micaela Castillo100% (4)
- ECOSYSTEMDocument10 pagesECOSYSTEMRyanKingjimDiezUyNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis in PlantsDocument64 pagesPhotosynthesis in PlantsBianca CapadociaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 ChloroplastDocument43 pagesChapter 5 Chloroplastapi-302118206No ratings yet
- Photosynthesis PDFDocument21 pagesPhotosynthesis PDFShegNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis WorksheetDocument4 pagesPhotosynthesis WorksheetAl GNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7Document77 pagesChapter 7Joel CabañasNo ratings yet
- Gen Bio Mod 9-11Document7 pagesGen Bio Mod 9-11Arabella BrionesNo ratings yet
- Biology Unit 4 TOPIC 5: PhotosynthesisDocument8 pagesBiology Unit 4 TOPIC 5: PhotosynthesisSamara HusainNo ratings yet
- Unit 7. Autotrophic NutritionDocument48 pagesUnit 7. Autotrophic Nutritionmunyanezaolivier422No ratings yet
- Note TakingDocument1 pageNote TakingFirdausia AyuzuhriaNo ratings yet
- Structure of Chloroplasts AND Overview of PhotosynthesisDocument12 pagesStructure of Chloroplasts AND Overview of Photosynthesisapi-3859599No ratings yet
- Photosynthetic Processes: Chlorophyll and PigmentsDocument5 pagesPhotosynthetic Processes: Chlorophyll and PigmentsLyka LigsonNo ratings yet
- PhotosynthesisDocument13 pagesPhotosynthesisMina IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 Bioenergetics Review PacketDocument6 pagesUnit 3 Bioenergetics Review PacketShannon ErdmanNo ratings yet
- Biology Notes Unit TwoDocument158 pagesBiology Notes Unit TwoBlohsh KeenenNo ratings yet
- MITOCHONDRIONDocument6 pagesMITOCHONDRIONCheradee AnimNo ratings yet
- Lesson1 2Document4 pagesLesson1 2Cheradee AnimNo ratings yet
- 5A 2 Chloroplasts and ChlorophyllDocument11 pages5A 2 Chloroplasts and Chlorophyllkarima akterNo ratings yet
- Energy MetabolismDocument4 pagesEnergy MetabolismKaren ParkNo ratings yet
- Organelles and Evolution: The Endosymbiotic TheoryDocument24 pagesOrganelles and Evolution: The Endosymbiotic Theory2853hildaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3. Crop ScienceDocument57 pagesLesson 3. Crop ScienceKa Hilie Escote MiguelNo ratings yet
- KloroplasDocument26 pagesKloroplasnovela memiasihNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 PhotosynthesisDocument12 pagesChapter 10 PhotosynthesisstarcandypricessNo ratings yet
- The PhotosynthesisDocument5 pagesThe Photosynthesisamity nocedaNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis and Cellular RespirationDocument8 pagesPhotosynthesis and Cellular RespirationFatima DariaNo ratings yet
- Biology - Module 5Document11 pagesBiology - Module 5ASHLEY MONICA PLATANo ratings yet
- Biology ReviewerDocument7 pagesBiology Revieweribrahim coladaNo ratings yet
- Labbio Sat DangPhuongQuynh Prelab3Document3 pagesLabbio Sat DangPhuongQuynh Prelab3Quynh Dang PhuongNo ratings yet
- Utilizing Energy For LifeDocument41 pagesUtilizing Energy For LifeJOHN PAUL MACALLINGNo ratings yet
- PhotosynthesisDocument15 pagesPhotosynthesishurainsahar21No ratings yet
- Chloroplast and PhotosynthesisDocument19 pagesChloroplast and PhotosynthesisFizul HelmiNo ratings yet
- Nutrition in Plants 1 PDFDocument6 pagesNutrition in Plants 1 PDFNakshatra PaliwalNo ratings yet
- Definitions For Photosynthesis 1Document7 pagesDefinitions For Photosynthesis 1api-242369572No ratings yet
- BIOL111 1st Sem, Final TermDocument40 pagesBIOL111 1st Sem, Final TermJasmine CatanaNo ratings yet
- Chloroplast and Photosynthesis: For Advanced Cell and Molecular BiologyDocument33 pagesChloroplast and Photosynthesis: For Advanced Cell and Molecular BiologyJean Rose GenovaNo ratings yet
- How To Be A PlantDocument12 pagesHow To Be A PlantsextansNo ratings yet