Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Muscle Cells Muscle Tissue Filaments Smooth Muscle Skeletal Muscle Cardiac Muscle Striations Sea Anemone Sea Cucumbers
Muscle Cells Muscle Tissue Filaments Smooth Muscle Skeletal Muscle Cardiac Muscle Striations Sea Anemone Sea Cucumbers
Uploaded by
sandeshshiva0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views1 pageMuscle tissue is composed of muscle cells (myocytes) that form contractile tissue to produce force and cause motion. There are three main types of muscle tissue: smooth muscle, skeletal muscle, and cardiac muscle. Smooth muscle contracts slowly and is found within organs, skeletal muscle contracts rapidly but has limited extension and is found in appendages and jaws, and cardiac muscle is only located in the heart.
Original Description:
Muscle Tissue
Original Title
Muscle Tissue
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentMuscle tissue is composed of muscle cells (myocytes) that form contractile tissue to produce force and cause motion. There are three main types of muscle tissue: smooth muscle, skeletal muscle, and cardiac muscle. Smooth muscle contracts slowly and is found within organs, skeletal muscle contracts rapidly but has limited extension and is found in appendages and jaws, and cardiac muscle is only located in the heart.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views1 pageMuscle Cells Muscle Tissue Filaments Smooth Muscle Skeletal Muscle Cardiac Muscle Striations Sea Anemone Sea Cucumbers
Muscle Cells Muscle Tissue Filaments Smooth Muscle Skeletal Muscle Cardiac Muscle Striations Sea Anemone Sea Cucumbers
Uploaded by
sandeshshivaMuscle tissue is composed of muscle cells (myocytes) that form contractile tissue to produce force and cause motion. There are three main types of muscle tissue: smooth muscle, skeletal muscle, and cardiac muscle. Smooth muscle contracts slowly and is found within organs, skeletal muscle contracts rapidly but has limited extension and is found in appendages and jaws, and cardiac muscle is only located in the heart.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 1
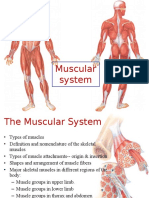
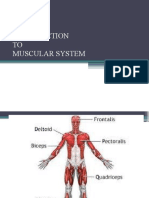
Muscle tissue
Muscle cells (myocytes) form the active contractile
tissue of the body. Muscle tissue functions to
produce force and cause motion, either locomotion
or movement within internal organs. Muscle is
formed of contractile filaments and is separated
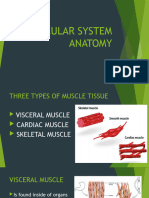
into three main types; smooth muscle, skeletal
muscle and cardiac muscle. Smooth muscle has
no striations when examined microscopically. It
contracts slowly but maintains contractibility over a
wide range of stretch lengths. It is found in such
organs as sea anemone tentacles and the body wall
of sea cucumbers. Skeletal muscle contracts rapidly
but has a limited range of extension. It is found in
the movement of appendages and jaws. Obliquely
striated muscle is intermediate between the other
two. The filaments are staggered and this is the
type of muscle found in earthworms that can
extend slowly or make rapid contractions.[18] In
higher animals striated muscles occur in bundles
attached to bone to provide movement and are
often arranged in antagonistic sets. Smooth muscle
is found in the walls of
the uterus, bladder, intestines, stomach, oesophagu
s, respiratory airways, and blood vessels. Cardiac
muscle is found only in the heart, allowing it to
contract and pump blood round the body.
You might also like
- Muscular SystemDocument26 pagesMuscular Systemlubnab75% (4)
- Muscle TissueDocument1 pageMuscle TissuesandeshshivaNo ratings yet
- MYOLOGYDocument20 pagesMYOLOGYNatty ChikumbaNo ratings yet
- The Muscular SystemDocument14 pagesThe Muscular SystemOana Maria FrancNo ratings yet
- UNIT-6 Muscular SystemDocument48 pagesUNIT-6 Muscular SystemChandan ShahNo ratings yet
- Sistem Otot Muskular 2 (Muscular System)Document38 pagesSistem Otot Muskular 2 (Muscular System)PaRaDoX eLaKSaMaNaNo ratings yet
- Muscular System AnatomyDocument23 pagesMuscular System Anatomymichaelryann madayagNo ratings yet
- Ilovepdf Merged 1 13Document13 pagesIlovepdf Merged 1 13Abdulrahman UdayNo ratings yet
- Basic Human Anatomy 1Document55 pagesBasic Human Anatomy 1ZzzNo ratings yet
- Muscular System Anatomy Muscle TypesDocument5 pagesMuscular System Anatomy Muscle TypesĘđı AzøıcăNo ratings yet
- Embryology: Abdulrahman Uday AbdulfatahDocument27 pagesEmbryology: Abdulrahman Uday AbdulfatahAbdulrahman UdayNo ratings yet
- Unit Four: Muscular System: Cilia Flagellum AmoeboidDocument7 pagesUnit Four: Muscular System: Cilia Flagellum AmoeboidKath RubioNo ratings yet
- Muscular System AnatomyDocument12 pagesMuscular System AnatomyTishonna DouglasNo ratings yet
- MUSCLE, BONE AND JOINTSDocument13 pagesMUSCLE, BONE AND JOINTSGunjan ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology Lecture Notes Unit 6 - The Muscular SystemDocument9 pagesAnatomy and Physiology Lecture Notes Unit 6 - The Muscular Systemnur100% (1)
- Muscle TissuesDocument2 pagesMuscle TissuesCathleen MarquezNo ratings yet
- ANATOMY of The Musculoskeletal SystemDocument3 pagesANATOMY of The Musculoskeletal Systemsigfred02No ratings yet
- Justine May Arcos: TypesDocument2 pagesJustine May Arcos: TypesJenniferFajutnaoArcosNo ratings yet
- The Skeleton and Muscles: Muscular & Skeletal SystemDocument2 pagesThe Skeleton and Muscles: Muscular & Skeletal SystemAbhinavNo ratings yet
- Muscular SystemDocument8 pagesMuscular Systemdadawonderful345No ratings yet
- AnatomyDocument17 pagesAnatomyAb To zine doNo ratings yet
- Title: Sub-Structures of Musculoskeletal SystemDocument6 pagesTitle: Sub-Structures of Musculoskeletal SystemMaheenNo ratings yet
- Muscular System: Cardiac Muscle Skeletal MuscleDocument10 pagesMuscular System: Cardiac Muscle Skeletal MuscleCherry Mae TapacionNo ratings yet
- Sketetal SystemDocument11 pagesSketetal SystemBryan JagroopNo ratings yet
- Reading 4 The Muscular SystemDocument16 pagesReading 4 The Muscular Systemlephuongvy1406No ratings yet
- Anatomy Lec 6 MuscleDocument12 pagesAnatomy Lec 6 Muscleidrimuha333No ratings yet
- Skeletal SystemDocument19 pagesSkeletal Systemsmbdy tbhhhNo ratings yet
- The Musculosketal SystemDocument4 pagesThe Musculosketal SystemNgọc HânNo ratings yet
- The Musculoskeletal SystemDocument20 pagesThe Musculoskeletal SystembenitawafoNo ratings yet
- Lesson Proper For Week 9Document5 pagesLesson Proper For Week 9Merlyn NavarroNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 11 Biology Chapter 20 Locomotion and Movement Revision NotesDocument24 pagesCBSE Class 11 Biology Chapter 20 Locomotion and Movement Revision NotesTanishNo ratings yet
- Muscular SystemDocument8 pagesMuscular SystemZoological science classesNo ratings yet
- What Do You Call The Arrowed Part?Document13 pagesWhat Do You Call The Arrowed Part?Earl GenodipaNo ratings yet
- General Veterinary Macroscopic Anatomy: MYOLOGYDocument38 pagesGeneral Veterinary Macroscopic Anatomy: MYOLOGYneanna100% (1)
- Paper of Musculoskeletal FinishDocument23 pagesPaper of Musculoskeletal FinishHaris FernandoNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument23 pagesAnatomy and Physiologyapi-464344582100% (1)
- The Muscular TissueDocument23 pagesThe Muscular TissueMuhammad Salisu IliyasuNo ratings yet
- Muscle TissuesDocument9 pagesMuscle Tissuesangelo beldaNo ratings yet
- Muscle and Connective TissueDocument8 pagesMuscle and Connective Tissuedavoujohn0No ratings yet
- Make-Up of The Human BodyDocument7 pagesMake-Up of The Human BodyMariam GamosNo ratings yet
- Muscle SystemDocument7 pagesMuscle System910907No ratings yet
- Chronic OsteomyelitisDocument35 pagesChronic OsteomyelitisMelissa Gines100% (2)
- Muscular SystemDocument29 pagesMuscular SystemJoanna Alecxa PagunsanNo ratings yet
- MusclesDocument13 pagesMusclessoulpatch_85100% (1)
- Topic 2 FIT MEDocument7 pagesTopic 2 FIT MESleepy HeadNo ratings yet
- Unit Iv Soft Tissue Mechanics The Soft Tissues of The Body:: Kripa's Notes.Document14 pagesUnit Iv Soft Tissue Mechanics The Soft Tissues of The Body:: Kripa's Notes.Kripa NNo ratings yet
- Muscular SystemDocument8 pagesMuscular Systemtheodore_estradaNo ratings yet
- Human Anatomy - Lec. 2 - GR1Document9 pagesHuman Anatomy - Lec. 2 - GR1bmydwoybx482No ratings yet
- Chapter IV - All About Muscles: Joint, Muscle, Tendon & LigamentDocument5 pagesChapter IV - All About Muscles: Joint, Muscle, Tendon & LigamentIndranil SinhaNo ratings yet
- Animal TissuesDocument10 pagesAnimal TissuesAlvin PaboresNo ratings yet
- Lec 3 Musculoskeletal SystemDocument33 pagesLec 3 Musculoskeletal SystemRavand BamerniNo ratings yet
- Human Body TissuesDocument11 pagesHuman Body Tissuesapi-277775953No ratings yet
- Exercise No. 6 Muscle TissueDocument10 pagesExercise No. 6 Muscle TissueRyan Aaron Cruz ParNo ratings yet
- 4 MyologyDocument57 pages4 MyologyAbhijith S. PNo ratings yet
- Skeletal MuscleDocument32 pagesSkeletal MuscleArfiNo ratings yet
- Ns Elec 4 - Muscular SystemDocument4 pagesNs Elec 4 - Muscular SystemONGLENGCO WILSON JAKE V.No ratings yet
- Naw TrainingDocument34 pagesNaw Trainingganesh pNo ratings yet
- Innovations Submersible Pressure Transmitter: Fluid Sensors & Diagnostic Systems WWWDocument4 pagesInnovations Submersible Pressure Transmitter: Fluid Sensors & Diagnostic Systems WWWsandeshshivaNo ratings yet
- Innovations LMT Sensor: Fluid Sensors WWWDocument4 pagesInnovations LMT Sensor: Fluid Sensors WWWsandeshshivaNo ratings yet
- Ifm Applicationreports 2019 GBDocument78 pagesIfm Applicationreports 2019 GBsandeshshivaNo ratings yet
- ZA Ifm RF-identification 2010Document6 pagesZA Ifm RF-identification 2010sandeshshivaNo ratings yet
- Innovations PT100 Sensors For Industrial Applications: Fluid Sensor Technology WWWDocument4 pagesInnovations PT100 Sensors For Industrial Applications: Fluid Sensor Technology WWWsandeshshivaNo ratings yet
- The Compact All-Rounder. Identification of 1D and 2D Codes Using The New Multicode ReaderDocument6 pagesThe Compact All-Rounder. Identification of 1D and 2D Codes Using The New Multicode ReadersandeshshivaNo ratings yet
- Profibus PA Pressure and Temperature: InnovationsDocument6 pagesProfibus PA Pressure and Temperature: InnovationssandeshshivaNo ratings yet
- Innovations RFID For Production and LogisticsDocument4 pagesInnovations RFID For Production and LogisticssandeshshivaNo ratings yet
- Fusion of Electronic Pressure Sensor and Analogue DisplayDocument6 pagesFusion of Electronic Pressure Sensor and Analogue DisplaysandeshshivaNo ratings yet
- Innovations IO-Link Memory Plug: Diagnostic Systems WWWDocument4 pagesInnovations IO-Link Memory Plug: Diagnostic Systems WWWsandeshshivaNo ratings yet
- 3D Image Sensing Using Smart Pixel Technology: Shape, Size and VolumeDocument7 pages3D Image Sensing Using Smart Pixel Technology: Shape, Size and VolumesandeshshivaNo ratings yet
- Innovations Full-Metal Pressure Sensor For Hygienic ApplicationsDocument4 pagesInnovations Full-Metal Pressure Sensor For Hygienic ApplicationssandeshshivaNo ratings yet
- Innovations O2D Image Sensor: Fluid Sensors and Diagnostic SystemsDocument4 pagesInnovations O2D Image Sensor: Fluid Sensors and Diagnostic SystemssandeshshivaNo ratings yet
- Innovations Full Metal Inductive Sensors - With 2-Wire TechnologyDocument4 pagesInnovations Full Metal Inductive Sensors - With 2-Wire TechnologysandeshshivaNo ratings yet
- Fast & Robust Mechatronic Flow SensorsDocument4 pagesFast & Robust Mechatronic Flow SensorssandeshshivaNo ratings yet
- ZA Ifm Octavis Brochure 10Document8 pagesZA Ifm Octavis Brochure 10sandeshshivaNo ratings yet
- Ifm Octavis Brochure 2013 ZaDocument12 pagesIfm Octavis Brochure 2013 ZasandeshshivaNo ratings yet
- ZA Ifm Ecolink Brochure 10Document24 pagesZA Ifm Ecolink Brochure 10sandeshshivaNo ratings yet
- Innovations Valvis With Integrated AS-i ChipDocument4 pagesInnovations Valvis With Integrated AS-i ChipsandeshshivaNo ratings yet
- ZA Ifm Efector GWR Brochure 10Document4 pagesZA Ifm Efector GWR Brochure 10sandeshshivaNo ratings yet
- Innovations T-Slot Cylinder Sensors and ATEX Applications: Fluid Sensors & Diagnostic Systems WWWDocument6 pagesInnovations T-Slot Cylinder Sensors and ATEX Applications: Fluid Sensors & Diagnostic Systems WWWsandeshshivaNo ratings yet
- Innovations Compressed Air Meter: Fluid Sensors & Diagnostic Systems WWWDocument4 pagesInnovations Compressed Air Meter: Fluid Sensors & Diagnostic Systems WWWsandeshshivaNo ratings yet
- Stereosternum Tumidum (Meaning "Rigid Chest") (Stereos,: Genus Marine Reptile Karoo Basin South AfricaDocument1 pageStereosternum Tumidum (Meaning "Rigid Chest") (Stereos,: Genus Marine Reptile Karoo Basin South AfricasandeshshivaNo ratings yet
- Innovations Cooling and Protection Box: Positions Senosrs & Object Recognition WWWDocument4 pagesInnovations Cooling and Protection Box: Positions Senosrs & Object Recognition WWWsandeshshivaNo ratings yet
- Mesosaurus Was One of The First Reptiles Known: Tetrapods Late DevonianDocument1 pageMesosaurus Was One of The First Reptiles Known: Tetrapods Late DevoniansandeshshivaNo ratings yet
- ZA Ifm AS-i Profinet Gateway Brochure 11Document4 pagesZA Ifm AS-i Profinet Gateway Brochure 11sandeshshivaNo ratings yet
- EunotosaurusDocument1 pageEunotosaurussandeshshivaNo ratings yet
- Top 100 Startups in India To Watch in 2018 - List of Best Startups in IndiaDocument8 pagesTop 100 Startups in India To Watch in 2018 - List of Best Startups in IndiasandeshshivaNo ratings yet
- Theory Whitehill Melo Irati: Mesosaurus Was Significant in ProvidingDocument1 pageTheory Whitehill Melo Irati: Mesosaurus Was Significant in ProvidingsandeshshivaNo ratings yet
- Mesosaurus (Meaning "Middle Lizard") Is An ExtinctDocument1 pageMesosaurus (Meaning "Middle Lizard") Is An ExtinctsandeshshivaNo ratings yet