Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Nervous System, Immune System and Cell Signalling: Unit 5
Nervous System, Immune System and Cell Signalling: Unit 5
Uploaded by
Sucharita Naha0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views18 pagesThe document summarizes key aspects of the nervous system. It discusses the two main cell types - glial cells and nerve cells. It describes how nerve cells generate action potentials in response to stimuli and how they communicate via synapses. It also provides an overview of the central nervous system, including the brain and spinal cord, and the peripheral nervous system. Finally, it briefly discusses some nervous system diseases and computer-based neural networks.
Original Description:
Biology for engineers
Original Title
Nervous System
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document summarizes key aspects of the nervous system. It discusses the two main cell types - glial cells and nerve cells. It describes how nerve cells generate action potentials in response to stimuli and how they communicate via synapses. It also provides an overview of the central nervous system, including the brain and spinal cord, and the peripheral nervous system. Finally, it briefly discusses some nervous system diseases and computer-based neural networks.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views18 pagesNervous System, Immune System and Cell Signalling: Unit 5
Nervous System, Immune System and Cell Signalling: Unit 5
Uploaded by
Sucharita NahaThe document summarizes key aspects of the nervous system. It discusses the two main cell types - glial cells and nerve cells. It describes how nerve cells generate action potentials in response to stimuli and how they communicate via synapses. It also provides an overview of the central nervous system, including the brain and spinal cord, and the peripheral nervous system. Finally, it briefly discusses some nervous system diseases and computer-based neural networks.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 18
Unit 5
NERVOUS SYSTEM, IMMUNE SYSTEM AND
CELL SIGNALLING
NERVOUS SYSTEM
CELLS OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM
• The complex nature of the brain
and associated nervous system
allow the human beings to
perform activities superior to
other animals.
• The highly sophisticated neural
machine, the brain, accomplishes
this task by using nerve cells and
the connections between them.
• The nervous system has two
classes of cell: glial cells and
nerve cells.
1. SUPPORTING CELLS :GLIAL CELLS
TYPES OF GLIAL CELLS
2. NERVE CELLS
TYPES OF NERVE CELLS
SYNAPSE
ACTION POTENTIAL
• The unique feature of the neurons to generate an electrical current in response to excitation is called action
potential.
• After entry of sodium ion from outside, they travel to axon hillock where the summation of all electrical
currents occur.
• Neural signals which are excitatory open Na+ channels while others which are inhibiotory open Cl- and K+
channels
• Depending on the strength of the signals, the axon hillock decides whether to propagate or not propagate the
action potential.
ACTION POTENTIAL
ORGANIZATION OF NERVOUS SYSTEN
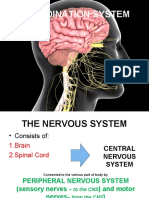
CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM
CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM
• Largest part of the brain (specifically the forebrain
• Cerebral cortex is thrown into folds (gyri) and fissures
(sulci).
• Cerebral cortex divided into lobes i.e temporal, frontal,
parietal and occipital by theses grooves .
• Control functions like thinking speech, emotions, vision,
pain, hearing etc.
Diencephalon has two parts: Thalamus and Hypothalamus
PERIPHERAL NERVOUS SYSTEM
Exerts a maintenance
control following a
Sensory neurons and sympathetic nervous
sensory and motor response
nerves of voluntary
Fight or flight response during
which the body is prepared to run
away or resist danger
NEUROTRANSMITTORS
DISEASES OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM
1. Dementia is another disorder associated with aging seen in patients over 60.
Most common type of dementia observed in Western countries is Alzheimer’s disease.
• Loss of neurons in the cortex, hippocampus
regions.
• Deposition of amyloid plaques containing
beta amyloid protein.
2. Parkinson disease
• Parkinson is usually observed between the ages of 50-60.
• Environmental toxins may be responsible for onset of the disease.
• Destruction of cell bodies and neurons that produce dopamine.
COMPUTER BASED NEURAL NETWORKS
• Brain has certain remarkable qualities which makes it at par with any
computers like
1. Its performance tends to degrade gracefully under partial
damage and partial recovery from damage is possible.
2. It performs massively parallel computations extremely
efficiently.
3. It supports our intelligence and self awareness through yet to
be determined mechanism.
• Neural Networks attempt to bring computers a little closer to the
brains' capabilities by imitating certain aspects of the brain in a
simplified way.
• Neural networks are not biological rather only elements of a program
or silicon circuits.
• Although these networks are not as powerful as human brain, they can
be trained to perform useful functions.
• Two concepts were responsible for emergence of neural networks (i)
Statistical mechanics (ii) back propagation algorithm.
• Neural networks have been applied to different applications like
aerospace, automotive, banking, defence, electronics, mathematics etc.
You might also like
- Consultants List-ADCEDocument6 pagesConsultants List-ADCEJaveed Taji100% (3)
- t1080s ManualDocument191 pagest1080s ManualMorena Estatal Arizona100% (5)
- Neurons and SynapseDocument44 pagesNeurons and Synapsethummiepurple100% (4)
- L6 - Nervous TissueDocument8 pagesL6 - Nervous TissueDea Marienila CuberoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3ADocument28 pagesChapter 3AjNo ratings yet
- Cohen - B7.5 - MSK - Central - and - Peripheral - Nervous - System - Histology - 19-20Document80 pagesCohen - B7.5 - MSK - Central - and - Peripheral - Nervous - System - Histology - 19-20Monica Hitomi MekaruNo ratings yet
- Myers 8th Ed. CH 2 NotesDocument85 pagesMyers 8th Ed. CH 2 NotesEric RedderNo ratings yet
- Medical Surgical Nursing PinoyDocument67 pagesMedical Surgical Nursing Pinoyalfred31191% (23)
- Histology Nervous TissueDocument27 pagesHistology Nervous Tissueaimi BatrisyiaNo ratings yet
- ITP - Chapter 3-6Document18 pagesITP - Chapter 3-6KARYLLE MAE MACOROLNo ratings yet
- Konsep Dasar Ilmu Biokimia Dan Biologi Molekuler Untuk Sistem SarafDocument31 pagesKonsep Dasar Ilmu Biokimia Dan Biologi Molekuler Untuk Sistem SarafdiandraNo ratings yet
- Med Surg NotesDocument64 pagesMed Surg NotesRAYMUND IAN ABALOS100% (2)
- 1 Part I Central Nervous System 4zaDocument32 pages1 Part I Central Nervous System 4zaapi-302883249No ratings yet
- Chapter 1,2,3Document8 pagesChapter 1,2,3세핌No ratings yet
- The Nervous System: © 2009 The Mcgraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All Rights ReservedDocument110 pagesThe Nervous System: © 2009 The Mcgraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All Rights ReservedMica BernardoNo ratings yet
- Lecture4 - The Nervous SystemDocument17 pagesLecture4 - The Nervous SystemVivek ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- CH 02 OnlineDocument28 pagesCH 02 OnlineBastian CollaoNo ratings yet
- 2020-2021 AP 1 Lecture 8 Nervous System 1Document39 pages2020-2021 AP 1 Lecture 8 Nervous System 1OscarJaiNo ratings yet
- L1 SBM Neuro 1Document88 pagesL1 SBM Neuro 1Sohil PatelNo ratings yet
- Muscle TissueDocument61 pagesMuscle TissueCatherine Joy SalongaNo ratings yet
- Nervous TissueDocument12 pagesNervous TissueTanveesh BajajNo ratings yet
- Fisiologi Manusia: DR Mellova Amir MSCDocument52 pagesFisiologi Manusia: DR Mellova Amir MSCRizal adhitya100% (1)
- Nervous TissueDocument10 pagesNervous TissueWrigley PatioNo ratings yet
- ScienceDocument16 pagesScienceAis BranzuelaNo ratings yet
- 1.7 Introduction To Neuroanatomy PDFDocument80 pages1.7 Introduction To Neuroanatomy PDFCarina SuarezNo ratings yet
- Neurons 130508030319 Phpapp01Document38 pagesNeurons 130508030319 Phpapp01hosbadawi.hbNo ratings yet
- Functions of The Nervous SystemDocument5 pagesFunctions of The Nervous SystemMarion Joy GanayoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 - Nervous SystemDocument12 pagesChapter 8 - Nervous SystemlalaNo ratings yet
- Hhis Weeks 13 16 Lecture NotesDocument22 pagesHhis Weeks 13 16 Lecture NotesOwkay HNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument6 pagesNervous SystemGracielle Angelyka PeraltaNo ratings yet
- Bio CH12 F4 StudywithadminDocument20 pagesBio CH12 F4 StudywithadminMUHAMMAD FAREEZ HAIKAL MOHD SHAIFUDDINNo ratings yet
- Central Nervous System NewDocument34 pagesCentral Nervous System NewGabrielle GreyNo ratings yet
- Fisiologi Manusia: DR Mellova Amir MSCDocument52 pagesFisiologi Manusia: DR Mellova Amir MSCRizal AdhityaNo ratings yet
- Medical SurgicalDocument119 pagesMedical SurgicalNursyNurseNo ratings yet
- Nervous System: Spinal CordDocument20 pagesNervous System: Spinal CordLucas ManaliliNo ratings yet
- Transes Nervous SystemDocument13 pagesTranses Nervous SystemAlther LorenNo ratings yet
- Nervous System Phisiology of Nervous Tissues. SynapsesDocument65 pagesNervous System Phisiology of Nervous Tissues. Synapsessatyagraha84No ratings yet
- Nervous TissueDocument49 pagesNervous TissueDAVE CANALETANo ratings yet
- NeuroDocument46 pagesNeuroje-ann catedralNo ratings yet
- Unit 4Document56 pagesUnit 4adithyaNo ratings yet
- Unit Five - Human Biology and Health Ppt-RevisedDocument342 pagesUnit Five - Human Biology and Health Ppt-Revisedsamuelgorfu58No ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument65 pagesNervous System2gn8xxb6mwNo ratings yet
- Chap8 Nervous Transes-1-1Document8 pagesChap8 Nervous Transes-1-1y30ny30nNo ratings yet
- Nervous CoordinationDocument36 pagesNervous CoordinationOlamide AyindeNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument1 pageNervous SystemHannahnel Anasco QuidatoNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument125 pagesNervous SystemGIRLLYN BURZONNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument11 pagesNervous SystemYUAN FRANCIS SINGCULANNo ratings yet
- Integration and Coordination - SG3Document180 pagesIntegration and Coordination - SG3Marcos AlbaridaNo ratings yet
- UNIT 7 Nervous System Sept 2023Document94 pagesUNIT 7 Nervous System Sept 2023ndamanomhataabisai7No ratings yet
- Nervous SYSTEM: by Animal Physiology StaffDocument37 pagesNervous SYSTEM: by Animal Physiology StaffSyifarhNo ratings yet
- Excitable TissueDocument117 pagesExcitable Tissueur.yared21100% (1)
- Patterns of Nerve Injury and Neuropathies: The Motor UnitDocument6 pagesPatterns of Nerve Injury and Neuropathies: The Motor UnitLaura TapiaNo ratings yet
- Nervous-System (New)Document18 pagesNervous-System (New)harucodm210No ratings yet
- Chapter 3 & 4 The Anatomy of The Nervous System and Neural TransmissionDocument47 pagesChapter 3 & 4 The Anatomy of The Nervous System and Neural Transmissionjohn rey adizNo ratings yet
- Mind at Rest: How Neuron Structure Evolves in the Sleep Cycle.From EverandMind at Rest: How Neuron Structure Evolves in the Sleep Cycle.No ratings yet
- How The Brain Works: Understanding Brain Function, Thought and PersonalityFrom EverandHow The Brain Works: Understanding Brain Function, Thought and PersonalityNo ratings yet
- Hollow Fiber Membrane ContactorsDocument47 pagesHollow Fiber Membrane ContactorsEvelyn AntunesNo ratings yet
- Copper Tube HandbookDocument66 pagesCopper Tube HandbookRafael Leonardo GomezNo ratings yet
- ECELAWSDocument14 pagesECELAWSGilbey's Jhon LadionNo ratings yet
- Zimbra To Office 365 Migration GuideDocument6 pagesZimbra To Office 365 Migration GuideEDSON ARIEL AJÚ GARCÍANo ratings yet
- WF D02A Energy MeterDocument10 pagesWF D02A Energy MeterfioNo ratings yet
- 2020 Can Pelvic Floor Muscle TrainingDocument2 pages2020 Can Pelvic Floor Muscle Trainingjuan pabloNo ratings yet
- Dogmatism, Religion, and Psychological Type.Document16 pagesDogmatism, Religion, and Psychological Type.ciprilisticusNo ratings yet
- MPG Engineering and Manufacturing Software Market Brief - September 2022Document11 pagesMPG Engineering and Manufacturing Software Market Brief - September 2022joeNo ratings yet
- Timeline of Indian History - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument24 pagesTimeline of Indian History - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaPrabhu Charan TejaNo ratings yet
- Rtx3 Wireless Expansion V5.3: Reference and Installation ManualDocument24 pagesRtx3 Wireless Expansion V5.3: Reference and Installation ManualCatalin HoratiuNo ratings yet
- HVT DS HAEFELY 9231-Capacitor V2206Document4 pagesHVT DS HAEFELY 9231-Capacitor V2206sunilNo ratings yet
- Checklist - Turning Client To Lateral or Prone PositionDocument3 pagesChecklist - Turning Client To Lateral or Prone PositionNorhaina AminNo ratings yet
- Assignment 5Document9 pagesAssignment 5wacih58121No ratings yet
- Therapeutic Potential of Heterocyclic Pyrimidine Scaffolds: Review Open AccessDocument29 pagesTherapeutic Potential of Heterocyclic Pyrimidine Scaffolds: Review Open AccessWalid EbaiedNo ratings yet
- Jacob BohmeDocument12 pagesJacob BohmeTimothy Edwards100% (1)
- Fuels and CombustionDocument28 pagesFuels and CombustionDrupad PatelNo ratings yet
- Analisis Fungsi Kepemimpinan Camat Kubu Kabupaten Rokan HilirDocument14 pagesAnalisis Fungsi Kepemimpinan Camat Kubu Kabupaten Rokan Hilirtoto saepul anwarNo ratings yet
- The Heart of Memory by Alison Strobel, ExcerptDocument49 pagesThe Heart of Memory by Alison Strobel, ExcerptZondervanNo ratings yet
- MOEP - Public-Private Partnership Development in Thermal Power Generation, Thermal Power Department, Myanmar Electric Power EnterpriseDocument15 pagesMOEP - Public-Private Partnership Development in Thermal Power Generation, Thermal Power Department, Myanmar Electric Power EnterpriseTim DingNo ratings yet
- Marketing Communications in The Digital AgeDocument49 pagesMarketing Communications in The Digital Age2m shoppingNo ratings yet
- 130724Document20 pages130724Caracal MohNo ratings yet
- McDonalds Supplier Workplace AccountabilityDocument3 pagesMcDonalds Supplier Workplace Accountabilityjamil voraNo ratings yet
- World Religions Exam Review 2024Document3 pagesWorld Religions Exam Review 2024Marina SolakaNo ratings yet
- Understanding The Gender Pay Gap: Women in Business and ManagementDocument8 pagesUnderstanding The Gender Pay Gap: Women in Business and Managementmostafa aliNo ratings yet
- Sortimo Xpress: Proven Configurations For Your VehicleDocument7 pagesSortimo Xpress: Proven Configurations For Your VehicleAjdeLSNo ratings yet
- Kundalini YogaDocument153 pagesKundalini Yogaprajjwal singhNo ratings yet
- SilverCret Internetradio 4 in 1 - SIRD 14 C1Document158 pagesSilverCret Internetradio 4 in 1 - SIRD 14 C1Haito GombatNo ratings yet
- Untitled: Pandas PD OsDocument55 pagesUntitled: Pandas PD OsGustavo Cano GallegosNo ratings yet