Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 viewsVentilation: Hannah Kathlyn U. Espinosa
Ventilation: Hannah Kathlyn U. Espinosa
Uploaded by
Hannah KathlynThe exchange of air between the lungs and the atmosphere so that oxygen can be exchanged for carbon dioxide in the alveoli (the tiny air sacs in the lungs).
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Vent. SystemDocument42 pagesVent. SystemAzman ScxNo ratings yet
- HVAC Services in Buildings: Ar. Antara Nandy Assistant Professor Rani Rashmoni College of Architecture, Durgapur (W.B)Document18 pagesHVAC Services in Buildings: Ar. Antara Nandy Assistant Professor Rani Rashmoni College of Architecture, Durgapur (W.B)Archi PinuNo ratings yet
- Lecture Week 3Document23 pagesLecture Week 3Saad SohailNo ratings yet
- Topic3 Ventilation Part 2Document51 pagesTopic3 Ventilation Part 2Anisha AdzihanNo ratings yet
- Mechanical VentatilationDocument17 pagesMechanical VentatilationAkriti GhildiyalNo ratings yet
- Natural N Mechanical VentilationDocument33 pagesNatural N Mechanical VentilationdevrishabhNo ratings yet
- Online 2020-Session 18 B VentilationDocument1 pageOnline 2020-Session 18 B VentilationExy DelgadoNo ratings yet
- mt1 SeatworkDocument3 pagesmt1 SeatworkMhel Maverick AbalosNo ratings yet
- Topic3 Ventilation Part 2Document32 pagesTopic3 Ventilation Part 2elleyashahariNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Ventilation SystemDocument12 pagesMechanical Ventilation SystemTom JosephNo ratings yet
- Ventilation and Its ImportanceDocument41 pagesVentilation and Its Importancejoy abraham100% (1)
- Topic3 Ventilation Part 2 PDFDocument32 pagesTopic3 Ventilation Part 2 PDFFrancis TiehNo ratings yet
- Air Conditioning SystemDocument9 pagesAir Conditioning SystemFahmy AfiffNo ratings yet
- Func of VentilationDocument3 pagesFunc of Ventilationdinsha dineshNo ratings yet
- Lesson 11 - 13Document11 pagesLesson 11 - 13jhess QuevadaNo ratings yet
- Building Services-Iii: Hvac, Lifts and Escalators and Fire FightingDocument22 pagesBuilding Services-Iii: Hvac, Lifts and Escalators and Fire FightingANURAG GAGANNo ratings yet
- HVAC - Part-1Document63 pagesHVAC - Part-1ShubhaNo ratings yet
- M&E Topic3b (Mechanical Ventilation)Document28 pagesM&E Topic3b (Mechanical Ventilation)Izzat AdibNo ratings yet
- Unit IDocument32 pagesUnit IParzivalNo ratings yet
- VentilationDocument29 pagesVentilationGaurika GroverNo ratings yet
- Reading Lecture 5-6 Mechanical VentilationDocument13 pagesReading Lecture 5-6 Mechanical VentilationMd. Rizwan Hasan Kabir ShovonNo ratings yet
- Abe114 Finals MergeDocument349 pagesAbe114 Finals MergeJomarie EstorgioNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Ventilation: By-Shallaki Agrawal Sybdes-Id Itm IdmDocument5 pagesMechanical Ventilation: By-Shallaki Agrawal Sybdes-Id Itm Idmshallaki agrawalNo ratings yet
- Diploma 2 in Construction-Building Services 3: More Building Service Systems Are Listed On The Next Slide .Document48 pagesDiploma 2 in Construction-Building Services 3: More Building Service Systems Are Listed On The Next Slide .Thabiso Fire MpuleNo ratings yet
- VentilationDocument28 pagesVentilationTannum Negi0% (1)
- Mac Mod 16 FinalsDocument12 pagesMac Mod 16 FinalsNathanael BerganosNo ratings yet
- Flipped Classroom Activity - PHDocument15 pagesFlipped Classroom Activity - PH3344 Shubham ChouguleNo ratings yet
- Industrial VentilationDocument70 pagesIndustrial VentilationAnkur Sharma86% (7)
- Ventilation and Air-ConditioningDocument93 pagesVentilation and Air-ConditioningEmmanuel P Dube100% (2)
- AIRCONDocument7 pagesAIRCONDECIPOLO, KENNETH JOHN E.No ratings yet
- Climatology PPT 3-Day Lighting and Natural Ventilation PDFDocument13 pagesClimatology PPT 3-Day Lighting and Natural Ventilation PDFMushthaq MahmoodNo ratings yet
- ABALOS, Mhel Maverick S. MT Seatwork 1Document3 pagesABALOS, Mhel Maverick S. MT Seatwork 1Mhel Maverick AbalosNo ratings yet
- DDWR 1413 - Environmental Physics and SustainabilityDocument36 pagesDDWR 1413 - Environmental Physics and SustainabilityAnGie LeeNo ratings yet
- MechVent 062906Document2 pagesMechVent 062906Rabinder BakhshiNo ratings yet
- Introduction To System in BuildingsDocument59 pagesIntroduction To System in Buildingsnora hajiNo ratings yet
- Exp 2Document7 pagesExp 2Philip Anthony MasilangNo ratings yet
- Ventilation MechanismDocument13 pagesVentilation Mechanismshreyash guptaNo ratings yet
- Hvac PoDocument2 pagesHvac PoJhon Ciryl M. CalayNo ratings yet
- Ventilation SystemDocument22 pagesVentilation SystemPrakriti Goel100% (3)
- Natural VentilationDocument3 pagesNatural VentilationGeeryl Tayone100% (1)
- ACT Notes (Ventilation)Document4 pagesACT Notes (Ventilation)Sasmita SahooNo ratings yet
- VentilationDocument1 pageVentilationMithila ReleNo ratings yet
- Natural Ventilation Jose SantiagoDocument13 pagesNatural Ventilation Jose SantiagoRuta PawarNo ratings yet
- Ventilation: MDM Nurul Aini/Qus 3206Document22 pagesVentilation: MDM Nurul Aini/Qus 3206Anisha NaiduNo ratings yet
- Topic:-Applications of Hvac in Industries: Submitted By:-Sandeep Kumar B4802B29 REG - NO 10807893Document6 pagesTopic:-Applications of Hvac in Industries: Submitted By:-Sandeep Kumar B4802B29 REG - NO 10807893shailesh singhNo ratings yet
- Module 3 - Engineering Architecture - Hvac & ControlsDocument20 pagesModule 3 - Engineering Architecture - Hvac & ControlsĐặng Gia HoàngNo ratings yet
- HVAC SystemDocument5 pagesHVAC SystemMrinal Kanti RoyNo ratings yet
- What Is Ventilation?Document54 pagesWhat Is Ventilation?Misganaw MekonnenNo ratings yet
- AcousticsDocument5 pagesAcousticsarchi042No ratings yet
- Q302 Hra3Document5 pagesQ302 Hra3vinNo ratings yet
- Ventilation System in Buildings: BY Associate Prof. Dr. Yahya Bin Mohamad YatimDocument47 pagesVentilation System in Buildings: BY Associate Prof. Dr. Yahya Bin Mohamad YatimRasmen ABD. HALUNNo ratings yet
- Hvac TerminologiesDocument4 pagesHvac TerminologiesUrvashi SindhiNo ratings yet
- Services: Literature StudyDocument45 pagesServices: Literature StudySabapathyNo ratings yet
- BLAUBERG Industrial FansDocument40 pagesBLAUBERG Industrial FansBadiNo ratings yet
- Is SEM 4 VentilationDocument11 pagesIs SEM 4 VentilationKhushi ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Sage University IndoreDocument20 pagesSage University IndoreVARSHITA SINGHNo ratings yet
- Infiltration and VentilationDocument20 pagesInfiltration and Ventilationayesha shahidNo ratings yet
- Principles of Natural and Mechanical VentilationDocument37 pagesPrinciples of Natural and Mechanical VentilationSameera Bommisetty100% (2)
- Temperature and Humidity Independent Control (THIC) of Air-conditioning SystemFrom EverandTemperature and Humidity Independent Control (THIC) of Air-conditioning SystemNo ratings yet
- The Complete HVAC BIBLE for Beginners: The Most Practical & Updated Guide to Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning Systems | Installation, Troubleshooting and Repair | Residential & CommercialFrom EverandThe Complete HVAC BIBLE for Beginners: The Most Practical & Updated Guide to Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning Systems | Installation, Troubleshooting and Repair | Residential & CommercialNo ratings yet
Ventilation: Hannah Kathlyn U. Espinosa
Ventilation: Hannah Kathlyn U. Espinosa
Uploaded by
Hannah Kathlyn0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views11 pagesThe exchange of air between the lungs and the atmosphere so that oxygen can be exchanged for carbon dioxide in the alveoli (the tiny air sacs in the lungs).
Original Title
Ventilation
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe exchange of air between the lungs and the atmosphere so that oxygen can be exchanged for carbon dioxide in the alveoli (the tiny air sacs in the lungs).
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views11 pagesVentilation: Hannah Kathlyn U. Espinosa
Ventilation: Hannah Kathlyn U. Espinosa
Uploaded by
Hannah KathlynThe exchange of air between the lungs and the atmosphere so that oxygen can be exchanged for carbon dioxide in the alveoli (the tiny air sacs in the lungs).
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 11
VENTILATION
Hannah Kathlyn U. Espinosa
Is the process of “changing” or replacing
air in any space to provide indoor air
quality (control temperature, replenish
oxygen, remove moisture, odors, smoke,
heat, dust, airborne bacteria and carbon
dioxide)
VENTILATION SYSTEM
Natural ventilation - is the flow of
outdoor air caused by wind and air
density differences
Mechanical (forced) ventilation - is
driven by mechanical work
Hybrid ventilation - combination of
natural and mechanical ventilation
Natural ventilation
Natural forces drive outdoor air through
purpose-built, building envelope openings.
Purpose-built openings include windows,
doors, solar chimneys, wind towers and
trickle ventilators.
Mechanical Ventilation
Dynamic pressure of a mechanical device.
Types of Mechanical ventilation
A circulation system such as a ceiling fan, which creates
internal air movement, but does not introduce fresh air.
A pressure system, in which fresh outside air is blown into
the building by inlet fans, creating a higher internal
pressure than the outside air.
A vacuum system, in which stale internal air is extracted
from the building by an exhaust fan, creating lower
pressure inside the building than the outside air.
A balanced system that uses both inlet and extract fans,
maintaining the internal air pressure at a similar level to
the outside air and so reducing air infiltration and draughts.
A local exhaust system that extracts local sources
of heat or contaminants at their source, such as cooker
hoods, fume cupboards and so on.
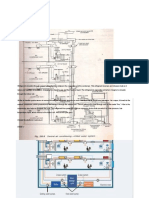
Pressure system
Ciculation system Vacuum system
Local exhaust system
HYBRID VENTILATION
Controlled combination of a Natural
Ventilation and Mechanical Ventilation.
You might also like
- Vent. SystemDocument42 pagesVent. SystemAzman ScxNo ratings yet
- HVAC Services in Buildings: Ar. Antara Nandy Assistant Professor Rani Rashmoni College of Architecture, Durgapur (W.B)Document18 pagesHVAC Services in Buildings: Ar. Antara Nandy Assistant Professor Rani Rashmoni College of Architecture, Durgapur (W.B)Archi PinuNo ratings yet
- Lecture Week 3Document23 pagesLecture Week 3Saad SohailNo ratings yet
- Topic3 Ventilation Part 2Document51 pagesTopic3 Ventilation Part 2Anisha AdzihanNo ratings yet
- Mechanical VentatilationDocument17 pagesMechanical VentatilationAkriti GhildiyalNo ratings yet
- Natural N Mechanical VentilationDocument33 pagesNatural N Mechanical VentilationdevrishabhNo ratings yet
- Online 2020-Session 18 B VentilationDocument1 pageOnline 2020-Session 18 B VentilationExy DelgadoNo ratings yet
- mt1 SeatworkDocument3 pagesmt1 SeatworkMhel Maverick AbalosNo ratings yet
- Topic3 Ventilation Part 2Document32 pagesTopic3 Ventilation Part 2elleyashahariNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Ventilation SystemDocument12 pagesMechanical Ventilation SystemTom JosephNo ratings yet
- Ventilation and Its ImportanceDocument41 pagesVentilation and Its Importancejoy abraham100% (1)
- Topic3 Ventilation Part 2 PDFDocument32 pagesTopic3 Ventilation Part 2 PDFFrancis TiehNo ratings yet
- Air Conditioning SystemDocument9 pagesAir Conditioning SystemFahmy AfiffNo ratings yet
- Func of VentilationDocument3 pagesFunc of Ventilationdinsha dineshNo ratings yet
- Lesson 11 - 13Document11 pagesLesson 11 - 13jhess QuevadaNo ratings yet
- Building Services-Iii: Hvac, Lifts and Escalators and Fire FightingDocument22 pagesBuilding Services-Iii: Hvac, Lifts and Escalators and Fire FightingANURAG GAGANNo ratings yet
- HVAC - Part-1Document63 pagesHVAC - Part-1ShubhaNo ratings yet
- M&E Topic3b (Mechanical Ventilation)Document28 pagesM&E Topic3b (Mechanical Ventilation)Izzat AdibNo ratings yet
- Unit IDocument32 pagesUnit IParzivalNo ratings yet
- VentilationDocument29 pagesVentilationGaurika GroverNo ratings yet
- Reading Lecture 5-6 Mechanical VentilationDocument13 pagesReading Lecture 5-6 Mechanical VentilationMd. Rizwan Hasan Kabir ShovonNo ratings yet
- Abe114 Finals MergeDocument349 pagesAbe114 Finals MergeJomarie EstorgioNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Ventilation: By-Shallaki Agrawal Sybdes-Id Itm IdmDocument5 pagesMechanical Ventilation: By-Shallaki Agrawal Sybdes-Id Itm Idmshallaki agrawalNo ratings yet
- Diploma 2 in Construction-Building Services 3: More Building Service Systems Are Listed On The Next Slide .Document48 pagesDiploma 2 in Construction-Building Services 3: More Building Service Systems Are Listed On The Next Slide .Thabiso Fire MpuleNo ratings yet
- VentilationDocument28 pagesVentilationTannum Negi0% (1)
- Mac Mod 16 FinalsDocument12 pagesMac Mod 16 FinalsNathanael BerganosNo ratings yet
- Flipped Classroom Activity - PHDocument15 pagesFlipped Classroom Activity - PH3344 Shubham ChouguleNo ratings yet
- Industrial VentilationDocument70 pagesIndustrial VentilationAnkur Sharma86% (7)
- Ventilation and Air-ConditioningDocument93 pagesVentilation and Air-ConditioningEmmanuel P Dube100% (2)
- AIRCONDocument7 pagesAIRCONDECIPOLO, KENNETH JOHN E.No ratings yet
- Climatology PPT 3-Day Lighting and Natural Ventilation PDFDocument13 pagesClimatology PPT 3-Day Lighting and Natural Ventilation PDFMushthaq MahmoodNo ratings yet
- ABALOS, Mhel Maverick S. MT Seatwork 1Document3 pagesABALOS, Mhel Maverick S. MT Seatwork 1Mhel Maverick AbalosNo ratings yet
- DDWR 1413 - Environmental Physics and SustainabilityDocument36 pagesDDWR 1413 - Environmental Physics and SustainabilityAnGie LeeNo ratings yet
- MechVent 062906Document2 pagesMechVent 062906Rabinder BakhshiNo ratings yet
- Introduction To System in BuildingsDocument59 pagesIntroduction To System in Buildingsnora hajiNo ratings yet
- Exp 2Document7 pagesExp 2Philip Anthony MasilangNo ratings yet
- Ventilation MechanismDocument13 pagesVentilation Mechanismshreyash guptaNo ratings yet
- Hvac PoDocument2 pagesHvac PoJhon Ciryl M. CalayNo ratings yet
- Ventilation SystemDocument22 pagesVentilation SystemPrakriti Goel100% (3)
- Natural VentilationDocument3 pagesNatural VentilationGeeryl Tayone100% (1)
- ACT Notes (Ventilation)Document4 pagesACT Notes (Ventilation)Sasmita SahooNo ratings yet
- VentilationDocument1 pageVentilationMithila ReleNo ratings yet
- Natural Ventilation Jose SantiagoDocument13 pagesNatural Ventilation Jose SantiagoRuta PawarNo ratings yet
- Ventilation: MDM Nurul Aini/Qus 3206Document22 pagesVentilation: MDM Nurul Aini/Qus 3206Anisha NaiduNo ratings yet
- Topic:-Applications of Hvac in Industries: Submitted By:-Sandeep Kumar B4802B29 REG - NO 10807893Document6 pagesTopic:-Applications of Hvac in Industries: Submitted By:-Sandeep Kumar B4802B29 REG - NO 10807893shailesh singhNo ratings yet
- Module 3 - Engineering Architecture - Hvac & ControlsDocument20 pagesModule 3 - Engineering Architecture - Hvac & ControlsĐặng Gia HoàngNo ratings yet
- HVAC SystemDocument5 pagesHVAC SystemMrinal Kanti RoyNo ratings yet
- What Is Ventilation?Document54 pagesWhat Is Ventilation?Misganaw MekonnenNo ratings yet
- AcousticsDocument5 pagesAcousticsarchi042No ratings yet
- Q302 Hra3Document5 pagesQ302 Hra3vinNo ratings yet
- Ventilation System in Buildings: BY Associate Prof. Dr. Yahya Bin Mohamad YatimDocument47 pagesVentilation System in Buildings: BY Associate Prof. Dr. Yahya Bin Mohamad YatimRasmen ABD. HALUNNo ratings yet
- Hvac TerminologiesDocument4 pagesHvac TerminologiesUrvashi SindhiNo ratings yet
- Services: Literature StudyDocument45 pagesServices: Literature StudySabapathyNo ratings yet
- BLAUBERG Industrial FansDocument40 pagesBLAUBERG Industrial FansBadiNo ratings yet
- Is SEM 4 VentilationDocument11 pagesIs SEM 4 VentilationKhushi ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Sage University IndoreDocument20 pagesSage University IndoreVARSHITA SINGHNo ratings yet
- Infiltration and VentilationDocument20 pagesInfiltration and Ventilationayesha shahidNo ratings yet
- Principles of Natural and Mechanical VentilationDocument37 pagesPrinciples of Natural and Mechanical VentilationSameera Bommisetty100% (2)
- Temperature and Humidity Independent Control (THIC) of Air-conditioning SystemFrom EverandTemperature and Humidity Independent Control (THIC) of Air-conditioning SystemNo ratings yet
- The Complete HVAC BIBLE for Beginners: The Most Practical & Updated Guide to Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning Systems | Installation, Troubleshooting and Repair | Residential & CommercialFrom EverandThe Complete HVAC BIBLE for Beginners: The Most Practical & Updated Guide to Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning Systems | Installation, Troubleshooting and Repair | Residential & CommercialNo ratings yet