Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Mobile Phones: by Balanica Andrei, Gheorghe Vlad, Nicola Luca, Pirvu Mihai
Mobile Phones: by Balanica Andrei, Gheorghe Vlad, Nicola Luca, Pirvu Mihai
Uploaded by
Vlad Nenes0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
31 views19 pagesMobile phones have evolved from early radio telephone experiments in the early 20th century to today's multifunctional smartphones. Key developments include the first handheld mobile phone in 1973, the launch of the first commercial cellular network in 1979, the 2G digital network in 1991, and 3G networks in 2001 enabling higher data speeds. Modern phones run operating systems and support a wide variety of apps available through application stores. Common phone components include processors, batteries, displays, and speakers, while popular phone uses involve content distribution, mobile payments, and tracking, though driving while using a phone can be unsafe.
Original Description:
.
Original Title
Mobile Phones
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentMobile phones have evolved from early radio telephone experiments in the early 20th century to today's multifunctional smartphones. Key developments include the first handheld mobile phone in 1973, the launch of the first commercial cellular network in 1979, the 2G digital network in 1991, and 3G networks in 2001 enabling higher data speeds. Modern phones run operating systems and support a wide variety of apps available through application stores. Common phone components include processors, batteries, displays, and speakers, while popular phone uses involve content distribution, mobile payments, and tracking, though driving while using a phone can be unsafe.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
31 views19 pagesMobile Phones: by Balanica Andrei, Gheorghe Vlad, Nicola Luca, Pirvu Mihai
Mobile Phones: by Balanica Andrei, Gheorghe Vlad, Nicola Luca, Pirvu Mihai
Uploaded by
Vlad NenesMobile phones have evolved from early radio telephone experiments in the early 20th century to today's multifunctional smartphones. Key developments include the first handheld mobile phone in 1973, the launch of the first commercial cellular network in 1979, the 2G digital network in 1991, and 3G networks in 2001 enabling higher data speeds. Modern phones run operating systems and support a wide variety of apps available through application stores. Common phone components include processors, batteries, displays, and speakers, while popular phone uses involve content distribution, mobile payments, and tracking, though driving while using a phone can be unsafe.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 19
Mobile phones
BY BALANICA ANDREI, GHEORGHE VLAD,
NICOLA LUCA, PIRVU MIHAI
Summary
● History
● Software
● Hardware
● Usage
The Historical
Point of view
● A handheld mobile radio telephone was
envisioned in the early stages of radio
engineering.
● 1917 - finnish inventor filed a patent for a “pocket-
size folding telephone with a very thin carbon
microphone“
● Early predecessors of cellular phones
included analog radio communications (ships and
trains).
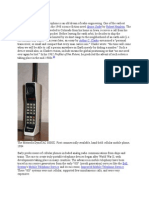
● 1973 - The first handheld cellular
mobile phone: John F.
Mitchell, Martin Cooper of Motorola.
● 1979 - The first commercial
automated cellular network
(Japan): Nippon Telegraph and
Telephone.
● 1981 - simultaneous launch of
the Nordic Mobile
Telephone (NMT) system in
Denmark, Finland, Norway, and
Sweden.
● Several other countries then
followed in the early to mid-1980s.
● 1991 - 2G (Finland): Radiolinja (GSM standard). This sparked competition
in the sector as the new operators challenged the incumbent 1G network
operators.
● 2001 - 3G was launched in Japan, followed by 3.5G, 3G+ or turbo 3G
enhancements based on the HSPA family, allowing UMTS networks to
have higher data transfer speeds and capacity.
Hardware
Common components found on all phones are:
● CPU (processor of phones).
● battery (power source for the phone functions).
● input mechanism (to allow the user to interact with the phone).
● Display (echoes the user's typing, displays text messages, contacts, and more).
● Speakers for sound.
● SIM cards.
Central Processing Unit
Display
Sound
Battery
Software: Mobile operating
system
● A mobile operating system (or mobile OS) is an operating
system for phones, tablets, smartwatches, or other mobile
devices.
Mobile App
● A mobile app is a computer program
designed to run on a mobile device, such as
a smartphone. The term "app" is a short-
form of the term "software application".
Application stores
Main application stores :
● App Store
● Google Play Store
● App World
Usage
What are the uses of a
mobile phone?
Different types of use of a mobile phone:
● Content distribution
● Mobile tracking
● Mobile banking and payment
● Usage while driving
Different types of use
Content distribution
Different types of use
Mobile tracking
Mobile banking and payment
● easy to use
● more and more shop accept mobile
payment
● always with you
● don't have to take your wallet
everywhere you go
While driving
● not safe
● the phone is a reason of inattention
● using a cell phone reduces the amount
of brain activity while driving by 37
percent
● mobile phones have driving mode
Thank you for
your attention!
You might also like
- A Seminar Report On 5GDocument17 pagesA Seminar Report On 5GSameer Tiwari100% (3)
- Essential 4G Guide: Learn 4G Wireless In One DayFrom EverandEssential 4G Guide: Learn 4G Wireless In One DayRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (12)
- Mobile Commerce: New Opportunities For B2B and B2C Services Offered by New Mobile Communication TechnologiesDocument59 pagesMobile Commerce: New Opportunities For B2B and B2C Services Offered by New Mobile Communication TechnologiesSrinivas AvNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 MA PART 1Document63 pagesUnit 1 MA PART 1Jatin SharmaNo ratings yet
- Mobile PhoneDocument22 pagesMobile PhoneelisiaNo ratings yet
- Features of Latest Mobile Phones and Pdas in Indian and Global MarketsDocument20 pagesFeatures of Latest Mobile Phones and Pdas in Indian and Global MarketsShievangi Sharma100% (1)
- Mobile CommunicationDocument13 pagesMobile CommunicationZannat E Noor AobonyNo ratings yet
- History: Mobile Phone Cellular Phone Cell Phone Hand PhoneDocument10 pagesHistory: Mobile Phone Cellular Phone Cell Phone Hand Phoneyouthere56No ratings yet
- 1GDocument2 pages1GPriya KrishnaNo ratings yet
- 4G Technology: By: Mangesh V. KandalgaonkarDocument13 pages4G Technology: By: Mangesh V. KandalgaonkarMangesh KandalgaonkarNo ratings yet
- Bangladesh University of Business and TechnologyDocument15 pagesBangladesh University of Business and TechnologyAtiqueNo ratings yet
- Photo EssayDocument14 pagesPhoto Essaypptes123No ratings yet
- Term Paper of Econom Ics Topic: - Oligopoly-A Study of Various Mobile Phone Service ProvidersDocument13 pagesTerm Paper of Econom Ics Topic: - Oligopoly-A Study of Various Mobile Phone Service Providersmiraadil00No ratings yet
- Mobile Phone RMDocument15 pagesMobile Phone RMPOOJANo ratings yet
- A Mobile Phone or MobileDocument14 pagesA Mobile Phone or MobileTineswaran SehgarNo ratings yet
- Branding 1 PDFDocument73 pagesBranding 1 PDFHarsh SudraNo ratings yet
- PhoneDocument22 pagesPhoneseyed.mohammadreza.hadianNo ratings yet
- History of ComputersDocument14 pagesHistory of ComputersKING SOLOMONNo ratings yet
- Contiue of Black BookDocument5 pagesContiue of Black BookRayaan QureshiNo ratings yet
- Mobile Computing Leture Ammar 2Document56 pagesMobile Computing Leture Ammar 2Abhishek raj MishraNo ratings yet
- HistoryDocument5 pagesHistorymahi2607No ratings yet
- WCMC - Lesson1Document21 pagesWCMC - Lesson1betselot tadesseNo ratings yet
- NTT DocomoDocument2 pagesNTT Docomo2203854No ratings yet
- Cellular PhonesDocument14 pagesCellular PhonesCMYLNo ratings yet
- A Mobile PhoneDocument4 pagesA Mobile Phonesembakarani thevagumaranNo ratings yet
- Mobile PhoneDocument24 pagesMobile Phonestevensteeler083No ratings yet
- 1G (Or 1-G) Refers To The First Generation Of: Nippon Telegraph and TelephoneDocument2 pages1G (Or 1-G) Refers To The First Generation Of: Nippon Telegraph and Telephonerahul sharmaNo ratings yet
- wk2 - The Mobile EcosystemDocument28 pageswk2 - The Mobile EcosystemnangayebokhamNo ratings yet
- Analysis of The Introduction and Diffusion of Cell Phone TechnologyDocument7 pagesAnalysis of The Introduction and Diffusion of Cell Phone TechnologySagar GuptaNo ratings yet
- History of Wireless CommunicationDocument3 pagesHistory of Wireless CommunicationJimmy MirabunaNo ratings yet
- Cell PhoneDocument15 pagesCell PhoneSuresh NatarajanNo ratings yet
- Consumer Behavior Towards Mobile Phones in Rural Areas: U.S. Patent 887,357 Nathan B. Stubblefield Murray, KentuckyDocument24 pagesConsumer Behavior Towards Mobile Phones in Rural Areas: U.S. Patent 887,357 Nathan B. Stubblefield Murray, Kentuckyphaneedhar reddyNo ratings yet
- Generations of Mobile Wireless Technology: A Survey: Mudit Ratana Bhalla Anand Vardhan BhallaDocument7 pagesGenerations of Mobile Wireless Technology: A Survey: Mudit Ratana Bhalla Anand Vardhan BhallaJyoti Prakash DashNo ratings yet
- Mobile PhoneDocument7 pagesMobile PhoneAdalberto MacdonaldNo ratings yet
- TYPEF OF Mobile - Phone PDFDocument14 pagesTYPEF OF Mobile - Phone PDFhemaliNo ratings yet
- Vijayanand Kakade.: K H Kabbur Institute of TechnologyDocument20 pagesVijayanand Kakade.: K H Kabbur Institute of TechnologysachinmpatilNo ratings yet
- JyotiDocument9 pagesJyotideepika_goyal92481No ratings yet
- MobileDocument12 pagesMobileGokul RBNo ratings yet
- Ingles Vi - Secion 6Document14 pagesIngles Vi - Secion 6Kevin Jeanpol Peña PomaNo ratings yet
- Group 2 It ReportDocument44 pagesGroup 2 It ReportSteve Jhon James TantingNo ratings yet
- Evolution of Phones p1Document2 pagesEvolution of Phones p1Eun-ho ParkNo ratings yet
- Mobile Application Development1 (1) - WatermarkDocument43 pagesMobile Application Development1 (1) - Watermarkrigzen namgailNo ratings yet
- Robert Heinlein: Space CadetDocument5 pagesRobert Heinlein: Space Cadetdamian00005No ratings yet
- Mobile Technology1Document12 pagesMobile Technology1AnoopKumarNissadNo ratings yet
- Mobile Phone: Navigation Search Improve It Verifying References Talk PageDocument16 pagesMobile Phone: Navigation Search Improve It Verifying References Talk PageVijayangg VijiNo ratings yet
- Survey of Mobile PhoneDocument37 pagesSurvey of Mobile PhoneVarun JainNo ratings yet
- UNIT-2 (Part-1)Document25 pagesUNIT-2 (Part-1)2k22csestudentid080No ratings yet
- Mobile Phone - DocxDocument11 pagesMobile Phone - DocxFaizan AhmedNo ratings yet
- Tech. GenerationDocument4 pagesTech. GenerationParul JainNo ratings yet
- Generations and Standards of Wireless TechnologiesDocument11 pagesGenerations and Standards of Wireless TechnologiesJane Erestain BuenaobraNo ratings yet
- Cell PhoneDocument13 pagesCell PhoneSomnath KoriNo ratings yet
- Evolution of Phones p2Document4 pagesEvolution of Phones p2Eun-ho ParkNo ratings yet
- Physics Project: Submitted By: Anmol Puri Xii-DDocument20 pagesPhysics Project: Submitted By: Anmol Puri Xii-DBeenu PuriNo ratings yet
- Application StoresDocument8 pagesApplication Storessembakarani thevagumaranNo ratings yet
- NFCDocument21 pagesNFCnav1991navNo ratings yet
- Mobile Phone: "Cell Phone" Redirects Here. For The Film, See - For The Handphone Film, SeeDocument27 pagesMobile Phone: "Cell Phone" Redirects Here. For The Film, See - For The Handphone Film, Seesanjaydubey3No ratings yet
- Mobile PhoneDocument15 pagesMobile PhonePrateek AgarwalNo ratings yet
- RTG 005 DataDocument2 pagesRTG 005 Datarakesh0072No ratings yet
- Grade 8 L-1Document10 pagesGrade 8 L-1Kavish RawatNo ratings yet
- Performance Price Capabilities Size: A Full Spectrum of Spectrum Analyzer SolutionsDocument2 pagesPerformance Price Capabilities Size: A Full Spectrum of Spectrum Analyzer SolutionsVictorNo ratings yet
- 408ULS Brochure Sercel enDocument4 pages408ULS Brochure Sercel enAnonymous f01BFKqNo ratings yet
- Wan TechnologyDocument24 pagesWan TechnologyjhfjfNo ratings yet
- Subject Title: Analog Circuits: 18EC42 Model Question Paper-2 With Effect From 2019-20 (CBCS Scheme)Document3 pagesSubject Title: Analog Circuits: 18EC42 Model Question Paper-2 With Effect From 2019-20 (CBCS Scheme)VijaykumarPatilNo ratings yet
- Elements of Embedded SystemsDocument40 pagesElements of Embedded SystemsAsante WilliamNo ratings yet
- AssignmentDocument1 pageAssignmentnesib mNo ratings yet
- PRBSDocument4 pagesPRBSshabi09040% (1)
- Work Immersion ModuleDocument32 pagesWork Immersion Modulew3w100% (1)
- QuickZChargerZAC DCDocument2 pagesQuickZChargerZAC DCLucaspasNo ratings yet
- Upgrading The ProtectionDocument4 pagesUpgrading The ProtectionMukesh KumarNo ratings yet
- 1.3 Future Scaling: Where Systems and Technology Meet: 25 Digest of Technical PapersDocument5 pages1.3 Future Scaling: Where Systems and Technology Meet: 25 Digest of Technical Papersck maitiNo ratings yet
- Noveltech Character ManualDocument3 pagesNoveltech Character ManualAnton VorozhtsovNo ratings yet
- LG j10hd Owner S ManualDocument39 pagesLG j10hd Owner S ManualZdravko Lučić100% (1)
- Course Structure and Syllabus: Dr. Babasaheb Ambedkar Technological University, LonereDocument122 pagesCourse Structure and Syllabus: Dr. Babasaheb Ambedkar Technological University, LonereANGEL 69No ratings yet
- Digit AC Ammeter, VoltmeterDocument7 pagesDigit AC Ammeter, VoltmeterSuhas AcharyaNo ratings yet
- Tecsun Pl880 ManualDocument0 pagesTecsun Pl880 Manual251416No ratings yet
- COC2 EditedDocument91 pagesCOC2 Editededwin jaudianNo ratings yet
- Cable Fault LocationDocument3 pagesCable Fault LocationJannela yernaiduNo ratings yet
- F1618 Apc 306-308Document3 pagesF1618 Apc 306-308Mathi AlaganNo ratings yet
- Manuals SEW-3055W 170117 ENDocument66 pagesManuals SEW-3055W 170117 ENFrancisco VegaNo ratings yet
- Mpin TDocument55 pagesMpin Tzinabuhaile26No ratings yet
- DIR-905L A1 Manual v1.00 (DI) PDFDocument96 pagesDIR-905L A1 Manual v1.00 (DI) PDFmarcos_nNo ratings yet
- Cumulus Data SheetDocument8 pagesCumulus Data SheetHerland Mauricio Poppe HurtadoNo ratings yet
- JPEG and MPEG Image CompressionDocument3 pagesJPEG and MPEG Image CompressionE.GANGADURAI AP-I - ECENo ratings yet
- PIC16C7X: 8-Bit CMOS Microcontrollers With A/D ConverterDocument34 pagesPIC16C7X: 8-Bit CMOS Microcontrollers With A/D ConvertersureshNo ratings yet
- RK903 Datasheet - V1.2 - 20120309Document26 pagesRK903 Datasheet - V1.2 - 20120309Roger TruemanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Introduction To Wireless Communications 2023Document30 pagesChapter 1 - Introduction To Wireless Communications 2023rokomNo ratings yet
- B.N.M. Institute of Technology: VII SemesterDocument54 pagesB.N.M. Institute of Technology: VII SemesterAbhishek SinghNo ratings yet