Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
59 viewsAbrasive Flow Machining
Abrasive Flow Machining
Uploaded by
fhjThis document discusses abrasive flow machining (AFM), a finishing process that uses a semi-solid abrasive putty to remove small amounts of material from workpieces. It can deburr, radius, polish, and produce mirror finishes. AFM is classified as one-way, two-way, or orbital depending on the direction the abrasive flows. Two-way AFM, where the abrasive is extruded back and forth, is most common. AFM provides precise finishing for complex parts but has low material removal rates and high costs. It is used in aerospace, medical, and other industries to improve surfaces.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Service ManualHGJAA-E, Generator Set 5.5-7.0 KW Nov 29, 2017Document204 pagesService ManualHGJAA-E, Generator Set 5.5-7.0 KW Nov 29, 2017Anonymous wBoLqkF100% (2)
- SPC4 Bolt BrochureDocument2 pagesSPC4 Bolt BrochureDoug HeinrichsNo ratings yet
- SOP of Waste Oil DrainDocument17 pagesSOP of Waste Oil DrainGyanendra Narayan NayakNo ratings yet
- Abrasive Jet MachiningDocument12 pagesAbrasive Jet MachiningTejas SuratiNo ratings yet
- Abrasive Jet Machining (AJM)Document31 pagesAbrasive Jet Machining (AJM)Abhishek KumarNo ratings yet
- Electrochemical Grinding Ecg 160216024442Document15 pagesElectrochemical Grinding Ecg 160216024442sreejith2786No ratings yet
- Ultrasonic Machinig: Click To Edit Master Title StyleDocument16 pagesUltrasonic Machinig: Click To Edit Master Title Stylebunty231No ratings yet
- Unit - 6Document22 pagesUnit - 6N Dhanunjaya Rao BorraNo ratings yet
- Electro Chemical MachiningDocument3 pagesElectro Chemical MachiningRishi RajNo ratings yet
- UNIT-2 Ultrasonic MachiningDocument73 pagesUNIT-2 Ultrasonic MachiningraghurockramNo ratings yet
- UCMP Unit 1Document16 pagesUCMP Unit 1Sreedhar ReddyNo ratings yet
- Plasma Arc MachiningDocument24 pagesPlasma Arc MachiningArnav SharmaNo ratings yet
- Abrasive Flow Machining (AFM)Document21 pagesAbrasive Flow Machining (AFM)Abhishek KumarNo ratings yet
- Plasma Arc MachiningDocument12 pagesPlasma Arc MachiningAfsarShaikhNo ratings yet
- Plasma Arc Machining (PAM)Document27 pagesPlasma Arc Machining (PAM)nikunjlimbachiyaNo ratings yet
- IEM-UNIT-III NotesDocument26 pagesIEM-UNIT-III NotesVinay KumarNo ratings yet
- Electrochemical Grinding-2Document13 pagesElectrochemical Grinding-2BhUPindER KhelaNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Abrasive Flow MachiningDocument20 pagesMagnetic Abrasive Flow Machiningsamarth111670100% (2)
- Chemical MachiningDocument23 pagesChemical MachiningAbhishek Chadaga100% (6)
- Chapter 2 - Overview of Hybrid Machining ProcessesDocument32 pagesChapter 2 - Overview of Hybrid Machining ProcessesAman BansalNo ratings yet
- Lendi Process Manual PDFDocument43 pagesLendi Process Manual PDFTejaswini PydiNo ratings yet
- EDMDocument36 pagesEDMshifas 558No ratings yet
- IEM Notes Unit 2Document19 pagesIEM Notes Unit 2Nageswara Rao Thota100% (1)
- DR Rajesh MongiaDocument54 pagesDR Rajesh MongiaAnonymous 8umLvvHuNo ratings yet
- Unit-4 Advanced Machining ProcessesDocument61 pagesUnit-4 Advanced Machining ProcessesHarshalPatilNo ratings yet
- UNIT II Turret LatheDocument29 pagesUNIT II Turret LathePalak NaikNo ratings yet
- Ch-4 LatheDocument103 pagesCh-4 LatheSachin SinghNo ratings yet
- A Rajesh Kannan: (With Previous Year DOTE One Mark Quest. &answers)Document23 pagesA Rajesh Kannan: (With Previous Year DOTE One Mark Quest. &answers)Lovely Shalih0% (1)
- Ucmp NotesDocument46 pagesUcmp NotesAnonymous fowICTKNo ratings yet
- IQAC GuidelinesDocument30 pagesIQAC GuidelinesTirumalarao Pechetty100% (1)
- Chapter 07 - Non-Traditional MachiningDocument34 pagesChapter 07 - Non-Traditional MachiningNurul AsyilahNo ratings yet
- 2010aug21 - Public Speaking - Please Download and Then View, To Appreciate Better The Animation AspectsDocument31 pages2010aug21 - Public Speaking - Please Download and Then View, To Appreciate Better The Animation AspectsViswanadham Vangapally100% (1)
- Department of Mechanical Engineering: Welcome The Chairman & Members of The NBA Peer TeamDocument106 pagesDepartment of Mechanical Engineering: Welcome The Chairman & Members of The NBA Peer TeamAnonymous p8bHAAx75% (4)
- Chapter 26-Nontraditional MachiningDocument67 pagesChapter 26-Nontraditional MachiningHassan AliNo ratings yet
- Welcome To The Lecture On Unconventional Machining ProcessesDocument26 pagesWelcome To The Lecture On Unconventional Machining ProcessesFaysal Ahmed100% (1)
- Ultrasonic Machining (USM)Document19 pagesUltrasonic Machining (USM)RakeshSaini100% (2)
- 20 7 2012Document64 pages20 7 2012tristanlandonNo ratings yet
- Theory of Metal CuttingDocument65 pagesTheory of Metal CuttingKhalid BhinderNo ratings yet
- Electrochemical Machining (ECM) and GrindingDocument29 pagesElectrochemical Machining (ECM) and GrindingPradip PatelNo ratings yet
- Modern Manufacturing TechnologyDocument15 pagesModern Manufacturing TechnologyTHE NORTHCAP UNIVERSITYNo ratings yet
- EdmDocument31 pagesEdmSuvin PsNo ratings yet
- ECDMDocument9 pagesECDMRobert NayakNo ratings yet
- Metal Cutting TheoryDocument19 pagesMetal Cutting TheoryAbhishek BordoloiNo ratings yet
- V-20090916 - How To Communicate With Superiors, Subordinates & PeersDocument19 pagesV-20090916 - How To Communicate With Superiors, Subordinates & PeersViswanadham VangapallyNo ratings yet
- Edm PDFDocument32 pagesEdm PDFPrashantJangidNo ratings yet
- Obe and Nba AccreditationDocument40 pagesObe and Nba AccreditationG Venkata Nagesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Unit II - Turning MachinesDocument137 pagesUnit II - Turning MachinesKanda SamyNo ratings yet
- Merchant CircleDocument16 pagesMerchant CircleRaka-theredsdevilslovers CinthaCeiwectia Dont'likeplaygirls0% (1)
- ELID GrindingDocument43 pagesELID GrindingStephen.K67% (3)
- Ucmp 2 Mark With AnswerDocument17 pagesUcmp 2 Mark With AnsweranithayesurajNo ratings yet
- Hybrid Machining: Made By:-Hiragar Yashkumar Dalpatbhai Guidede By:-Alok SirDocument28 pagesHybrid Machining: Made By:-Hiragar Yashkumar Dalpatbhai Guidede By:-Alok SirYash Hiragar100% (1)
- Unconventional Machining ProcessDocument39 pagesUnconventional Machining Processuday bavandla100% (1)
- Vibration Assisted EDMDocument13 pagesVibration Assisted EDMSanjay KumarNo ratings yet
- Public Speaking OutlineDocument3 pagesPublic Speaking OutlineThalia LauNo ratings yet
- Electrostream Drilling PDFDocument2 pagesElectrostream Drilling PDFHOD MechanicalNo ratings yet
- Electron Beam MachiningDocument18 pagesElectron Beam MachiningAbhishek KumarNo ratings yet
- Recent Trends in Non-Traditional Machining Processes: Unit - 5Document12 pagesRecent Trends in Non-Traditional Machining Processes: Unit - 5DISHA VNo ratings yet
- Chemical MachiningDocument11 pagesChemical MachiningBayu Prayoga Part IINo ratings yet
- Abrasive Flow Machining: Process Principle, Parameters and CapabilitiesDocument19 pagesAbrasive Flow Machining: Process Principle, Parameters and CapabilitiesAnuj ThakkarNo ratings yet
- Abrasive Flow MachiningDocument27 pagesAbrasive Flow MachiningKAMALJEET SINGHNo ratings yet
- Advanced Finishing ProcessesDocument23 pagesAdvanced Finishing ProcessesADWAITH G SNo ratings yet
- Abrasive Flow Machining: Process Principle, Parameters and CapabilitiesDocument13 pagesAbrasive Flow Machining: Process Principle, Parameters and CapabilitiesNishant SinhaNo ratings yet
- Metallic Oxynitride Thin Films by Reactive Sputtering and Related Deposition Methods: Process, Properties and ApplicationsFrom EverandMetallic Oxynitride Thin Films by Reactive Sputtering and Related Deposition Methods: Process, Properties and ApplicationsNo ratings yet
- FujikuraDocument23 pagesFujikuraJoel GuiaoNo ratings yet
- CHM624 Experiment (Edited Feb2015)Document14 pagesCHM624 Experiment (Edited Feb2015)Suliza SueNo ratings yet
- Problemario B.E. Segundo ParcialDocument4 pagesProblemario B.E. Segundo ParcialjorgeNo ratings yet
- Nail Making Machine, Rajkot Wire ProductsDocument17 pagesNail Making Machine, Rajkot Wire ProductsMilanPadariyaNo ratings yet
- Sae J169-1985Document4 pagesSae J169-1985nelliNo ratings yet
- Aluminium ChlorohydrateDocument2 pagesAluminium ChlorohydrateAnandNo ratings yet
- A 1008 - A 1008M - 01 Qtewmdgtmdfb PDFDocument7 pagesA 1008 - A 1008M - 01 Qtewmdgtmdfb PDFTiến Lượng NguyễnNo ratings yet
- 1 K-Tron K2MLS100, Loss-In-Weight Feeder - Food Processing Machines and Equipment - Second Hand Machinery - WotolDocument5 pages1 K-Tron K2MLS100, Loss-In-Weight Feeder - Food Processing Machines and Equipment - Second Hand Machinery - WotolrajabalaNo ratings yet
- Thermal Products - Materiais LizDocument8 pagesThermal Products - Materiais LizRui Carlos Delgado Lopes AlvesNo ratings yet
- Gas Metal Arc Welding (GMAW) : University of Kuala Lumpur - Malaysia France InstituteDocument16 pagesGas Metal Arc Welding (GMAW) : University of Kuala Lumpur - Malaysia France InstituteKamarul Nizam100% (1)
- Simhapuri Energy Private Limited: C&I Work Progress DetailsDocument6 pagesSimhapuri Energy Private Limited: C&I Work Progress DetailsPraveen KpNo ratings yet
- LESSON 8: Supplier Partnership and TQMDocument4 pagesLESSON 8: Supplier Partnership and TQMLeshauna CaleighNo ratings yet
- Table of Specification: Obrero Elementary School First Grading Summative Test No. 1Document10 pagesTable of Specification: Obrero Elementary School First Grading Summative Test No. 1aldwinamistaNo ratings yet
- VESTA Electric Heat Exchanger Data SheetJAN06 - 000Document2 pagesVESTA Electric Heat Exchanger Data SheetJAN06 - 000happale2002100% (1)
- Cac 2019Document68 pagesCac 2019Alina Maria VerNo ratings yet
- TIMKEN Maintenance ToolsDocument16 pagesTIMKEN Maintenance ToolsIgor JuricNo ratings yet
- Bending Machine Sustarin Rollers Nargesa - 4Document1 pageBending Machine Sustarin Rollers Nargesa - 4yossef albanaNo ratings yet
- AFD 350 - Disc DiffuserDocument2 pagesAFD 350 - Disc DiffusernicefireworkNo ratings yet
- 117eq - Mechanical Measurements and Instrumentation PDFDocument8 pages117eq - Mechanical Measurements and Instrumentation PDFvenkiscribd444100% (1)
- RASCHIG-Ring DataDocument23 pagesRASCHIG-Ring Datalhphong021191No ratings yet
- MAK205 Chapter3Document7 pagesMAK205 Chapter3Guo JingNo ratings yet
- Msds - Penetrant Skl-sp1Document3 pagesMsds - Penetrant Skl-sp1Iksan Adityo MulyoNo ratings yet
- Paragon HistoryDocument19 pagesParagon Historyphani_rapNo ratings yet
- CT660 BrochureDocument21 pagesCT660 BrochureCarlos Abel Conza LopezNo ratings yet
- Instruction Manual For Tohin Rotary Vane Blower HC Type 100331Document13 pagesInstruction Manual For Tohin Rotary Vane Blower HC Type 100331tujiohNo ratings yet
- X854Document10 pagesX854RimNo ratings yet
- MEMS C-3 - End Sem Exam, Dec.-2020Document15 pagesMEMS C-3 - End Sem Exam, Dec.-2020VarunNo ratings yet
Abrasive Flow Machining
Abrasive Flow Machining
Uploaded by
fhj0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
59 views12 pagesThis document discusses abrasive flow machining (AFM), a finishing process that uses a semi-solid abrasive putty to remove small amounts of material from workpieces. It can deburr, radius, polish, and produce mirror finishes. AFM is classified as one-way, two-way, or orbital depending on the direction the abrasive flows. Two-way AFM, where the abrasive is extruded back and forth, is most common. AFM provides precise finishing for complex parts but has low material removal rates and high costs. It is used in aerospace, medical, and other industries to improve surfaces.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document discusses abrasive flow machining (AFM), a finishing process that uses a semi-solid abrasive putty to remove small amounts of material from workpieces. It can deburr, radius, polish, and produce mirror finishes. AFM is classified as one-way, two-way, or orbital depending on the direction the abrasive flows. Two-way AFM, where the abrasive is extruded back and forth, is most common. AFM provides precise finishing for complex parts but has low material removal rates and high costs. It is used in aerospace, medical, and other industries to improve surfaces.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
59 views12 pagesAbrasive Flow Machining
Abrasive Flow Machining
Uploaded by
fhjThis document discusses abrasive flow machining (AFM), a finishing process that uses a semi-solid abrasive putty to remove small amounts of material from workpieces. It can deburr, radius, polish, and produce mirror finishes. AFM is classified as one-way, two-way, or orbital depending on the direction the abrasive flows. Two-way AFM, where the abrasive is extruded back and forth, is most common. AFM provides precise finishing for complex parts but has low material removal rates and high costs. It is used in aerospace, medical, and other industries to improve surfaces.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 12
Abrasive Flow Machining
Process Principle, Classification and Applications
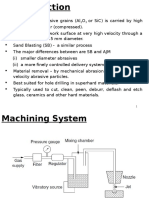
Process Principle
AFM is a finishing process that removes a small quantity of
material.
It uses semi-solid, abrasive laden putty through or across a
work piece.
Abrasive is extruded across edges or surfaces to deburr,
radius, polish, remove recast, perform mirror surface
machining.
A hydraulic ram forces the abrasive medium through the work
piece.
As abrasive medium flows through the part, its velocity will
change with the different cross – sectional areas.
Due to its low MRR, it is not suited for mass material removal.
It is used for finishing in metals, ceramics, and many plastics
in uniform manner.
Abrasive Materials
Abrasives Abrasive grain size used in AFM
varies from 500 grit (tiny hole)
• Aluminum oxide to 8 grit (stock removal and
• Silicon carbide stocking).
• Boron carbide Large abrasives are used to cut
faster.
• Diamond
Small abrasives are used for
Polymeric medium better surface finish as well as
Viscoelastic polymer- shows they can reach narrow surfaces
change in viscosity when under easily.
pressure
Classification of AFM
AFM is classified into three categories viz.
1. One way AFM
2. Two way AFM
3. Orbital AFM
One Way Abrasive Flow Machining
One-way flow AFM processing
pushes abrasive media through
the work piece in only one
direction, allowing the media
to exit freely from the part.
Advantages of One-way AFM
• Faster cycle processing
• Easy clean-up
• Media temperature control generally
not required
• Able to process larger parts
• Simpler tooling and part change-over
• Accurately replicates air or liquids
natural flow
Two Way Abrasive Flow Machining
Most widely used among the
three.
The typical two-way flow AFM
process uses two vertically
opposed cylinders to extrude an
abrasive media back and forth
through or around passages
formed by the workpiece and
tooling. Abrasive action occurs
wherever the media enters and
passes through the most
restrictive passages
Advantages of Two-way AFM
• Excellent process control
• Can finish both ID and OD of
component
• Good control of radius generation
• Fully automated system
capabilities
• Faster setup & quick-change
tooling
• Faster change-over of media
Orbital Abrasive Flow Machining
Surface and edge finishing are achieved
by rapid, low amplitude, oscillations of
the work piece relative to a self forming
elastic plastic abrasive polishing tool.
The tool is a pad or layer of abrasive-
laden elastic plastic medium (similar to
that used in two way abrasive flow
finishing), but typically higher in
viscosity and more in elastic.
Advantages of Orbital AFM
Faster cycle processing
Excellent process control
Excellent surface finish for complex
inner surfaces
Disadvantages of Abrasive Flow Machining
Low Material Removal Rate
High Cost
(i) High Setup Cost
(ii) High Cost of Abrasive Medium
Applications
Aerospace industry
• Improved surface quality
• Enhanced cycle fatigue strength
• Optimized combustion and hydraulics
• Increased airflow
• Extended component life
Medical Industry
• Eliminate the surface
imperfections where dangerous
contaminates can
reside
• Improved functionality,
durability and reliability of
medicalcomponents
• Enhanced uniformity and
cleanliness of surfaces,
• Extended component life
Thank You
You might also like
- Service ManualHGJAA-E, Generator Set 5.5-7.0 KW Nov 29, 2017Document204 pagesService ManualHGJAA-E, Generator Set 5.5-7.0 KW Nov 29, 2017Anonymous wBoLqkF100% (2)
- SPC4 Bolt BrochureDocument2 pagesSPC4 Bolt BrochureDoug HeinrichsNo ratings yet
- SOP of Waste Oil DrainDocument17 pagesSOP of Waste Oil DrainGyanendra Narayan NayakNo ratings yet
- Abrasive Jet MachiningDocument12 pagesAbrasive Jet MachiningTejas SuratiNo ratings yet
- Abrasive Jet Machining (AJM)Document31 pagesAbrasive Jet Machining (AJM)Abhishek KumarNo ratings yet
- Electrochemical Grinding Ecg 160216024442Document15 pagesElectrochemical Grinding Ecg 160216024442sreejith2786No ratings yet
- Ultrasonic Machinig: Click To Edit Master Title StyleDocument16 pagesUltrasonic Machinig: Click To Edit Master Title Stylebunty231No ratings yet
- Unit - 6Document22 pagesUnit - 6N Dhanunjaya Rao BorraNo ratings yet
- Electro Chemical MachiningDocument3 pagesElectro Chemical MachiningRishi RajNo ratings yet
- UNIT-2 Ultrasonic MachiningDocument73 pagesUNIT-2 Ultrasonic MachiningraghurockramNo ratings yet
- UCMP Unit 1Document16 pagesUCMP Unit 1Sreedhar ReddyNo ratings yet
- Plasma Arc MachiningDocument24 pagesPlasma Arc MachiningArnav SharmaNo ratings yet
- Abrasive Flow Machining (AFM)Document21 pagesAbrasive Flow Machining (AFM)Abhishek KumarNo ratings yet
- Plasma Arc MachiningDocument12 pagesPlasma Arc MachiningAfsarShaikhNo ratings yet
- Plasma Arc Machining (PAM)Document27 pagesPlasma Arc Machining (PAM)nikunjlimbachiyaNo ratings yet
- IEM-UNIT-III NotesDocument26 pagesIEM-UNIT-III NotesVinay KumarNo ratings yet
- Electrochemical Grinding-2Document13 pagesElectrochemical Grinding-2BhUPindER KhelaNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Abrasive Flow MachiningDocument20 pagesMagnetic Abrasive Flow Machiningsamarth111670100% (2)
- Chemical MachiningDocument23 pagesChemical MachiningAbhishek Chadaga100% (6)
- Chapter 2 - Overview of Hybrid Machining ProcessesDocument32 pagesChapter 2 - Overview of Hybrid Machining ProcessesAman BansalNo ratings yet
- Lendi Process Manual PDFDocument43 pagesLendi Process Manual PDFTejaswini PydiNo ratings yet
- EDMDocument36 pagesEDMshifas 558No ratings yet
- IEM Notes Unit 2Document19 pagesIEM Notes Unit 2Nageswara Rao Thota100% (1)
- DR Rajesh MongiaDocument54 pagesDR Rajesh MongiaAnonymous 8umLvvHuNo ratings yet
- Unit-4 Advanced Machining ProcessesDocument61 pagesUnit-4 Advanced Machining ProcessesHarshalPatilNo ratings yet
- UNIT II Turret LatheDocument29 pagesUNIT II Turret LathePalak NaikNo ratings yet
- Ch-4 LatheDocument103 pagesCh-4 LatheSachin SinghNo ratings yet
- A Rajesh Kannan: (With Previous Year DOTE One Mark Quest. &answers)Document23 pagesA Rajesh Kannan: (With Previous Year DOTE One Mark Quest. &answers)Lovely Shalih0% (1)
- Ucmp NotesDocument46 pagesUcmp NotesAnonymous fowICTKNo ratings yet
- IQAC GuidelinesDocument30 pagesIQAC GuidelinesTirumalarao Pechetty100% (1)
- Chapter 07 - Non-Traditional MachiningDocument34 pagesChapter 07 - Non-Traditional MachiningNurul AsyilahNo ratings yet
- 2010aug21 - Public Speaking - Please Download and Then View, To Appreciate Better The Animation AspectsDocument31 pages2010aug21 - Public Speaking - Please Download and Then View, To Appreciate Better The Animation AspectsViswanadham Vangapally100% (1)
- Department of Mechanical Engineering: Welcome The Chairman & Members of The NBA Peer TeamDocument106 pagesDepartment of Mechanical Engineering: Welcome The Chairman & Members of The NBA Peer TeamAnonymous p8bHAAx75% (4)
- Chapter 26-Nontraditional MachiningDocument67 pagesChapter 26-Nontraditional MachiningHassan AliNo ratings yet
- Welcome To The Lecture On Unconventional Machining ProcessesDocument26 pagesWelcome To The Lecture On Unconventional Machining ProcessesFaysal Ahmed100% (1)
- Ultrasonic Machining (USM)Document19 pagesUltrasonic Machining (USM)RakeshSaini100% (2)
- 20 7 2012Document64 pages20 7 2012tristanlandonNo ratings yet
- Theory of Metal CuttingDocument65 pagesTheory of Metal CuttingKhalid BhinderNo ratings yet
- Electrochemical Machining (ECM) and GrindingDocument29 pagesElectrochemical Machining (ECM) and GrindingPradip PatelNo ratings yet
- Modern Manufacturing TechnologyDocument15 pagesModern Manufacturing TechnologyTHE NORTHCAP UNIVERSITYNo ratings yet
- EdmDocument31 pagesEdmSuvin PsNo ratings yet
- ECDMDocument9 pagesECDMRobert NayakNo ratings yet
- Metal Cutting TheoryDocument19 pagesMetal Cutting TheoryAbhishek BordoloiNo ratings yet
- V-20090916 - How To Communicate With Superiors, Subordinates & PeersDocument19 pagesV-20090916 - How To Communicate With Superiors, Subordinates & PeersViswanadham VangapallyNo ratings yet
- Edm PDFDocument32 pagesEdm PDFPrashantJangidNo ratings yet
- Obe and Nba AccreditationDocument40 pagesObe and Nba AccreditationG Venkata Nagesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Unit II - Turning MachinesDocument137 pagesUnit II - Turning MachinesKanda SamyNo ratings yet
- Merchant CircleDocument16 pagesMerchant CircleRaka-theredsdevilslovers CinthaCeiwectia Dont'likeplaygirls0% (1)
- ELID GrindingDocument43 pagesELID GrindingStephen.K67% (3)
- Ucmp 2 Mark With AnswerDocument17 pagesUcmp 2 Mark With AnsweranithayesurajNo ratings yet
- Hybrid Machining: Made By:-Hiragar Yashkumar Dalpatbhai Guidede By:-Alok SirDocument28 pagesHybrid Machining: Made By:-Hiragar Yashkumar Dalpatbhai Guidede By:-Alok SirYash Hiragar100% (1)
- Unconventional Machining ProcessDocument39 pagesUnconventional Machining Processuday bavandla100% (1)
- Vibration Assisted EDMDocument13 pagesVibration Assisted EDMSanjay KumarNo ratings yet
- Public Speaking OutlineDocument3 pagesPublic Speaking OutlineThalia LauNo ratings yet
- Electrostream Drilling PDFDocument2 pagesElectrostream Drilling PDFHOD MechanicalNo ratings yet
- Electron Beam MachiningDocument18 pagesElectron Beam MachiningAbhishek KumarNo ratings yet
- Recent Trends in Non-Traditional Machining Processes: Unit - 5Document12 pagesRecent Trends in Non-Traditional Machining Processes: Unit - 5DISHA VNo ratings yet
- Chemical MachiningDocument11 pagesChemical MachiningBayu Prayoga Part IINo ratings yet
- Abrasive Flow Machining: Process Principle, Parameters and CapabilitiesDocument19 pagesAbrasive Flow Machining: Process Principle, Parameters and CapabilitiesAnuj ThakkarNo ratings yet
- Abrasive Flow MachiningDocument27 pagesAbrasive Flow MachiningKAMALJEET SINGHNo ratings yet
- Advanced Finishing ProcessesDocument23 pagesAdvanced Finishing ProcessesADWAITH G SNo ratings yet
- Abrasive Flow Machining: Process Principle, Parameters and CapabilitiesDocument13 pagesAbrasive Flow Machining: Process Principle, Parameters and CapabilitiesNishant SinhaNo ratings yet
- Metallic Oxynitride Thin Films by Reactive Sputtering and Related Deposition Methods: Process, Properties and ApplicationsFrom EverandMetallic Oxynitride Thin Films by Reactive Sputtering and Related Deposition Methods: Process, Properties and ApplicationsNo ratings yet
- FujikuraDocument23 pagesFujikuraJoel GuiaoNo ratings yet
- CHM624 Experiment (Edited Feb2015)Document14 pagesCHM624 Experiment (Edited Feb2015)Suliza SueNo ratings yet
- Problemario B.E. Segundo ParcialDocument4 pagesProblemario B.E. Segundo ParcialjorgeNo ratings yet
- Nail Making Machine, Rajkot Wire ProductsDocument17 pagesNail Making Machine, Rajkot Wire ProductsMilanPadariyaNo ratings yet
- Sae J169-1985Document4 pagesSae J169-1985nelliNo ratings yet
- Aluminium ChlorohydrateDocument2 pagesAluminium ChlorohydrateAnandNo ratings yet
- A 1008 - A 1008M - 01 Qtewmdgtmdfb PDFDocument7 pagesA 1008 - A 1008M - 01 Qtewmdgtmdfb PDFTiến Lượng NguyễnNo ratings yet
- 1 K-Tron K2MLS100, Loss-In-Weight Feeder - Food Processing Machines and Equipment - Second Hand Machinery - WotolDocument5 pages1 K-Tron K2MLS100, Loss-In-Weight Feeder - Food Processing Machines and Equipment - Second Hand Machinery - WotolrajabalaNo ratings yet
- Thermal Products - Materiais LizDocument8 pagesThermal Products - Materiais LizRui Carlos Delgado Lopes AlvesNo ratings yet
- Gas Metal Arc Welding (GMAW) : University of Kuala Lumpur - Malaysia France InstituteDocument16 pagesGas Metal Arc Welding (GMAW) : University of Kuala Lumpur - Malaysia France InstituteKamarul Nizam100% (1)
- Simhapuri Energy Private Limited: C&I Work Progress DetailsDocument6 pagesSimhapuri Energy Private Limited: C&I Work Progress DetailsPraveen KpNo ratings yet
- LESSON 8: Supplier Partnership and TQMDocument4 pagesLESSON 8: Supplier Partnership and TQMLeshauna CaleighNo ratings yet
- Table of Specification: Obrero Elementary School First Grading Summative Test No. 1Document10 pagesTable of Specification: Obrero Elementary School First Grading Summative Test No. 1aldwinamistaNo ratings yet
- VESTA Electric Heat Exchanger Data SheetJAN06 - 000Document2 pagesVESTA Electric Heat Exchanger Data SheetJAN06 - 000happale2002100% (1)
- Cac 2019Document68 pagesCac 2019Alina Maria VerNo ratings yet
- TIMKEN Maintenance ToolsDocument16 pagesTIMKEN Maintenance ToolsIgor JuricNo ratings yet
- Bending Machine Sustarin Rollers Nargesa - 4Document1 pageBending Machine Sustarin Rollers Nargesa - 4yossef albanaNo ratings yet
- AFD 350 - Disc DiffuserDocument2 pagesAFD 350 - Disc DiffusernicefireworkNo ratings yet
- 117eq - Mechanical Measurements and Instrumentation PDFDocument8 pages117eq - Mechanical Measurements and Instrumentation PDFvenkiscribd444100% (1)
- RASCHIG-Ring DataDocument23 pagesRASCHIG-Ring Datalhphong021191No ratings yet
- MAK205 Chapter3Document7 pagesMAK205 Chapter3Guo JingNo ratings yet
- Msds - Penetrant Skl-sp1Document3 pagesMsds - Penetrant Skl-sp1Iksan Adityo MulyoNo ratings yet
- Paragon HistoryDocument19 pagesParagon Historyphani_rapNo ratings yet
- CT660 BrochureDocument21 pagesCT660 BrochureCarlos Abel Conza LopezNo ratings yet
- Instruction Manual For Tohin Rotary Vane Blower HC Type 100331Document13 pagesInstruction Manual For Tohin Rotary Vane Blower HC Type 100331tujiohNo ratings yet
- X854Document10 pagesX854RimNo ratings yet
- MEMS C-3 - End Sem Exam, Dec.-2020Document15 pagesMEMS C-3 - End Sem Exam, Dec.-2020VarunNo ratings yet