Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Project On e Vehicle
Project On e Vehicle
Uploaded by
Pavan Sai NadipenaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Project On e Vehicle
Project On e Vehicle
Uploaded by
Pavan Sai NadipenaCopyright:
Available Formats
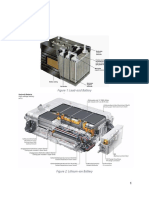
PROJECT ON E VEHICLE
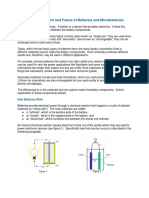
RECHARGEABLE batteries were first introduced in 1859 when the first rechargeable
lead–acid battery was invented by the French inventor Gaston Plante [1]. Lead–acid
batteries are used in several applications where cost is more important than space
and weight, typically preferred as backup batteries for uninterruptable power supply
(UPS) and alarm systems, as well as automotive lighting and ignition applications
(unsuitable for portable appliances). Almost four decades beyond this invention, the
nickel–cadmium (NiCd) battery was invented and widely used in low-power
applications. One major limitation of NiCd batteries is the “memory effect”
phenomenon, which is a term used to describe the degradation in the battery
capacity when it is partly charged and discharged. In addition, because of cadmium,
these batteries are not environmentally friendly. Then, in the 1990s, nickel–metal–
hydride (NiMH) and lithium-ion (Li-ion) batteries were invented and commercialized.
These batteries have higher energy and power densities compared with lead–acid and
NiCd batteries and do not suffer from the memory effect. In particular, Li-ion batteries
have the highest
braking energy.
You might also like
- A Project Report On HR Practices and Policies at Amararaja Batteries LimitedDocument51 pagesA Project Report On HR Practices and Policies at Amararaja Batteries LimitedRamesh Ramz100% (1)
- Energy - Batteries in A Portable World - A Handbook On Rechargeable Batteries For Non-Engineers - 2Nd Ed - I Buchman (Cadex Electronics) - 2001Document149 pagesEnergy - Batteries in A Portable World - A Handbook On Rechargeable Batteries For Non-Engineers - 2Nd Ed - I Buchman (Cadex Electronics) - 2001fabioffNo ratings yet
- "Substitution of Rechargeable Nicd Batteries: by Arne O. NilssonDocument20 pages"Substitution of Rechargeable Nicd Batteries: by Arne O. NilssonSid RcNo ratings yet
- Comparison of Batteries Used in Electrical Vehicles: (A Review)Document5 pagesComparison of Batteries Used in Electrical Vehicles: (A Review)pierre abreu mackleine100% (1)
- Electric Vehicle BatteriesDocument12 pagesElectric Vehicle Batteriestushar borkarNo ratings yet
- Lead Acid & Ni-CD BatteriesDocument22 pagesLead Acid & Ni-CD Batteriesnishanth nishanthNo ratings yet
- Rechargeablebatteriesreport Dev 160926110353Document24 pagesRechargeablebatteriesreport Dev 160926110353Sudhanshu sekhar PadhiNo ratings yet
- Deep Cycle Battery FAQDocument23 pagesDeep Cycle Battery FAQDrew7362No ratings yet
- Batteries PresentationDocument21 pagesBatteries PresentationS ANo ratings yet
- BatteriesDocument30 pagesBatteriessunamisurendar123No ratings yet
- Baterias NicdDocument18 pagesBaterias NicdErika RamírezNo ratings yet
- Lithium Titanate LTO Anode High Rate Cycle Life BatteriesDocument8 pagesLithium Titanate LTO Anode High Rate Cycle Life BatteriesFrancisca PinoNo ratings yet
- Project Paper 1Document50 pagesProject Paper 1yadanar htaysanNo ratings yet
- Baterai Nickel CadDocument34 pagesBaterai Nickel CadMuhammad MaulaniNo ratings yet
- The Past, Present and Future of Batteries and MicrobatteriesDocument8 pagesThe Past, Present and Future of Batteries and Microbatteriesanacer55No ratings yet
- Used Battery Disposal - Quick Guide - Office of Environmental Health and SafetyDocument4 pagesUsed Battery Disposal - Quick Guide - Office of Environmental Health and SafetyAhmet KerimNo ratings yet
- 05 Chapter 1Document36 pages05 Chapter 1RaghuNo ratings yet
- Cadmium Battery (Nicd Battery or Nicad Battery) Is A Type ofDocument1 pageCadmium Battery (Nicd Battery or Nicad Battery) Is A Type ofsrisaitejaswiniNo ratings yet
- Electric Vehicle BatteryDocument30 pagesElectric Vehicle BatteryUpendraJavaNo ratings yet
- Batteries - Fifty Years of Materials DevelopmentDocument20 pagesBatteries - Fifty Years of Materials DevelopmentLucas SerenaNo ratings yet
- Sodium Ionbattery 16 02 2023Document22 pagesSodium Ionbattery 16 02 2023venugopalan srinivasanNo ratings yet
- Aluminium-Air BatteryDocument6 pagesAluminium-Air BatterypopularsodaNo ratings yet
- Electric Vehicle BatteryDocument24 pagesElectric Vehicle BatteryMonica Canaf100% (1)
- DNK Power Battery Design EbookDocument14 pagesDNK Power Battery Design EbookFaisalNo ratings yet
- Mobil Tenaga NuklirDocument2 pagesMobil Tenaga NuklirWahyu Indra Kusuma IINo ratings yet
- BatteryDocument45 pagesBatteryQuang Linh LêNo ratings yet
- Nickel-Iron Batteries (Edison Cell)Document8 pagesNickel-Iron Batteries (Edison Cell)Centaur ArcherNo ratings yet
- Battery Selection & TestingDocument104 pagesBattery Selection & Testingsrivenkatesh81100% (1)
- Battery Types: Which Batteries To Use?Document5 pagesBattery Types: Which Batteries To Use?Ivana MatkovicNo ratings yet
- History of E-CarsDocument4 pagesHistory of E-CarsKiệt Tuấn HuỳnhNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument30 pagesUntitledRahul KumarNo ratings yet
- Nickel Cadmium Battery: Nicd Is Derived From TheDocument14 pagesNickel Cadmium Battery: Nicd Is Derived From TheHannan AhmedNo ratings yet
- AutomobilesDocument21 pagesAutomobilesGautam SauravNo ratings yet
- Carbide LampDocument6 pagesCarbide LampAdelCNo ratings yet
- 21st Century DevicesDocument9 pages21st Century Devicesapi-291709474No ratings yet
- Tesla's Battery Supply Chain - A Growing ConcernDocument24 pagesTesla's Battery Supply Chain - A Growing ConcernbeyzakeklikNo ratings yet
- BATTERİESDocument21 pagesBATTERİESsudegrpnarr0No ratings yet
- Electric Car Battery TypesDocument12 pagesElectric Car Battery Typesnouman khanNo ratings yet
- International University of Travnik Faculty of Polytechnic SciencesDocument15 pagesInternational University of Travnik Faculty of Polytechnic Sciencesnevermind100% (1)
- Dimming of The Light BulbDocument3 pagesDimming of The Light BulbJayati AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Batteries Fuel Cell ElectrolysisDocument15 pagesBatteries Fuel Cell Electrolysisaljon lindayaoNo ratings yet
- AEE - Automotive Electrical and ElectronicsDocument78 pagesAEE - Automotive Electrical and ElectronicsKarthik BabuNo ratings yet
- 6 Types of Lithium-Ion Batteries - Lithium Investing NewsDocument3 pages6 Types of Lithium-Ion Batteries - Lithium Investing NewsmikaelbillonNo ratings yet
- History of Battery DevelopmentDocument24 pagesHistory of Battery DevelopmentSenthil KumarNo ratings yet
- Academic Reading SampleDocument3 pagesAcademic Reading Samplereddy100% (1)
- Electric BatteryDocument7 pagesElectric Batteryayush.2023No ratings yet
- Long Hard Road: The Lithium-Ion Battery and the Electric CarFrom EverandLong Hard Road: The Lithium-Ion Battery and the Electric CarNo ratings yet
- Everything You Ever Wanted to Know About an Electric Vehicle but Were Afraid to AskFrom EverandEverything You Ever Wanted to Know About an Electric Vehicle but Were Afraid to AskNo ratings yet
- Optics and Wheels - A story of lighting from the primitive torch to the sealed beam headlampFrom EverandOptics and Wheels - A story of lighting from the primitive torch to the sealed beam headlampNo ratings yet
- Summary of The War Below by Ernest Scheyder: Lithium, Copper, and the Global Battle to Power Our LivesFrom EverandSummary of The War Below by Ernest Scheyder: Lithium, Copper, and the Global Battle to Power Our LivesNo ratings yet
- Something New in Model Boat Building - How to Make Out-of-the Ordinary Model Boats with Simple Tools and MaterialsFrom EverandSomething New in Model Boat Building - How to Make Out-of-the Ordinary Model Boats with Simple Tools and MaterialsNo ratings yet