Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Three Tier Architecture
Three Tier Architecture
Uploaded by
Roopa R0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
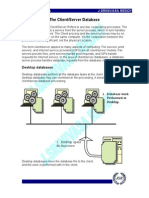
22 views24 pagesThere are several DBMS architectures, including physical centralized, basic 2-tier client-server, and three-tier client-server architectures. The physical centralized architecture combines all components into a single system. The basic 2-tier client-server architecture separates specialized servers and clients. The three-tier client-server architecture introduces an intermediate application server between the client and database server.
Original Description:
CLIENT SERVER
Original Title
THREE TIER ARCHITECTURE
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThere are several DBMS architectures, including physical centralized, basic 2-tier client-server, and three-tier client-server architectures. The physical centralized architecture combines all components into a single system. The basic 2-tier client-server architecture separates specialized servers and clients. The three-tier client-server architecture introduces an intermediate application server between the client and database server.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
22 views24 pagesThree Tier Architecture
Three Tier Architecture
Uploaded by
Roopa RThere are several DBMS architectures, including physical centralized, basic 2-tier client-server, and three-tier client-server architectures. The physical centralized architecture combines all components into a single system. The basic 2-tier client-server architecture separates specialized servers and clients. The three-tier client-server architecture introduces an intermediate application server between the client and database server.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 24
DBMS ARCHITECTURES
ROOPA R,ISE DEPT. 9/14/2019
DBMS ARCHITECTURES
There is a wide variety of different DBMS architectures
•A Physical Centralized Architecture
•Basic 2-tier Client-Server Architectures
•Three Tier Client-Server Architecture
ROOPA R,ISE DEPT. 9/14/2019
Centralized DBMS:
◦ Combines everything into single system including-
DBMS software, hardware, application programs,
and user interface processing software.
◦ The reason was that most users accessed such
systems via computer terminals that did not have
processing power and only provided display
capabilities.
◦ User can still connect through a remote terminal –
however, all processing is done at centralized site
through various communication networks.
ROOPA R,ISE DEPT. 9/14/2019
ROOPA R,ISE DEPT. 9/14/2019
As prices of hardware declined, most users
replaced their terminals with PCs and
workstations. ROOPA R,ISE DEPT. 9/14/2019
ROOPA R,ISE DEPT. 9/14/2019
Disadvantages heavy network traffic high total
costs of ownership (TCO) - maintain a full
instance of the DBMS on each client (workstation)
complex integrity, concurrency and recovery
control - multiple DBMSs may concurrently access
the same shared file
ROOPA R,ISE DEPT. 9/14/2019
Basic 2-tier Client-Server Architectures
• Specialized Servers with Specialized functions
• Print server
• File server
• DBMS server
• Web server
• Email server
• Clients can access the specialized servers as
needed
ROOPA R,ISE DEPT. 9/14/2019
ROOPA R,ISE DEPT. 9/14/2019
DBMS Server
• Provides database query and transaction services to the clients
• Relational DBMS servers are often called SQL servers, query servers,
or transaction servers
• Applications running on clients utilize an Application Program
Interface (API) to access server databases via standard interface such
as:
• ODBC: Open Database Connectivity standard
• JDBC: for Java programming access
• Client and server must install appropriate client module and server
module software for ODBC or JDBC
Two Tier Client-Server Architecture
• A client program may connect to several DBMSs, sometimes called
the data sources.
• In general, data sources can be files or other non-DBMS software
that manages data. Other variations of clients are possible: e.g., in
some object DBMSs, more functionality is transferred to clients
including data dictionary functions, optimization and recovery across
multiple servers, etc.
ROOPA R,ISE DEPT. 9/14/2019
ROOPA R,ISE DEPT. 9/14/2019
ROOPA R,ISE DEPT. 9/14/2019
ROOPA R,ISE DEPT. 9/14/2019
ROOPA R,ISE DEPT. 9/14/2019
ROOPA R,ISE DEPT. 9/14/2019
ROOPA R,ISE DEPT. 9/14/2019
Common for Web applications
Intermediate Layer called application server or
web server:
◦ Stores the web connectivity software and the business
logic part of the application used to access the
corresponding data from the database server
◦ Acts like a conduit for sending partially processed
data between the database server and the client.
Three-tier architecture can enhance security:
◦ Database server only accessible via middle tier
◦ Clients cannot directly access database server
ROOPA R,ISE DEPT. 9/14/2019
ROOPA R,ISE DEPT. 9/14/2019
ROOPA R,ISE DEPT. 9/14/2019
ROOPA R,ISE DEPT. 9/14/2019
ROOPA R,ISE DEPT. 9/14/2019
Based on the data model used
◦ Traditional: Relational, Network, Hierarchical.
◦ Emerging: Object-oriented, Object-relational.
Other classifications
◦ Single-user (typically used with personal
computers)
vs. multi-user (most DBMSs).
◦ Centralized (uses a single computer with one
database)
vs. distributed (uses multiple computers, multiple
databases)
ROOPA R,ISE DEPT. 9/14/2019
Homogeneous DDBMS
Heterogeneous DDBMS
Federated or Multidatabase Systems
Distributed Database Systems have now come
to be known as client-server based database
systems because:
◦ They do not support a totally distributed
environment, but rather a set of database servers
supporting a set of clients.
ROOPA R,ISE DEPT. 9/14/2019
Data Models and Their Categories
Schemas, Instances, and States
Three-Schema Architecture
Data Independence
DBMS Languages and Interfaces
Database System Utilities and Tools
Centralized and Client-Server Architectures
Classification of DBMSs
ROOPA R,ISE DEPT. 9/14/2019
You might also like
- Home Work-9Document3 pagesHome Work-9zahed83No ratings yet
- RESTful Java Web Services Interview Questions You'll Most Likely Be Asked: Second EditionFrom EverandRESTful Java Web Services Interview Questions You'll Most Likely Be Asked: Second EditionNo ratings yet
- Procedimientos Almacenados de MySQL en Visual BasicDocument3 pagesProcedimientos Almacenados de MySQL en Visual Basicosmarcelo100% (1)
- Client Server DatabaseDocument5 pagesClient Server DatabaseBoobalan RNo ratings yet
- 04 Introducing Client ServerDocument3 pages04 Introducing Client ServerMuhammad IqbalNo ratings yet
- Client Server DatabasesDocument20 pagesClient Server DatabasesPrince RanaNo ratings yet
- DB Environment, Centralized / Client-Server Architecture For DBMSDocument19 pagesDB Environment, Centralized / Client-Server Architecture For DBMSVickyNo ratings yet
- DATABASEDocument53 pagesDATABASEMarufNo ratings yet
- Database SystemDocument36 pagesDatabase SystemJus feelingNo ratings yet
- Introduction of DB: Database System Concepts and ArchitectureDocument36 pagesIntroduction of DB: Database System Concepts and ArchitectureMichelle JaraNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 1Document47 pagesLecture 2 1AMAN ULLAHNo ratings yet
- The Client/Server Database: Presented ByDocument19 pagesThe Client/Server Database: Presented Byrahul_rvimNo ratings yet
- Unit1 SecondDocument29 pagesUnit1 Seconddhanrajpandya26No ratings yet
- PPTDocument36 pagesPPTShahina Shawls Shaa100% (1)
- Hamideh-L03 - Client-Server Database EnvironmentDocument45 pagesHamideh-L03 - Client-Server Database EnvironmentAndikaNo ratings yet
- Client-Server Databases PDFDocument15 pagesClient-Server Databases PDFshylaja_pNo ratings yet
- Database System Concepts and ArchitectureDocument19 pagesDatabase System Concepts and ArchitectureAbdirisak MohamudNo ratings yet
- Ex No: 1 Study of Client-Server Based RDBMS, Oodbms and OrdbmsDocument12 pagesEx No: 1 Study of Client-Server Based RDBMS, Oodbms and OrdbmsPoorniTheGreatNo ratings yet
- Database Application DevelopmentDocument45 pagesDatabase Application DevelopmentWenny HuNo ratings yet
- Hoffer Edm PP Ch08Document42 pagesHoffer Edm PP Ch08Deepaklekhraj MalusareNo ratings yet
- Jeffrey A. Hoffer, Mary B. Prescott, Fred R. Mcfadden: Modern Database Management 8 EditionDocument25 pagesJeffrey A. Hoffer, Mary B. Prescott, Fred R. Mcfadden: Modern Database Management 8 EditionFarooq ShadNo ratings yet
- 2 Data ModelsDocument30 pages2 Data ModelsIsmail ZebNo ratings yet
- Data Base System Ch2Document31 pagesData Base System Ch2betiadmaNo ratings yet
- Client ServerDocument5 pagesClient ServerBenny BoomNo ratings yet
- L4-DBMS ArchitectureDocument13 pagesL4-DBMS ArchitectureLloydNo ratings yet
- The Client/Server Database Environment: © Prentice Hall, 2002 1Document28 pagesThe Client/Server Database Environment: © Prentice Hall, 2002 1aaghaz hussainNo ratings yet
- Database System Concepts and ArchitectureDocument40 pagesDatabase System Concepts and ArchitectureRao Haris Rafique KhanNo ratings yet
- E-Commerce ArchitectureDocument7 pagesE-Commerce ArchitectureVinay KorekarNo ratings yet
- Database System Concepts and ArchitectureDocument38 pagesDatabase System Concepts and ArchitectureUsman IlamdinNo ratings yet
- Ms. Archana Kero, Asst. Prof., Department of CA & IT, SgrritsDocument64 pagesMs. Archana Kero, Asst. Prof., Department of CA & IT, SgrritsPraveen KusugalNo ratings yet
- The Client/Server Database Environment: Modern Database Management 8 EditionDocument25 pagesThe Client/Server Database Environment: Modern Database Management 8 EditionDEv KaushalNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document32 pagesChapter 2arahulvarma451No ratings yet
- Chapter 2: Database System Concepts and ArchitectureDocument45 pagesChapter 2: Database System Concepts and Architectureabubakar kaleemNo ratings yet
- Introducing Relational Database Products-2Document43 pagesIntroducing Relational Database Products-2Dastan AkatovNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Database / RdbmsDocument18 pagesIntroduction To Database / RdbmsMaria PanesNo ratings yet
- PPUD Pr1Document3 pagesPPUD Pr1Godil saqlenNo ratings yet
- Database-Lecture 1Document39 pagesDatabase-Lecture 1evarist madahaNo ratings yet
- Ejb 1Document55 pagesEjb 1mohansujiNo ratings yet
- L03 - DBMS ArchitectureDocument33 pagesL03 - DBMS ArchitectureARYAN TYAGINo ratings yet
- 02-Database Architecture - StudytonightDocument2 pages02-Database Architecture - StudytonightFani Pramudita NugrahaNo ratings yet
- Unit - 1 - Part3 - DBMS ArchitectureDocument4 pagesUnit - 1 - Part3 - DBMS ArchitectureAnmol MogalaiNo ratings yet
- The Client/Server Database: RDBMS Concepts J.Srinivasa ReddyDocument8 pagesThe Client/Server Database: RDBMS Concepts J.Srinivasa ReddyvamshichatlaNo ratings yet
- Report of PupilpodDocument20 pagesReport of Pupilpodramya raghunandanNo ratings yet
- Database System Environment: D Mukherjee Assistant Professor - IT AreaDocument22 pagesDatabase System Environment: D Mukherjee Assistant Professor - IT AreaRishi SinghNo ratings yet
- Midterm LecturesDocument56 pagesMidterm LecturesMahiraa ShahzadiNo ratings yet
- Data Models (CH 2)Document7 pagesData Models (CH 2)Kartik MandlaNo ratings yet
- MIS 385/MBA 664 Systems Implementation With DBMS/ Database ManagementDocument25 pagesMIS 385/MBA 664 Systems Implementation With DBMS/ Database ManagementMayur AbhinavNo ratings yet
- DB Lec 07Document20 pagesDB Lec 07hammadrajpoot3366qaNo ratings yet
- Network Programming Lesson 1: Huynh Cong Phap, PHDDocument114 pagesNetwork Programming Lesson 1: Huynh Cong Phap, PHDQuang ThoNo ratings yet
- Database Systems: ArchitectureDocument16 pagesDatabase Systems: Architecturebhumika.verma00No ratings yet
- Client ServerDocument32 pagesClient ServerJoel wakhunguNo ratings yet
- Application ArchitectureDocument39 pagesApplication ArchitectureSumit ChauhanNo ratings yet
- CHP 9Document30 pagesCHP 9ayzal noorNo ratings yet
- Chapter 14Document88 pagesChapter 14Fatima Al-ThwadiNo ratings yet
- The Advantages of Client/Server ComputingDocument5 pagesThe Advantages of Client/Server ComputingPuspala ManojkumarNo ratings yet
- Distributed DatabaseDocument9 pagesDistributed DatabaseAvani GadhaviNo ratings yet
- Client ServerDocument3 pagesClient ServerSubramonia Muthu Perumal PillaiNo ratings yet
- Database Programming - by NadeeraDocument12 pagesDatabase Programming - by NadeeraYovin LekamgeNo ratings yet
- Assignment 03Document15 pagesAssignment 03Sana UllahNo ratings yet
- R2DBC Revealed: Reactive Relational Database Connectivity for Java and JVM ProgrammersFrom EverandR2DBC Revealed: Reactive Relational Database Connectivity for Java and JVM ProgrammersNo ratings yet
- Cloning ProcedureDocument12 pagesCloning Proceduremaruthi631No ratings yet
- AVL Tree AssignmentDocument2 pagesAVL Tree Assignmentishqi92No ratings yet
- (Real World Research) Bill Gillham-Case Study Research Methods-Continuum (2000)Document112 pages(Real World Research) Bill Gillham-Case Study Research Methods-Continuum (2000)Çisem Tamişci0% (1)
- A Definition of Business AnalyticsDocument4 pagesA Definition of Business AnalyticsBalhansNo ratings yet
- Network File System (NFS)Document2 pagesNetwork File System (NFS)Rahul BhaleraoNo ratings yet
- Data Science Training On Statistical Techniques For AnalyticsDocument154 pagesData Science Training On Statistical Techniques For AnalyticsArun Kumar GNo ratings yet
- Numerical Differentiation of Equally Spaced and Not Equally SpaceDocument10 pagesNumerical Differentiation of Equally Spaced and Not Equally Spacethazin2512002No ratings yet
- Data Science MCQ Topics: Protect Your Account Without Compromising On Speed or ConnectionDocument6 pagesData Science MCQ Topics: Protect Your Account Without Compromising On Speed or ConnectionABCNo ratings yet
- Unit IvDocument72 pagesUnit IvJyothikaNo ratings yet
- BISP Teradata BasicsDocument72 pagesBISP Teradata BasicsVitthal TapashiNo ratings yet
- 184.big Data Analytics A Classification of Data Quality Assessment and Improvement MethodsDocument8 pages184.big Data Analytics A Classification of Data Quality Assessment and Improvement MethodsDivi DivyaNo ratings yet
- Magento Chapagain CollectionDocument8 pagesMagento Chapagain CollectionSantosh KumarNo ratings yet
- Use Simple Relational Databases CompletedDocument22 pagesUse Simple Relational Databases CompletedÇrox Rmg PunkNo ratings yet
- Qualitative Research: Dosen Pengampu: Ayu Rizki Septiana .M.PDDocument12 pagesQualitative Research: Dosen Pengampu: Ayu Rizki Septiana .M.PDEndouYukioNo ratings yet
- Creating Advanced Queries and Enhancing Table DesignDocument30 pagesCreating Advanced Queries and Enhancing Table DesignkpchakNo ratings yet
- DBMSLabManual SureshDocument34 pagesDBMSLabManual SureshSiva SankarNo ratings yet
- Gartner - Go - Beyond - Machine - Learning - and - Leverage - Other - AI - ApproachesDocument14 pagesGartner - Go - Beyond - Machine - Learning - and - Leverage - Other - AI - ApproachesAnand GovindarajanNo ratings yet
- (Abstract Data Types Using Arrays) : Fast NUCES - Department of Computer ScienceDocument11 pages(Abstract Data Types Using Arrays) : Fast NUCES - Department of Computer ScienceNehaNo ratings yet
- Networker Module For Database and Applications 19.2 Admin GuideDocument554 pagesNetworker Module For Database and Applications 19.2 Admin GuideMohsin El K'jijiNo ratings yet
- Zakir-Thesis DefenseDocument27 pagesZakir-Thesis DefenseZakir AhmedNo ratings yet
- A Study On Impact of Smartphone AddictioDocument4 pagesA Study On Impact of Smartphone AddictiotansuoragotNo ratings yet
- Informatica QnsDocument10 pagesInformatica QnssanguinerkNo ratings yet
- ADM203 L13 TroubleshootingDocument19 pagesADM203 L13 TroubleshootingSriraksha SrinivasanNo ratings yet
- 1st Out of Class Peta 2nd QTR 2019-2020Document8 pages1st Out of Class Peta 2nd QTR 2019-2020Paulina StalkerNo ratings yet
- Final Examination Qualitative ResearchDocument5 pagesFinal Examination Qualitative ResearchRAHMAT ALI PUTRANo ratings yet
- SQL PreparationDocument4 pagesSQL Preparationbhanu prakashNo ratings yet
- Json RpgleDocument7 pagesJson RpgleHoraciomorenoNo ratings yet
- Mongo DB Comparison With Influxdb: Compared Mongo With Postgres Nosql Product Timescaledb, According Timescaledb BlogDocument2 pagesMongo DB Comparison With Influxdb: Compared Mongo With Postgres Nosql Product Timescaledb, According Timescaledb BlogAditya GangulyNo ratings yet
- Reporting Schema Without Process ModelDocument21 pagesReporting Schema Without Process Modelvinit1448No ratings yet