Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Hydro Cefalu S
Hydro Cefalu S
Uploaded by
Andi Muliana Sultani0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
22 views24 pagesThis document discusses hydrocephalus, which is an abnormal enlargement of the ventricles due to excessive accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid. It affects 1-1.5% of the population and can be congenital or acquired. Symptoms in neonates and infants include head enlargement and bulging fontanelles, while in children symptoms include headaches and vomiting. Treatment goals are to relieve hydrocephalus and its complications. Surgical treatment via shunt placement is usually needed to drain cerebrospinal fluid from the ventricles to the peritoneum or right atrium. Shunt infection is a serious complication.
Original Description:
materi kuliah
Original Title
Hydro Cefalu s
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document discusses hydrocephalus, which is an abnormal enlargement of the ventricles due to excessive accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid. It affects 1-1.5% of the population and can be congenital or acquired. Symptoms in neonates and infants include head enlargement and bulging fontanelles, while in children symptoms include headaches and vomiting. Treatment goals are to relieve hydrocephalus and its complications. Surgical treatment via shunt placement is usually needed to drain cerebrospinal fluid from the ventricles to the peritoneum or right atrium. Shunt infection is a serious complication.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
22 views24 pagesHydro Cefalu S
Hydro Cefalu S
Uploaded by
Andi Muliana SultaniThis document discusses hydrocephalus, which is an abnormal enlargement of the ventricles due to excessive accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid. It affects 1-1.5% of the population and can be congenital or acquired. Symptoms in neonates and infants include head enlargement and bulging fontanelles, while in children symptoms include headaches and vomiting. Treatment goals are to relieve hydrocephalus and its complications. Surgical treatment via shunt placement is usually needed to drain cerebrospinal fluid from the ventricles to the peritoneum or right atrium. Shunt infection is a serious complication.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 24
Andi Ihwan, SpBS
Bagian Bedah Saraf FK Unhas
Abnormal enlargement of the ventricels due to an
excessive accumultion of CSF resulting from a
disturbance of its flow, absorption or secretion.
Prevalence : 1-1,5%
Type:
Patophysiology
Communicating
Noncommunicating
Present
Congenital : 0,9-1,8/1000 birth
Acquired
Neonatus - Infancy
Progresive head enlargement
Cranium enlarges ata rate > facial growth
Bulging fontanelle
Enlargement of scalp veins (vena ectasis)
Macewen’s sign: cracked pot sound
Sunset phenomenom
Splitting cranial sutures
Transilumination
Children:
headache, vomiting, diplopia, ataxia, visual loss,
behavioral changes
Raise ICP, Cushing’s triad: bradycardia, hypertension,
decreased RR
Symptom
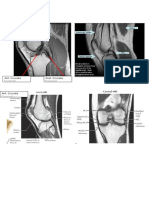
Imaging:
USG
Head CT Scan
MRI
Plain X-Ray
Brain atropy
Hydranencephaly
Developmental anomaly: agenesis corpus
callosum
Goals:
Relieve hydrocephaly
Treat complications
Manage problem resulting from effects of
disorder on psychomotor development
USUALLY SURGICAL!
Medical:
Diuretics: Furosemida : 1 mg/kg/day TID
Acetazolamide : 25 mg/kg/days TID
Temporary: Eksternal ventricular drain
Persistent : Shunt
Endoscopic Third Ventriculostomy (ETV)
Therapy of choice!
Direct removal of source of obstruction
(neoplasm, cyst, or hematoma)
Most require shunt procedure to drain CSF
from ventricles to extracranial area; usually
peritoneum(VP shunt), or right atrium (VA
shunt) for absorption.
Type:
VP (ventriculoperitoneal)
shunt
VA (ventriculoatrial)
shunt
VPl (ventriculopleural)
shunt
LP (Lumboperitoneal)
shunt
Shunt infection is most serious complication!
Period of greatest risk is 1 to 2 months
following placement.
Staph and strep most common organisms
Mechanical difficulties
kinking, plugging, migration of tubing.
Malfunction is most often by mechanical
obstruction!
Look for signs of increased ICP; fever,
inflammation and abdominal pain.
Slit ventricel
Subdural hematoma
Underlying
disease
Cerebral mantle
24
You might also like
- Nclex Study Content - UseDocument65 pagesNclex Study Content - Usesbrooks6914100% (22)
- PericarditisDocument52 pagesPericarditissanjivdasNo ratings yet
- ICP Head InjuryDocument57 pagesICP Head InjuryWengel RedkissNo ratings yet
- Hydrocephalus 170704144233Document56 pagesHydrocephalus 170704144233Pratyaksha TiwariNo ratings yet
- Hydrocephalus: Prepared By: Sita PariyarDocument38 pagesHydrocephalus: Prepared By: Sita PariyarSarita PariyarNo ratings yet
- Hydro Cep Hal UsDocument11 pagesHydro Cep Hal UsEmmanuel MukukaNo ratings yet
- Short Case Hydrocephalus: by Febrianto Haba Bunga, S.Ked Consultant DR .Donny Argie, SP - BSDocument29 pagesShort Case Hydrocephalus: by Febrianto Haba Bunga, S.Ked Consultant DR .Donny Argie, SP - BSErkoNo ratings yet
- Oncologic EmergenciesDocument48 pagesOncologic EmergenciesStephen Joseph GarciaNo ratings yet
- Obstetric EmergenciesDocument44 pagesObstetric EmergenciesVijith.V.kumarNo ratings yet
- HYDROCEPHALUSDocument17 pagesHYDROCEPHALUSSalim FatmaNo ratings yet
- HydrocephalusDocument22 pagesHydrocephalusVinayaka Musale100% (1)
- Massive Intracranial Fluid CollectionDocument29 pagesMassive Intracranial Fluid CollectionAiza QenNo ratings yet
- Prepared by dr.mohammed abdalla khidir ةحفص 1Document5 pagesPrepared by dr.mohammed abdalla khidir ةحفص 1DijattxNo ratings yet
- HydrocephalusDocument33 pagesHydrocephalusrajan kumar100% (2)
- ميحرلا نمحرلا الله مسب Birth InjuryDocument45 pagesميحرلا نمحرلا الله مسب Birth InjuryhassanunderstandNo ratings yet
- Neurological Disorders Key NotesDocument31 pagesNeurological Disorders Key NotesHannah aswiniNo ratings yet
- Birth InjuriesDocument2 pagesBirth InjuriesMohd FadhliNo ratings yet
- Alarm Symptoms of Hematoonco in Pediatrics: Dr. Cece Alfalah, M.Biomed, Sp.A (K) Pediatric Hematology and OncologyDocument22 pagesAlarm Symptoms of Hematoonco in Pediatrics: Dr. Cece Alfalah, M.Biomed, Sp.A (K) Pediatric Hematology and OncologyMuhammad ArifNo ratings yet
- Hydrocephalus: Mira Octavionita Michael SalimDocument17 pagesHydrocephalus: Mira Octavionita Michael SalimMichelle SalimNo ratings yet
- Hydrocephalus: Dr. Tondi Maspian Tjili SPBS, M.KesDocument34 pagesHydrocephalus: Dr. Tondi Maspian Tjili SPBS, M.KesLuthfianaNo ratings yet
- Acute Scrotum ปี4Document18 pagesAcute Scrotum ปี4fackxy4.18No ratings yet
- Congenital DisordersDocument160 pagesCongenital DisordersGloria MachariaNo ratings yet
- Pulmonary EmbolismDocument19 pagesPulmonary EmbolismIbrahimNo ratings yet
- Hydrocephalus PresentationDocument49 pagesHydrocephalus PresentationSourina BeraNo ratings yet
- HydrocephalusDocument33 pagesHydrocephalusRoselyn VelascoNo ratings yet
- 6-Health Problems Common in PreschoolerDocument36 pages6-Health Problems Common in PreschoolerPam Lala100% (2)
- Birthinjuries Dr.M.maniDocument65 pagesBirthinjuries Dr.M.manimaniNo ratings yet
- Lecture 01 Hemorrh-Diat KaplanDocument53 pagesLecture 01 Hemorrh-Diat KaplanАбдул Насер МохаммадізмаелNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Pathology: Disease Cause/Risk Factors SymptomsDocument12 pagesPediatric Pathology: Disease Cause/Risk Factors SymptomsherethemindNo ratings yet
- Terminology and Medical AbbreviationDocument54 pagesTerminology and Medical AbbreviationSuverna ChaturvediNo ratings yet
- Hydrocephalus and Meningitis, Seizures PPTZDocument71 pagesHydrocephalus and Meningitis, Seizures PPTZSakthi DeviNo ratings yet
- (Radiology) RADIOLOGIDocument82 pages(Radiology) RADIOLOGIIrham KhairiNo ratings yet
- EXAM CompiledDocument19 pagesEXAM CompiledAhmad Fuad HasbollahNo ratings yet
- Hydrocephalus - Pediatrics - MSD Manual Professional EditionDocument4 pagesHydrocephalus - Pediatrics - MSD Manual Professional EditionTONY GO AWAYNo ratings yet
- All Previous Essay SurgeryDocument170 pagesAll Previous Essay Surgeryalsfyabdullah2021No ratings yet
- HydrocepalusDocument25 pagesHydrocepalusRastu MaharthaNo ratings yet
- Hydrocephalus: Mr. Fadi J. Zaben RN MSN IMET2000, Ramallah February, 2013Document30 pagesHydrocephalus: Mr. Fadi J. Zaben RN MSN IMET2000, Ramallah February, 2013WisnuBaskoro100% (1)
- MT 2Document56 pagesMT 2Bibek goitNo ratings yet
- Pharmacotherapy of VTEDocument80 pagesPharmacotherapy of VTEAbera JamboNo ratings yet
- I.W. Crandon Section of Surgery Division of Neurosurgery University of The West IndiesDocument38 pagesI.W. Crandon Section of Surgery Division of Neurosurgery University of The West IndiesdivinaNo ratings yet
- RevisionDocument9 pagesRevisionF6imNo ratings yet
- Acuteurologicalconditions 130121123140 Phpapp01Document58 pagesAcuteurologicalconditions 130121123140 Phpapp01Dr. NasrumminallahNo ratings yet
- CSFHypotensionDocument52 pagesCSFHypotensionSoumavo DasNo ratings yet
- Oncologic EmergenciesDocument32 pagesOncologic EmergenciesDemocrito Louierick Plaza VI100% (1)
- Testicular Disorders Freeman 2013Document56 pagesTesticular Disorders Freeman 2013Evan PermanaNo ratings yet
- Birth TraumaDocument41 pagesBirth TraumaIbrahim Rasim100% (1)
- GauravDocument34 pagesGauravnareshnkdocstopNo ratings yet
- Neuro Reviewer 2Document33 pagesNeuro Reviewer 2joanneNo ratings yet
- Testiculartorsion Alias OrkitisDocument18 pagesTesticulartorsion Alias OrkitisNabilaNo ratings yet
- Scrotal ProblemsDocument22 pagesScrotal ProblemsbigtemptationNo ratings yet
- Blok 25: Suryadi Susanto Pediatric Departement Krida Wacana Christian UniversityDocument57 pagesBlok 25: Suryadi Susanto Pediatric Departement Krida Wacana Christian UniversityJoseph RivaldoNo ratings yet
- Patent Ductus Arteriosus - Most Common Congenital Heart Defect Symptoms DependDocument5 pagesPatent Ductus Arteriosus - Most Common Congenital Heart Defect Symptoms DependANNENo ratings yet
- Counselling On Disorders - NotesDocument5 pagesCounselling On Disorders - NotesRichard BudNo ratings yet
- Acute Scrotum: DR - Ameer Alaraji College of Medicine, Fabms, FJMC, High Speciality in UrologyDocument63 pagesAcute Scrotum: DR - Ameer Alaraji College of Medicine, Fabms, FJMC, High Speciality in UrologyHaider Nadhem AL-rubaiNo ratings yet
- Nclex BulletsDocument34 pagesNclex Bulletssaroberts2202100% (1)
- Hydrocephalus AND Neural Tube DefectDocument7 pagesHydrocephalus AND Neural Tube DefectTherese ArellanoNo ratings yet
- Hydrocephalus AND Neural Tube DefectDocument7 pagesHydrocephalus AND Neural Tube DefectTherese ArellanoNo ratings yet
- Maestroke BriefDocument5 pagesMaestroke BriefNurse NotesNo ratings yet