Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Wsse PPT 6046
Wsse PPT 6046
Uploaded by
Paras Kathvadiya0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
239 views17 pagesThis document discusses wastewater treatment and sludge digestion processes. It explains that wastewater comes from residences, commercial and industrial institutions, and is treated in a 3-stage municipal treatment plant involving primary, secondary, and tertiary treatment. The secondary treatment uses an activated sludge process with aeration tanks, clarifiers, and lagoon systems. Sludge is further treated through aerobic or anaerobic digestion or composting to reduce volume and decompose organic matter.
Original Description:
Original Title
wsse ppt 6046.pptx
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document discusses wastewater treatment and sludge digestion processes. It explains that wastewater comes from residences, commercial and industrial institutions, and is treated in a 3-stage municipal treatment plant involving primary, secondary, and tertiary treatment. The secondary treatment uses an activated sludge process with aeration tanks, clarifiers, and lagoon systems. Sludge is further treated through aerobic or anaerobic digestion or composting to reduce volume and decompose organic matter.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
239 views17 pagesWsse PPT 6046
Wsse PPT 6046
Uploaded by
Paras KathvadiyaThis document discusses wastewater treatment and sludge digestion processes. It explains that wastewater comes from residences, commercial and industrial institutions, and is treated in a 3-stage municipal treatment plant involving primary, secondary, and tertiary treatment. The secondary treatment uses an activated sludge process with aeration tanks, clarifiers, and lagoon systems. Sludge is further treated through aerobic or anaerobic digestion or composting to reduce volume and decompose organic matter.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 17
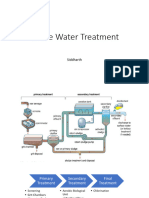
WASTEWATER TREATMENT
AND SLUDGE DIGESTION PR
OCESS
By Paras kathvadiya
What is wastewater treatment
• Usually refer to sewage treatment, or dom
estic wastewater treatment
• process of removing contaminants from w
astewater, both runoff and domestic
Where does wastewater come from
?
• Residences (kitchen, bathroom)
• Commercial institution
• Industrial institution (usually require specia
lized treatment process)
How can it be treated?
• collected and transported via a network of
pipes and pump stations to a municipal tre
atment plant
3 stages of water treatment
• Primary
– solids are separated
• Secondary
– dissolved biological matter is converted into a solid m
ass by using water-borne bacteria
– 95% of the suspended molecules should be removed
• Tertiary
– biological solids are neutralized then disposed, and tr
eated water may be disinfected chemically or physical
ly
Activated sludge
• mixed community of microorganisms
• Both aerobic and anaerobic bacteria may
exist
• Biological floc is formed
5 physical components of activated
sludge process
• aeration tank
– oxygen is introduced into the system
• aeration source
– ensure that adequate oxygen is fed into the tank
– provided pure oxygen or compressed air
• secondary clarifiers
– activated-sludge solids separate from the surrounding
wastewater
• Lagoon Systems
– hold the waste-water for several months
– natural degradation of sewage
– Usually reeds are preferred
Advanced Treatment
• Nitrogen removal
– Ammonia (NH3) → nitrite (NO2-)→ nitrate (NO3-)
• Phosphorous removal
– Precipitation with iron or aluminums salt
• Lead to eutrophication
• May cause algae bloom
Sludge treatment
• Primary sludge usually have strong odors
• Secondary sludge have high concentration
of microorganism
• Goals of treatments are:
– Reduce odors
– Remove water reduce volume
– Decompose organic matter
• Untreated sludge are about 97 percent water
• Settling can reduce about 92 to 96 percent of
water
• dried sludge is called a sludge cake
3 different sludge treatments
• Aerobic digestion
• Anaerobic digestion
• composting
Aerobic digestion
• Bacterial process
• Need oxygen
• Consume organic matter
• Convert into carbon dioxide (CO2)
Anaerobic digestion
• Bacterial process
• Do not require oxygen
• Consume organic matter
• Produce biogas, which can be used in gen
erators for electricity
Summary
You might also like
- Siemens Siremobil Compact Error CodesDocument160 pagesSiemens Siremobil Compact Error CodesHabib93% (30)
- The Lemegeton - Goetia (Book I)Document50 pagesThe Lemegeton - Goetia (Book I)api-3700162No ratings yet
- How Industrial Businesses Can Reduce Production Costs With Reverse Osmosis: Industrial Reverse OsmosisFrom EverandHow Industrial Businesses Can Reduce Production Costs With Reverse Osmosis: Industrial Reverse OsmosisRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Lower Extremity Reconstruction Plastic SurgeryDocument65 pagesLower Extremity Reconstruction Plastic SurgeryJuan MoscaNo ratings yet
- IMO Resolution 1050 - Entry Into Enclosed Spaces PDFDocument14 pagesIMO Resolution 1050 - Entry Into Enclosed Spaces PDFpgupta71No ratings yet
- Wsse PPT 6046Document17 pagesWsse PPT 6046Paras KathvadiyaNo ratings yet
- What Is Wastewater TreatmentDocument37 pagesWhat Is Wastewater TreatmentAdaCatapangNo ratings yet
- Waste Water TreatmentDocument37 pagesWaste Water TreatmentWaleed Khalid100% (3)
- Lecture 0 Overview Wastewater TreatmentDocument37 pagesLecture 0 Overview Wastewater TreatmentALEX NDIRANGUNo ratings yet
- Prepared By: Yateesh Gupta 100106389 Me'd'Document15 pagesPrepared By: Yateesh Gupta 100106389 Me'd'Yateesh GuptaNo ratings yet
- WWTPPT 161203034016Document30 pagesWWTPPT 161203034016Lavish100% (1)
- Waste Water Treatment PresentationDocument37 pagesWaste Water Treatment PresentationGeofrey S BajeNo ratings yet
- Physical Unit OperationsDocument45 pagesPhysical Unit OperationsSeHa Hassan86% (7)
- Domestic Waste and Waste TreatmentDocument42 pagesDomestic Waste and Waste TreatmenterhanzorerNo ratings yet
- Wastewater TreatmentDocument44 pagesWastewater TreatmentGiancarlo SantosNo ratings yet
- Malaviya National Institute of Technology Jaipur: Department of Chemical EngineeringDocument29 pagesMalaviya National Institute of Technology Jaipur: Department of Chemical EngineeringSHIVANK CHATURVEDINo ratings yet
- Waste Water TreatmentDocument44 pagesWaste Water TreatmentSangeethika Madubashini T. Hettige100% (1)
- Waste Water TreatmentDocument28 pagesWaste Water TreatmentRoseNavyaNo ratings yet
- L7-Sewage TreatmentF - For SpectrumDocument58 pagesL7-Sewage TreatmentF - For SpectrumWAN NURULAIN ARIBAH BINTI WAN HASSANNo ratings yet
- CH4 Wastewater Treat PRIMARY SECONDARY TERTIARY 39Document60 pagesCH4 Wastewater Treat PRIMARY SECONDARY TERTIARY 39Dr Mohamed OmerNo ratings yet
- Wastewater Treatment PlantsDocument64 pagesWastewater Treatment PlantssyakirohNo ratings yet
- Lect CE364 Wk6Document14 pagesLect CE364 Wk6kishankeithellNo ratings yet
- Lect 2Document64 pagesLect 2Patricia Jayshree Samuel JacobNo ratings yet
- Sewage Microbiology TreatmentDocument18 pagesSewage Microbiology Treatmentpratik singhNo ratings yet
- O Ce 39 Assignment 2Document11 pagesO Ce 39 Assignment 2kbgainsanNo ratings yet
- D. WWTP SecondaryDocument37 pagesD. WWTP Secondaryzairulh7No ratings yet
- The Treatmend and Disposal of Human WasteDocument33 pagesThe Treatmend and Disposal of Human WasteBasari Odal100% (1)
- Effluent Discharge System and StructureDocument19 pagesEffluent Discharge System and StructureRajan KumarNo ratings yet
- Sewage Wastewater Treatment GP 6Document9 pagesSewage Wastewater Treatment GP 6njsy02No ratings yet
- Lec 8Document32 pagesLec 8vuasiatechNo ratings yet
- Treatment Processes: ScreensDocument5 pagesTreatment Processes: ScreensSajil KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Characteristics of Wastewater: Environmental Engineering Unit-IDocument124 pagesCharacteristics of Wastewater: Environmental Engineering Unit-IDragos NojeaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 6 - Waste Water Treatment MethodsDocument45 pagesLecture 6 - Waste Water Treatment MethodsHamza RiazNo ratings yet
- Current Industrial Wastewater Treatment Processes: Dairy IndustriesDocument36 pagesCurrent Industrial Wastewater Treatment Processes: Dairy IndustriesMarlen TrejoNo ratings yet
- Lecture - WWT Methods and DisposalDocument31 pagesLecture - WWT Methods and Disposalmdhillonhasnain1122No ratings yet
- Lecture 12 - Waste Water Treatment MethodsDocument41 pagesLecture 12 - Waste Water Treatment MethodsUsman KhalidNo ratings yet
- Water Purification and Wastewater TreatmentDocument32 pagesWater Purification and Wastewater Treatmentrishit_aNo ratings yet
- Waterwaste Treatment: by Group 2 Lester Orosco Wenji Prellijera Dominick Salenga Renzo Dineros Erwin PatombonDocument26 pagesWaterwaste Treatment: by Group 2 Lester Orosco Wenji Prellijera Dominick Salenga Renzo Dineros Erwin PatombonDominic SalengaNo ratings yet
- Bioreactors For Wastewater TreatmentDocument40 pagesBioreactors For Wastewater TreatmentPatricia Jayshree Samuel JacobNo ratings yet
- Sewage Treatment PlantDocument38 pagesSewage Treatment PlantNirupam Kolankiroll 55No ratings yet
- Sewage Treatment (NRES 102)Document59 pagesSewage Treatment (NRES 102)Trevor HammanNo ratings yet
- Wastewater ExamDocument9 pagesWastewater ExamSanti PoNo ratings yet
- Wastewater Treatment: Department of Civil Engineering Indian Institute of Technology KharagpurDocument25 pagesWastewater Treatment: Department of Civil Engineering Indian Institute of Technology KharagpurJanmejaya SethyNo ratings yet
- Steps of Water Purification ProcessDocument13 pagesSteps of Water Purification Processcods1223No ratings yet
- Sewage Treatment Processes: Mohit Pal JoshiDocument44 pagesSewage Treatment Processes: Mohit Pal JoshiArrik KhannaNo ratings yet
- Unit 2Document95 pagesUnit 2rangaNo ratings yet
- Air Water PollutionDocument79 pagesAir Water PollutionÅyìshą RəəmNo ratings yet
- Unit 5Document59 pagesUnit 5rangaNo ratings yet
- Water TreamentDocument74 pagesWater TreamentCindy JavaNo ratings yet
- Sewage Treatment PlantDocument38 pagesSewage Treatment PlantKylle Mana100% (1)
- Sewage Treatment Plant: By: Abhishek Jat Aditi Singh Parihar Aishwarya & Akshay ShahDocument27 pagesSewage Treatment Plant: By: Abhishek Jat Aditi Singh Parihar Aishwarya & Akshay Shahbhobho100% (1)
- UNIT IV WasteDocument8 pagesUNIT IV WasteViswapriya K.PNo ratings yet
- Waste Water TreatmentDocument17 pagesWaste Water TreatmentSOURABH GANGWARNo ratings yet
- Sludge Management Fog Management Land Discharge of WastewaterDocument18 pagesSludge Management Fog Management Land Discharge of WastewaterNeil RyanNo ratings yet
- Wastewater TreatmentDocument9 pagesWastewater TreatmentreymoreNo ratings yet
- ETP - Basic - 01.08.2019Document31 pagesETP - Basic - 01.08.2019Hardik ShahNo ratings yet
- Apes - Chapter 21 Water PollutionDocument66 pagesApes - Chapter 21 Water PollutionZaman RaiNo ratings yet
- Water TreatmentDocument43 pagesWater TreatmentQuqan TahirNo ratings yet
- Environmental LectureDocument56 pagesEnvironmental LectureDean Joyce AlborotoNo ratings yet
- Alternative Arrangement For Sewage Disposal 1Document13 pagesAlternative Arrangement For Sewage Disposal 1Geetika GuptaNo ratings yet
- Lectuer 15Document29 pagesLectuer 15deekshupapareddyNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1-Sewage Waste TreatmentDocument11 pagesLesson 1-Sewage Waste TreatmentEvelyn PattNo ratings yet
- Water TreatmentDocument43 pagesWater TreatmentTAHIR SRKNo ratings yet
- How Reverse Osmosis Works: A Look at Industrial ROFrom EverandHow Reverse Osmosis Works: A Look at Industrial RORating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (2)
- Chain of InfectionDocument8 pagesChain of Infectionkim mimiNo ratings yet
- THE BATH BOX & ALL GLOWS X Basha Market 2023Document1 pageTHE BATH BOX & ALL GLOWS X Basha Market 2023rosidfitria6No ratings yet
- NPSHDocument17 pagesNPSHcrazynup100% (3)
- Magnet Motor Unit Exam Review KeyDocument4 pagesMagnet Motor Unit Exam Review Keyapi-110202130No ratings yet
- BMW Hydrogen 7 PresentationDocument9 pagesBMW Hydrogen 7 PresentationSam LauNo ratings yet
- AC 43.13-1B Section 5 Penetrant InspectionDocument8 pagesAC 43.13-1B Section 5 Penetrant Inspection320338100% (1)
- Department of Education: Daily Lesson PlanDocument14 pagesDepartment of Education: Daily Lesson PlanSharlene Jane Roque AporboNo ratings yet
- Fitgurlmel's 365 Food Guide by Melissa AlcantaraDocument27 pagesFitgurlmel's 365 Food Guide by Melissa AlcantaraSinem YukselNo ratings yet
- 904 TheBockSagaDocument6 pages904 TheBockSagaDick SmithNo ratings yet
- 182 Cost Comparison StudyDocument123 pages182 Cost Comparison StudymisznurulhudaNo ratings yet
- Техническая документация B2412S-1WR2 PDFDocument6 pagesТехническая документация B2412S-1WR2 PDFИльнур ТагировNo ratings yet
- Beating The Bonk QuestionsDocument1 pageBeating The Bonk Questionst3xxaNo ratings yet
- Gma1!2!2015 ContinutDocument64 pagesGma1!2!2015 ContinutSon HoangNo ratings yet
- Vapor and Combined Power CyclesDocument33 pagesVapor and Combined Power CyclesOtuagaNo ratings yet
- Science Journalism HandbookDocument38 pagesScience Journalism HandbookSartika DewiNo ratings yet
- A Narrative Report On Informing The Barangay 1 and Barangay 9Document3 pagesA Narrative Report On Informing The Barangay 1 and Barangay 9Heugh Gerard Rizo33% (3)
- Gullixson SermonDocument44 pagesGullixson SermonRock ArtadiNo ratings yet
- Anti-Inflammatory and Analgesic Activities of Flavonoid and Saponin Fractions From Zizyphus Lotus (L.) LamDocument5 pagesAnti-Inflammatory and Analgesic Activities of Flavonoid and Saponin Fractions From Zizyphus Lotus (L.) LamDaris UntoroNo ratings yet
- Amethyst - Hearts of ChaosDocument17 pagesAmethyst - Hearts of ChaosRodolfo Gorveña100% (2)
- Seismic Data ProcessingDocument45 pagesSeismic Data ProcessingFayyaz AbbasiNo ratings yet
- F-760-001 HACCP PlanDocument3 pagesF-760-001 HACCP PlanglennysNo ratings yet
- Jon Krohn Metis Deep Learning 2017-05-01Document107 pagesJon Krohn Metis Deep Learning 2017-05-01Arnaldo Preso De LigaNo ratings yet
- GP MCQ 6Document4 pagesGP MCQ 6Marta MoreiraNo ratings yet
- Polaris Battery Labs: Case SummaryDocument2 pagesPolaris Battery Labs: Case SummaryHassanNo ratings yet
- Tool Life When High Speed Ball Nose End Milling Inconel 718: Adrian Sharman, Richard C. Dewes, David K. AspinwallDocument7 pagesTool Life When High Speed Ball Nose End Milling Inconel 718: Adrian Sharman, Richard C. Dewes, David K. AspinwallKin HamzahNo ratings yet
- Molecular Biology Sars-Cov-2 (Covid-19) Detection by Qualitative RT-PCRDocument2 pagesMolecular Biology Sars-Cov-2 (Covid-19) Detection by Qualitative RT-PCRAaryan K MNo ratings yet