Professional Documents
Culture Documents
CEFR
CEFR
Uploaded by
Luthfi Imama0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
36 views14 pagesThe document summarizes the historical development of the Common European Framework of Reference for Languages (CEFR). It began in the 1960s with a focus on language learning for communication. In the 1970s, specifications were developed for language learning objectives covering linguistic, sociolinguistic, discourse, and other competencies. In the 1990s, the Council of Europe developed a comprehensive framework for language learning, teaching, and assessment. The official version was launched in 2001 and provides descriptions of proficiency levels and learning objectives.
Original Description:
Original Title
CEFR.pptx
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document summarizes the historical development of the Common European Framework of Reference for Languages (CEFR). It began in the 1960s with a focus on language learning for communication. In the 1970s, specifications were developed for language learning objectives covering linguistic, sociolinguistic, discourse, and other competencies. In the 1990s, the Council of Europe developed a comprehensive framework for language learning, teaching, and assessment. The official version was launched in 2001 and provides descriptions of proficiency levels and learning objectives.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
36 views14 pagesCEFR
CEFR
Uploaded by
Luthfi ImamaThe document summarizes the historical development of the Common European Framework of Reference for Languages (CEFR). It began in the 1960s with a focus on language learning for communication. In the 1970s, specifications were developed for language learning objectives covering linguistic, sociolinguistic, discourse, and other competencies. In the 1990s, the Council of Europe developed a comprehensive framework for language learning, teaching, and assessment. The official version was launched in 2001 and provides descriptions of proficiency levels and learning objectives.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 14
Mohammad Luthfi
Erhans Bonyardo K.L
Historical overview of the development of the
CEFR
1960’s: Language learning for communication initiatives
Focused on:
Language learning for communication
promoting a learner centred
actional and positive approach.
1970’s: Specifications for language learning objectives.
focusing on scope and levels:
Linguistic,
sociolinguistic,
discourse,
socio-cultural,
and social competence.
1990 -> The Council of Europe was develop a comprehensive framework for language learning,
teaching and assessment in general.
2001: the official version was launched in January 2001
What is CEFR?
What is CEFR?
CEFR is methodology?
It’s not a methodology, you can use your own style for
achieving new levels.
Should we teach grammar?
How they communicate and understand written and spoken
text.
Why we learn CEFR?
It is not a tool to promote Europe, it is a basic framework.
Reception: receiving and processing input
Production: includes both speaking and writing
activities.
Interaction: Spoken interaction is considered to
be the origin of language, with interpersonal,
collaborative and transactional functions.
Illustrative Descriptor Scales
Spoken reception
Spoken production
Spoken Interaction
⇒ promoting plurilingualism and diversification in the
choice of languages in the curriculum
⇒ supporting the development and demonstration of
the plurilingual profile of individual learners
⇒ developing and reviewing the content of language
curricula and defining positive ‘can do’ descriptors adapted
Main objectives of
to the age, interests and needs of learners
the CEFR:
⇒ designing and developing textbooks and teaching
material
⇒ supporting teacher education and cooperation among
teachers of different languages
⇒ enhancing quality and success in learning, teaching and
assessment
⇒ facilitating transparency in testing and the
comparability of certifications
Essence
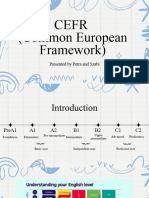
Six levels of foreign language proficiency
This system makes it possible to:
establish learning and teaching objectives
review curricula
design teaching materials and
provide a basis for recognizing language qualifications thus facilitating educational and
occupational mobility.
Learning, teaching, assessment
Relating examinations to the CEFR
Levels, descriptors and content specifications
Common Reference Levels
VIDEO
A1
A2
B1
B2
C1 and C2
The CEFR has been written with two main aims:
to encourage practitioners of all kinds in the language
field, including language learners themselves, to
reflect on questions regarding the analysis of
learning/teaching situations.
to make it easier for practitioners to explain to each
other and to their clientèle what they wish learners to
achieve, and how they may do so.
References
http://www.coe.int/en/web/common-european-framework-reference-
languages/home
University of Cambridge (ESOL Examinations)
Youtube
Teacher Guide to the common European Framework
You might also like
- Bisb - Bank StatementDocument23 pagesBisb - Bank Statementazstartup.bhNo ratings yet
- Principles and Guidelines of An Effective Language Art and Multiliteracies CurriculumnDocument10 pagesPrinciples and Guidelines of An Effective Language Art and Multiliteracies CurriculumnPrince josua RivasNo ratings yet
- Biomedical Applications of Soft RoboticsDocument11 pagesBiomedical Applications of Soft RoboticsAbdul Rehman100% (2)
- ADDIE Model For Development of E-CoursesDocument6 pagesADDIE Model For Development of E-CoursesMuhammad Arif IzzudinNo ratings yet
- SM CH PDFDocument18 pagesSM CH PDFHector NaranjoNo ratings yet
- PESTLE Analysis For Rolls RoyceDocument2 pagesPESTLE Analysis For Rolls Roycephi podcastNo ratings yet
- GRAMMAR TRANSLATION METHOD - DADIVAS FinalDocument28 pagesGRAMMAR TRANSLATION METHOD - DADIVAS Finalmelyn dadivasNo ratings yet
- The Grammar Translation Method: Didactics of Foreign Languages I by Felipe Parra Villegas Carlos AcevedoDocument13 pagesThe Grammar Translation Method: Didactics of Foreign Languages I by Felipe Parra Villegas Carlos AcevedofelordmaxNo ratings yet
- Communication SkillsDocument100 pagesCommunication Skillspraveen kaushikNo ratings yet
- Prof. Zuraida's SlidesDocument36 pagesProf. Zuraida's SlidesNirmala SundrarajNo ratings yet
- EI 407 Technical ReportsDocument32 pagesEI 407 Technical Reportschimwanda100% (1)
- Planning: "Planning Is Deciding in Advance What To Do, How To Do It, When To Doitandwhoistodoit"Document22 pagesPlanning: "Planning Is Deciding in Advance What To Do, How To Do It, When To Doitandwhoistodoit"Tijo ThomasNo ratings yet
- Flipped Classroom Lesson - Plan About MechatronicsDocument16 pagesFlipped Classroom Lesson - Plan About MechatronicsDanang KusnadiNo ratings yet
- Your Free Guide To Our PMP Preparation Course: Project Management Professional (PMP) EditionDocument11 pagesYour Free Guide To Our PMP Preparation Course: Project Management Professional (PMP) EditionRASHEED YUSUFNo ratings yet
- Test 1: Note If You Are Facing Any Difficulty Uploading Your Answers, Please Inform MeDocument3 pagesTest 1: Note If You Are Facing Any Difficulty Uploading Your Answers, Please Inform MewakeyyNo ratings yet
- Cefr SlidesDocument36 pagesCefr SlidesEmilyNo ratings yet
- FAR570 Jul 2020 Set 1 (Sesi 1) - QDocument4 pagesFAR570 Jul 2020 Set 1 (Sesi 1) - QNURUL NAZAHANNIE MOHAMAD NAJIBNo ratings yet
- Energy Efficiency Initiatives in MalaysiaDocument24 pagesEnergy Efficiency Initiatives in MalaysiaMohd Helmy Hakimie RozlanNo ratings yet
- Curriculum StudiesDocument6 pagesCurriculum StudiesSyed AliNo ratings yet
- SPAN Guidelines For Voluntary Water Efficient Products Labelling SchemeDocument41 pagesSPAN Guidelines For Voluntary Water Efficient Products Labelling SchemeThor Yi ChunNo ratings yet
- Abstract Writing: What Is An Abstract?Document8 pagesAbstract Writing: What Is An Abstract?pintu ramNo ratings yet
- Enhancing Energy Efficiency in MalaysiaDocument35 pagesEnhancing Energy Efficiency in MalaysiaMc Eswaran100% (2)
- Malaysian Qualifications Framework MQF 2nd EditionDocument44 pagesMalaysian Qualifications Framework MQF 2nd Editionapi-402181038No ratings yet
- Training Program 532Document5 pagesTraining Program 532api-287195886No ratings yet
- M - 1.3 - Training DesignDocument38 pagesM - 1.3 - Training DesignLGED Manikganj100% (1)
- 21st Century PedagogyDocument89 pages21st Century Pedagogyanon_860117019No ratings yet
- TSL 3105Document11 pagesTSL 3105Fadziela MaidinNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 and 2 Concepts CMDocument51 pagesLecture 1 and 2 Concepts CMAbdul Ghaffar JaafarNo ratings yet
- Conducting Training ProgrammDocument18 pagesConducting Training Programmjyotikumari30No ratings yet
- Category Analyst Planogram Specialist in Tampa Bay FL Resume Karen JamaiDocument2 pagesCategory Analyst Planogram Specialist in Tampa Bay FL Resume Karen JamaikarenjamaiNo ratings yet
- Name: Shital Gosavi Div: MMS-A Roll No.: 09Document15 pagesName: Shital Gosavi Div: MMS-A Roll No.: 09sheetaljerryNo ratings yet
- Process ModelsDocument11 pagesProcess ModelsRajesh KannaNo ratings yet
- How To Use Google Meet For Online Teaching and Distance LearningDocument27 pagesHow To Use Google Meet For Online Teaching and Distance LearningTuni KapNo ratings yet
- Effective Public SpeakingDocument20 pagesEffective Public SpeakingMohd Azmi ArifinNo ratings yet
- Ch-1 Introduction To E-LearningDocument17 pagesCh-1 Introduction To E-LearningAditya VarmaNo ratings yet
- Establishing Language Skills in Europe TDocument10 pagesEstablishing Language Skills in Europe TWaheed M JumaniNo ratings yet
- Cefr Familiarisation Training: Primary /preschoolDocument200 pagesCefr Familiarisation Training: Primary /preschoolNor AzreenNo ratings yet
- Cefr Familiarisation Training: PrimaryDocument181 pagesCefr Familiarisation Training: PrimaryDamia IB IINo ratings yet
- Lecture NoDocument12 pagesLecture Noدفع الله محمدNo ratings yet
- Seminarski Dunja UzelacDocument20 pagesSeminarski Dunja UzelacDunja UzelacNo ratings yet
- CEFR NotesDocument1 pageCEFR NotesJimmy MingNo ratings yet
- Applying CEFR To Your CurriculumDocument40 pagesApplying CEFR To Your CurriculumAdina FarcasNo ratings yet
- The Impact of The CEFR - FiguerasDocument9 pagesThe Impact of The CEFR - FiguerasPennyNo ratings yet
- Cambridge - Measuring Acadmeic Language ProficiencyDocument32 pagesCambridge - Measuring Acadmeic Language Proficiencyolgataga2No ratings yet
- CEFR RequirementsDocument16 pagesCEFR RequirementsIsmatbek BaymukhammedovNo ratings yet
- Common European Framework of Reference For Languages: Learning, Teaching, AssessmentDocument24 pagesCommon European Framework of Reference For Languages: Learning, Teaching, Assessmentcarlitos_coolNo ratings yet
- Myp-Brief Language-Acquisition 2015Document2 pagesMyp-Brief Language-Acquisition 2015api-291276192No ratings yet
- Common European Framework (CEFR) 2022 Applied LinguisticsDocument44 pagesCommon European Framework (CEFR) 2022 Applied LinguisticsChristina AgnadaNo ratings yet
- CEFR PresentationDocument8 pagesCEFR Presentationvaripetra45No ratings yet
- Cascade Presentation Slides Lower Secondary (Final)Document134 pagesCascade Presentation Slides Lower Secondary (Final)jia3No ratings yet
- Impact of CefrDocument9 pagesImpact of CefrOvistasNo ratings yet
- North Forum Paper enDocument11 pagesNorth Forum Paper enAndrea MarleyNo ratings yet
- Nuevo Curriculo Ingles 2017Document92 pagesNuevo Curriculo Ingles 2017Joe Felipe Vera OchoaNo ratings yet
- Bgu Tomo 2curriculo 191 320Document130 pagesBgu Tomo 2curriculo 191 320gabrielacalvache1222No ratings yet
- A Synopsis of The Common EuropeanDocument4 pagesA Synopsis of The Common EuropeanJose Mario Castillejo GalvisNo ratings yet
- The Common European Framework of ReferenDocument20 pagesThe Common European Framework of ReferenMohamed Said100% (1)
- Area de Ingles PDFDocument92 pagesArea de Ingles PDFSarita Dahiana Orellana BarahonaNo ratings yet
- B1 Complete PackageDocument69 pagesB1 Complete PackageKhin San ThitNo ratings yet
- A1 Complete Package PDFDocument84 pagesA1 Complete Package PDFKatarzynaNo ratings yet
- Testing ResearchDocument16 pagesTesting ResearchSedat KorkmazNo ratings yet
- Prog Ang 1annéeDocument17 pagesProg Ang 1annéeYoussef MzabiNo ratings yet
- Curriculum Syllabus and Lesson PlanningDocument27 pagesCurriculum Syllabus and Lesson Planningapi-2627869580% (1)
- K 12 English Language CurriculumDocument29 pagesK 12 English Language CurriculumNieve MiraNo ratings yet
- Terms 2024Document2 pagesTerms 2024lorecandoit2024No ratings yet
- 2013 Example 03Document107 pages2013 Example 03eouahiauNo ratings yet
- HR Assistant - Job DescriptionDocument2 pagesHR Assistant - Job DescriptionArchana GiriNo ratings yet
- 2016 ORION Consolidated Audit ReportDocument112 pages2016 ORION Consolidated Audit ReportJoachim VIALLONNo ratings yet
- Aquinas Natural LawDocument50 pagesAquinas Natural Lawanon-300637No ratings yet
- Parkers' AstrologyDocument424 pagesParkers' Astrologyvictoria20051998No ratings yet
- Query Optimization MCQDocument12 pagesQuery Optimization MCQSameer vermaNo ratings yet
- Bye Laws in HistoryDocument28 pagesBye Laws in HistorySaroj KayasthaNo ratings yet
- Metodo Hach HierroDocument6 pagesMetodo Hach HierroJESSICA VANESSA ARISMENDI AVILEZNo ratings yet
- Manual 360 VisonicDocument70 pagesManual 360 VisonicRicardo Ortega Carbajal0% (1)
- Employees Satisfaction in Indian Oil Corporation LimitedDocument14 pagesEmployees Satisfaction in Indian Oil Corporation LimitedBharat Makkar100% (1)
- Consumer Brand Relationship PDFDocument8 pagesConsumer Brand Relationship PDFAkshada JagtapNo ratings yet
- PC/SC Partial Documentation of The API: PMDZ061-AE 24/09/2009Document32 pagesPC/SC Partial Documentation of The API: PMDZ061-AE 24/09/2009manskebe6121No ratings yet
- Using Pragmatics in Elt Focus PaperDocument5 pagesUsing Pragmatics in Elt Focus PaperThiri Min SinNo ratings yet
- 'The Real Book Guide' by Jazz TutorialDocument4 pages'The Real Book Guide' by Jazz Tutorialchrismovie100% (2)
- Tilt TableDocument2 pagesTilt TablenikhilNo ratings yet
- CCBP Learners With Backlogs-01!12!2021Document10 pagesCCBP Learners With Backlogs-01!12!2021MohdHussainNo ratings yet
- 1.2c atDocument3 pages1.2c atenyw160309No ratings yet
- Grade 9 Charity WHLP (Week 6, Quarter 1)Document5 pagesGrade 9 Charity WHLP (Week 6, Quarter 1)Giezelle LeopandoNo ratings yet
- Three-Phase Induction MotorsDocument36 pagesThree-Phase Induction MotorsCARMEN DIMITRIUNo ratings yet
- Surface Preparation Standards JotunDocument2 pagesSurface Preparation Standards JotunbacabacabacaNo ratings yet
- Example #14 Tunnel With Concrete Lining: Civilfem Manual of Advanced Examples - Ingeciber, S.A.Document14 pagesExample #14 Tunnel With Concrete Lining: Civilfem Manual of Advanced Examples - Ingeciber, S.A.Andre OliveiraNo ratings yet
- Lesson 7B The PassDocument5 pagesLesson 7B The PassJessel GulfericaNo ratings yet
- The Elusive Chemical Potential PDFDocument12 pagesThe Elusive Chemical Potential PDFbonesisaliveNo ratings yet
- 7th World Congress On Bearing, Joints, and Seismic SystemDocument2 pages7th World Congress On Bearing, Joints, and Seismic SystemFelix HotamaNo ratings yet
- EID Vol15No1Document151 pagesEID Vol15No1ImmortalYawnNo ratings yet
- A119.I.D.001 Rev01 Control ArchitectureDocument1 pageA119.I.D.001 Rev01 Control ArchitecturepolrequenamartosNo ratings yet