Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Value Analysis and Value Engineering
Value Analysis and Value Engineering
Uploaded by
Abhinav Sharma0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
331 views30 pagesValue analysis is a technique used to reduce costs through a systematic and organized approach. It focuses on determining the minimum cost required for a product to meet its intended functions. Value is divided into functional value, esteem value, and cost value. Applying value analysis leads to improved product design, high quality, efficiency, cost savings, and idea generation. The process involves gathering information, measuring performance, analyzing functions, generating ideas, and presenting recommendations.
Original Description:
Original Title
291306153-Value-Analysis-and-Value-Engineering.ppt
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentValue analysis is a technique used to reduce costs through a systematic and organized approach. It focuses on determining the minimum cost required for a product to meet its intended functions. Value is divided into functional value, esteem value, and cost value. Applying value analysis leads to improved product design, high quality, efficiency, cost savings, and idea generation. The process involves gathering information, measuring performance, analyzing functions, generating ideas, and presenting recommendations.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as ppt, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
331 views30 pagesValue Analysis and Value Engineering
Value Analysis and Value Engineering
Uploaded by
Abhinav SharmaValue analysis is a technique used to reduce costs through a systematic and organized approach. It focuses on determining the minimum cost required for a product to meet its intended functions. Value is divided into functional value, esteem value, and cost value. Applying value analysis leads to improved product design, high quality, efficiency, cost savings, and idea generation. The process involves gathering information, measuring performance, analyzing functions, generating ideas, and presenting recommendations.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as ppt, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 30
OPERATIONS MANAGEMENT
Value Analysis
1. Cost reduction technique.
2. Organised creative approach.
3. Main focuses.
4. Birth – Second World War.
5. Recent years -
• Value Engineering.
• Molecular Engineering.
• Vertical Thinking.
What is Value
The minimum money which has to be expended in
purchasing or manufacturing a product to create the
appropriate use of esteem factors.
Division Of Value
1. Use of functional Value.
2. Esteem Value.
3. Cost Value.
4. Exchange Value.
Advantages of Value Analysis
It leads to improvements in product design so that, most appropriate
products are produced .
High quality (value) is maintained.
All-round efficiency is achieved by eliminating waste of various types.
Cost savings provide a measure for judging managerial effectiveness.
New ideas are generated and incorporated.
Teams spirit and morale are improved.
Areas requiring attention and improvement are pin pointed.
Procedure of Value Analysis
There is no standard approach or procedure
Ascertaining the needs and wants of customers.
Specifying the function of products and components.
Determining the appropriate cost of desired
performance.
Identifying better alternatives in terms of works
procedures.
Implementation of Value Analysis
Identifying the function:-
Primary.
Secondary.
Evaluation of the function by comparison :-
Basic question
“does the function accomplish reliability at the best cost “
Develop Alternatives.
Value Analysis Steps
1. Gather Information.
2. Measure Performance.
3. Analyse Functions.
4. Generate Ideas.
5. Evaluate and Rank Ideas.
6. Develop and Expand Ideas.
7. Present Ideas.
Value Engineering
Value engineering is a total of management which
approaches the question of saving cost from the
point of view of ‘value’.
Requires co-operation of all functional departments.
In large organisations, there are value engineering
teams having full time jobs.
Value Engineering
Value and cost
Value = Function
Cost
Value: What the product is worth to the customer.
Function: Properties and qualities of product.
Cost: Money value of materials used, Labour & indirect
costs.
Value Engineering
Suggestion schemes
Suggestion scheme facilitates the work of value
engineering team.
The scheme helps in the changes of value
engineering and makes it implementation easier.
Value Engineering
Requirement of a product
Use.
Esteem.
It is essential to be considered how much to be
added in order to sell the part.
The reasonable price of a product can be obtained
by comparing with a comparative product.
Value Engineering Approach
No standard approach – discuss with team members.
Subject Basic question Analysis Answer
Function What functions 1) Is there any possibility of elimination?
are performed? 2) What alternative methods are available?
Material What is the 1) Can alternative material be used?
material 2) Can the specification be amended?
specification?
What quantity of 1) Is the size or weight of material excessive?
material should be 2) Can the quality be reduced?
used? 3) Will a cheaper material serve the same
purpose?
4) Is the cutting done economically without
waste?
Value Engineering Approach
Subject Basic question Analysis Answer
Labour Which are the direct 1) Are all the operations necessary?
labour costs? 2) Will alternative operations be cheaper?
3) Can certain assembly operations be modified?
Process Are the best 1) Are all the operations necessary?
Processes being 2) Will alternative operations be cheaper?
used? 3) Can certain assembly operations be modified?
Standardization Are the materials or 1) Can the materials be standardized?
components 2) Can a number of product use standard (common)
standard? parts?
3) Can methods be standardized?
Waste Control
Reasons for wastages in industry
Obsolescence
Surplus
Scrap
Role of Management in waste control
Proper inventory control
Materials management
Effective Co-ordination among departments
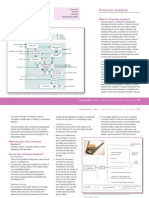
Input-Output Analysis
Systematic study of production structure.
Predict total production of each year.
Production structure of all the industries are to be
grouped together.
Output material of 1 sector becomes input raw-
materials for the other.
Original Information Innovation Evaluation Choice Implementation Review
Phase Phase Phase Phase Phase Phase Phase
1. Product Design and Development
1. Factors considered in product design :-
Customer’s requirement.
Operator’s Convenience.
Types of materials.
Work methods and equipment.
1. Product Design and Development
2. Design.
3. Planning.
4. Specialized function.
5. Visible in long run.
2. Application of Value Engineering
Overall quality and performance.
Work together to reduce cost.
Latest developments.
Service function.
Desired objective.
3. Simplification of Product
1. Elimination of undesirable features.
2. The main purpose is to improve quality and to
reduce unit costs.
Reduce cost and prices.
Reduction of undesirable materials.
3. Benefits.
You might also like
- ISO-TS 16949 Practice TestDocument18 pagesISO-TS 16949 Practice TestManan Bakshi100% (1)
- Financial Time Series Analysis and Prediction With Feature Engineering and Support Vector Machines - Newton - LinchenDocument5 pagesFinancial Time Series Analysis and Prediction With Feature Engineering and Support Vector Machines - Newton - LinchenNewton Linchen100% (1)
- Concurrent EngineeringDocument12 pagesConcurrent Engineeringamit chaudhari100% (1)
- Function AnalysisDocument4 pagesFunction AnalysisWanAtikatulAsmaNo ratings yet
- Me349 DFM Lecture NotesDocument22 pagesMe349 DFM Lecture NotesChethan Sk0% (1)
- Process Turtle Diagram - Assignment EngineeringDocument1 pageProcess Turtle Diagram - Assignment EngineeringShara Jane DelmoNo ratings yet
- DFM Checklist ExcelVersionDocument11 pagesDFM Checklist ExcelVersionMark Wilkinson100% (2)
- New Product DevelopmentDocument18 pagesNew Product DevelopmentSarvar PathanNo ratings yet
- Quality PlanningDocument6 pagesQuality Planningano_ni_mouseNo ratings yet
- A Smart Motor Controller For E-Bike Applications PDFDocument4 pagesA Smart Motor Controller For E-Bike Applications PDFaungwinnaing100% (1)
- Dfma Lecture Notes PDFDocument71 pagesDfma Lecture Notes PDFlithish RangarajanNo ratings yet
- Engineering Drawing BASICSDocument111 pagesEngineering Drawing BASICSSrikanth SriNo ratings yet
- Quality Management System at Construction Project: A Questionnaire SurveyDocument5 pagesQuality Management System at Construction Project: A Questionnaire SurveyReynaldo NyotoNo ratings yet
- Workshop On GD & T: Faculty: Abhijeet ChinchorkarDocument75 pagesWorkshop On GD & T: Faculty: Abhijeet ChinchorkarRajdeep SinghNo ratings yet
- Function Analysis System Technique: Lesson 09Document11 pagesFunction Analysis System Technique: Lesson 09arun100% (1)
- Value AnalysisDocument8 pagesValue AnalysisAnonymous DQGLUZxHNo ratings yet
- Value Engineering PDFDocument24 pagesValue Engineering PDFsanjeewa herath100% (1)
- Victora Tool Engineers Pvt. LTD.: Department: Quality Prepared By: Rakesh KumarDocument29 pagesVictora Tool Engineers Pvt. LTD.: Department: Quality Prepared By: Rakesh KumarrakeshNo ratings yet
- Value Engineering and Value Analysis PDFDocument14 pagesValue Engineering and Value Analysis PDFSukhinderpal Singh100% (2)
- Function Analysis System Technique DiagramDocument7 pagesFunction Analysis System Technique DiagramTharayilJamesNo ratings yet
- ME2037 Maintenance EngineeringDocument46 pagesME2037 Maintenance Engineeringrp0212100% (2)
- Some More Objective Questions With AnswersDocument44 pagesSome More Objective Questions With AnswersPratyush Solanki100% (1)
- Introduction To Design For Assembly and Manufacturing: (Cost Effective)Document81 pagesIntroduction To Design For Assembly and Manufacturing: (Cost Effective)maladcondomNo ratings yet
- Lecture 6-Quality Function DeploymentDocument32 pagesLecture 6-Quality Function Deploymentjatinag990100% (1)
- Manufacturing and Operations ManagementDocument52 pagesManufacturing and Operations ManagementRohit Dhaware100% (1)
- GD & TDocument90 pagesGD & TgurlambaNo ratings yet
- Submitted By,: Jarzid Alam Alomgir Badsha Saif MahabubDocument26 pagesSubmitted By,: Jarzid Alam Alomgir Badsha Saif MahabubSaif KhanNo ratings yet
- Question # 1 DefineDocument17 pagesQuestion # 1 DefineHayyaAli100% (2)
- Sample Test Method and Value EngineeringDocument4 pagesSample Test Method and Value EngineeringbahreabdellaNo ratings yet
- Form - Feasibility Review FormDocument3 pagesForm - Feasibility Review FormmatrixmazeNo ratings yet
- Predetermined Time StudyDocument5 pagesPredetermined Time StudyJerome BayocbocNo ratings yet
- Measurement Systems Analysis: Total Quality ManagementDocument17 pagesMeasurement Systems Analysis: Total Quality Managementkhamaludin100% (1)
- Cmmi Documentation For Maturity Level 2Document8 pagesCmmi Documentation For Maturity Level 2Hamid HamidNo ratings yet
- Industrial Engineering Is A Branch ofDocument10 pagesIndustrial Engineering Is A Branch ofashokkumarNo ratings yet
- Quality Control Flow Chart (10.12.22)Document2 pagesQuality Control Flow Chart (10.12.22)mido_20067581No ratings yet
- Tolerance Design Using Taguchi MethodsDocument30 pagesTolerance Design Using Taguchi MethodsEdNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Total Quality Management: Abu Naser Mohammad SaifDocument36 pagesIntroduction To Total Quality Management: Abu Naser Mohammad SaifAbu Raihan Pervez100% (1)
- PFMEA Question PaperDocument4 pagesPFMEA Question PaperGarv The Pride0% (1)
- Value EngineeringDocument52 pagesValue EngineeringAMIT SOLANKINo ratings yet
- IATF16949+Chapter+21 +Automotive+Core+ToolsDocument18 pagesIATF16949+Chapter+21 +Automotive+Core+ToolsNhựt Nguyễn HữuNo ratings yet
- Six Sigma in Precast ProductionDocument11 pagesSix Sigma in Precast Productionravi1625100% (1)
- Spaghetti DiagramDocument12 pagesSpaghetti DiagramelevendotNo ratings yet
- Work MeasurementDocument5 pagesWork MeasurementAvinash SagarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Equipment Life and Replacement ProceduresDocument26 pagesChapter 3 Equipment Life and Replacement ProceduresMurali Krishna Reddy Arikatla100% (2)
- Rejection Analysis Procedure PDFDocument7 pagesRejection Analysis Procedure PDFsmartsatish100% (1)
- DFMaDocument1 pageDFMavenkatkrishnaNo ratings yet
- Modern Construction TechnologyDocument17 pagesModern Construction TechnologyASWIN GEORGE100% (1)
- Value EngineeringDocument14 pagesValue EngineeringManmeet SinghNo ratings yet
- Kaizen CriteriaDocument4 pagesKaizen Criteriaj_buan67% (3)
- 2 Minutes For My SafetyDocument9 pages2 Minutes For My SafetyAnugrah Putra Ra100% (1)
- Six Sigma Lecture NotesDocument84 pagesSix Sigma Lecture NotesRyan Jeffrey Padua Curbano100% (1)
- COPQ KPI How To MeasureDocument2 pagesCOPQ KPI How To MeasureNguyễn Tiến Dũng100% (1)
- Project Jig & Fixture (Jig Drawing)Document6 pagesProject Jig & Fixture (Jig Drawing)adibah ismail100% (1)
- Design For Six Sigma & Robust Design of Products and Processes For QualityDocument36 pagesDesign For Six Sigma & Robust Design of Products and Processes For Qualityshankarbt83100% (1)
- 10 Quality Function DeploymentDocument33 pages10 Quality Function DeploymentRian JanuarsyahNo ratings yet
- Experiments MontgomeryDocument111 pagesExperiments MontgomeryJaka Permana SoebagjoNo ratings yet
- Design Fmea ChecklistDocument10 pagesDesign Fmea Checklistdrrmm2sNo ratings yet
- Introduction To TPM PDFDocument58 pagesIntroduction To TPM PDFArchan raj100% (1)
- AIAG VDA DFMEA TrainingDocument68 pagesAIAG VDA DFMEA TrainingAtul SURVE100% (2)
- Poka YokeDocument33 pagesPoka YokejanisahebNo ratings yet
- AMS - Hollier MehodsDocument78 pagesAMS - Hollier MehodsKapil MittalNo ratings yet
- Operations ManagementDocument30 pagesOperations ManagementAsma KhanNo ratings yet
- Grade 6 Worksheet DypisDocument2 pagesGrade 6 Worksheet DypisPehel MehtaNo ratings yet
- System Development Invoice - Audit ToolDocument2 pagesSystem Development Invoice - Audit ToolVictorNo ratings yet
- Study On Effect of Manual Metal Arc Welding Process Parameters On Width of Heat Affected Zone (Haz) For Ms 1005 SteelDocument8 pagesStudy On Effect of Manual Metal Arc Welding Process Parameters On Width of Heat Affected Zone (Haz) For Ms 1005 SteelAngga Pamilu PutraNo ratings yet
- ITSM Gap Analysis TemplateDocument57 pagesITSM Gap Analysis TemplateSuresh RajamaniNo ratings yet
- The Duality of Human Nature in Oscar Wilde's The Importance of Being EarnestDocument28 pagesThe Duality of Human Nature in Oscar Wilde's The Importance of Being EarnestSowmya ShreeNo ratings yet
- Filt Ers: 2 ElectrofiltersDocument8 pagesFilt Ers: 2 ElectrofiltersElancheran RengaNo ratings yet
- Peek - POLYETHER ETHER KETONEDocument58 pagesPeek - POLYETHER ETHER KETONEBryan Jesher Dela Cruz100% (1)
- Mini Capstone Final Project Implementation and AssessmentDocument8 pagesMini Capstone Final Project Implementation and AssessmentSodium ChlorideNo ratings yet
- Fxrate 06 06 2023Document2 pagesFxrate 06 06 2023ShohanNo ratings yet
- 1.b Pin-P3.4-Of-8051-Microcontroller-Is-Known-As-Timer...Document5 pages1.b Pin-P3.4-Of-8051-Microcontroller-Is-Known-As-Timer...তানভীর তাঈনNo ratings yet
- PHOTOCOPIABLE Gateway B1 Workbook AnswerDocument2 pagesPHOTOCOPIABLE Gateway B1 Workbook Answerhaler kolokNo ratings yet
- The Autism Diagnostic Observation Schedule, Module 4: Application of The Revised Algorithms in An Independent, Well-Defined, Dutch Sample (N 93)Document11 pagesThe Autism Diagnostic Observation Schedule, Module 4: Application of The Revised Algorithms in An Independent, Well-Defined, Dutch Sample (N 93)Laura CamusNo ratings yet
- GEC PE003 Module 1 CheckedDocument21 pagesGEC PE003 Module 1 CheckedJianica SalesNo ratings yet
- IEC61850 Substation Communication ArchitectureDocument326 pagesIEC61850 Substation Communication ArchitectureMichael Parohinog Gregas100% (1)
- Siemens 3VT MCCBDocument39 pagesSiemens 3VT MCCBerkamlakar2234No ratings yet
- Ple New Entry Codes 2024Document93 pagesPle New Entry Codes 2024luqmanluqs2No ratings yet
- Torrent WorkingDocument7 pagesTorrent WorkingsirmadamstudNo ratings yet
- Santa Cruz Scanner FreqsDocument35 pagesSanta Cruz Scanner FreqsdonsterthemonsterNo ratings yet
- 50 Programing QuotesDocument3 pages50 Programing QuotesFreddy MoncadaNo ratings yet
- WSS ProdCat 2013 Lowres Final v2 PDFDocument861 pagesWSS ProdCat 2013 Lowres Final v2 PDFJuriandi SaputraNo ratings yet
- The Sabbath As FreedomDocument14 pagesThe Sabbath As Freedomapi-232715913No ratings yet
- Integration EVS AvidTM V4.3 PDFDocument113 pagesIntegration EVS AvidTM V4.3 PDFLaurentiu IacobNo ratings yet
- Activity-2-White. Gadfrey Jahn PDocument2 pagesActivity-2-White. Gadfrey Jahn PGadfrey jahn WhiteNo ratings yet
- Understand Trading in 2 Hours SteveRyanDocument63 pagesUnderstand Trading in 2 Hours SteveRyanAkash Biswal100% (3)
- Temario Final Ingles 5°b PrimariaDocument1 pageTemario Final Ingles 5°b PrimariainstitutovalladolidNo ratings yet
- NIDAR, Franced Haggai G. The Brain Is The Vehicle of The MindDocument1 pageNIDAR, Franced Haggai G. The Brain Is The Vehicle of The MindHaggai NidarNo ratings yet
- Selection of Fuses For The Protection of TransformersDocument14 pagesSelection of Fuses For The Protection of Transformersgalaxyebn100% (11)
- Letters From England: by Don Manuel Alvarez EspriellaDocument2 pagesLetters From England: by Don Manuel Alvarez EspriellaPickering and ChattoNo ratings yet