Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
173 viewsDehydration
Dehydration
Uploaded by
ArmySapphireDehydration occurs when the body loses more fluid than is replaced and it doesn't have enough water to function properly. Symptoms range from mild to severe depending on how much fluid is lost. Mild dehydration involves thirst and dry mouth while severe dehydration includes lack of urination, dizziness, and fainting. Treatment involves replacing lost fluids and electrolytes, with oral rehydration solutions effective for mild dehydration and IV fluids for severe cases. Preventing dehydration means drinking fluids regularly, especially when ill, active, or in hot weather.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Control of Communicable Diseases ManualDocument715 pagesControl of Communicable Diseases ManualChris Mahfood100% (4)
- Divine Energy Activator User GuideDocument8 pagesDivine Energy Activator User GuideOladele JoshuaNo ratings yet
- F U N W I S E: Know Your Symptom Severity Score!Document2 pagesF U N W I S E: Know Your Symptom Severity Score!Jamie Sebastian50% (2)
- Abundance Prayer With Archangel RaphaelDocument1 pageAbundance Prayer With Archangel RaphaelhshffhdhNo ratings yet
- Is There Scientific Proof We Can Heal OurselvesDocument10 pagesIs There Scientific Proof We Can Heal Ourselvesblackvenum100% (1)
- Fast Metabolism DietDocument17 pagesFast Metabolism DietOlympia Markellou100% (1)
- Heal Yourself in 15 DaysDocument37 pagesHeal Yourself in 15 DaysAtma Love100% (3)
- 10 Benefits of Drinking Hot Water - How Can It Help Your Health - PDFDocument15 pages10 Benefits of Drinking Hot Water - How Can It Help Your Health - PDFMisgun SamuelNo ratings yet
- 2000 NASS Injury Coding Manual (From Docket)Document202 pages2000 NASS Injury Coding Manual (From Docket)Barbara Moroski-BrowneNo ratings yet
- Spiders - Handbook of India...., 1987 by B K Tikader PDFDocument274 pagesSpiders - Handbook of India...., 1987 by B K Tikader PDFRanbir Singh100% (1)
- Folklore Herbs of Manipur Phytopharmacology - Additional Source of Green Medicines D. D. Joshi (Z-Library)Document376 pagesFolklore Herbs of Manipur Phytopharmacology - Additional Source of Green Medicines D. D. Joshi (Z-Library)khairunnqureshiNo ratings yet
- The Complete Book of Vitamins and Minerals For Health - Vaughn, Lewis Faelten, Sharon - 1988 - EmmDocument760 pagesThe Complete Book of Vitamins and Minerals For Health - Vaughn, Lewis Faelten, Sharon - 1988 - EmmahmadalouNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Distress Syndrome LapkasDocument49 pagesRespiratory Distress Syndrome LapkasThamarai SomuNo ratings yet
- Kitchen Living Food Dehydrator Manual enDocument21 pagesKitchen Living Food Dehydrator Manual enJohn WalesNo ratings yet
- Mary Ann E. Lopez Man RN LPTDocument45 pagesMary Ann E. Lopez Man RN LPT1S VILLEGAS GabrielNo ratings yet
- 81 Health TipsDocument8 pages81 Health TipsYateen GharatNo ratings yet
- Breads, Wraps and Crackers, Dehydrated Style - A Collection of Rawsome Recipes From Our Dehydrator To Yours (Fresh Ideas From Our Kitchen Ebook Series 1)Document80 pagesBreads, Wraps and Crackers, Dehydrated Style - A Collection of Rawsome Recipes From Our Dehydrator To Yours (Fresh Ideas From Our Kitchen Ebook Series 1)muhammad augusfiarNo ratings yet
- Doctors With A Healing Touch PDFDocument4 pagesDoctors With A Healing Touch PDFprakashsahooNo ratings yet
- AwakeningDocument52 pagesAwakeninglev2468No ratings yet
- Cure Headache NaturallyDocument4 pagesCure Headache NaturallySN WijesinheNo ratings yet
- Anti Detox PromiseDocument2 pagesAnti Detox PromiseMarketplaceNo ratings yet
- Ebook Final CompleteDocument18 pagesEbook Final CompleteMike UyNo ratings yet
- Acute Kidney InjuryDocument4 pagesAcute Kidney Injurys.khan9211rediffmail.comNo ratings yet
- Do Plants Have Feelings - Book PDFDocument19 pagesDo Plants Have Feelings - Book PDFapi-340951588No ratings yet
- 2017 Healing Hashimotos Summit ScheduleDocument7 pages2017 Healing Hashimotos Summit ScheduleZulfikar Haidar0% (1)
- Medicinal Plants Roots Barks 2nd EditionDocument85 pagesMedicinal Plants Roots Barks 2nd EditionchubbyNo ratings yet
- Skin Manifestation of Nutritional DisordersDocument33 pagesSkin Manifestation of Nutritional DisordersSonia Sirait100% (2)
- Herbal Plants: Keeping Our Traditional Wisdom AliveDocument16 pagesHerbal Plants: Keeping Our Traditional Wisdom AliveDeaths ComingNo ratings yet
- 2012: DNA Upgrade, The Shift and AscensionDocument21 pages2012: DNA Upgrade, The Shift and AscensioniamdinesNo ratings yet
- How To Achieve Good Health & Longevity?Document57 pagesHow To Achieve Good Health & Longevity?lauchen32100% (1)
- AyurvedaDocument27 pagesAyurvedaJagNo ratings yet
- Secrets of Mind Body HealingDocument17 pagesSecrets of Mind Body Healingtemporal130100% (1)
- Perfect SkinDocument28 pagesPerfect SkinJason Emmanuel100% (2)
- Click Here To Learn The Number 1 Secret To Manifest Your Dream LifeDocument13 pagesClick Here To Learn The Number 1 Secret To Manifest Your Dream LifeBradley Whittaker100% (1)
- IMproving Diagnosis in MedicineDocument42 pagesIMproving Diagnosis in MedicineleeNo ratings yet
- The Source-Sirshree Brief AbstractDocument5 pagesThe Source-Sirshree Brief AbstractShyam SoniNo ratings yet
- Suzie BiofeedbackSDCRIDocument3 pagesSuzie BiofeedbackSDCRIocortezlariosNo ratings yet
- Alkaline Food Chart 04 2020 RossBridgefordDocument112 pagesAlkaline Food Chart 04 2020 RossBridgefordm100% (1)
- Selfhealing PDFDocument110 pagesSelfhealing PDFMelo EugenioNo ratings yet
- 10 Golden Rules For Success in Life - UpfoundrDocument9 pages10 Golden Rules For Success in Life - UpfoundrBipin Kumar100% (1)
- What Are TincturesDocument2 pagesWhat Are TincturesLilia PanciucNo ratings yet
- Beck Protocol Handbook PDFDocument86 pagesBeck Protocol Handbook PDFEPNo ratings yet
- GallstoneDocument4 pagesGallstoneJovelle ReyesNo ratings yet
- How To Use Self-Hypnosis For Self-ImprovementDocument24 pagesHow To Use Self-Hypnosis For Self-ImprovementCarlos EmilioNo ratings yet
- Bone Disease, Any of The Diseases or Injuries That Affect HumanDocument10 pagesBone Disease, Any of The Diseases or Injuries That Affect Humanrichelle joy reyesNo ratings yet
- Better Gro Whats Wrong With My OrchidDocument1 pageBetter Gro Whats Wrong With My OrchidManuel Elliot Ortiz SepúlvedaNo ratings yet
- Beyond Ben Gay-ADocument17 pagesBeyond Ben Gay-AsadyNo ratings yet
- Ten Essentials of Herbal Safety - Chestnut School of Herbal Medicine.20240531132514311Document24 pagesTen Essentials of Herbal Safety - Chestnut School of Herbal Medicine.20240531132514311DrNicole BarssoumNo ratings yet
- Gingko Biloba - A Wonder DrugDocument2 pagesGingko Biloba - A Wonder Drugsterling3No ratings yet
- Circadian Rhythm - SleepafsDocument4 pagesCircadian Rhythm - SleepafsAfian PrasetyoNo ratings yet
- The Science and Ethics of Stem Cell ResearchDocument80 pagesThe Science and Ethics of Stem Cell Researchgirls_moetNo ratings yet
- 005 - Module 2 - Part 3Document16 pages005 - Module 2 - Part 3Amina AgovićNo ratings yet
- Ayurvedic Guide To The Best Sleep of Your Life - May2018Document14 pagesAyurvedic Guide To The Best Sleep of Your Life - May2018satyakosarajuNo ratings yet
- Heavy Metal DetoxDocument22 pagesHeavy Metal DetoxMey SandrasigaranNo ratings yet
- 30 Natural Remedies You Need To Know AboutDocument38 pages30 Natural Remedies You Need To Know AboutMaria BarbaliaNo ratings yet
- Redox Signaling (Wikipedia)Document5 pagesRedox Signaling (Wikipedia)gotglutNo ratings yet
- Energetic Eyehealing - The New Paradigm of Eye Medicine CategoriesDocument6 pagesEnergetic Eyehealing - The New Paradigm of Eye Medicine CategoriesMadon MariaNo ratings yet
- Health in A Natural WayDocument160 pagesHealth in A Natural Wayapi-27242818100% (1)
- NeckDocument40 pagesNeckPrabhat Kumar SinghNo ratings yet
- Wheat Grass-A Perfect Food and Its Anti-Microbial Properties From TheDocument12 pagesWheat Grass-A Perfect Food and Its Anti-Microbial Properties From TheDimasNo ratings yet
- Thoughts Are ThingsDocument124 pagesThoughts Are ThingsbrianroemmeleNo ratings yet
- Catheterization Insertion and RemovalDocument5 pagesCatheterization Insertion and RemovalArmySapphireNo ratings yet
- Edited Final FNCP OUTPUT and HTDocument24 pagesEdited Final FNCP OUTPUT and HTArmySapphireNo ratings yet
- BY Nelson Munthali Dip/RNDocument56 pagesBY Nelson Munthali Dip/RNArmySapphireNo ratings yet
- Foley Catheterization Insertion and RemovalDocument5 pagesFoley Catheterization Insertion and RemovalArmySapphireNo ratings yet
- Alona Nutrition Across The LifespanDocument12 pagesAlona Nutrition Across The LifespanArmySapphireNo ratings yet
- Activity 2 Answer The Following Questions: 10 Points EachDocument4 pagesActivity 2 Answer The Following Questions: 10 Points EachArmySapphireNo ratings yet
- Nutrition Across The Lifespan/ Life Stages: A. Nutrition in PregnancyDocument12 pagesNutrition Across The Lifespan/ Life Stages: A. Nutrition in PregnancyArmySapphireNo ratings yet
- Synchronous Wednesday Activity PeDocument2 pagesSynchronous Wednesday Activity PeArmySapphireNo ratings yet
- Swimming Events in Philippine HistoryDocument3 pagesSwimming Events in Philippine HistoryArmySapphireNo ratings yet
- Low Cholesterol Diet For Heart FailureDocument3 pagesLow Cholesterol Diet For Heart FailureArmySapphireNo ratings yet
- NSTP LAW and IRR TableDocument8 pagesNSTP LAW and IRR TableArmySapphireNo ratings yet
- What Is NSTPDocument1 pageWhat Is NSTPArmySapphireNo ratings yet
- Purpose:: Procedure: Rationale: Introduce Yourself and Inform Pregnant Woman About The ProcedureDocument5 pagesPurpose:: Procedure: Rationale: Introduce Yourself and Inform Pregnant Woman About The ProcedureArmySapphire100% (1)
- What Causes of Type 2 Diabetes?: Critique PaperDocument4 pagesWhat Causes of Type 2 Diabetes?: Critique PaperArmySapphireNo ratings yet
- What Activities Are Expected For NSTP 1Document2 pagesWhat Activities Are Expected For NSTP 1ArmySapphire100% (1)
- NSTP Module 1 IntroductionDocument10 pagesNSTP Module 1 IntroductionArmySapphireNo ratings yet
- (Sauteed Mung Beans) Recipe: Munggo GuisadoDocument1 page(Sauteed Mung Beans) Recipe: Munggo GuisadoArmySapphireNo ratings yet
- Swimming Equipment and SkillDocument3 pagesSwimming Equipment and SkillArmySapphireNo ratings yet
- NSTP Module 3-Duties and Responsibilities of A CitizenDocument21 pagesNSTP Module 3-Duties and Responsibilities of A CitizenArmySapphire100% (1)
- Jane - Lecture of Typology and Coping IndexDocument14 pagesJane - Lecture of Typology and Coping IndexArmySapphireNo ratings yet
- Olita (2) Activity SharingDocument1 pageOlita (2) Activity SharingArmySapphireNo ratings yet
- Bioethics NOTES 108 - Week 2Document6 pagesBioethics NOTES 108 - Week 2ArmySapphireNo ratings yet
- Nursing Diagnoses PharmaDocument3 pagesNursing Diagnoses PharmaArmySapphireNo ratings yet
- UTS Midterm SlideDocument47 pagesUTS Midterm SlideArmySapphireNo ratings yet
- Good Practice For Law Enforcement Officials Policing DemonstrationsDocument2 pagesGood Practice For Law Enforcement Officials Policing DemonstrationsArmySapphireNo ratings yet
- What Is Cancer - National Cancer Institute PDFDocument7 pagesWhat Is Cancer - National Cancer Institute PDFAlexis CastilloNo ratings yet
- Dengue Cases May Reach 20,000: Dengue Cases in Cebu City Up by 35-Percent Since JanuaryDocument3 pagesDengue Cases May Reach 20,000: Dengue Cases in Cebu City Up by 35-Percent Since JanuaryIrene InsoNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Understanding The Classification of MicroorganismsDocument18 pages1.1 Understanding The Classification of MicroorganismsHannanNashruddin100% (1)
- LPM (Terminology) - 1Document5 pagesLPM (Terminology) - 1Ganesh LahaneNo ratings yet
- Polycythemia in NewbornDocument25 pagesPolycythemia in NewbornTheva Thy100% (2)
- Second Symposium On The Definition and Management of XisDocument7 pagesSecond Symposium On The Definition and Management of XisbrookswalshNo ratings yet
- Carbimazole Induced HypothyroidismDocument8 pagesCarbimazole Induced HypothyroidismFaiqa Alee ChughtaiNo ratings yet
- Psfox fs1Document2 pagesPsfox fs1api-237614415No ratings yet
- Compartment SyndromeDocument61 pagesCompartment SyndromeIgnatius Rheza SetiawanNo ratings yet
- In Vitro Anthelminthic Activities of Four Medicinal Plants: Against Haemonchus ContortusDocument5 pagesIn Vitro Anthelminthic Activities of Four Medicinal Plants: Against Haemonchus ContortusSyvelmarie TinteNo ratings yet
- NCMB 316Document46 pagesNCMB 316andreatrojilloNo ratings yet
- Bruce Frantzis - Qi Gong BreathingDocument3 pagesBruce Frantzis - Qi Gong Breathingkabshiel100% (2)
- Parasitology ReviewerDocument17 pagesParasitology Reviewerlouie100% (1)
- Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19) : Situation Report - 102Document16 pagesCoronavirus Disease (COVID-19) : Situation Report - 102CityNewsTorontoNo ratings yet
- Oral RevalidaDocument98 pagesOral RevalidaJay ArNo ratings yet
- Clinical Review - KEDRABDocument97 pagesClinical Review - KEDRABcoolchapNo ratings yet
- Local Anesthetics AgentsDocument56 pagesLocal Anesthetics AgentsIyad Abou-Rabii100% (1)
- Circulatory InsectsDocument7 pagesCirculatory Insectsmith777No ratings yet
- Color Doppler Imaging Codes:: ND RDDocument46 pagesColor Doppler Imaging Codes:: ND RDGervin Brian EspinoNo ratings yet
- GASTROINSTINAL TRACT Robbins 8th EditionDocument4 pagesGASTROINSTINAL TRACT Robbins 8th EditionLim EricNo ratings yet
- Function of MitochondriaDocument5 pagesFunction of MitochondriaArshia NazirNo ratings yet
- GR 3 WTR SQDocument6 pagesGR 3 WTR SQDanilo Fronda Jr.No ratings yet
- 13 1.lung Auscultation#8E2EDocument23 pages13 1.lung Auscultation#8E2EAlina CazanNo ratings yet
- Benifits of SuvarnaprashanDocument2 pagesBenifits of Suvarnaprashanharish4ayur100% (1)
- Urogenital Symptoms in Neurologic Patients.14Document20 pagesUrogenital Symptoms in Neurologic Patients.14Fawad JanNo ratings yet
- Coconut Oil PullingDocument8 pagesCoconut Oil PullingshivaNo ratings yet
Dehydration
Dehydration
Uploaded by
ArmySapphire0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
173 views11 pagesDehydration occurs when the body loses more fluid than is replaced and it doesn't have enough water to function properly. Symptoms range from mild to severe depending on how much fluid is lost. Mild dehydration involves thirst and dry mouth while severe dehydration includes lack of urination, dizziness, and fainting. Treatment involves replacing lost fluids and electrolytes, with oral rehydration solutions effective for mild dehydration and IV fluids for severe cases. Preventing dehydration means drinking fluids regularly, especially when ill, active, or in hot weather.
Original Description:
Original Title
Dehydration.pptx
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentDehydration occurs when the body loses more fluid than is replaced and it doesn't have enough water to function properly. Symptoms range from mild to severe depending on how much fluid is lost. Mild dehydration involves thirst and dry mouth while severe dehydration includes lack of urination, dizziness, and fainting. Treatment involves replacing lost fluids and electrolytes, with oral rehydration solutions effective for mild dehydration and IV fluids for severe cases. Preventing dehydration means drinking fluids regularly, especially when ill, active, or in hot weather.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
173 views11 pagesDehydration
Dehydration
Uploaded by
ArmySapphireDehydration occurs when the body loses more fluid than is replaced and it doesn't have enough water to function properly. Symptoms range from mild to severe depending on how much fluid is lost. Mild dehydration involves thirst and dry mouth while severe dehydration includes lack of urination, dizziness, and fainting. Treatment involves replacing lost fluids and electrolytes, with oral rehydration solutions effective for mild dehydration and IV fluids for severe cases. Preventing dehydration means drinking fluids regularly, especially when ill, active, or in hot weather.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 11
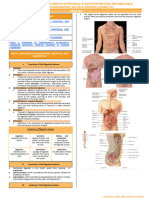
Dehydration happens when your body doesn't have as much water as it needs.
Without enough, your body can't function properly.
Mild Moderate Severe
Depending on how much fluid is missing from your body.
Signs of mild or moderate Signs of severe dehydration
dehydration include: include:
Thirst Not peeing or having very dark yellow
Dry or sticky mouth pee
Not peeing very much Very dry skin
Dark yellow pee Feeling dizzy
Dry, cool skin Rapid heartbeat
Headache Rapid breathing
Muscle cramps Sunken eyes
Sleepiness, lack of energy, confusion
or irritability
Fainting
It’s normal to lose water from your
body every day by sweating,
breathing, peeing, and pooping,
and through tears and saliva(spit).
Usually you replace the lost liquid
by drinking fluids and eating foods
that contain water. If you lose too
much water or don’t drink and eat
enough, you can get dehydrated.
You can lose more water You may not replace the
than usual with: water you lose because:
A fever You’re busy and forget to drink
Diarrhea enough.
Vomiting You don’t realize you’re thirsty.
Excessive sweating You don’t feel like drinking because
Peeing a lot (Diabetes and you have a sore
some medications like water throat or mouth sores, or you’re
pills -- also called diuretics -- can sick to your stomach.
make you pee more often.)
There is no standard recommendation for daily
fluid intake because fluid requirements are different
for different people and vary with age, climate, and
level of physical activity. Passing urine that is light-
yellow coloured is a good sign of adequate hydration.
Also, thirst is not always a reliable early indicator of
dehydration. In some people, particularly older adults,
dehydration precedes feeling thirsty. It is important,
therefore, to increase water intake during hot weather
or when ill.
Dehydration can be prevented by:
Drinking plenty of fluids every day, especially when the weather is hot or
when exercising
Eating foods with high water content, eg: fruits and vegetables
Drinking plenty of fluids, including rehydration solutions if fever,
vomiting, or diarrhoea is present. Do not wait for signs of dehydration.
Drinking extra fluids when feeling unwell due to a short-term illness, eg:
cold, influenza, bronchitis.
People with kidney stones should drink plenty of fluid every day to lower
the chances of developing another stone.
The only effective treatment for
dehydration is to replace lost fluids
and lost electrolytes. The best
approach to dehydration treatment
depends on age, the severity of
dehydration and its cause.
For infants and children who have
become dehydrated from diarrhea,
vomiting or fever, use an over-the-
counter oral rehydration solution.
These solutions contain water and
salts in specific proportions to
replenish both fluids and electrolytes.
Start with about a teaspoon (5
milliliters) every one to five minutes
and increase as tolerated. It may be
easier to use a syringe for very young
children. Older children can be
given diluted sports drinks. Use 1
part sports drink to 1 part water. Most adults with mild to moderate
dehydration from diarrhea, vomiting
or fever can improve their condition
by drinking more water or other
liquids. Diarrhea may be worsened
by full-strength fruit juice and soft
drinks.
If you work or exercise outdoors during hot
or humid weather, cool water is your best
bet. Sports drinks containing electrolytes
and a carbohydrate solution also may be
helpful.
Children and adults who are severely
dehydrated should be treated by
emergency personnel arriving in an
ambulance or in a hospital emergency
room. Salts and fluids delivered
through a vein (intravenously) are
absorbed quickly and speed recovery.
You might also like
- Control of Communicable Diseases ManualDocument715 pagesControl of Communicable Diseases ManualChris Mahfood100% (4)
- Divine Energy Activator User GuideDocument8 pagesDivine Energy Activator User GuideOladele JoshuaNo ratings yet
- F U N W I S E: Know Your Symptom Severity Score!Document2 pagesF U N W I S E: Know Your Symptom Severity Score!Jamie Sebastian50% (2)
- Abundance Prayer With Archangel RaphaelDocument1 pageAbundance Prayer With Archangel RaphaelhshffhdhNo ratings yet
- Is There Scientific Proof We Can Heal OurselvesDocument10 pagesIs There Scientific Proof We Can Heal Ourselvesblackvenum100% (1)
- Fast Metabolism DietDocument17 pagesFast Metabolism DietOlympia Markellou100% (1)
- Heal Yourself in 15 DaysDocument37 pagesHeal Yourself in 15 DaysAtma Love100% (3)
- 10 Benefits of Drinking Hot Water - How Can It Help Your Health - PDFDocument15 pages10 Benefits of Drinking Hot Water - How Can It Help Your Health - PDFMisgun SamuelNo ratings yet
- 2000 NASS Injury Coding Manual (From Docket)Document202 pages2000 NASS Injury Coding Manual (From Docket)Barbara Moroski-BrowneNo ratings yet
- Spiders - Handbook of India...., 1987 by B K Tikader PDFDocument274 pagesSpiders - Handbook of India...., 1987 by B K Tikader PDFRanbir Singh100% (1)
- Folklore Herbs of Manipur Phytopharmacology - Additional Source of Green Medicines D. D. Joshi (Z-Library)Document376 pagesFolklore Herbs of Manipur Phytopharmacology - Additional Source of Green Medicines D. D. Joshi (Z-Library)khairunnqureshiNo ratings yet
- The Complete Book of Vitamins and Minerals For Health - Vaughn, Lewis Faelten, Sharon - 1988 - EmmDocument760 pagesThe Complete Book of Vitamins and Minerals For Health - Vaughn, Lewis Faelten, Sharon - 1988 - EmmahmadalouNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Distress Syndrome LapkasDocument49 pagesRespiratory Distress Syndrome LapkasThamarai SomuNo ratings yet
- Kitchen Living Food Dehydrator Manual enDocument21 pagesKitchen Living Food Dehydrator Manual enJohn WalesNo ratings yet
- Mary Ann E. Lopez Man RN LPTDocument45 pagesMary Ann E. Lopez Man RN LPT1S VILLEGAS GabrielNo ratings yet
- 81 Health TipsDocument8 pages81 Health TipsYateen GharatNo ratings yet
- Breads, Wraps and Crackers, Dehydrated Style - A Collection of Rawsome Recipes From Our Dehydrator To Yours (Fresh Ideas From Our Kitchen Ebook Series 1)Document80 pagesBreads, Wraps and Crackers, Dehydrated Style - A Collection of Rawsome Recipes From Our Dehydrator To Yours (Fresh Ideas From Our Kitchen Ebook Series 1)muhammad augusfiarNo ratings yet
- Doctors With A Healing Touch PDFDocument4 pagesDoctors With A Healing Touch PDFprakashsahooNo ratings yet
- AwakeningDocument52 pagesAwakeninglev2468No ratings yet
- Cure Headache NaturallyDocument4 pagesCure Headache NaturallySN WijesinheNo ratings yet
- Anti Detox PromiseDocument2 pagesAnti Detox PromiseMarketplaceNo ratings yet
- Ebook Final CompleteDocument18 pagesEbook Final CompleteMike UyNo ratings yet
- Acute Kidney InjuryDocument4 pagesAcute Kidney Injurys.khan9211rediffmail.comNo ratings yet
- Do Plants Have Feelings - Book PDFDocument19 pagesDo Plants Have Feelings - Book PDFapi-340951588No ratings yet
- 2017 Healing Hashimotos Summit ScheduleDocument7 pages2017 Healing Hashimotos Summit ScheduleZulfikar Haidar0% (1)
- Medicinal Plants Roots Barks 2nd EditionDocument85 pagesMedicinal Plants Roots Barks 2nd EditionchubbyNo ratings yet
- Skin Manifestation of Nutritional DisordersDocument33 pagesSkin Manifestation of Nutritional DisordersSonia Sirait100% (2)
- Herbal Plants: Keeping Our Traditional Wisdom AliveDocument16 pagesHerbal Plants: Keeping Our Traditional Wisdom AliveDeaths ComingNo ratings yet
- 2012: DNA Upgrade, The Shift and AscensionDocument21 pages2012: DNA Upgrade, The Shift and AscensioniamdinesNo ratings yet
- How To Achieve Good Health & Longevity?Document57 pagesHow To Achieve Good Health & Longevity?lauchen32100% (1)
- AyurvedaDocument27 pagesAyurvedaJagNo ratings yet
- Secrets of Mind Body HealingDocument17 pagesSecrets of Mind Body Healingtemporal130100% (1)
- Perfect SkinDocument28 pagesPerfect SkinJason Emmanuel100% (2)
- Click Here To Learn The Number 1 Secret To Manifest Your Dream LifeDocument13 pagesClick Here To Learn The Number 1 Secret To Manifest Your Dream LifeBradley Whittaker100% (1)
- IMproving Diagnosis in MedicineDocument42 pagesIMproving Diagnosis in MedicineleeNo ratings yet
- The Source-Sirshree Brief AbstractDocument5 pagesThe Source-Sirshree Brief AbstractShyam SoniNo ratings yet
- Suzie BiofeedbackSDCRIDocument3 pagesSuzie BiofeedbackSDCRIocortezlariosNo ratings yet
- Alkaline Food Chart 04 2020 RossBridgefordDocument112 pagesAlkaline Food Chart 04 2020 RossBridgefordm100% (1)
- Selfhealing PDFDocument110 pagesSelfhealing PDFMelo EugenioNo ratings yet
- 10 Golden Rules For Success in Life - UpfoundrDocument9 pages10 Golden Rules For Success in Life - UpfoundrBipin Kumar100% (1)
- What Are TincturesDocument2 pagesWhat Are TincturesLilia PanciucNo ratings yet
- Beck Protocol Handbook PDFDocument86 pagesBeck Protocol Handbook PDFEPNo ratings yet
- GallstoneDocument4 pagesGallstoneJovelle ReyesNo ratings yet
- How To Use Self-Hypnosis For Self-ImprovementDocument24 pagesHow To Use Self-Hypnosis For Self-ImprovementCarlos EmilioNo ratings yet
- Bone Disease, Any of The Diseases or Injuries That Affect HumanDocument10 pagesBone Disease, Any of The Diseases or Injuries That Affect Humanrichelle joy reyesNo ratings yet
- Better Gro Whats Wrong With My OrchidDocument1 pageBetter Gro Whats Wrong With My OrchidManuel Elliot Ortiz SepúlvedaNo ratings yet
- Beyond Ben Gay-ADocument17 pagesBeyond Ben Gay-AsadyNo ratings yet
- Ten Essentials of Herbal Safety - Chestnut School of Herbal Medicine.20240531132514311Document24 pagesTen Essentials of Herbal Safety - Chestnut School of Herbal Medicine.20240531132514311DrNicole BarssoumNo ratings yet
- Gingko Biloba - A Wonder DrugDocument2 pagesGingko Biloba - A Wonder Drugsterling3No ratings yet
- Circadian Rhythm - SleepafsDocument4 pagesCircadian Rhythm - SleepafsAfian PrasetyoNo ratings yet
- The Science and Ethics of Stem Cell ResearchDocument80 pagesThe Science and Ethics of Stem Cell Researchgirls_moetNo ratings yet
- 005 - Module 2 - Part 3Document16 pages005 - Module 2 - Part 3Amina AgovićNo ratings yet
- Ayurvedic Guide To The Best Sleep of Your Life - May2018Document14 pagesAyurvedic Guide To The Best Sleep of Your Life - May2018satyakosarajuNo ratings yet
- Heavy Metal DetoxDocument22 pagesHeavy Metal DetoxMey SandrasigaranNo ratings yet
- 30 Natural Remedies You Need To Know AboutDocument38 pages30 Natural Remedies You Need To Know AboutMaria BarbaliaNo ratings yet
- Redox Signaling (Wikipedia)Document5 pagesRedox Signaling (Wikipedia)gotglutNo ratings yet
- Energetic Eyehealing - The New Paradigm of Eye Medicine CategoriesDocument6 pagesEnergetic Eyehealing - The New Paradigm of Eye Medicine CategoriesMadon MariaNo ratings yet
- Health in A Natural WayDocument160 pagesHealth in A Natural Wayapi-27242818100% (1)
- NeckDocument40 pagesNeckPrabhat Kumar SinghNo ratings yet
- Wheat Grass-A Perfect Food and Its Anti-Microbial Properties From TheDocument12 pagesWheat Grass-A Perfect Food and Its Anti-Microbial Properties From TheDimasNo ratings yet
- Thoughts Are ThingsDocument124 pagesThoughts Are ThingsbrianroemmeleNo ratings yet
- Catheterization Insertion and RemovalDocument5 pagesCatheterization Insertion and RemovalArmySapphireNo ratings yet
- Edited Final FNCP OUTPUT and HTDocument24 pagesEdited Final FNCP OUTPUT and HTArmySapphireNo ratings yet
- BY Nelson Munthali Dip/RNDocument56 pagesBY Nelson Munthali Dip/RNArmySapphireNo ratings yet
- Foley Catheterization Insertion and RemovalDocument5 pagesFoley Catheterization Insertion and RemovalArmySapphireNo ratings yet
- Alona Nutrition Across The LifespanDocument12 pagesAlona Nutrition Across The LifespanArmySapphireNo ratings yet
- Activity 2 Answer The Following Questions: 10 Points EachDocument4 pagesActivity 2 Answer The Following Questions: 10 Points EachArmySapphireNo ratings yet
- Nutrition Across The Lifespan/ Life Stages: A. Nutrition in PregnancyDocument12 pagesNutrition Across The Lifespan/ Life Stages: A. Nutrition in PregnancyArmySapphireNo ratings yet
- Synchronous Wednesday Activity PeDocument2 pagesSynchronous Wednesday Activity PeArmySapphireNo ratings yet
- Swimming Events in Philippine HistoryDocument3 pagesSwimming Events in Philippine HistoryArmySapphireNo ratings yet
- Low Cholesterol Diet For Heart FailureDocument3 pagesLow Cholesterol Diet For Heart FailureArmySapphireNo ratings yet
- NSTP LAW and IRR TableDocument8 pagesNSTP LAW and IRR TableArmySapphireNo ratings yet
- What Is NSTPDocument1 pageWhat Is NSTPArmySapphireNo ratings yet
- Purpose:: Procedure: Rationale: Introduce Yourself and Inform Pregnant Woman About The ProcedureDocument5 pagesPurpose:: Procedure: Rationale: Introduce Yourself and Inform Pregnant Woman About The ProcedureArmySapphire100% (1)
- What Causes of Type 2 Diabetes?: Critique PaperDocument4 pagesWhat Causes of Type 2 Diabetes?: Critique PaperArmySapphireNo ratings yet
- What Activities Are Expected For NSTP 1Document2 pagesWhat Activities Are Expected For NSTP 1ArmySapphire100% (1)
- NSTP Module 1 IntroductionDocument10 pagesNSTP Module 1 IntroductionArmySapphireNo ratings yet
- (Sauteed Mung Beans) Recipe: Munggo GuisadoDocument1 page(Sauteed Mung Beans) Recipe: Munggo GuisadoArmySapphireNo ratings yet
- Swimming Equipment and SkillDocument3 pagesSwimming Equipment and SkillArmySapphireNo ratings yet
- NSTP Module 3-Duties and Responsibilities of A CitizenDocument21 pagesNSTP Module 3-Duties and Responsibilities of A CitizenArmySapphire100% (1)
- Jane - Lecture of Typology and Coping IndexDocument14 pagesJane - Lecture of Typology and Coping IndexArmySapphireNo ratings yet
- Olita (2) Activity SharingDocument1 pageOlita (2) Activity SharingArmySapphireNo ratings yet
- Bioethics NOTES 108 - Week 2Document6 pagesBioethics NOTES 108 - Week 2ArmySapphireNo ratings yet
- Nursing Diagnoses PharmaDocument3 pagesNursing Diagnoses PharmaArmySapphireNo ratings yet
- UTS Midterm SlideDocument47 pagesUTS Midterm SlideArmySapphireNo ratings yet
- Good Practice For Law Enforcement Officials Policing DemonstrationsDocument2 pagesGood Practice For Law Enforcement Officials Policing DemonstrationsArmySapphireNo ratings yet
- What Is Cancer - National Cancer Institute PDFDocument7 pagesWhat Is Cancer - National Cancer Institute PDFAlexis CastilloNo ratings yet
- Dengue Cases May Reach 20,000: Dengue Cases in Cebu City Up by 35-Percent Since JanuaryDocument3 pagesDengue Cases May Reach 20,000: Dengue Cases in Cebu City Up by 35-Percent Since JanuaryIrene InsoNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Understanding The Classification of MicroorganismsDocument18 pages1.1 Understanding The Classification of MicroorganismsHannanNashruddin100% (1)
- LPM (Terminology) - 1Document5 pagesLPM (Terminology) - 1Ganesh LahaneNo ratings yet
- Polycythemia in NewbornDocument25 pagesPolycythemia in NewbornTheva Thy100% (2)
- Second Symposium On The Definition and Management of XisDocument7 pagesSecond Symposium On The Definition and Management of XisbrookswalshNo ratings yet
- Carbimazole Induced HypothyroidismDocument8 pagesCarbimazole Induced HypothyroidismFaiqa Alee ChughtaiNo ratings yet
- Psfox fs1Document2 pagesPsfox fs1api-237614415No ratings yet
- Compartment SyndromeDocument61 pagesCompartment SyndromeIgnatius Rheza SetiawanNo ratings yet
- In Vitro Anthelminthic Activities of Four Medicinal Plants: Against Haemonchus ContortusDocument5 pagesIn Vitro Anthelminthic Activities of Four Medicinal Plants: Against Haemonchus ContortusSyvelmarie TinteNo ratings yet
- NCMB 316Document46 pagesNCMB 316andreatrojilloNo ratings yet
- Bruce Frantzis - Qi Gong BreathingDocument3 pagesBruce Frantzis - Qi Gong Breathingkabshiel100% (2)
- Parasitology ReviewerDocument17 pagesParasitology Reviewerlouie100% (1)
- Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19) : Situation Report - 102Document16 pagesCoronavirus Disease (COVID-19) : Situation Report - 102CityNewsTorontoNo ratings yet
- Oral RevalidaDocument98 pagesOral RevalidaJay ArNo ratings yet
- Clinical Review - KEDRABDocument97 pagesClinical Review - KEDRABcoolchapNo ratings yet
- Local Anesthetics AgentsDocument56 pagesLocal Anesthetics AgentsIyad Abou-Rabii100% (1)
- Circulatory InsectsDocument7 pagesCirculatory Insectsmith777No ratings yet
- Color Doppler Imaging Codes:: ND RDDocument46 pagesColor Doppler Imaging Codes:: ND RDGervin Brian EspinoNo ratings yet
- GASTROINSTINAL TRACT Robbins 8th EditionDocument4 pagesGASTROINSTINAL TRACT Robbins 8th EditionLim EricNo ratings yet
- Function of MitochondriaDocument5 pagesFunction of MitochondriaArshia NazirNo ratings yet
- GR 3 WTR SQDocument6 pagesGR 3 WTR SQDanilo Fronda Jr.No ratings yet
- 13 1.lung Auscultation#8E2EDocument23 pages13 1.lung Auscultation#8E2EAlina CazanNo ratings yet
- Benifits of SuvarnaprashanDocument2 pagesBenifits of Suvarnaprashanharish4ayur100% (1)
- Urogenital Symptoms in Neurologic Patients.14Document20 pagesUrogenital Symptoms in Neurologic Patients.14Fawad JanNo ratings yet
- Coconut Oil PullingDocument8 pagesCoconut Oil PullingshivaNo ratings yet