Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
39 viewsDeformation of Rocks
Deformation of Rocks
Uploaded by
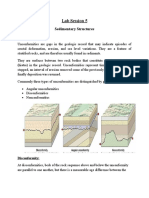
Angel Magulod Alon AlonThe document discusses different types of rock folds that can form due to compressional or extensional forces. It defines monoclines as step-like folds with zones of increased dip, and describes how folds can form differentially over underlying faults or due to reactivation of older faults. It also defines anticlines as arch-shaped folds where the oldest strata are in the core, and synclines as the opposite where youngest strata are in the core. Recumbent folds are described as having a nearly horizontal axial plane.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Structural Geology AND Rock MechanicsDocument34 pagesStructural Geology AND Rock Mechanicsjek vin0% (1)
- LRFD - Manual For Engineered Wood ConstructionDocument100 pagesLRFD - Manual For Engineered Wood ConstructionDedy Kristianto100% (2)
- Folds and FaultsDocument31 pagesFolds and FaultsDeepesh KhandelwalNo ratings yet
- Deformation, Mountain Building, and The Evolution of ContinentsDocument87 pagesDeformation, Mountain Building, and The Evolution of ContinentsOsman AydınNo ratings yet
- Geologi DasarDocument88 pagesGeologi DasaraisyahssNo ratings yet
- Structural Geology (Faults)Document17 pagesStructural Geology (Faults)Linet MwikaliNo ratings yet
- FOLDSand FAULTSDocument21 pagesFOLDSand FAULTSC John AquinoNo ratings yet
- Ol. 8 Continued.Document31 pagesOl. 8 Continued.Salman Bin TariqNo ratings yet
- Deformational Features of RocksDocument42 pagesDeformational Features of Rocksthareenda100% (1)
- Folds&Faults PresentationDocument17 pagesFolds&Faults Presentationcrown212No ratings yet
- Structural GeologyDocument90 pagesStructural GeologyBalsam Qusay Mohammed100% (1)
- The Formation of Faults and FoldsDocument21 pagesThe Formation of Faults and FoldsJeremiah Dela PeñaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1Document61 pagesLecture 1tornadoturbineNo ratings yet
- Structuralgeology 1 130917081715 Phpapp01Document116 pagesStructuralgeology 1 130917081715 Phpapp01Bikash Kumar Panda0% (1)
- Geological Structures - 2020Document34 pagesGeological Structures - 2020ASAMENEWNo ratings yet
- Geological StructuresDocument25 pagesGeological StructuresSyahdan HamzahNo ratings yet
- Structural GeologyDocument115 pagesStructural GeologyYuvaraj DNo ratings yet
- Structural Geology and Rock Mechanics: October 10, 2019 Presented By: Arizval MendozaDocument19 pagesStructural Geology and Rock Mechanics: October 10, 2019 Presented By: Arizval MendozaDaryl Sy Su100% (1)
- May Be Defined As Undulations or Bends orDocument6 pagesMay Be Defined As Undulations or Bends oranalyn lacapNo ratings yet
- Geology and Soils - A1Document34 pagesGeology and Soils - A1Sukriti GopalakrishnanNo ratings yet
- Structural GeologyDocument68 pagesStructural GeologyAnkit JharotiyaNo ratings yet
- Folds, Faults, and Other Records of Rock DeformationDocument90 pagesFolds, Faults, and Other Records of Rock DeformationAbdul Moeed KalsonNo ratings yet
- 5.structural GeologyDocument46 pages5.structural Geologysamir bardewaNo ratings yet
- Movement of Plates Lead To Formation of Folds and Faults: Lesson 5Document24 pagesMovement of Plates Lead To Formation of Folds and Faults: Lesson 5Jester DayaoNo ratings yet
- Folds & FaultsDocument17 pagesFolds & FaultsJojebelle Kate Iyog-cabanletNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 - Rock Deformation in NatureDocument27 pagesLecture 2 - Rock Deformation in NatureBrian KissingerNo ratings yet
- Rock Deformation: Structural GeologyDocument8 pagesRock Deformation: Structural Geologyمحمد باسم محمد حسين ANo ratings yet
- Group 7 PresentationDocument18 pagesGroup 7 PresentationRiz Ann Joy CasumpangNo ratings yet
- Physical Geography NotesDocument16 pagesPhysical Geography NotesVernon88% (26)
- Presentation of Pet GeoDocument46 pagesPresentation of Pet GeononolashariNo ratings yet
- Sesar NaikDocument61 pagesSesar NaikTito TahtaNo ratings yet
- المحاضرة الثامنةDocument25 pagesالمحاضرة الثامنةfarrah.taNo ratings yet
- Hawass University IOT: Railway Assignment Geological Structure Related To TunnelingDocument14 pagesHawass University IOT: Railway Assignment Geological Structure Related To TunnelingAndualem KidusNo ratings yet
- Deformation of Rock: Stress and StrainDocument13 pagesDeformation of Rock: Stress and Strainaprillia frinandaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1: Introduction, Geological Structures, Primary StructuresDocument56 pagesLecture 1: Introduction, Geological Structures, Primary StructuresHerold Riwaldo SitindaonNo ratings yet
- Folding and Faulting 2Document40 pagesFolding and Faulting 2Maria PaulineNo ratings yet
- Structural Geology GroundwaterDocument109 pagesStructural Geology Groundwaterkiran_ran99No ratings yet
- Lab Session 5Document5 pagesLab Session 5Musab UsmanNo ratings yet
- Landforming ProcessesDocument37 pagesLandforming ProcessesHari OmNo ratings yet
- Geology ReportDocument21 pagesGeology ReportDaniela EmbornalNo ratings yet
- Folding and FaultingDocument16 pagesFolding and FaultingSpangle StarNo ratings yet
- Lesson-2 2Document29 pagesLesson-2 2RexTheKingNo ratings yet
- Presentation #1 Folding &faultingDocument25 pagesPresentation #1 Folding &faultingNathan McintoshNo ratings yet
- Folding and FaultingDocument16 pagesFolding and FaultingRajesh ranaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 Notes: Section 1 How Rock DeformsDocument8 pagesChapter 11 Notes: Section 1 How Rock DeformsPrincess KimberlyNo ratings yet
- Kuliah Struktur GeologiDocument75 pagesKuliah Struktur GeologiAshabul KahfiNo ratings yet
- Folding and FaultingDocument16 pagesFolding and FaultingDeepesh KhandelwalNo ratings yet
- Folding and FaultingDocument16 pagesFolding and FaultingTikTok ProductionsNo ratings yet
- Geology: Deformation and MountainsDocument37 pagesGeology: Deformation and MountainsJordan WommackNo ratings yet
- Unit 4Document15 pagesUnit 4Godson GodsonNo ratings yet
- ES1121 SP2024 Lecture 12Document53 pagesES1121 SP2024 Lecture 12harshith.revuruNo ratings yet
- Mountain BuildingDocument34 pagesMountain BuildingElla BalingitNo ratings yet
- 4 Geological StructuresDocument35 pages4 Geological StructuresZahoor Ahmad100% (1)
- Geology Chapter 5Document38 pagesGeology Chapter 5Mohd Syafiq Akmal100% (1)
- Structural Geology PDFDocument485 pagesStructural Geology PDFMaria Angelica Villarreal100% (18)
- Group 6 Geological StructuresDocument50 pagesGroup 6 Geological StructuresAlexa Francoise Arao TanoNo ratings yet
- Geological Structures: Folds: School of Earth Sciences SRTM University, Nanded - 431 606 Maharashtra, INDIADocument45 pagesGeological Structures: Folds: School of Earth Sciences SRTM University, Nanded - 431 606 Maharashtra, INDIAMangam RajkumarNo ratings yet
- Structural GeologyDocument35 pagesStructural GeologyYounas BilalNo ratings yet
- Crustal DeformationDocument7 pagesCrustal DeformationKiarana Fleischer100% (1)
- Prince Lucky PPT For Group 4 ReportingDocument37 pagesPrince Lucky PPT For Group 4 ReportingKlent ReyesNo ratings yet
- Egyptain Codes of Practice For Steel Construction (LRFD & Asd) in A Copmuter Program FormDocument10 pagesEgyptain Codes of Practice For Steel Construction (LRFD & Asd) in A Copmuter Program FormWesam SaidNo ratings yet
- Multiple Choice QuestionscivilDocument19 pagesMultiple Choice Questionscivilashish kushNo ratings yet
- Geotechnical Problem Solving: Book DescriptionDocument9 pagesGeotechnical Problem Solving: Book DescriptionSadaqat AliNo ratings yet
- Laporan XtractDocument8 pagesLaporan XtractIndra SidikNo ratings yet
- Test On Cyclic Creep Behavior of Mucky Clay in Shanghai Under Step Cyclic LoadingDocument8 pagesTest On Cyclic Creep Behavior of Mucky Clay in Shanghai Under Step Cyclic LoadingJoselle RuizNo ratings yet
- Semi-Analytical Buckling Code Development of Stiffened and Unstiffened Paltes With A Free EdgeDocument114 pagesSemi-Analytical Buckling Code Development of Stiffened and Unstiffened Paltes With A Free EdgeH AnimeNo ratings yet
- Geography Notes - Earthquakes and VulcanicityDocument3 pagesGeography Notes - Earthquakes and VulcanicityBlessing ErenNo ratings yet
- Base Plate DesignDocument9 pagesBase Plate DesignbuildconNo ratings yet
- Principle Stresses Calc.Document19 pagesPrinciple Stresses Calc.Abdallah AL-AbbadiNo ratings yet
- Slab Design Wsd-Usd-Tanvir Edition PDFDocument6 pagesSlab Design Wsd-Usd-Tanvir Edition PDFTanvir Hossain TuhinNo ratings yet
- Seismic Risks For Embankments: Key ConceptsDocument28 pagesSeismic Risks For Embankments: Key ConceptsPedro Troncoso AcuñaNo ratings yet
- ASCE 7-22 CH 11com - For PC - SouDocument58 pagesASCE 7-22 CH 11com - For PC - SousharethefilesNo ratings yet
- Composites Testing MechineDocument32 pagesComposites Testing MechineRahmawati FitrianingtyasNo ratings yet
- Fracture Analysis of Compact Tension SpecimenDocument7 pagesFracture Analysis of Compact Tension SpecimenIJORAT100% (1)
- Lecture 3 Bending and Shear in Beams PHG A8 Oct17 PDFDocument30 pagesLecture 3 Bending and Shear in Beams PHG A8 Oct17 PDFEvi32No ratings yet
- Exp SteelDocument3 pagesExp Steelantikabantika658No ratings yet
- 47CDocument9 pages47CDarshit D RajNo ratings yet
- S6 - EC8-Lisbon - A PLUMIER PDFDocument130 pagesS6 - EC8-Lisbon - A PLUMIER PDFFatih ÇELİKERNo ratings yet
- Cracking Behavior in Reinforced Concrete Members With Steel Fibers: A Comprehensive Experimental StudyDocument11 pagesCracking Behavior in Reinforced Concrete Members With Steel Fibers: A Comprehensive Experimental StudyJuan Carlos Vivas MontesNo ratings yet
- Seismic Waves Week 3Document33 pagesSeismic Waves Week 3DonnaNo ratings yet
- 6 R Design 13.88 Section A-ADocument4 pages6 R Design 13.88 Section A-AsudipNo ratings yet
- Lecture 14 - Design of Composite Members (Part III)Document50 pagesLecture 14 - Design of Composite Members (Part III)basitNo ratings yet
- Karantoni - Confined Masonry As Practical Seismic Construction Alternative-The Experience From The 2014 Cephalonia EarthquakeDocument21 pagesKarantoni - Confined Masonry As Practical Seismic Construction Alternative-The Experience From The 2014 Cephalonia EarthquakeSergio Alonso SunleyNo ratings yet
- Mechanics of Material Lab 07Document21 pagesMechanics of Material Lab 07Syed Suleman Ayub - Section-BNo ratings yet
- CT - General Properties of Matter - Sheets General Properties of Matter - 22012022 - Xi Physics Elasticity 01, 02Document3 pagesCT - General Properties of Matter - Sheets General Properties of Matter - 22012022 - Xi Physics Elasticity 01, 02Anita Akhilesh YadavNo ratings yet
- Strength Evaluation of Shotcrete Repaired Beams: Aci Structural Journal Technical PaperDocument5 pagesStrength Evaluation of Shotcrete Repaired Beams: Aci Structural Journal Technical PaperpicottNo ratings yet
- CIVIL B Tech Projects - IIT KanpurDocument2 pagesCIVIL B Tech Projects - IIT Kanpurjayaram miryalaNo ratings yet
- Beam - Timber Prop - 500Wx500D - 1st - 20200730Document10 pagesBeam - Timber Prop - 500Wx500D - 1st - 20200730Chung Him Joe ChanNo ratings yet
Deformation of Rocks
Deformation of Rocks
Uploaded by
Angel Magulod Alon Alon0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
39 views10 pagesThe document discusses different types of rock folds that can form due to compressional or extensional forces. It defines monoclines as step-like folds with zones of increased dip, and describes how folds can form differentially over underlying faults or due to reactivation of older faults. It also defines anticlines as arch-shaped folds where the oldest strata are in the core, and synclines as the opposite where youngest strata are in the core. Recumbent folds are described as having a nearly horizontal axial plane.
Original Description:
rocks
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses different types of rock folds that can form due to compressional or extensional forces. It defines monoclines as step-like folds with zones of increased dip, and describes how folds can form differentially over underlying faults or due to reactivation of older faults. It also defines anticlines as arch-shaped folds where the oldest strata are in the core, and synclines as the opposite where youngest strata are in the core. Recumbent folds are described as having a nearly horizontal axial plane.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
39 views10 pagesDeformation of Rocks
Deformation of Rocks
Uploaded by
Angel Magulod Alon AlonThe document discusses different types of rock folds that can form due to compressional or extensional forces. It defines monoclines as step-like folds with zones of increased dip, and describes how folds can form differentially over underlying faults or due to reactivation of older faults. It also defines anticlines as arch-shaped folds where the oldest strata are in the core, and synclines as the opposite where youngest strata are in the core. Recumbent folds are described as having a nearly horizontal axial plane.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 10
Angel Alon Alon
Allysa Faye Bayona
Chrizza Erica Fajardo
Jherome Garcia
John Aaron Esguerra
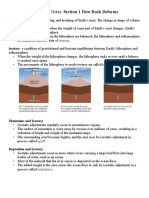
• Changes in the shape and/or volume substances
• Changes in the shape and volume occur when stress
and strain causes rock to buckle
• A fold can be defined as a bend in rock that is the
response to compressional forces
• The rock material must have the ability to deform
under pressure and heat
• Pressure must not exceed the internal strength of the
rock. If it does, fracturing occurs.
• Deformation must be applied slowly.
• A monocline (or, rarely, a monoform) is a
step-like fold in rock strata consisting of a
zone of steeper dip within an otherwise
horizontal or gently-dipping sequence.
• By differential compaction over an underlying
structure, particularly a large fault at the edge of a
basin due to the greater compactibility of the basin
fill, the amplitude of the fold will die out gradually
upwards.
• By mild reactivation of an earlier extensional
faultduring a phase of inversion causing folding in the
overlying sequence.
• As a form of fault propagation fold during upward
propagation of an extensional fault in basement into
an overlying cover sequence.
• As a form of fault propagation fold during upward
propagation of a reverse fault in basement into an
overlying cover sequence.
• In structural geology, an anticline is a type of fold that is an arch-like
shape and has its oldest beds at its core.
• A typical anticline is convex up in which the hinge or crest is the location
where the curvature is greatest, and the limbs are the sides of the fold
that dipaway from the hinge.
• Anticlines can be recognized and differentiated from antiformsby a
sequence of rock layers that become progressively older toward the
center of the fold.
• The progressing age of the rock strata towards
the core and uplifted center, are the trademark
indications for evidence of anticlines on a
geologic map
• A syncline is a fold in which the youngest rocks occur
in the core of a fold whereas the oldest rocks occur in
the core of an anticline.
• Where the relative ages of rocks are not known the
term synform and not syncline should be used to
describe folds where layers are bent downwards so
that they dip towards the fold axis, and antiform and not
anticline .
• One of the types of fold
• A recumbent fold is one in which the axial plane is essentially
horizontal, with the limit of variation of axial-planar dip, and the
resulting limit of plunge being 10°
• It is a sideways-closing neutral structure that is neither a synformal
nor an antiformal fold.
• A fold which is folded over on itself.
• Commonly found in the core of mountain ranges •we
call the combination of a fault and a fold in a rock an
over thrust fault.
• Faults forn in a rocks when the stresses overcome the
internal strength of the rock resulting in a fracture.
You might also like
- Structural Geology AND Rock MechanicsDocument34 pagesStructural Geology AND Rock Mechanicsjek vin0% (1)
- LRFD - Manual For Engineered Wood ConstructionDocument100 pagesLRFD - Manual For Engineered Wood ConstructionDedy Kristianto100% (2)
- Folds and FaultsDocument31 pagesFolds and FaultsDeepesh KhandelwalNo ratings yet
- Deformation, Mountain Building, and The Evolution of ContinentsDocument87 pagesDeformation, Mountain Building, and The Evolution of ContinentsOsman AydınNo ratings yet
- Geologi DasarDocument88 pagesGeologi DasaraisyahssNo ratings yet
- Structural Geology (Faults)Document17 pagesStructural Geology (Faults)Linet MwikaliNo ratings yet
- FOLDSand FAULTSDocument21 pagesFOLDSand FAULTSC John AquinoNo ratings yet
- Ol. 8 Continued.Document31 pagesOl. 8 Continued.Salman Bin TariqNo ratings yet
- Deformational Features of RocksDocument42 pagesDeformational Features of Rocksthareenda100% (1)
- Folds&Faults PresentationDocument17 pagesFolds&Faults Presentationcrown212No ratings yet
- Structural GeologyDocument90 pagesStructural GeologyBalsam Qusay Mohammed100% (1)
- The Formation of Faults and FoldsDocument21 pagesThe Formation of Faults and FoldsJeremiah Dela PeñaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1Document61 pagesLecture 1tornadoturbineNo ratings yet
- Structuralgeology 1 130917081715 Phpapp01Document116 pagesStructuralgeology 1 130917081715 Phpapp01Bikash Kumar Panda0% (1)
- Geological Structures - 2020Document34 pagesGeological Structures - 2020ASAMENEWNo ratings yet
- Geological StructuresDocument25 pagesGeological StructuresSyahdan HamzahNo ratings yet
- Structural GeologyDocument115 pagesStructural GeologyYuvaraj DNo ratings yet
- Structural Geology and Rock Mechanics: October 10, 2019 Presented By: Arizval MendozaDocument19 pagesStructural Geology and Rock Mechanics: October 10, 2019 Presented By: Arizval MendozaDaryl Sy Su100% (1)
- May Be Defined As Undulations or Bends orDocument6 pagesMay Be Defined As Undulations or Bends oranalyn lacapNo ratings yet
- Geology and Soils - A1Document34 pagesGeology and Soils - A1Sukriti GopalakrishnanNo ratings yet
- Structural GeologyDocument68 pagesStructural GeologyAnkit JharotiyaNo ratings yet
- Folds, Faults, and Other Records of Rock DeformationDocument90 pagesFolds, Faults, and Other Records of Rock DeformationAbdul Moeed KalsonNo ratings yet
- 5.structural GeologyDocument46 pages5.structural Geologysamir bardewaNo ratings yet
- Movement of Plates Lead To Formation of Folds and Faults: Lesson 5Document24 pagesMovement of Plates Lead To Formation of Folds and Faults: Lesson 5Jester DayaoNo ratings yet
- Folds & FaultsDocument17 pagesFolds & FaultsJojebelle Kate Iyog-cabanletNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 - Rock Deformation in NatureDocument27 pagesLecture 2 - Rock Deformation in NatureBrian KissingerNo ratings yet
- Rock Deformation: Structural GeologyDocument8 pagesRock Deformation: Structural Geologyمحمد باسم محمد حسين ANo ratings yet
- Group 7 PresentationDocument18 pagesGroup 7 PresentationRiz Ann Joy CasumpangNo ratings yet
- Physical Geography NotesDocument16 pagesPhysical Geography NotesVernon88% (26)
- Presentation of Pet GeoDocument46 pagesPresentation of Pet GeononolashariNo ratings yet
- Sesar NaikDocument61 pagesSesar NaikTito TahtaNo ratings yet
- المحاضرة الثامنةDocument25 pagesالمحاضرة الثامنةfarrah.taNo ratings yet
- Hawass University IOT: Railway Assignment Geological Structure Related To TunnelingDocument14 pagesHawass University IOT: Railway Assignment Geological Structure Related To TunnelingAndualem KidusNo ratings yet
- Deformation of Rock: Stress and StrainDocument13 pagesDeformation of Rock: Stress and Strainaprillia frinandaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1: Introduction, Geological Structures, Primary StructuresDocument56 pagesLecture 1: Introduction, Geological Structures, Primary StructuresHerold Riwaldo SitindaonNo ratings yet
- Folding and Faulting 2Document40 pagesFolding and Faulting 2Maria PaulineNo ratings yet
- Structural Geology GroundwaterDocument109 pagesStructural Geology Groundwaterkiran_ran99No ratings yet
- Lab Session 5Document5 pagesLab Session 5Musab UsmanNo ratings yet
- Landforming ProcessesDocument37 pagesLandforming ProcessesHari OmNo ratings yet
- Geology ReportDocument21 pagesGeology ReportDaniela EmbornalNo ratings yet
- Folding and FaultingDocument16 pagesFolding and FaultingSpangle StarNo ratings yet
- Lesson-2 2Document29 pagesLesson-2 2RexTheKingNo ratings yet
- Presentation #1 Folding &faultingDocument25 pagesPresentation #1 Folding &faultingNathan McintoshNo ratings yet
- Folding and FaultingDocument16 pagesFolding and FaultingRajesh ranaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 Notes: Section 1 How Rock DeformsDocument8 pagesChapter 11 Notes: Section 1 How Rock DeformsPrincess KimberlyNo ratings yet
- Kuliah Struktur GeologiDocument75 pagesKuliah Struktur GeologiAshabul KahfiNo ratings yet
- Folding and FaultingDocument16 pagesFolding and FaultingDeepesh KhandelwalNo ratings yet
- Folding and FaultingDocument16 pagesFolding and FaultingTikTok ProductionsNo ratings yet
- Geology: Deformation and MountainsDocument37 pagesGeology: Deformation and MountainsJordan WommackNo ratings yet
- Unit 4Document15 pagesUnit 4Godson GodsonNo ratings yet
- ES1121 SP2024 Lecture 12Document53 pagesES1121 SP2024 Lecture 12harshith.revuruNo ratings yet
- Mountain BuildingDocument34 pagesMountain BuildingElla BalingitNo ratings yet
- 4 Geological StructuresDocument35 pages4 Geological StructuresZahoor Ahmad100% (1)
- Geology Chapter 5Document38 pagesGeology Chapter 5Mohd Syafiq Akmal100% (1)
- Structural Geology PDFDocument485 pagesStructural Geology PDFMaria Angelica Villarreal100% (18)
- Group 6 Geological StructuresDocument50 pagesGroup 6 Geological StructuresAlexa Francoise Arao TanoNo ratings yet
- Geological Structures: Folds: School of Earth Sciences SRTM University, Nanded - 431 606 Maharashtra, INDIADocument45 pagesGeological Structures: Folds: School of Earth Sciences SRTM University, Nanded - 431 606 Maharashtra, INDIAMangam RajkumarNo ratings yet
- Structural GeologyDocument35 pagesStructural GeologyYounas BilalNo ratings yet
- Crustal DeformationDocument7 pagesCrustal DeformationKiarana Fleischer100% (1)
- Prince Lucky PPT For Group 4 ReportingDocument37 pagesPrince Lucky PPT For Group 4 ReportingKlent ReyesNo ratings yet
- Egyptain Codes of Practice For Steel Construction (LRFD & Asd) in A Copmuter Program FormDocument10 pagesEgyptain Codes of Practice For Steel Construction (LRFD & Asd) in A Copmuter Program FormWesam SaidNo ratings yet
- Multiple Choice QuestionscivilDocument19 pagesMultiple Choice Questionscivilashish kushNo ratings yet
- Geotechnical Problem Solving: Book DescriptionDocument9 pagesGeotechnical Problem Solving: Book DescriptionSadaqat AliNo ratings yet
- Laporan XtractDocument8 pagesLaporan XtractIndra SidikNo ratings yet
- Test On Cyclic Creep Behavior of Mucky Clay in Shanghai Under Step Cyclic LoadingDocument8 pagesTest On Cyclic Creep Behavior of Mucky Clay in Shanghai Under Step Cyclic LoadingJoselle RuizNo ratings yet
- Semi-Analytical Buckling Code Development of Stiffened and Unstiffened Paltes With A Free EdgeDocument114 pagesSemi-Analytical Buckling Code Development of Stiffened and Unstiffened Paltes With A Free EdgeH AnimeNo ratings yet
- Geography Notes - Earthquakes and VulcanicityDocument3 pagesGeography Notes - Earthquakes and VulcanicityBlessing ErenNo ratings yet
- Base Plate DesignDocument9 pagesBase Plate DesignbuildconNo ratings yet
- Principle Stresses Calc.Document19 pagesPrinciple Stresses Calc.Abdallah AL-AbbadiNo ratings yet
- Slab Design Wsd-Usd-Tanvir Edition PDFDocument6 pagesSlab Design Wsd-Usd-Tanvir Edition PDFTanvir Hossain TuhinNo ratings yet
- Seismic Risks For Embankments: Key ConceptsDocument28 pagesSeismic Risks For Embankments: Key ConceptsPedro Troncoso AcuñaNo ratings yet
- ASCE 7-22 CH 11com - For PC - SouDocument58 pagesASCE 7-22 CH 11com - For PC - SousharethefilesNo ratings yet
- Composites Testing MechineDocument32 pagesComposites Testing MechineRahmawati FitrianingtyasNo ratings yet
- Fracture Analysis of Compact Tension SpecimenDocument7 pagesFracture Analysis of Compact Tension SpecimenIJORAT100% (1)
- Lecture 3 Bending and Shear in Beams PHG A8 Oct17 PDFDocument30 pagesLecture 3 Bending and Shear in Beams PHG A8 Oct17 PDFEvi32No ratings yet
- Exp SteelDocument3 pagesExp Steelantikabantika658No ratings yet
- 47CDocument9 pages47CDarshit D RajNo ratings yet
- S6 - EC8-Lisbon - A PLUMIER PDFDocument130 pagesS6 - EC8-Lisbon - A PLUMIER PDFFatih ÇELİKERNo ratings yet
- Cracking Behavior in Reinforced Concrete Members With Steel Fibers: A Comprehensive Experimental StudyDocument11 pagesCracking Behavior in Reinforced Concrete Members With Steel Fibers: A Comprehensive Experimental StudyJuan Carlos Vivas MontesNo ratings yet
- Seismic Waves Week 3Document33 pagesSeismic Waves Week 3DonnaNo ratings yet
- 6 R Design 13.88 Section A-ADocument4 pages6 R Design 13.88 Section A-AsudipNo ratings yet
- Lecture 14 - Design of Composite Members (Part III)Document50 pagesLecture 14 - Design of Composite Members (Part III)basitNo ratings yet
- Karantoni - Confined Masonry As Practical Seismic Construction Alternative-The Experience From The 2014 Cephalonia EarthquakeDocument21 pagesKarantoni - Confined Masonry As Practical Seismic Construction Alternative-The Experience From The 2014 Cephalonia EarthquakeSergio Alonso SunleyNo ratings yet
- Mechanics of Material Lab 07Document21 pagesMechanics of Material Lab 07Syed Suleman Ayub - Section-BNo ratings yet
- CT - General Properties of Matter - Sheets General Properties of Matter - 22012022 - Xi Physics Elasticity 01, 02Document3 pagesCT - General Properties of Matter - Sheets General Properties of Matter - 22012022 - Xi Physics Elasticity 01, 02Anita Akhilesh YadavNo ratings yet
- Strength Evaluation of Shotcrete Repaired Beams: Aci Structural Journal Technical PaperDocument5 pagesStrength Evaluation of Shotcrete Repaired Beams: Aci Structural Journal Technical PaperpicottNo ratings yet
- CIVIL B Tech Projects - IIT KanpurDocument2 pagesCIVIL B Tech Projects - IIT Kanpurjayaram miryalaNo ratings yet
- Beam - Timber Prop - 500Wx500D - 1st - 20200730Document10 pagesBeam - Timber Prop - 500Wx500D - 1st - 20200730Chung Him Joe ChanNo ratings yet