Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Biological Control: Many Beneficial Insects Eat Their Own Species
Biological Control: Many Beneficial Insects Eat Their Own Species
Uploaded by
Muhammad Usman0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views11 pagesThis document discusses different types of biological control agents that can be used to control pest populations, including beneficial predators, parasitoids, and microbial organisms. Predators like ladybugs, lacewings, and dragonflies consume other insect pests. Parasitoids lay eggs inside host insects and larvae, eventually killing them. Microbial control uses fungi, bacteria, and viruses to infect and kill pests. While biological controls have advantages over pesticides, there are also challenges to ensure synchronization with pest life cycles and environmental conditions that impact agent effectiveness.
Original Description:
Original Title
Biological control.pptx
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document discusses different types of biological control agents that can be used to control pest populations, including beneficial predators, parasitoids, and microbial organisms. Predators like ladybugs, lacewings, and dragonflies consume other insect pests. Parasitoids lay eggs inside host insects and larvae, eventually killing them. Microbial control uses fungi, bacteria, and viruses to infect and kill pests. While biological controls have advantages over pesticides, there are also challenges to ensure synchronization with pest life cycles and environmental conditions that impact agent effectiveness.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views11 pagesBiological Control: Many Beneficial Insects Eat Their Own Species
Biological Control: Many Beneficial Insects Eat Their Own Species
Uploaded by
Muhammad UsmanThis document discusses different types of biological control agents that can be used to control pest populations, including beneficial predators, parasitoids, and microbial organisms. Predators like ladybugs, lacewings, and dragonflies consume other insect pests. Parasitoids lay eggs inside host insects and larvae, eventually killing them. Microbial control uses fungi, bacteria, and viruses to infect and kill pests. While biological controls have advantages over pesticides, there are also challenges to ensure synchronization with pest life cycles and environmental conditions that impact agent effectiveness.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 11
Biological control
Many beneficial insects eat their own species
Preying mantis and Lacewing Larvae
Predators
Omnivorous predators eat many other insects
• Dragonflies
• Damselflies
• Preying mentis
• Lacewings
• Assassin bugs
• Lady bird beetle
Predators
• Many programmes aimed at conservation of these predators accuring
naturally
Difficulties
• Move to new source when pest population is reduces for which release as
these are mobile
• May eat other beneficial insects
• Some are specialist feeding upon single host
Vidalia beetle to control cottony cushion scale
• 16% of projects have been successful for specialist predators
Parasitoid
• Mostly from Hymenoptera and Diptera but also from other orders
Egg parasitoid
• Lay eggs in each host eggs
• Parasitoid larvae develop inside the host eggs eventually killing it
• High level of parasitism achieved by egg parasitoids
• Monitoring percentage of eggs is part of IPM programme for several pest
• When sufficient high parasitism is present under field condition, insecticides
are not applied
Trichogramma
• Similarly larval parasitoids lay eggs inside the larvae
• Adult lay one to several eggs in the host larvae
Ichneumodis and Braconids
• Most of the adult of parasitoids feed upon nectars
Disadvantages
• Host searching capacity may be strongly reduced duo to weather condition
• Only female search
• Often best searcher lay fewer eggs
Synchronization
Causing the parasitoids to fail to reduced host population
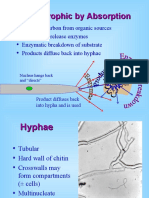
Microbial control
• Control the pest by micro organism
• Bacteria, virus, fungi and nematodes are microbial control agent
Epizootic
• An epidemic of pathogens against arthropods
• Under favorable condition epizootic can kill the insect resulting in a
population crash
Fungi
• Fungi of genus Entomophthora
• Kill the aphid lepidopterans caterpillars and grasshoppers
• Fungi require moisture, so under dry conditions delays may occur that allow
the pest populations to explore
Beauveria bassiana
Metarrhizium
Bacteria
• Bacillus thuringensis is the most widely used pathogens
• Bt produces an insecticidal crystal protein known as endotoxin
• When endotoxin is ingested by insect larvae it becomes toxic
• There are different strains of Bt
• Bt is non toxic to worm blooded animals
Lepidopterans pests
Viruses
• Record from Lepidoptera, Hymenoptera and Diptera
• After ingestion insect show no symptoms for 4 days to 3 weeks
• Dead larvae hang from the tops of the plants
• Difficult to culture
You might also like
- Alien Taxonomy ProjectDocument14 pagesAlien Taxonomy Projectapi-27604256733% (3)
- Maternal Anatomy WilliamsDocument60 pagesMaternal Anatomy WilliamsZari Novela100% (2)
- Basic Lesson Plan Class 8 Microorganism Friend and FoeDocument53 pagesBasic Lesson Plan Class 8 Microorganism Friend and FoeRasika PK Gore86% (22)
- Development of Uterus and Congenital Anomalies: Done By: Jabir AL Araimi ID# 0333145Document21 pagesDevelopment of Uterus and Congenital Anomalies: Done By: Jabir AL Araimi ID# 0333145jabirNo ratings yet
- Infectious DiseaseDocument81 pagesInfectious DiseaseAmit Gandhi67% (3)
- IPM MealybugsDocument24 pagesIPM Mealybugskumail100% (1)
- Chapter 3.nature of Biological Control AgentsDocument80 pagesChapter 3.nature of Biological Control AgentsExposer NBNo ratings yet
- Microbial Control of Insect-PestsDocument46 pagesMicrobial Control of Insect-PestsLalani AakashNo ratings yet
- Predation and ParasitismDocument23 pagesPredation and Parasitismvera febriyantiNo ratings yet
- Control de Mosques - Alternatives Al Control Quã Mic - 2023Document41 pagesControl de Mosques - Alternatives Al Control Quã Mic - 2023Claudia Romero ManriqueNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4. Predation and ParasitismDocument17 pagesLesson 4. Predation and ParasitismShaneen AngeliqueNo ratings yet
- Integrated Pest Management For Corn (Zea MaysDocument21 pagesIntegrated Pest Management For Corn (Zea MayscholzNo ratings yet
- Classification of FungiDocument17 pagesClassification of Fungicyrilsenior06No ratings yet
- Molecular Cell Biology Prof. D. Karunagaran Department of Biotechnology Indian Institute of Technology MadrasDocument7 pagesMolecular Cell Biology Prof. D. Karunagaran Department of Biotechnology Indian Institute of Technology Madrasvignesh9489No ratings yet
- Submitted By:: Vaniya Ravikumar G. REG NO: 2010118141 Plant Pathology 2 SEMESTER M.Sc. (Agri) N.M.C.A, N.A.U, NAVSARIDocument13 pagesSubmitted By:: Vaniya Ravikumar G. REG NO: 2010118141 Plant Pathology 2 SEMESTER M.Sc. (Agri) N.M.C.A, N.A.U, NAVSARIRAMESH CHAUDHARYNo ratings yet
- Management of Pest and Diseases of MushroomDocument23 pagesManagement of Pest and Diseases of MushroomRudhranNo ratings yet
- Pranjali BiocontolDocument59 pagesPranjali BiocontolParas AryaNo ratings yet
- Raj PPT - 2Document25 pagesRaj PPT - 2SarojNo ratings yet
- Biopesticides and Integrated Pest ManagementDocument22 pagesBiopesticides and Integrated Pest ManagementaiswaryadashNo ratings yet
- Biodiversity: Protista MoneraDocument11 pagesBiodiversity: Protista MoneraridwanNo ratings yet
- Kingdom: FUNGI: DR /amr El-SayedDocument42 pagesKingdom: FUNGI: DR /amr El-Sayedomar mohamedNo ratings yet
- Parasitiod Lecture 7Document17 pagesParasitiod Lecture 7Muhammad uzairNo ratings yet
- Pest ManagementDocument34 pagesPest ManagementDr. Mohammed SayedNo ratings yet
- Week 7 PP10 LecturesDocument34 pagesWeek 7 PP10 LecturesHannymie maurealNo ratings yet
- Biological Control of PestsDocument12 pagesBiological Control of PestsAdlin PricillaNo ratings yet
- Bio PesticideDocument13 pagesBio PesticideArun MalhotraNo ratings yet
- Day 2 Additional Lecture Notes For Genetics Cell Bio Microbio and AnaphyDocument91 pagesDay 2 Additional Lecture Notes For Genetics Cell Bio Microbio and AnaphyJeffrey PolisticoNo ratings yet
- Management of Rice Diseases: Nancy P. CastillaDocument50 pagesManagement of Rice Diseases: Nancy P. CastillaHilierima MiguelNo ratings yet
- Natural EnemiesDocument34 pagesNatural EnemiesAsimNo ratings yet
- PESTICIDESDocument65 pagesPESTICIDESMuhammad Masoom AkhtarNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Parasitology'23 230517 171647Document135 pagesIntroduction To Parasitology'23 230517 171647lawrencenandowNo ratings yet
- 14042020151201class Note Lecture 3-Predator and Parasitoids Final1Document10 pages14042020151201class Note Lecture 3-Predator and Parasitoids Final1vidhya associateNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - MT 112 TermsDocument9 pagesChapter 1 - MT 112 TermsJessie AzarragaNo ratings yet
- Detrimental Insects GraceDocument24 pagesDetrimental Insects GraceGraceNo ratings yet
- Parasite and Communicable Disease PDFDocument58 pagesParasite and Communicable Disease PDFDr Dhruva PrasadNo ratings yet
- Integrated Pest Management On Vegetables For Insect Pests and Vectors in South TexasDocument20 pagesIntegrated Pest Management On Vegetables For Insect Pests and Vectors in South TexasCharlote MontefalconNo ratings yet
- 3 KingdomsDocument8 pages3 KingdomsJan AglibotNo ratings yet
- Roles of Insects For HumanDocument58 pagesRoles of Insects For Humannovita manaluNo ratings yet
- Survival Mechanisms of Plant Pathogens & Disease ManagementDocument16 pagesSurvival Mechanisms of Plant Pathogens & Disease ManagementSri MulyaniNo ratings yet
- Microbial InsecticideDocument8 pagesMicrobial InsecticidebiosciencesNo ratings yet
- Non Pesticide ManagementDocument34 pagesNon Pesticide Managementapi-441599558No ratings yet
- CH 26 - The FungiDocument29 pagesCH 26 - The FungiBronwyn JuliusNo ratings yet
- Arthropods of Medical ImportanceDocument6 pagesArthropods of Medical ImportanceMarlon Ursua BagalayosNo ratings yet
- Yeasts 2023Document82 pagesYeasts 2023am6443559No ratings yet
- Bio330 Exp 1Document43 pagesBio330 Exp 1patriciaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Medical Mycology 2023Document54 pagesIntroduction To Medical Mycology 2023Samuel fikaduNo ratings yet
- Uc 2 Hand Out 2Document15 pagesUc 2 Hand Out 2Mercy BonggoNo ratings yet
- Biological Control of PathogensDocument28 pagesBiological Control of PathogensFrederick M. CiriacoNo ratings yet
- Biological Pest ControlDocument32 pagesBiological Pest ControlTaufiqul ArifNo ratings yet
- Introduction To ParasitologyDocument21 pagesIntroduction To Parasitologyning ningNo ratings yet
- Protists and FungiDocument25 pagesProtists and Fungichasing catNo ratings yet
- Parasites - Protists & ArthropodsDocument85 pagesParasites - Protists & ArthropodsNicoelNo ratings yet
- Domain Kingdom PhylumDocument74 pagesDomain Kingdom PhylumRia PerezNo ratings yet
- 4 - Integrated Pest ManagementDocument60 pages4 - Integrated Pest ManagementAnkit RathaurNo ratings yet
- MicroorganismsDocument2 pagesMicroorganismsAngelika TibayanNo ratings yet
- 6 Kingdoms of Life Lecture NotesDocument83 pages6 Kingdoms of Life Lecture Notesledereh1No ratings yet
- Nature of Biological Control AgentsDocument16 pagesNature of Biological Control Agentsnida.ratillaNo ratings yet
- Hibiscus ProblemsDocument60 pagesHibiscus ProblemsShantanu HolkarNo ratings yet
- Kingdom FungiDocument31 pagesKingdom Fungiraul sinatoNo ratings yet
- CPRO 0413 IV. Insect PathologyDocument42 pagesCPRO 0413 IV. Insect PathologyKay PonilasNo ratings yet
- Abaca Common Pest and DiseasesDocument25 pagesAbaca Common Pest and Diseasesfrances tabuyogNo ratings yet
- The Mycophile's Handbook: From Spores to Harvest: Your Comprehensive Guide to MushroomFrom EverandThe Mycophile's Handbook: From Spores to Harvest: Your Comprehensive Guide to MushroomNo ratings yet
- Birds in Georgia Part 1Document293 pagesBirds in Georgia Part 1ASAP Wildlife RemovalNo ratings yet
- On The Farm: CAT Duck Donkey DOG COW Goat Rabbit Horse HEN SheepDocument2 pagesOn The Farm: CAT Duck Donkey DOG COW Goat Rabbit Horse HEN SheepAndreea IoanaNo ratings yet
- Activity in Science No 4-5Document4 pagesActivity in Science No 4-5Zeph Quinton100% (2)
- Vaccination in Broilers Farming and Disease Control - AgrifarmingDocument3 pagesVaccination in Broilers Farming and Disease Control - AgrifarmingMadan Mohan Sharan SinghNo ratings yet
- Straightforward Upp Int Scope and SequenceDocument4 pagesStraightforward Upp Int Scope and SequencestudentNo ratings yet
- Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary EducationDocument4 pagesCambridge International General Certificate of Secondary EducationlachippaNo ratings yet
- ParrotsDocument1 pageParrotsglh00No ratings yet
- The Digestive SystemDocument17 pagesThe Digestive SystemHHHNo ratings yet
- A and B Graded Semen Stations in IndiaDocument6 pagesA and B Graded Semen Stations in IndiaVicky VickyNo ratings yet
- Kenneth Patchen 2004 9Document35 pagesKenneth Patchen 2004 9NyX 17No ratings yet
- De Tham Khao 8Document8 pagesDe Tham Khao 8Trầnn HàphươnggNo ratings yet
- Summarizing: Getting To TheDocument34 pagesSummarizing: Getting To TheammarNo ratings yet
- Pijar Destha Nuzulqa - Topic 8 ExerciseDocument2 pagesPijar Destha Nuzulqa - Topic 8 ExercisePijar Destha NuzulqaNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Parts of SpeechDocument29 pagesUnit 1 Parts of Speechrasheady100% (1)
- Tiki Taka CK SurgeryDocument50 pagesTiki Taka CK SurgeryEmad MerganNo ratings yet
- Preliminary For Schools Reading Sample Test 2 Question PaperDocument12 pagesPreliminary For Schools Reading Sample Test 2 Question PaperEduard BotezNo ratings yet
- Cat: Sitting: (By Roswitha Mueller)Document4 pagesCat: Sitting: (By Roswitha Mueller)mklarströmNo ratings yet
- People V Collado DigestDocument3 pagesPeople V Collado DigestErika PotianNo ratings yet
- Dry Sex: 1 Health Risks 3 External LinksDocument2 pagesDry Sex: 1 Health Risks 3 External LinkssuzyNo ratings yet
- Resident Mammals FIDEC vs. Sec. ReyesDocument4 pagesResident Mammals FIDEC vs. Sec. ReyesDawn Jessa Go0% (1)
- Cardiovascular Physiology NodrmDocument528 pagesCardiovascular Physiology NodrmEmmanuel PrahNo ratings yet
- AGRI 22 Lecture Handout - CASE - 2ndsem 2018-2019Document6 pagesAGRI 22 Lecture Handout - CASE - 2ndsem 2018-2019Ivan James BaetNo ratings yet
- Pelvic Floor ExercisesDocument2 pagesPelvic Floor Exercisesajuhaseen100% (1)
- Libretto Donnerstag EngDocument74 pagesLibretto Donnerstag EngAnargyros DeniososNo ratings yet
- The Year of The Pig: Tales From The Chinese ZodiacDocument9 pagesThe Year of The Pig: Tales From The Chinese ZodiacImmediumNo ratings yet
- Braciole: Recipe-VideoDocument18 pagesBraciole: Recipe-VideoLavinia LupulescuNo ratings yet
- BiologyDocument10 pagesBiologyNur FarhanimNo ratings yet