Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Java Ii Programming Swingmvc Some Advanced Swing
Java Ii Programming Swingmvc Some Advanced Swing
Uploaded by
sante85Copyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Using Built-In Functions: Module OverviewDocument24 pagesUsing Built-In Functions: Module OverviewBobe Danut100% (1)
- Compound Patterns PDFDocument12 pagesCompound Patterns PDFWilly WonkaNo ratings yet
- Jtable: Open Computing Institute, IncDocument39 pagesJtable: Open Computing Institute, IncjaydeepsweNo ratings yet
- Solutions 101Document1 pageSolutions 101Charana StudiosNo ratings yet
- Observer and Observable An Introduction To The Observer Interface and Observable Class Using The Model/View/Controller Architecture As A GuideDocument9 pagesObserver and Observable An Introduction To The Observer Interface and Observable Class Using The Model/View/Controller Architecture As A Guideprasad.dls100% (1)
- Java SwingDocument69 pagesJava SwingAmolNo ratings yet
- Java SwingDocument51 pagesJava SwingAmolNo ratings yet
- IOI - BasicsDocument11 pagesIOI - BasicsamitvohraNo ratings yet
- Presented by Naresh & KiranDocument22 pagesPresented by Naresh & KiranNaimesh ShahNo ratings yet
- Java - JTable, Jtree, JDBCDocument13 pagesJava - JTable, Jtree, JDBCAlex SiabNo ratings yet
- 6.ALV Object Model NotesDocument14 pages6.ALV Object Model NotesNagesh reddyNo ratings yet
- 23 MVC TableDocument10 pages23 MVC TableEben AlbertoNo ratings yet
- JTree Part 1Document11 pagesJTree Part 1Anduin WrynnNo ratings yet
- Unit-2 SwingsDocument117 pagesUnit-2 SwingsOnkar GuttiNo ratings yet
- Stanford CS193p: Developing Applications For iOS Fall 2011Document66 pagesStanford CS193p: Developing Applications For iOS Fall 2011Aryuna Abaycaran Patiño ArizaNo ratings yet
- Model ViewDocument35 pagesModel ViewnishantapatilNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13Document36 pagesChapter 13Debashish RoyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 SwingsDocument33 pagesChapter 10 SwingsfdknkndfNo ratings yet
- Introduction To JFC/SwingDocument75 pagesIntroduction To JFC/SwingKhyatiMakwanaNo ratings yet
- Java QnA Unit4Document25 pagesJava QnA Unit4tyct826No ratings yet
- Data Crow Developer Guide: Tips and Tricks For DevelopersDocument31 pagesData Crow Developer Guide: Tips and Tricks For Developersfjmbn6No ratings yet
- Angular Material Data Table - A Complete ExampleDocument45 pagesAngular Material Data Table - A Complete ExampleOULED SAHELNo ratings yet
- Model-View-Controller: Two (Or More!) Views Is Normal. Examples: MS WordDocument14 pagesModel-View-Controller: Two (Or More!) Views Is Normal. Examples: MS WordZikica PetkovicNo ratings yet
- Change Data CaptureDocument10 pagesChange Data CaptureShivprasad ShahapurkarNo ratings yet
- Behavioral Models: by Dr. Noman HasanyDocument26 pagesBehavioral Models: by Dr. Noman HasanyMuhammad ShahidNo ratings yet
- 4) CKM (Checking Knowledge Module) :: 1) Flow ControlDocument4 pages4) CKM (Checking Knowledge Module) :: 1) Flow ControlDilip Kumar AluguNo ratings yet
- Class Com - Sun.java - Swing.jtableDocument48 pagesClass Com - Sun.java - Swing.jtableXavier JoaquimNo ratings yet
- JText FieldDocument45 pagesJText FielddrsolicNo ratings yet
- TPA - Windows Phone: Data Binding, MVVMDocument24 pagesTPA - Windows Phone: Data Binding, MVVMDamian ChmielewskiNo ratings yet
- GADmpDocument13 pagesGADmpTashu RanaNo ratings yet
- ABAP Objects Design Patterns (MVC and Singleton)Document12 pagesABAP Objects Design Patterns (MVC and Singleton)Sathish BollabattulaNo ratings yet
- Power System SimulatorDocument11 pagesPower System Simulatorbilal nagoriNo ratings yet
- Lab 1 (System Specification in VDM-SL)Document19 pagesLab 1 (System Specification in VDM-SL)omargamalelzikyNo ratings yet
- Growing Java Beans: A Code-Based Intro To Java's Component ArchitectureDocument12 pagesGrowing Java Beans: A Code-Based Intro To Java's Component ArchitectureDayamani KambhampatiNo ratings yet
- Observer and JTableDocument5 pagesObserver and JTableOana IonelNo ratings yet
- Xtra Grid New FeaturesDocument8 pagesXtra Grid New Featuresa7451tNo ratings yet
- Entity Framework in The Enterprise - Notes by Julie LermanDocument4 pagesEntity Framework in The Enterprise - Notes by Julie LermanZoranMatuškoNo ratings yet
- Oracle Reports 6i Press - ReleaseDocument99 pagesOracle Reports 6i Press - ReleaseNelson CastroNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4.2 Understand Design PatternsDocument10 pagesChapter 4.2 Understand Design PatternsShivasangaryNo ratings yet
- Solutions 104Document1 pageSolutions 104Charana StudiosNo ratings yet
- Chapter-2 SwingDocument70 pagesChapter-2 SwingshreyaNo ratings yet
- Unit 5Document85 pagesUnit 5Keerthika AngelNo ratings yet
- UI Software Architectur-L9Document19 pagesUI Software Architectur-L9anto_effendiNo ratings yet
- Tutorial DSL TestTroubleshootingDocument6 pagesTutorial DSL TestTroubleshootingKike BecerraNo ratings yet
- Angular JS-8Document87 pagesAngular JS-8Aishwarya KoreNo ratings yet
- Magento Interview Questions and AnswersDocument14 pagesMagento Interview Questions and AnswersSantosh KumarNo ratings yet
- MG2201 - Process Modeling and Design MethodologyDocument10 pagesMG2201 - Process Modeling and Design MethodologyShimelis MakonnenNo ratings yet
- Using MVC With Swing ComponentsDocument18 pagesUsing MVC With Swing ComponentsKal-el KryptonNo ratings yet
- Alv ProgrammingDocument27 pagesAlv Programmingkevin lauNo ratings yet
- Swing: CS-328 Dick Steflik John MarguliesDocument32 pagesSwing: CS-328 Dick Steflik John MarguliesdaomNo ratings yet
- dbms94400Document22 pagesdbms9440021amtics440No ratings yet
- Swinging Into Swing: Leo S. Primero IIIDocument40 pagesSwinging Into Swing: Leo S. Primero IIIRemigio Rodríguez A.No ratings yet
- Optima PresentationDocument50 pagesOptima PresentationNaveedAhsanJafriNo ratings yet
- SQL TriggersStoredProcsFunctions UpdatedDocument26 pagesSQL TriggersStoredProcsFunctions UpdatedDeepak UpadhyayNo ratings yet
- Dbms440 FinalDocument22 pagesDbms440 Final21amtics440No ratings yet
- CZ Modelling CloudDocument21 pagesCZ Modelling CloudshashiNo ratings yet
- Final Analysis On Monno PDFDocument6 pagesFinal Analysis On Monno PDFbrsumonNo ratings yet
- Eee-III-Analog Electronic Circuits m1Document52 pagesEee-III-Analog Electronic Circuits m1My WritingsNo ratings yet
- Autism Social Skills Profile: Scott BelliniDocument5 pagesAutism Social Skills Profile: Scott BelliniFannyNo ratings yet
- Cad CamDocument4 pagesCad CamRavi BhaisareNo ratings yet
- Valerie Rosa Resume 3Document2 pagesValerie Rosa Resume 3api-715391361No ratings yet
- Panasonic Mini VRF Design Manual Multi Hvac Inc PDFDocument150 pagesPanasonic Mini VRF Design Manual Multi Hvac Inc PDFReymart ManablugNo ratings yet
- RRLDocument3 pagesRRLlena cpaNo ratings yet
- Laboratory ManualDocument62 pagesLaboratory Manualتبارك موسى كريم علوانNo ratings yet
- 4.3.2 Design Development Phase: Chapter 4 - Submission Phase GuidelinesDocument5 pages4.3.2 Design Development Phase: Chapter 4 - Submission Phase GuidelinesHamed AziziangilanNo ratings yet
- Research And: Alaa El-Ashkar, BDS, MS, Maha Taymour, BDS, PHD, and Adel El-Tannir, BDS, MSDDocument8 pagesResearch And: Alaa El-Ashkar, BDS, MS, Maha Taymour, BDS, PHD, and Adel El-Tannir, BDS, MSDDiana TanasaNo ratings yet
- Anusha Dadwani - ResumeDocument2 pagesAnusha Dadwani - Resumeapi-458585393No ratings yet
- The Assignment Problem: Examwise Marks Disrtibution-AssignmentDocument59 pagesThe Assignment Problem: Examwise Marks Disrtibution-AssignmentAlvo KamauNo ratings yet
- Difference Between Institute and University - Difference Between - Institute Vs UniversityDocument5 pagesDifference Between Institute and University - Difference Between - Institute Vs Universitytapar.dashNo ratings yet
- SustainabilityDocument37 pagesSustainabilityMarcin OsieckiNo ratings yet
- Definition of Physical EducationDocument8 pagesDefinition of Physical EducationAkhilesh Jain100% (2)
- School Education and Literacy Department Government of Sindh Office of The District Education Officer (E, S&H.S) District Central KarachiDocument15 pagesSchool Education and Literacy Department Government of Sindh Office of The District Education Officer (E, S&H.S) District Central KarachiNaya PakistanNo ratings yet
- Fire Dampers Installation Instructions: (Static and Dynamic)Document4 pagesFire Dampers Installation Instructions: (Static and Dynamic)sbalu12674No ratings yet
- Author - Docx C++ ProjectDocument10 pagesAuthor - Docx C++ ProjecteyobNo ratings yet
- The Magus AnalysisDocument114 pagesThe Magus AnalysisJohn ScottNo ratings yet
- Bksi CKRWDocument6 pagesBksi CKRWYuga Moga SugamaNo ratings yet
- Smart Cabin For Educational Complex: Prerana More, Vaishnavi Chaudhari & Guided By: Prof. Aarti PawarDocument4 pagesSmart Cabin For Educational Complex: Prerana More, Vaishnavi Chaudhari & Guided By: Prof. Aarti PawarPreranaNo ratings yet
- Aiou Mba ProspectusDocument32 pagesAiou Mba ProspectusHamza75% (8)
- Road Tanker Safety - Design, Equipment, and The Human Factor - SafeRackDocument8 pagesRoad Tanker Safety - Design, Equipment, and The Human Factor - SafeRackSultan MohammedNo ratings yet
- PointLink - Release Notes - R2.4.0.0 Rev.ADocument27 pagesPointLink - Release Notes - R2.4.0.0 Rev.AManuel MolinaNo ratings yet
- 06 - Transmission-7-8-921F-14 Sept.15Document29 pages06 - Transmission-7-8-921F-14 Sept.15Franky Fernandez100% (1)
- Video - Digital Video Recorder 440/480 SeriesDocument3 pagesVideo - Digital Video Recorder 440/480 SeriesMonir UjjamanNo ratings yet
- Research DossierDocument7 pagesResearch Dossierapi-253218159No ratings yet
- Sem 1 12 - 13 AnswerDocument14 pagesSem 1 12 - 13 AnswerBryan LeeNo ratings yet
- Regna Darnell (editor), Joshua Smith (editor), Michelle Hamilton (editor), Robert L. A. Hancock (editor) - The Franz Boas Papers, Volume 1_ Franz Boas as Public Intellectual―Theory, Ethnography, ActivDocument409 pagesRegna Darnell (editor), Joshua Smith (editor), Michelle Hamilton (editor), Robert L. A. Hancock (editor) - The Franz Boas Papers, Volume 1_ Franz Boas as Public Intellectual―Theory, Ethnography, ActivFacundo GuadagnoNo ratings yet
- AN ANALYSIS OF BAD LANGUAGE USED BY "SUM 41s" LYRICSDocument8 pagesAN ANALYSIS OF BAD LANGUAGE USED BY "SUM 41s" LYRICSHari Zajuli100% (1)
Java Ii Programming Swingmvc Some Advanced Swing
Java Ii Programming Swingmvc Some Advanced Swing
Uploaded by
sante85Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Java Ii Programming Swingmvc Some Advanced Swing
Java Ii Programming Swingmvc Some Advanced Swing
Uploaded by
sante85Copyright:
Available Formats
JAVA II PROGRAMMING
SWINGMVC
Some… Advanced Swing
MVC Architecture
Jtable
Jlist
JTextArea
Jscrollpane
More Layout Managers
ITP 220 Fall 07-- Slide 1
The Model-View-Controller Architecture
• Swing uses the model-view-controller architecture (MVC) as the fundamental design
behind each of its components
• Model
The model encompasses the state data for each component. There are different models
for different types of components. For example, the model of a menu might contain a
list of the menu items the user can select from. This information remains the same no
matter how the component is painted on the screen; model data always exists
independent of the component's visual representation.
• View
The view refers to how you see the component on the screen.
• Controller
The controller is the portion of the user interface that dictates how the component
interacts with events. Events come in many forms - a mouse click, gaining or losing
focus, a keyboard event, etc. The controller decides how each component will react to
the event - if it reacts at all.
ITP 220 Fall 07-- Slide 2
The Model-View-Controller Architecture
The model passes
its data to the view
for rendering
Model View
The controller The view determines
updates the model which events are passed
Controller
based on the events to the controller
received
View
Model
Controller
Component UI-Delegate
With Swing, the view and the controller are combined into a UI-Delegate object
ITP 220 Fall 07-- Slide 3
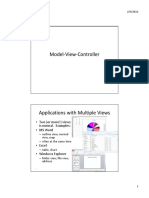
Tables
• Tables are used to display data in a spreadsheet fashion
• The JFC JTable is oriented toward displaying database records in
which each row displays a row in the database, and each column
displays different record’s values for the same field
ITP 220 Fall 07-- Slide 4
Class
JTable
• JTable is a user-interface component that presents data in a two-dimensional
table format
• The JTable has many features that make it possible to customize its rendering
and editing but provides defaults for these features.
• A JTable consists of:
– Rows of data
– Columns of data
– Column headers
– An editor, if you want cells to be editable
– A TableModel, usually a subclass of AbstractTableModel, which stores the table’s data
– A TableColumnModel, usually DefaultTableColumnModel, which controls the
behavior of the table’s columns and gives access to the TableColumns
– A ListSelectionModel, usually DefaultListSelectionModel, which keeps track
of the JTable’s currently selected row(s)
– A TableCellRenderer, usually an instance of DefaultCellRenderer
– Multiple TableColumns, which store graphical information about each column
– A JTableHeader which displays column headers
ITP 220 Fall 07-- Slide 5
Class
JTable
• Steps in creating and using JTable
– Create a JTable (there are 7 different constructors)
– Create a JScrollPane that can be used to scroll around the JTable
via createScrollPaneForTable()
– Place the JTable within a container
– Control whether grid lines should be drawn via setShowGrid()
– Specify a default value for a cell via setValueAt()
– Get the value for a cell via getValueAt()
– Make individual cells selectable via setCellSelectionEnabled()
– Find out which cells are selected via the JTable’s
ListSelectionModel and the TableColumnModel’s
ListSelectionModel
– Add new rows and columns via the JTable’s TableModel
ITP 220 Fall 07-- Slide 6
Class
AbstractTableModel
• AbstractTableModel is an abstract class that implements most of
the TableModel interface
• The TableModel methods that are not implemented are
getRowCount() , getColumnCount() , and getValueAt()
• Steps in creating and using AbstractTableModel
– Create an AbstractTableModel subclass
– Implement the getRowCount() , getColumnCount() , and
getValueAt() methods
– Instantiate an instance of the subclass
– Create a JTable using the subclass via new JTable( model )
ITP 220 Fall 07-- Slide 7
Class
AbstractTableModel
• To set up a table with 10 rows and 10 columns of
numbers:
TableModel dataModel = new AbstractTableModel() {
public int getColumnCount() { return 10; }
public int getRowCount() { return 10;}
public Object getValueAt(int row, int col) { return
new Integer(row*col); }
};
JTable table = new JTable(dataModel);
JScrollPane scrollpane = new JScrollPane(table);
ITP 220 Fall 07-- Slide 8
Class
DefaultTableModel
• DefaultTableModel is the JFC’s default subclass of the abstract
AbstractTableModel class
• If a JTable is created and no TableModel is specified, the JTable
creates an instance of DefaultJTableModel and uses it to hold the
table’s data
• If you have complex data, you may prefer to extend the
AbstractTableModel yourself
• Steps in creating and using DefaultTableModel
– Create a DefaultTableModel (there are 6 different constructors)
DefaultTableModel( Vector data, Vector columnIDs)
– Create a JTable using the DefaultTableModel via new
JTable(model)
ITP 220 Fall 07-- Slide 9
Class
DefaultTableModel
• Steps in creating and using DefaultTableModel
– Define a TableModelListener to receive
TableModelEvents when the model changes, or when one or
more cell’s contents change
– Add a row to the DefaultTableModel via addRow()
– Add a column to the DefaultTableModel via addColumn()
– Get the current value of a cell in a DefaultTableModel via
getValueAt()
– Move one or more rows via moveRow()
– Load a new set of data into a DefaultTableModel via
setDataVector()
– Get the number of rows or columns in a DefaultTableModel via
getRowCount() and getColumnCount()
ITP 220 Fall 07-- Slide 10
Class
TableColumn
• A TableColumn contains the graphical attributes for a single column of
data in a JTable’s model
• It stores information about the column header, the column height and
width, and how cells in the column should be drawn and edited
• Steps in creating and using TableColumn
– TableColumns are created automatically when columns are added to the
table model. They are accessed via the table column model via
getColumn()
– Specify the TableCellEditor to use when editing the TableColumn’s
cells
JCheckBox cbox = new JCheckBox()
DefaultCellEditor editor = new DefaultCellEditor(cbox)
tableColumn.setCellEditor(editor)
– Change the column header via setHeaderValue()
ITP 220 Fall 07-- Slide 11
Class
DefaultTableColumnModel
• DefaultTableColumnModel is the JFC’s default implementation
of the TableColumnModel interface
• This class is used to keep track of information about table columns. It
gives access to TableColumns and keeps track of general
characteristics of columns, like column margins and widths. It also
contains a ListSelectionModel that it uses to keep track of
which columns are currently selected
• Steps in creating and using DefaultTableColumnModel
– You will usually let the JTable create it
– Specify the selection mode for the DefaultTableColumnModel via
setSelectionMode()
ITP 220 Fall 07-- Slide 12
Class
DefaultTableColumnModel
• Steps in creating and using DefaultTableColumnModel
– Define a ColumnModelListener to receive
TableColumnModelEvents when a column is added, removed,
moved, margins are changed, or the column selection state changes
– Get the currently selected columns via getSelectedColumns()
ITP 220 Fall 07-- Slide 13
Class
JTableHeader
• A JTableHeader is a companion to JTable and contains the graphical
representation of the table’s column headers
• A JTableHeader does not display by default but will display if you place a
JTable into a JScrollPane created using the
createScrollPaneForTable() method
• A JTableHeader draws itself using information from the
TableColumnModel associated with the JTable
• Steps in creating and using JTableHeader
– You will usually let the JTable create it
– Change the TableCellRenderer used to draw a column’s header via
setHeaderRenderer()
– Enable/Disable column reordering via
setReorderingAllowed()
ITP 220 Fall 07-- Slide 14
Class
DefaultCellEditor
• DefaultCellEditor is an editor that can be used with a JTable
or a JTree to edit table cells and tree nodes
• It can edit in one of three ways: as a text field, as a check box, or as a
combo box
• Steps in creating and using a DefaultCellEditor
– Create a component to be used by the DefaultCellEditor and set its
properties
– Create a DefaultCellEditor using the component you just created
– Specify how many mouse clicks it takes to start the editor via
setClickCountToStart() (default is 2)
– Define a CellEditorListener to receive ChangeEvents when a
cell editing session ends
ITP 220 Fall 07-- Slide 15
JTable
Me th o d De sc rip tio n
void
addTableModelListener(
TableModelListener
listener )
Add a TableModelListener to the
TableModel. The TableModel will notify the
TableModelListener of changes in the
TableModel.
void
removeTableModelListener
( TableModelListener
listener )
Remove a previously added
TableModelListener from the TableModel.
Class getColumnClass(
int columnIndex )
Get the Class object for values in the column with
specified columnIndex.
int getColumnCount()
Get the number of columns in the TableModel.
String getColumnName(
int columnIndex )
Get the name of the column with the given columnIndex.
int getRowCount()
Get the number of rows in the TableModel.
TableModel interface methods and descriptions.
ITP 220 Fall 07-- Slide 16
JTable
Object
getValueAt(
int rowIndex,
int
columnIndex )
Get an Object reference to the value stored in the TableModel
at the given row and column indices.
void
setValueAt(
Object value,
int rowIndex,
int
columnIndex )
Set the value stored in the TableModel at the given row and
column indices.
boolean
isCellEditable
( int
rowIndex, int
columnIndex )
Return true if the cell at the given row and column indices is
editable.
TableModel interface methods and descriptions.
ITP 220 Fall 07-- Slide 17
You might also like
- Using Built-In Functions: Module OverviewDocument24 pagesUsing Built-In Functions: Module OverviewBobe Danut100% (1)
- Compound Patterns PDFDocument12 pagesCompound Patterns PDFWilly WonkaNo ratings yet
- Jtable: Open Computing Institute, IncDocument39 pagesJtable: Open Computing Institute, IncjaydeepsweNo ratings yet
- Solutions 101Document1 pageSolutions 101Charana StudiosNo ratings yet
- Observer and Observable An Introduction To The Observer Interface and Observable Class Using The Model/View/Controller Architecture As A GuideDocument9 pagesObserver and Observable An Introduction To The Observer Interface and Observable Class Using The Model/View/Controller Architecture As A Guideprasad.dls100% (1)
- Java SwingDocument69 pagesJava SwingAmolNo ratings yet
- Java SwingDocument51 pagesJava SwingAmolNo ratings yet
- IOI - BasicsDocument11 pagesIOI - BasicsamitvohraNo ratings yet
- Presented by Naresh & KiranDocument22 pagesPresented by Naresh & KiranNaimesh ShahNo ratings yet
- Java - JTable, Jtree, JDBCDocument13 pagesJava - JTable, Jtree, JDBCAlex SiabNo ratings yet
- 6.ALV Object Model NotesDocument14 pages6.ALV Object Model NotesNagesh reddyNo ratings yet
- 23 MVC TableDocument10 pages23 MVC TableEben AlbertoNo ratings yet
- JTree Part 1Document11 pagesJTree Part 1Anduin WrynnNo ratings yet
- Unit-2 SwingsDocument117 pagesUnit-2 SwingsOnkar GuttiNo ratings yet
- Stanford CS193p: Developing Applications For iOS Fall 2011Document66 pagesStanford CS193p: Developing Applications For iOS Fall 2011Aryuna Abaycaran Patiño ArizaNo ratings yet
- Model ViewDocument35 pagesModel ViewnishantapatilNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13Document36 pagesChapter 13Debashish RoyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 SwingsDocument33 pagesChapter 10 SwingsfdknkndfNo ratings yet
- Introduction To JFC/SwingDocument75 pagesIntroduction To JFC/SwingKhyatiMakwanaNo ratings yet
- Java QnA Unit4Document25 pagesJava QnA Unit4tyct826No ratings yet
- Data Crow Developer Guide: Tips and Tricks For DevelopersDocument31 pagesData Crow Developer Guide: Tips and Tricks For Developersfjmbn6No ratings yet
- Angular Material Data Table - A Complete ExampleDocument45 pagesAngular Material Data Table - A Complete ExampleOULED SAHELNo ratings yet
- Model-View-Controller: Two (Or More!) Views Is Normal. Examples: MS WordDocument14 pagesModel-View-Controller: Two (Or More!) Views Is Normal. Examples: MS WordZikica PetkovicNo ratings yet
- Change Data CaptureDocument10 pagesChange Data CaptureShivprasad ShahapurkarNo ratings yet
- Behavioral Models: by Dr. Noman HasanyDocument26 pagesBehavioral Models: by Dr. Noman HasanyMuhammad ShahidNo ratings yet
- 4) CKM (Checking Knowledge Module) :: 1) Flow ControlDocument4 pages4) CKM (Checking Knowledge Module) :: 1) Flow ControlDilip Kumar AluguNo ratings yet
- Class Com - Sun.java - Swing.jtableDocument48 pagesClass Com - Sun.java - Swing.jtableXavier JoaquimNo ratings yet
- JText FieldDocument45 pagesJText FielddrsolicNo ratings yet
- TPA - Windows Phone: Data Binding, MVVMDocument24 pagesTPA - Windows Phone: Data Binding, MVVMDamian ChmielewskiNo ratings yet
- GADmpDocument13 pagesGADmpTashu RanaNo ratings yet
- ABAP Objects Design Patterns (MVC and Singleton)Document12 pagesABAP Objects Design Patterns (MVC and Singleton)Sathish BollabattulaNo ratings yet
- Power System SimulatorDocument11 pagesPower System Simulatorbilal nagoriNo ratings yet
- Lab 1 (System Specification in VDM-SL)Document19 pagesLab 1 (System Specification in VDM-SL)omargamalelzikyNo ratings yet
- Growing Java Beans: A Code-Based Intro To Java's Component ArchitectureDocument12 pagesGrowing Java Beans: A Code-Based Intro To Java's Component ArchitectureDayamani KambhampatiNo ratings yet
- Observer and JTableDocument5 pagesObserver and JTableOana IonelNo ratings yet
- Xtra Grid New FeaturesDocument8 pagesXtra Grid New Featuresa7451tNo ratings yet
- Entity Framework in The Enterprise - Notes by Julie LermanDocument4 pagesEntity Framework in The Enterprise - Notes by Julie LermanZoranMatuškoNo ratings yet
- Oracle Reports 6i Press - ReleaseDocument99 pagesOracle Reports 6i Press - ReleaseNelson CastroNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4.2 Understand Design PatternsDocument10 pagesChapter 4.2 Understand Design PatternsShivasangaryNo ratings yet
- Solutions 104Document1 pageSolutions 104Charana StudiosNo ratings yet
- Chapter-2 SwingDocument70 pagesChapter-2 SwingshreyaNo ratings yet
- Unit 5Document85 pagesUnit 5Keerthika AngelNo ratings yet
- UI Software Architectur-L9Document19 pagesUI Software Architectur-L9anto_effendiNo ratings yet
- Tutorial DSL TestTroubleshootingDocument6 pagesTutorial DSL TestTroubleshootingKike BecerraNo ratings yet
- Angular JS-8Document87 pagesAngular JS-8Aishwarya KoreNo ratings yet
- Magento Interview Questions and AnswersDocument14 pagesMagento Interview Questions and AnswersSantosh KumarNo ratings yet
- MG2201 - Process Modeling and Design MethodologyDocument10 pagesMG2201 - Process Modeling and Design MethodologyShimelis MakonnenNo ratings yet
- Using MVC With Swing ComponentsDocument18 pagesUsing MVC With Swing ComponentsKal-el KryptonNo ratings yet
- Alv ProgrammingDocument27 pagesAlv Programmingkevin lauNo ratings yet
- Swing: CS-328 Dick Steflik John MarguliesDocument32 pagesSwing: CS-328 Dick Steflik John MarguliesdaomNo ratings yet
- dbms94400Document22 pagesdbms9440021amtics440No ratings yet
- Swinging Into Swing: Leo S. Primero IIIDocument40 pagesSwinging Into Swing: Leo S. Primero IIIRemigio Rodríguez A.No ratings yet
- Optima PresentationDocument50 pagesOptima PresentationNaveedAhsanJafriNo ratings yet
- SQL TriggersStoredProcsFunctions UpdatedDocument26 pagesSQL TriggersStoredProcsFunctions UpdatedDeepak UpadhyayNo ratings yet
- Dbms440 FinalDocument22 pagesDbms440 Final21amtics440No ratings yet
- CZ Modelling CloudDocument21 pagesCZ Modelling CloudshashiNo ratings yet
- Final Analysis On Monno PDFDocument6 pagesFinal Analysis On Monno PDFbrsumonNo ratings yet
- Eee-III-Analog Electronic Circuits m1Document52 pagesEee-III-Analog Electronic Circuits m1My WritingsNo ratings yet
- Autism Social Skills Profile: Scott BelliniDocument5 pagesAutism Social Skills Profile: Scott BelliniFannyNo ratings yet
- Cad CamDocument4 pagesCad CamRavi BhaisareNo ratings yet
- Valerie Rosa Resume 3Document2 pagesValerie Rosa Resume 3api-715391361No ratings yet
- Panasonic Mini VRF Design Manual Multi Hvac Inc PDFDocument150 pagesPanasonic Mini VRF Design Manual Multi Hvac Inc PDFReymart ManablugNo ratings yet
- RRLDocument3 pagesRRLlena cpaNo ratings yet
- Laboratory ManualDocument62 pagesLaboratory Manualتبارك موسى كريم علوانNo ratings yet
- 4.3.2 Design Development Phase: Chapter 4 - Submission Phase GuidelinesDocument5 pages4.3.2 Design Development Phase: Chapter 4 - Submission Phase GuidelinesHamed AziziangilanNo ratings yet
- Research And: Alaa El-Ashkar, BDS, MS, Maha Taymour, BDS, PHD, and Adel El-Tannir, BDS, MSDDocument8 pagesResearch And: Alaa El-Ashkar, BDS, MS, Maha Taymour, BDS, PHD, and Adel El-Tannir, BDS, MSDDiana TanasaNo ratings yet
- Anusha Dadwani - ResumeDocument2 pagesAnusha Dadwani - Resumeapi-458585393No ratings yet
- The Assignment Problem: Examwise Marks Disrtibution-AssignmentDocument59 pagesThe Assignment Problem: Examwise Marks Disrtibution-AssignmentAlvo KamauNo ratings yet
- Difference Between Institute and University - Difference Between - Institute Vs UniversityDocument5 pagesDifference Between Institute and University - Difference Between - Institute Vs Universitytapar.dashNo ratings yet
- SustainabilityDocument37 pagesSustainabilityMarcin OsieckiNo ratings yet
- Definition of Physical EducationDocument8 pagesDefinition of Physical EducationAkhilesh Jain100% (2)
- School Education and Literacy Department Government of Sindh Office of The District Education Officer (E, S&H.S) District Central KarachiDocument15 pagesSchool Education and Literacy Department Government of Sindh Office of The District Education Officer (E, S&H.S) District Central KarachiNaya PakistanNo ratings yet
- Fire Dampers Installation Instructions: (Static and Dynamic)Document4 pagesFire Dampers Installation Instructions: (Static and Dynamic)sbalu12674No ratings yet
- Author - Docx C++ ProjectDocument10 pagesAuthor - Docx C++ ProjecteyobNo ratings yet
- The Magus AnalysisDocument114 pagesThe Magus AnalysisJohn ScottNo ratings yet
- Bksi CKRWDocument6 pagesBksi CKRWYuga Moga SugamaNo ratings yet
- Smart Cabin For Educational Complex: Prerana More, Vaishnavi Chaudhari & Guided By: Prof. Aarti PawarDocument4 pagesSmart Cabin For Educational Complex: Prerana More, Vaishnavi Chaudhari & Guided By: Prof. Aarti PawarPreranaNo ratings yet
- Aiou Mba ProspectusDocument32 pagesAiou Mba ProspectusHamza75% (8)
- Road Tanker Safety - Design, Equipment, and The Human Factor - SafeRackDocument8 pagesRoad Tanker Safety - Design, Equipment, and The Human Factor - SafeRackSultan MohammedNo ratings yet
- PointLink - Release Notes - R2.4.0.0 Rev.ADocument27 pagesPointLink - Release Notes - R2.4.0.0 Rev.AManuel MolinaNo ratings yet
- 06 - Transmission-7-8-921F-14 Sept.15Document29 pages06 - Transmission-7-8-921F-14 Sept.15Franky Fernandez100% (1)
- Video - Digital Video Recorder 440/480 SeriesDocument3 pagesVideo - Digital Video Recorder 440/480 SeriesMonir UjjamanNo ratings yet
- Research DossierDocument7 pagesResearch Dossierapi-253218159No ratings yet
- Sem 1 12 - 13 AnswerDocument14 pagesSem 1 12 - 13 AnswerBryan LeeNo ratings yet
- Regna Darnell (editor), Joshua Smith (editor), Michelle Hamilton (editor), Robert L. A. Hancock (editor) - The Franz Boas Papers, Volume 1_ Franz Boas as Public Intellectual―Theory, Ethnography, ActivDocument409 pagesRegna Darnell (editor), Joshua Smith (editor), Michelle Hamilton (editor), Robert L. A. Hancock (editor) - The Franz Boas Papers, Volume 1_ Franz Boas as Public Intellectual―Theory, Ethnography, ActivFacundo GuadagnoNo ratings yet
- AN ANALYSIS OF BAD LANGUAGE USED BY "SUM 41s" LYRICSDocument8 pagesAN ANALYSIS OF BAD LANGUAGE USED BY "SUM 41s" LYRICSHari Zajuli100% (1)