Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Mesozoic Era Presentation
Mesozoic Era Presentation
Uploaded by
KingZhytt DrizOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Mesozoic Era Presentation
Mesozoic Era Presentation
Uploaded by
KingZhytt DrizCopyright:
Available Formats
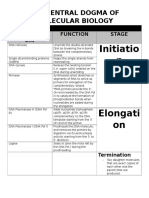
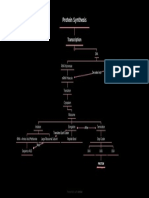
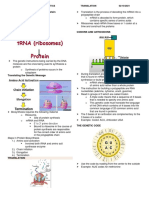
PROTEIN SYNTHESIS
Transcription Translation
(Occurs in the nucleus of
an eukaryotic cell)
DNA (Occurs in the cytoplasm
of an eukaryotic cell)
(Contains gene)
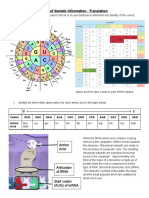
tRNA brought
Initiation Elongation Binding of mRNA
Amino acids
Gene Expression to the
and small ribosomal
Termination ribosome unit at the start
During initiation, the promoter Base pairing
region functions as a codon
recognition site for the RNA
The RNA polymerase slides between the
Once the RNA
polymerase to bind. This is
along the template DNA
strand. As the polymerase reaches complementary Large ribosomal 3 distinct
where the majority of gene complementary bases pair, the termination bases of mRNA unit binds to form
expression is controlled, by the RNA polymerase links point of the gene, codons and tRna the translation
regions are
either promoting or blocking nucleotides to the 3’ end the transcription is
access to this site by RNA of growing RNA molecule complete
anti codons
complex formed, E, P,
polymerase, Binding causes the and A
DNA double helix to unwind
and open
mRNA A charged tRNA Comlpex slides one
codon to the right, The
The entire
complex
molecule binds to the dissociates
uncharged tRNA exits
Sugar phosphate A site and a peptide from E site. A site is
Introns Exons backbones are bond forms between ready to accept a new
(Non-Coding part) (Codes or a protein) added its amino acid and charged tRNA, This Polypeptide will
the one attached to process will continue be modified and
the P site until the complex and extracted in
reaches the stop
Introns Splicing Mature mRNA codon where a release
lumen of the
(Ready for translation) digestive tract
(Uses spliceosome ) factor enters the A site
Translation King Zhytt C. Driz
XI-Euclid
You might also like
- CONCEPT MAP (Central Dogma of Molecular Biology)Document1 pageCONCEPT MAP (Central Dogma of Molecular Biology)ShekinahNo ratings yet
- MCB502 2020 Exam #1Document9 pagesMCB502 2020 Exam #1Cameron KeetonNo ratings yet
- Protein Synthesis SummaryDocument2 pagesProtein Synthesis SummaryTrinitee Wesner100% (1)
- 8c) Transcription Summary - 9744 - 2018Document1 page8c) Transcription Summary - 9744 - 20182022 EMMA WEN XUAN HANSONNo ratings yet
- Key Notes Genetic Material and Central DogmaDocument2 pagesKey Notes Genetic Material and Central DogmaSeiza WinchesterNo ratings yet
- Miniature Protein BIologyDocument83 pagesMiniature Protein BIologyPREET KANOOGANo ratings yet
- The Central Dogma of Molecular BiologyDocument4 pagesThe Central Dogma of Molecular BiologyJoshuaMondejarNo ratings yet
- Protein SynthesisDocument8 pagesProtein SynthesisDebbie NsefikNo ratings yet
- AP Biology: Gene ExpressionDocument4 pagesAP Biology: Gene ExpressionJiwon ShinNo ratings yet
- THE CENTRAL DOGMA HandoutDocument6 pagesTHE CENTRAL DOGMA HandoutLeah AturoNo ratings yet
- Fenomena Biomedik Dari Transkripsi Gen Hingga MetabolismeDocument45 pagesFenomena Biomedik Dari Transkripsi Gen Hingga MetabolismeratuurizkyNo ratings yet
- DNA Transcription and TranslationDocument2 pagesDNA Transcription and TranslationBrian Paguia100% (1)
- Protein SynthesisDocument1 pageProtein SynthesisChristopher TalaveraNo ratings yet
- Biochem: Gene Expression Part 2: Recap of Transcription (Part 1 of Lecture)Document14 pagesBiochem: Gene Expression Part 2: Recap of Transcription (Part 1 of Lecture)Von HippoNo ratings yet
- III. Gen Perk S2 - DIR 2021 - Pengontrolan Ekspresi GenDocument17 pagesIII. Gen Perk S2 - DIR 2021 - Pengontrolan Ekspresi GenSisy YuliantyNo ratings yet
- Green and Blue Lined Photosynthesis Biology Worksheet - 20240311 - 052508 - 0000Document2 pagesGreen and Blue Lined Photosynthesis Biology Worksheet - 20240311 - 052508 - 0000marioangelosurioNo ratings yet
- CYTO PL4 TranslationDocument9 pagesCYTO PL4 TranslationDanielle Anne Zamora-Matillosa LambanNo ratings yet
- Translation: The Systhesis of A Polypeptide ChainDocument3 pagesTranslation: The Systhesis of A Polypeptide ChainAizat HakimieNo ratings yet
- Week 1 of IGEMDocument68 pagesWeek 1 of IGEMXuejing DuNo ratings yet
- Bio Compare and ContrastDocument2 pagesBio Compare and ContrastRhea SivakumarNo ratings yet
- Gene Structure 1+2 - محمود منصورDocument3 pagesGene Structure 1+2 - محمود منصورانس ابوهيبةNo ratings yet
- 8d) Translation Summary - 9744 - 2017Document1 page8d) Translation Summary - 9744 - 2017saguNo ratings yet
- Gene To Protein FlashcardsDocument2 pagesGene To Protein FlashcardsTim DAVISNo ratings yet
- TranslationDocument42 pagesTranslationDeeptanshu PrakashNo ratings yet
- Biochem-Lec TransesDocument9 pagesBiochem-Lec TransesK CruzNo ratings yet
- Bio2 SA4 - Palermo, Rivera, ZenarosaDocument2 pagesBio2 SA4 - Palermo, Rivera, Zenarosabombarts190No ratings yet
- 8d) Translation Summary - 9744 - 2018Document1 page8d) Translation Summary - 9744 - 20182022 EMMA WEN XUAN HANSONNo ratings yet
- 4-BIOL 101 Study Guide Quiz 4Document5 pages4-BIOL 101 Study Guide Quiz 4Suraj NaikNo ratings yet
- Transcription and TranslationDocument9 pagesTranscription and TranslationlinhNo ratings yet
- Transcription FactorsDocument13 pagesTranscription Factorsfazila zahoorNo ratings yet
- MARY ANGELIQUE BANOGON (Steps in Gene Expression)Document2 pagesMARY ANGELIQUE BANOGON (Steps in Gene Expression)Mary Angelique BanogonNo ratings yet
- Types of RNA (Kashyap-Jayant, SHUATS)Document8 pagesTypes of RNA (Kashyap-Jayant, SHUATS)JAYANT KASHYAPNo ratings yet
- Lecture - 30oct13Document41 pagesLecture - 30oct13Dagon BrownNo ratings yet
- CYTO DNA TranslationDocument4 pagesCYTO DNA TranslationTherese TimbalNo ratings yet
- Transcription and Processing of Rna: The Steps of Gene Expression in Prokaryotic Cells: DNADocument8 pagesTranscription and Processing of Rna: The Steps of Gene Expression in Prokaryotic Cells: DNACindy GarciaNo ratings yet
- Types of RNA-Worksheet Omar IbrahimDocument5 pagesTypes of RNA-Worksheet Omar IbrahimOmar Ibrahim LNo ratings yet
- MOLECULAR GENETICS AND EVOLUTION-activityDocument2 pagesMOLECULAR GENETICS AND EVOLUTION-activityIvy ManagNo ratings yet
- Replication and Transciption of DnaDocument29 pagesReplication and Transciption of DnaTri Hiu AmborowatiNo ratings yet
- MolBioLec Quiz3Document3 pagesMolBioLec Quiz3angela verayeNo ratings yet
- Video Recap RNA Page 2Document1 pageVideo Recap RNA Page 2Strawberry RoNo ratings yet
- Eukaryotic Genomes: Organization, Regulation, and Evolution: Powerpoint Lectures ForDocument66 pagesEukaryotic Genomes: Organization, Regulation, and Evolution: Powerpoint Lectures Forxo_simpledreamNo ratings yet
- Polypeptide Synthesis: TranscriptionDocument3 pagesPolypeptide Synthesis: TranscriptionliklyNo ratings yet
- Translation ProcessDocument1 pageTranslation ProcesscelineNo ratings yet
- T Li TranslationDocument20 pagesT Li TranslationJosh LopezNo ratings yet
- Gene ExpressionDocument26 pagesGene Expressionceline.ayoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 17 - Transcription and TranslationDocument14 pagesChapter 17 - Transcription and TranslationAdonias NiyurukundoNo ratings yet
- Introduction To ScienceDocument16 pagesIntroduction To SciencevergelglazaroNo ratings yet
- D1.2 Protein SynthesisDocument56 pagesD1.2 Protein SynthesisgabrieldelriobetancourtNo ratings yet
- Central DogmaDocument48 pagesCentral Dogmajhem.me28No ratings yet
- Gene Expression - Protein SynthesisDocument39 pagesGene Expression - Protein SynthesisTawonga ManjiniNo ratings yet
- TranscriptionDocument15 pagesTranscriptioncamila hartmannNo ratings yet
- Protein SynthesisDocument3 pagesProtein Synthesis423003157No ratings yet
- 3D Molecular Translation Worksheetv21Document3 pages3D Molecular Translation Worksheetv21Jonas WelliverNo ratings yet
- General Biology TranscriptionDocument2 pagesGeneral Biology TranscriptionChristine Marylou PalomoNo ratings yet
- Biology Module5 Polypeptide Synthesis s6Document10 pagesBiology Module5 Polypeptide Synthesis s6gvsyjbkwndNo ratings yet
- IB Diploma Biology: Essential Idea: Transcription and Translation Allow The GeneticDocument37 pagesIB Diploma Biology: Essential Idea: Transcription and Translation Allow The GeneticClàudia VicenteNo ratings yet
- Transcription Study GuideDocument5 pagesTranscription Study GuideSubhajit AdakNo ratings yet
- TranslationDocument10 pagesTranslationapi-386303659No ratings yet
- Transcription & Translation Notes PDFDocument20 pagesTranscription & Translation Notes PDFManas RjNo ratings yet
- 5 TranscriptionDocument5 pages5 TranscriptionAnanthan C.RNo ratings yet
- Wind 123.1 PDFDocument30 pagesWind 123.1 PDFKingZhytt DrizNo ratings yet
- Research Template ASNHSDocument30 pagesResearch Template ASNHSKingZhytt DrizNo ratings yet
- King Zhytt C. Driz Grade Xi - EuclidDocument1 pageKing Zhytt C. Driz Grade Xi - EuclidKingZhytt DrizNo ratings yet
- Mesezoic EraDocument55 pagesMesezoic EraKingZhytt DrizNo ratings yet
- Entry 1Document2 pagesEntry 1KingZhytt DrizNo ratings yet
- AQA Biology 2 Revision Notes PDFDocument31 pagesAQA Biology 2 Revision Notes PDFRajashree MuNo ratings yet
- Bio 112 Exp 3 RajnishDocument9 pagesBio 112 Exp 3 RajnishRajnish ShreerajNo ratings yet
- 2229 FullDocument7 pages2229 FullRifqi Thirafi RamadhanNo ratings yet
- PD-L1 Expression in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer: Research ArticleDocument14 pagesPD-L1 Expression in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer: Research ArticleFebrian Parlangga MuisNo ratings yet
- WJEC GCSE Biology - Cells & Cell MembranesDocument4 pagesWJEC GCSE Biology - Cells & Cell MembranesMegan TaylorNo ratings yet
- A Synthesis On The Evidences That Living Organisms Possess The Different Characteristics of Living MatterDocument2 pagesA Synthesis On The Evidences That Living Organisms Possess The Different Characteristics of Living MatterJev De CastilloNo ratings yet
- Chapter-Wise DPP CONTENT1 PDFDocument2 pagesChapter-Wise DPP CONTENT1 PDFSahar Ahmed Laskar0% (2)
- 2023-04-20 en Biotechnology For Engineers 01 SS 2023Document455 pages2023-04-20 en Biotechnology For Engineers 01 SS 2023yuvaranikasinathan21No ratings yet
- Taxonomic ClassificationDocument3 pagesTaxonomic ClassificationHemant AggarwalNo ratings yet
- (Methods in Molecular Biology 1201) Christopher Peacock (Eds.) - Parasite Genomics Protocols-Humana Press (2015)Document372 pages(Methods in Molecular Biology 1201) Christopher Peacock (Eds.) - Parasite Genomics Protocols-Humana Press (2015)Jacques BernardNo ratings yet
- Jordan2017 Infectious BronchitisDocument28 pagesJordan2017 Infectious BronchitisVicente Vega SanchezNo ratings yet
- Law and Agriculture ProjectDocument15 pagesLaw and Agriculture Projectayush singhNo ratings yet
- Biology Virus NotesDocument7 pagesBiology Virus NotesTiffany Gallina100% (3)
- IPR Neg - 5th WeekDocument301 pagesIPR Neg - 5th WeekIMNo ratings yet
- Patho A 1. 11 Infectious Diseases Tagayuna 2015Document10 pagesPatho A 1. 11 Infectious Diseases Tagayuna 2015Ala'a Emerald AguamNo ratings yet
- RNA-Protein Complexes and Interactions - Methods and Protocols (PDFDrive)Document303 pagesRNA-Protein Complexes and Interactions - Methods and Protocols (PDFDrive)Gordillo GS100% (1)
- A Detailed Lesson Plan in Science 10: (Genetic Mutation)Document9 pagesA Detailed Lesson Plan in Science 10: (Genetic Mutation)Shiella Mae Baltazar BulauitanNo ratings yet
- Artikel Kesehatan Dalam Bahasa Inggris Dan Terjemahannya TerbaruDocument3 pagesArtikel Kesehatan Dalam Bahasa Inggris Dan Terjemahannya TerbaruRafaelDimasRizky67% (3)
- ViruzhinkiDocument20 pagesViruzhinkiЕгор ЧудовскийNo ratings yet
- Cell Organelles 11Document32 pagesCell Organelles 11Mamalumpong NnekaNo ratings yet
- Classification PPT - 2Document18 pagesClassification PPT - 2Meilanie Meigie Jacklien KaengNo ratings yet
- Gene TherapyDocument3 pagesGene TherapyGleeson Jay NiedoNo ratings yet
- 13 - Adverse Drug Reactions CausesDocument4 pages13 - Adverse Drug Reactions CausesRojas Evert AlonsoNo ratings yet
- Concept Map - Biology - 2018 - JulyDocument1 pageConcept Map - Biology - 2018 - JulyRahique ShuaibNo ratings yet
- Enzyme: Oleh Yana Cahyana Stp.,Dea.,Ph.DDocument21 pagesEnzyme: Oleh Yana Cahyana Stp.,Dea.,Ph.DDETA HARTININo ratings yet
- JNTUH MTech Biotech Syllabus (For Affiliated Colleges) 2010-2012Document40 pagesJNTUH MTech Biotech Syllabus (For Affiliated Colleges) 2010-2012Zahoorullah Shaik MohammedNo ratings yet
- Pharmaceutical Equivalence of Generic Essential DrugsDocument15 pagesPharmaceutical Equivalence of Generic Essential DrugsLiiz PinedaNo ratings yet
- Structure of Proteins - Primary, Secondary, Tertiary Structures, ExamplesDocument11 pagesStructure of Proteins - Primary, Secondary, Tertiary Structures, Examplesshary rajperNo ratings yet
- Experiments With Planaria PDFDocument40 pagesExperiments With Planaria PDFFrancisco Girbal Eiras0% (1)