Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Hapter: International Business Environment
Hapter: International Business Environment
Uploaded by
iqbalsidaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Hapter: International Business Environment
Hapter: International Business Environment
Uploaded by
iqbalsidaCopyright:
Available Formats
International Business Environment
Chapter
2
International
Business Environment
Copyright © 2007, Aseem Kumar
2-1 Export and Import Management Aseem Kumar Excel Books
International Business Environment
Any company operating in international markets across its national borders
actually deals with five sets of environments: domestic internal, domestic
external, foreign internal, foreign external and the international business
environment comprising of treaties, agreements and conventions. The dynamics
of the global marketplace are governed by the interplay of all five.
The major difference between domestic and international trade lies in the
different operating environments.
Copyright © 2007, Aseem Kumar
2-2 Export and Import Management Aseem Kumar Excel Books
International Business Environment
Factors governing international trade environment
Economic Factors
The growing economic interdependence among nations, coupled with rapid
industrialisation of business and globalisation of markets have contributed greatly
to blur the lines between international trade and foreign investment, between
domestic and foreign trade policies, and between foreign and local firms and
products. The results have been seen in terms of growing cooperation and
competition. Growing economic interdependence among nations has given
importance to supportive global economic institutions. These institutions in turn
have greatly influenced the economic and trade scenario worldwide.
Cont….
Copyright © 2007, Aseem Kumar
2-3 Export and Import Management Aseem Kumar Excel Books
International Business Environment
Social and Cultural Factors
Dealing with different expectations of people is the crux of cross-cultural
management and to be effective in this area, a company will need to develop a
broader understanding of the socio-cultural landscapes of its different markets. A
company working in an international business environment has to be in constant
touch with the tastes and preferences of its customers and must keep adapting its
products and marketing styles to match the same.
Languages, symbols, colours, signs and timings all vary in various parts of the
world. Care needs to be exercised to ensure their proper usage, which is in
keeping with the place. A firm has to understand the local culture of its market
and translate the same into its products and services, so as to reach out
effectively to its target customers. Many firms have failed in foreign markets, not
because they did not have good products but because they failed to connect with
the local sentiments of the customers. Cont….
Copyright © 2007, Aseem Kumar
2-4 Export and Import Management Aseem Kumar Excel Books
International Business Environment
Legal and Political Factors
Both political and legal systems of a country influence the conduct of business at
home and abroad. Any exporting company operating in different countries must
face different political and legal conditions. For this company to succeed, its
management must carefully study to analyse whether its corporate policies will fit
a different political and legal environment. Political stability is another major
issue. A company has to assess the political risk in any country of its business
operations. The legal framework comprising of various laws and rules is another
dimension of the external environment that influences business. Legal changes
need to be anticipated and their impact studied. This will lend an edge to
business by allowing sufficient time to consider its reactive moves. Even when a
company is considering entry into a new foreign market, it must have its legal
backup ready.
Cont….
Copyright © 2007, Aseem Kumar
2-5 Export and Import Management Aseem Kumar Excel Books
International Business Environment
Technological Factors
Technology is the prime pulling force for the global business. The state of
technological development differs in different countries and accordingly
infrastructure levels are in different stages of readiness. Global competition uses
technology as a distinct advantage to score over each other in areas of efficiency
maximisation, cost reduction, better service to the customers and other
stakeholders, new and better products and service delivery, etc. Working in more
than one country usually means working with different technologies or at least
different levels of technological states; therefore, the biggest challenge is how to
fill this technological divide? A global company's effectiveness to deal with these
challenges will determine its business prospects in the long run. Companies need
to anticipate technological change and develop a mechanism to upgrade to
required levels so as to succeed in a complex and rapidly evolving environment.
Most global companies are forced to work in multi-technological environments.
This is in keeping with the ‘Think Global Act Local ’ scenario. The development
of new technology and its useful applications is a technical pursuit, but its
seamless introduction across national boundaries is a management challenge.
Copyright © 2007, Aseem Kumar
2-6 Export and Import Management Aseem Kumar Excel Books
International Business Environment
GATT (General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade)
The General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade (GATT) was first signed in 1947. It
was designed to provide an international forum that encouraged free trade
between member states by regulating and reducing tariffs on traded goods and by
providing a common mechanism for resolving trade disputes. India was one of the
23 founding members of GATT.
GATT's main goal was to ensure that its member countries' relations in the field of
trade and economic endeavour be conducted with a view to:
Raising standards of living
Ensuring full employment
A large and steadily growing volume of real income and effective demand
Developing full use of resources of the world
Expanding production and exchange of goods
Copyright © 2007, Aseem Kumar
2-7 Export and Import Management Aseem Kumar Excel Books
International Business Environment
WTO (World Trade Organisation)
World Trade Organisation (WTO) is the global body dealing with the rules of
trade between nations. At its heart are WTO agreements, negotiated and signed
by bulk of the world's trading nations and ratified in their parliaments. The goal is
to help producers of goods and services, exporters, and importers conduct their
business. (www.wto.org). WTO is a successor to GATT.
WTO's primary objective is to help international trade flow smoothly, freely, fairly
and predictably. It aims to achieve this free trade between nations by:
Administering trade agreements
Acting as a forum for trade negotiations
Settling trade disputes
Reviewing national trade policies
Assisting developing countries in trade policy issues, through technical
assistance and training programmes
Cont….
Cooperating with other international organisations
Copyright © 2007, Aseem Kumar
2-8 Export and Import Management Aseem Kumar Excel Books
International Business Environment
WTO works on the following basic principles that serve as the foundation of the
multilateral trading system it supports.
1. Without discrimination - a country should not discriminate between its
trading partners.
2. Freer - barriers coming down through negotiation.
3. Predictable - foreign companies, investors and governments should be
confident that trade barriers (including tariffs and non-tariff barriers) should
not be raised arbitrarily and tariff rates and market-opening commitments
are ‘bound’ in the WTO.
4. More competitive - discouraging ‘unfair’ practices such as export subsidies
and dumping products at below cost to gain market share.
5. More beneficial for less developed countries - giving them more time to
adjust, greater flexibility, and special privileges.
Copyright © 2007, Aseem Kumar
2-9 Export and Import Management Aseem Kumar Excel Books
International Business Environment
In a Nutshell
WTO offers the following ten benefits:
1. The system helps promote peace
2. Disputes are handled constructively
3. Rules make life easier for all
4. Freer trade cuts the costs of living
5. It provides more choice of products and qualities
6. Trade raises incomes
7. Trade stimulates economic growth
8. The basic principles make life more efficient
9. Governments are shielded from lobbying
10. The system encourages good government
Copyright © 2007, Aseem Kumar
2-10 Export and Import Management Aseem Kumar Excel Books
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5825)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1093)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (852)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (903)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (541)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (349)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (823)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (403)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Sap MM Business Blue Print - SampleDocument78 pagesSap MM Business Blue Print - SampleSuvendu Bishoyi100% (21)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Term Paper (Dhaka Bank)Document25 pagesTerm Paper (Dhaka Bank)Nahid Hussain AdriNo ratings yet
- Origin of InsuranceDocument10 pagesOrigin of Insurancebha_goNo ratings yet
- Ceerje-Yeef Oj - Keàes 75 Keàjesæ (Keàe DevegoeveDocument1 pageCeerje-Yeef Oj - Keàes 75 Keàjesæ (Keàe Devegoevebha_goNo ratings yet
- Project On I.MDocument17 pagesProject On I.Mbha_goNo ratings yet
- Suhas Gopinath: Contributed By: Rajeev Roy, Associate Professor, XIMB, IndiaDocument14 pagesSuhas Gopinath: Contributed By: Rajeev Roy, Associate Professor, XIMB, IndiaNENIndiaNo ratings yet
- Methods of Foreign PaymentDocument28 pagesMethods of Foreign Paymentbha_goNo ratings yet
- A Study On Pepsi Company With Focus StrategyDocument43 pagesA Study On Pepsi Company With Focus Strategybha_goNo ratings yet
- Ready Project of PLC of Maruti 800Document27 pagesReady Project of PLC of Maruti 800bha_goNo ratings yet
- Marketing Matters: Pepsico'S Strategic FocusDocument7 pagesMarketing Matters: Pepsico'S Strategic Focusbha_goNo ratings yet
- Sub: Purchase Order For Fire Fighting SystemDocument1 pageSub: Purchase Order For Fire Fighting Systembha_goNo ratings yet
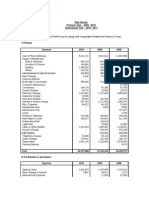
- Details of Expenses Debited To Profit & Loss A/c Along With Comparative Analysis For Previous 2 YearsDocument2 pagesDetails of Expenses Debited To Profit & Loss A/c Along With Comparative Analysis For Previous 2 Yearsbha_goNo ratings yet
- Axis Bank Axis Bank Axis Bank Axis Bank: Challan No./Itns 280Document1 pageAxis Bank Axis Bank Axis Bank Axis Bank: Challan No./Itns 280bha_goNo ratings yet
- List of Properties: SR - NO. S.No. (OLD) S.No. (NEW) Hissa NoDocument18 pagesList of Properties: SR - NO. S.No. (OLD) S.No. (NEW) Hissa Nobha_goNo ratings yet
- Itr-V: Indian Income Tax Return Verification FormDocument1 pageItr-V: Indian Income Tax Return Verification Formbha_goNo ratings yet
- Itr-V: Indian Income Tax Return Verification FormDocument1 pageItr-V: Indian Income Tax Return Verification Formbha_goNo ratings yet
- 4.export Channels of DistributionDocument24 pages4.export Channels of DistributionRayhan Atunu50% (2)
- Import PPRDocument3 pagesImport PPRaeeeNo ratings yet
- Australia 2007Document389 pagesAustralia 2007Tung PhamNo ratings yet
- Class Notes International FinancesDocument9 pagesClass Notes International FinancesMariabelen DoriaNo ratings yet
- Customs Summary Book Nov 20 by CA Yachana Mutha BhuratDocument52 pagesCustoms Summary Book Nov 20 by CA Yachana Mutha BhuratDevyani100% (2)
- Megh Man I 06Document1 pageMegh Man I 06KAYPEE MECHANICALNo ratings yet
- T1 Exercises QuestDocument4 pagesT1 Exercises QuestXin XiuNo ratings yet
- EFBS - UNIT 27 - Reading - ActivitiesDocument6 pagesEFBS - UNIT 27 - Reading - ActivitiesTrúc Đan HồNo ratings yet
- Acccount Receivable RevDocument35 pagesAcccount Receivable RevRADEN DIPONEGORONo ratings yet
- Money and Banking PPT QuestionsDocument41 pagesMoney and Banking PPT Questionszainab130831No ratings yet
- Bank Information Content: (USD/W)Document1 pageBank Information Content: (USD/W)David LeeNo ratings yet
- Archaic GlobalizationDocument16 pagesArchaic GlobalizationRowly Pearl Iradiel NedicNo ratings yet
- SubroseDocument78 pagesSubroseVikas KumarNo ratings yet
- Bill To / Ship To:: Qty Gross Amount Discount Other Charges Taxable Amount CGST SGST/ Ugst Igst Cess Total AmountDocument1 pageBill To / Ship To:: Qty Gross Amount Discount Other Charges Taxable Amount CGST SGST/ Ugst Igst Cess Total Amount1399Rimjhim GuptaNo ratings yet
- Lec 10 Capital Budgeting TechniquesDocument22 pagesLec 10 Capital Budgeting TechniquesAnikk HassanNo ratings yet
- IAS 36 Example: Calculation of WACCDocument36 pagesIAS 36 Example: Calculation of WACCJessyRityNo ratings yet
- Where To Find Large Datasets Open To The PublicDocument41 pagesWhere To Find Large Datasets Open To The PublicgeronimlNo ratings yet
- ESL Banking Reading Comprehension PassageDocument2 pagesESL Banking Reading Comprehension PassageAbdirashid OsmanNo ratings yet
- 10th Aug 21 - THANDA PANI - YELLOW CORN FCO - CIF DUBAI - 200KMTX12Document15 pages10th Aug 21 - THANDA PANI - YELLOW CORN FCO - CIF DUBAI - 200KMTX12Chandan JstNo ratings yet
- Gramophone Company of India LTD v. Birendra Bahadur Pandey - Decision of 21.02.84Document17 pagesGramophone Company of India LTD v. Birendra Bahadur Pandey - Decision of 21.02.84Piyush TyagiNo ratings yet
- MBFM4003Document3 pagesMBFM4003PreethiNo ratings yet
- Family TonyDocument7 pagesFamily Tonymswatiking69100% (1)
- The Contemporary WorldDocument15 pagesThe Contemporary Worldashley nicoleNo ratings yet
- Bangladesh Open University: BBA Program Semester: 192 (8 Level-AIS & Finance)Document11 pagesBangladesh Open University: BBA Program Semester: 192 (8 Level-AIS & Finance)monir mahmudNo ratings yet
- 22 To 27 - Appendix-XXII To XXVII (Page 326-334)Document9 pages22 To 27 - Appendix-XXII To XXVII (Page 326-334)08 Ajay Halder 11- CNo ratings yet
- JIEM PaperDocument28 pagesJIEM PaperAn MaiNo ratings yet
- Module 2 Practice Sets in Cash No AnswersDocument4 pagesModule 2 Practice Sets in Cash No AnswersRhea BadanaNo ratings yet
- Training Program by BFTI On ": "Rules and Procedures For Import, Export and CustomsDocument37 pagesTraining Program by BFTI On ": "Rules and Procedures For Import, Export and CustomsAlam (MDO)No ratings yet