Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Earth'S Magnetic Field and Magnetic Reversals: Lesson 12
Earth'S Magnetic Field and Magnetic Reversals: Lesson 12
Uploaded by
mila basbas0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views8 pages1) The document discusses Earth's magnetic field and magnetic reversals, where the positions of the magnetic north and south poles are interchanged due to changes in the direction of flow in the outer core.
2) As magma rises and cools, iron-rich minerals align with the magnetic field, forming "magnetic stripes" in rocks that indicate the polarity of the field at the time the rock formed.
3) These magnetic anomalies provide evidence of sea-floor spreading, as the stripes are mirrored on each side of mid-ocean ridges.
Original Description:
the trojan war
Original Title
Lesson 12b
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Document1) The document discusses Earth's magnetic field and magnetic reversals, where the positions of the magnetic north and south poles are interchanged due to changes in the direction of flow in the outer core.
2) As magma rises and cools, iron-rich minerals align with the magnetic field, forming "magnetic stripes" in rocks that indicate the polarity of the field at the time the rock formed.
3) These magnetic anomalies provide evidence of sea-floor spreading, as the stripes are mirrored on each side of mid-ocean ridges.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views8 pagesEarth'S Magnetic Field and Magnetic Reversals: Lesson 12
Earth'S Magnetic Field and Magnetic Reversals: Lesson 12
Uploaded by
mila basbas1) The document discusses Earth's magnetic field and magnetic reversals, where the positions of the magnetic north and south poles are interchanged due to changes in the direction of flow in the outer core.
2) As magma rises and cools, iron-rich minerals align with the magnetic field, forming "magnetic stripes" in rocks that indicate the polarity of the field at the time the rock formed.
3) These magnetic anomalies provide evidence of sea-floor spreading, as the stripes are mirrored on each side of mid-ocean ridges.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 8
LESSON 12
EARTH’S MAGNETIC FIELD AND
MAGNETIC REVERSALS
LESSON OBJECTIVES:
1. Define magnetic reversal;
2. Discuss how and why magnetic
poles flip or change;
3. Describe the magnetic
anomalies in the rocks ; and
4. Explain how magnetic
reversals provide evidence for
sea-floor spreading
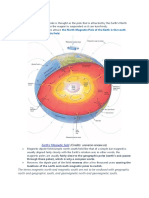
EARTH’S MAGNETIC FIELD
is a dipole. It has:
a.) North Magnetic
Pole
b.) South Magnetic
Pole
Importance:
1.) deflects solar
wind & protects life
on Earth from solar
wind or radiation
2.) allows us to use
a compass to
navigate around the
world.
Earth’s magnetic
poles are
constantly
changing
MAGNETIC REVERSAL
Also called
Geomagnetic
Reversal
It happens when
the positions of the
magnetic North pole
and magnetic South
Pole are
interchanged due to
the change in the
direction of flow in
the outer core.
This can be
observed or
explained through
the magnetic stripes
in rocks.
FORMATION OF MAGNETIC STRIPES IN ROCKS
As magma rises
and cools, iron and
magnesium
minerals(magnetite
) align themselves
to the Earth’s
magnetic field
“Magnetic Stripes”
are formed
- indicating the
polarity of the
earth’s magnetic
field the time the
crust was formed.
Magnetic stripes
are mirrored on
each side of the
mid-ocean ridge
NORMAL POLARITY
The present
direction of the
Earth’s magnetic
field
REVERSED POLARITY
The opposite of the
present field
PALEOMAGNETISM
The study of the
record of the Earth’s
magnetic field in
rocks, sediments or
archeological
materials
You might also like
- Lesson in Seafloor Spreading Magnetic Reversal and Theoryr of Plate TectonicDocument3 pagesLesson in Seafloor Spreading Magnetic Reversal and Theoryr of Plate TectonicChristine Mae Francisco BartoloNo ratings yet
- What Is Magnetic Reversal?: Wegener Had GuessedDocument2 pagesWhat Is Magnetic Reversal?: Wegener Had GuessedLhaika Maureen CasisNo ratings yet
- Fs 236 95 PDFDocument2 pagesFs 236 95 PDFprouserdesigner77No ratings yet
- Evidence For Plate Tectonics From Magnetics: William WilcockDocument31 pagesEvidence For Plate Tectonics From Magnetics: William Wilcockmokhamad rizkiNo ratings yet
- Ch-2. Earth's Magnetic Field DoneDocument60 pagesCh-2. Earth's Magnetic Field DoneKiran BNo ratings yet
- Earth Magnetic FieldDocument3 pagesEarth Magnetic FieldOtaku ManNo ratings yet
- WikiEarth's Magnetic FieldDocument17 pagesWikiEarth's Magnetic FieldMateria caicedoNo ratings yet
- Magnetism 3Document18 pagesMagnetism 3VinayKumarNo ratings yet
- Objective: Seismic Waves (P, S and Surface Waves) .: - Explore Properties ofDocument60 pagesObjective: Seismic Waves (P, S and Surface Waves) .: - Explore Properties ofnikki marbellaNo ratings yet
- POWER Nav1 - MIDTERM - Topic 1 & 2Document31 pagesPOWER Nav1 - MIDTERM - Topic 1 & 2CLIJOHN PABLO FORD100% (1)
- Plate TectonicsDocument10 pagesPlate TectonicsKayleighNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Pole Geomagnetic PoleDocument7 pagesMagnetic Pole Geomagnetic Poleravi rathodNo ratings yet
- Squares Sense, Global Mean Sea LevelDocument7 pagesSquares Sense, Global Mean Sea LevelAde RismanNo ratings yet
- Keynote Ias Geography Optional P-1 MaterialDocument55 pagesKeynote Ias Geography Optional P-1 Materialkarthik kNo ratings yet
- Magnetic ReversalDocument3 pagesMagnetic ReversalJean Carmel NoveloNo ratings yet
- Physics Project 2019 20Document13 pagesPhysics Project 2019 20Lavit AroraNo ratings yet
- Articulo InglésDocument3 pagesArticulo Inglésprado.alexaNo ratings yet
- Presentation 2Document4 pagesPresentation 2Johanne MontancesNo ratings yet
- WRISHA Qandeel Roll No.19Document9 pagesWRISHA Qandeel Roll No.19Warisha RanaNo ratings yet
- 6.5 Tectonics and EvidencesDocument28 pages6.5 Tectonics and Evidencesbook wormNo ratings yet
- Eip Revised2Document11 pagesEip Revised2api-404269299No ratings yet
- Magnetic Filed of EarthDocument25 pagesMagnetic Filed of EarthARIHANT SAWANT67% (3)
- CMP27Document1 pageCMP27jafasoh293No ratings yet
- Paleomagnetism See Floor Spreading Convectional CurrentsDocument3 pagesPaleomagnetism See Floor Spreading Convectional CurrentsVishal chaudharyNo ratings yet
- Earth's Magnetic Field - WikipediaDocument36 pagesEarth's Magnetic Field - WikipediaYaynabeba JenberNo ratings yet
- Earth Magnetic FieldDocument11 pagesEarth Magnetic FieldAreeb AhmedNo ratings yet
- A Model of SeaDocument21 pagesA Model of Searajan08ismNo ratings yet
- Navigation 1Document37 pagesNavigation 1Piche Parcon Dayatan100% (1)
- Magnetic ReversalDocument17 pagesMagnetic ReversalMariane HinanibanNo ratings yet
- Tektonik IndonesiaDocument8 pagesTektonik IndonesiaArfaq Fauqi RomadlonNo ratings yet
- Our Living Language: When Magma Rises To The Earth's Surface Ata MidDocument1 pageOur Living Language: When Magma Rises To The Earth's Surface Ata MidStephen LaraNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4 SEAFLOOR PDFDocument21 pagesLecture 4 SEAFLOOR PDFNasukha RifaiNo ratings yet
- Rock Magnetism: A Vibrating Sample Magnetometer, A Widely Used Tool For Measuring Magnetic HysteresisDocument5 pagesRock Magnetism: A Vibrating Sample Magnetometer, A Widely Used Tool For Measuring Magnetic HysteresisSolange Emox SalazarNo ratings yet
- Paleomagnetism: Aging The Ocean FloorDocument18 pagesPaleomagnetism: Aging The Ocean FloorAlimjan AblaNo ratings yet
- Paleomagnetism (Or Palaeomagnetism in The United Kingdom) Is The Study of The RecordDocument2 pagesPaleomagnetism (Or Palaeomagnetism in The United Kingdom) Is The Study of The RecordLeoNo ratings yet
- Untitled DocumentDocument1 pageUntitled DocumentAbsolutely GamingNo ratings yet
- Magnetic ReversalDocument7 pagesMagnetic ReversalJethro James Aguilar100% (1)
- Science 10 Q1 Week 7 The Earths Mechanism - Causes of Plate Movement 2Document30 pagesScience 10 Q1 Week 7 The Earths Mechanism - Causes of Plate Movement 2xan yxNo ratings yet
- Paleomagnetism LECTURE PDFDocument77 pagesPaleomagnetism LECTURE PDFMuhammad YusriadyNo ratings yet
- Earth MagnetismDocument24 pagesEarth MagnetismAyush Srivastava50% (2)
- Chapter Outline: - Magnetic Field and The Dipole - Magnetic Measurement (Washing) - Magnetic Remenance - Magneto-StratigraphyDocument58 pagesChapter Outline: - Magnetic Field and The Dipole - Magnetic Measurement (Washing) - Magnetic Remenance - Magneto-StratigraphySrinivasa Rao BogiNo ratings yet
- Solution Manual For Environmental Geology An Earth Systems Approach 2nd Edition by Merritts Menking DeWet ISBN 1429237430 9781429237437Document36 pagesSolution Manual For Environmental Geology An Earth Systems Approach 2nd Edition by Merritts Menking DeWet ISBN 1429237430 9781429237437stevenedwardsgjfdctxork100% (32)
- GeologyDocument3 pagesGeologyModassir RazaNo ratings yet
- Magnetic StripingDocument34 pagesMagnetic StripingQuella Zairah ReyesNo ratings yet
- Continental Drift and Plate TectonicsDocument6 pagesContinental Drift and Plate TectonicssaikumarreddyNo ratings yet
- The Earth's Magnetism: English For PhysicsDocument9 pagesThe Earth's Magnetism: English For PhysicsNga NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Chapt 3 MarshakDocument27 pagesChapt 3 Marshak周牮No ratings yet
- SMS 1201 A K M Mohiuddin FinalDocument16 pagesSMS 1201 A K M Mohiuddin FinalA.K.M. MohiuddinNo ratings yet
- Document 2Document3 pagesDocument 2kasun148No ratings yet
- The Magentic MethodDocument8 pagesThe Magentic MethodcarlosNo ratings yet
- Seafloor 11 Stem 1Document14 pagesSeafloor 11 Stem 1ENSANO, RHYNS G.No ratings yet
- Eip DraftDocument7 pagesEip Draftapi-404269299No ratings yet
- Jack Oughton - Planetary Science Presentation - A Brief Guide To Terrestrial Magnetism and Field ReversalsDocument22 pagesJack Oughton - Planetary Science Presentation - A Brief Guide To Terrestrial Magnetism and Field ReversalsJack OughtonNo ratings yet
- CH 01 TectonicsDocument46 pagesCH 01 TectonicsTORA TubeNo ratings yet
- J 1751-3928 2006 tb00284 XDocument26 pagesJ 1751-3928 2006 tb00284 XdamasM1No ratings yet
- Magnets Are CoolDocument5 pagesMagnets Are Coolhenryosullivan082No ratings yet
- Our Magnetic Earth: The Science of GeomagnetismFrom EverandOur Magnetic Earth: The Science of GeomagnetismRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (7)
- The Attractive Story of Magnetism with Max Axiom Super Scientist: 4D An Augmented Reading Science ExperienceFrom EverandThe Attractive Story of Magnetism with Max Axiom Super Scientist: 4D An Augmented Reading Science ExperienceNo ratings yet