Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Airconditioningsystem
Airconditioningsystem
Uploaded by
sampada0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
58 views14 pagesThe document discusses different types of air conditioning systems. It defines air conditioning as altering air properties to more favorable indoor conditions for health, comfort or industrial processes regardless of outdoor climate. There are four main types: window units which install in walls; split units with indoor and outdoor components; centralised units for large buildings; and packaged units for capacities between window and centralised units. The document then provides details on the functioning, components and applications of each type of air conditioning system.
Original Description:
Original Title
airconditioningsystem
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses different types of air conditioning systems. It defines air conditioning as altering air properties to more favorable indoor conditions for health, comfort or industrial processes regardless of outdoor climate. There are four main types: window units which install in walls; split units with indoor and outdoor components; centralised units for large buildings; and packaged units for capacities between window and centralised units. The document then provides details on the functioning, components and applications of each type of air conditioning system.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
58 views14 pagesAirconditioningsystem
Airconditioningsystem
Uploaded by
sampadaThe document discusses different types of air conditioning systems. It defines air conditioning as altering air properties to more favorable indoor conditions for health, comfort or industrial processes regardless of outdoor climate. There are four main types: window units which install in walls; split units with indoor and outdoor components; centralised units for large buildings; and packaged units for capacities between window and centralised units. The document then provides details on the functioning, components and applications of each type of air conditioning system.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 14
INTRODUCTION
Definition - Air conditioning is the process of
altering the properties of air to more favorable
conditions.
The control of these conditions may be desirable to
maintain the health and comfort of the occupants, or
to meet the requirements of industrial processes
irrespective of the external climatic conditions
PRINCIPLES OF AIR-CONDITIONING
The goal is to keep it more comfortable inside the house than it is
outside.
TYPE OF AIR-CONDITIONING
1) Window air-conditioning system
2) Split air-conditioning system
3) Centralised air-conditioning system
4) Package air-conditioning system
1) Windows Air-conditioning System
Window air conditioners are one of the most commonly
used and cheapest type of air conditioners.
To install one of these units, you need the space to make
a slot in the wall, and there should also be some open
space behind the wall.
Window air-conditioner units are reliable and simple-
to-install solution to keep a room cool while avoiding
the costly construction of a central air system.
Better yet, when the summer heat dies down, these
units can be easily removed for storage, and you can use
the window sill for other purpose
2) Split Air-Conditioning System
The split air conditioner comprises of two parts: the
outdoor unit and the indoor unit.
The outdoor unit, fitted outside the room, houses
components like the compressor, condenser and
expansion valve.
The indoor unit comprises the evaporator or cooling coil
and the cooling fan. For this unit you don’t have to make
any slot in the wall of the room.
Further, the present day split units have aesthetic looks
and add to the beauty of the room. The split air
conditioner can be used to cool one or two rooms
3) Centralised Air-Conditioning System
The central air conditioning plants or the systems are used when
large buildings, hotels, theaters, airports, shopping malls etc. are
to be air conditioned completely.
The window and split air conditioners are used for single rooms
or small office spaces.
If the whole building is to be cooled it is not economically viable
to put window or split air conditioner in each and every room.
4) Packaged Air-Conditioning System
The window and split air conditioners are usually used
for the small air conditioning capacities up to 5 tons.
The central air conditioning systems are used for where
the cooling loads extend beyond 20 tons.
The packaged air conditioners are used for the cooling
capacities in between these two extremes.
The packaged air conditioners are available in the fixed
rated capacities of 3,5, 7, 10 and 15 tons.
These units are used commonly in places like
restaurants, telephone exchanges, homes, small halls,
etc.
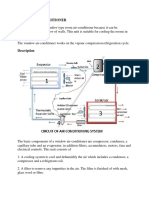
Compressor
-Inhaling the refrigerant from Cold refrigerant vapor and low
the suction channel pressure
- Compressing to the Evaporator
discharge channel. -Liquid turns to vapor
-Cold air flows out room
Hot refrigerant vapor and
high pressure
Cold refrigerant vapor and low
pressure
Condenser
-Remove heat from condenser
-Refrigerant vapor turn to liquid.
Expansion Valve
-Low the temperature and
pressure of liquid
Hot refrigerant vapor and -Control the flow rate in
high pressure -to the evaporator.
THE COOLANT
Heat is removed from the cooling by coolant.
Functions as a heat absorber from the evaporator
Good coolant must have features ;
1. Non toxic
2. Not explosive
3. Non-corrosive components
TONN OF REFRIGERATION
It is the amount of heat required to given out for the production
of 1 tonn of ice in 24 hrs from water at 0O .
The cycle of refrigeration consist of compresser, condenser,
collector, expansion valve, evaporator, or cooling coils and back
to compressor.
CAPACITY OF AC SUITABLITY IN PACKAGE UNIT SUITABLITY IN
UNIT TERMS OF AREA TERMS OF AREA
5 TR 80 SQ M
1 TR 15 SQ M
7.5 TR 120 SQ M
1.5 TR 25 SQ M 10 TR 160 SQ M
2 TR 30 SQ M 15 TR 250 SQ M
[Throw of air from ac unit is upto 5m distance]
Central AC plant is required above 20 tonns of refrigeration for areas above 500 sq m.
A central Ac plant with 15 tons refrigeration requires 50 sqm. with a clear height of 3.2m upto beam
soffit.
For 100 TR, w70 sqm area required with clear height upto beam soffit of 3.5
• The features of the air handling unit in each floor.
• A centralised cooling or chilling plant.
• Floorwise provision of airhandling unit which is also known as weather maker room.
• The AHU should have an area of 4.5 sqm for every hundred sqm area to be air conditioned and
clear height of 3m upto the clear bottom.
• The AHU should have a separate fresh air inlet at a rate of 0.3 sqm per tonn of refrigerator.
• The AHU slab should be designed for a load of 1800 kg/sqcm.
• The AHU contains beside fresh air inlet a blow unit and a netwoork of cooling coils wherein the
fresh air is bloom directly into the rooms or main AC duct leading to various rooms through
branch ducts.
• AHU should have a single leaf door opening outside. The shutter should be acoustically treated.
• The floor should be smooth with a nahani trap outlet.
• Each AHU serving 500 sqm area requires a size of 4.5 x 4.5 x 3m.
• Separate AHU should beprovided for areawise zones and the AHU should be as close as possible
to zone.
• Each AHU has to have a separate fresh air area which should not open out in polluted areas.
• The ACs ducts are made of more GI sheets or Aluminium sheets suitably insulated with non-
combustible material such as glass or asbestos wool
• all these ducts should be properly secured to the walls on the ceiling
• Water required for AC plant is 18 to 20 litres per tonne per hour taking into consideration 15
to 20% evaporation losses in cooling plants and towers.
You might also like
- PPT-1 For RAC Lect - GD SirDocument55 pagesPPT-1 For RAC Lect - GD SirKamal Kumar AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Hvac in Hotels: Done byDocument22 pagesHvac in Hotels: Done bySajeed AhmedNo ratings yet
- United States Air Force Academy Cadet ChapelDocument7 pagesUnited States Air Force Academy Cadet Chapelsampada100% (2)
- Airconditioningsystem-130910014923-Phpapp01-Converted-01 - Pravish SrivastavaDocument34 pagesAirconditioningsystem-130910014923-Phpapp01-Converted-01 - Pravish SrivastavaHarshal FuseNo ratings yet
- Air Conditioning SystemDocument18 pagesAir Conditioning SystemUmair MueedNo ratings yet
- Qus 3206 / MDM Nurul AiniDocument34 pagesQus 3206 / MDM Nurul AiniZeeshan AdilNo ratings yet
- AIR COND SYSTEM EditedDocument37 pagesAIR COND SYSTEM Editedmohd irfanNo ratings yet
- HVAC - Part-2Document49 pagesHVAC - Part-2Shubha100% (1)
- ECM216 BUILDING SERVICES Bab 2.2 Air ConditioningDocument8 pagesECM216 BUILDING SERVICES Bab 2.2 Air ConditioningAZUAN BIN AHMAD FAUZI75% (4)
- HVAC PresentationDocument54 pagesHVAC PresentationShiv Kumar Verma100% (3)
- Hvac AssignmentDocument9 pagesHvac AssignmentCharu GargNo ratings yet
- Hvac Systems: UNIT-2 Building Serivces and Intergration - IDocument31 pagesHvac Systems: UNIT-2 Building Serivces and Intergration - Ivishnu_2008100% (1)
- Building Assignment - Ii: ServicesDocument53 pagesBuilding Assignment - Ii: ServicesVivek SinghNo ratings yet
- WAC and VCRSDocument8 pagesWAC and VCRSShubham MishraNo ratings yet
- Building Service PDFDocument35 pagesBuilding Service PDFamirahNo ratings yet
- Air Conditioner & FanDocument29 pagesAir Conditioner & Fan0519 Pratyush JalanNo ratings yet
- Air-Conditioning SystemDocument54 pagesAir-Conditioning Systemhasrul_nizam100% (6)
- Window & Packaged Ac Chilled Water Plant: G.Siddharth Moorthe 12RBAR033Document14 pagesWindow & Packaged Ac Chilled Water Plant: G.Siddharth Moorthe 12RBAR033Logesh WaranNo ratings yet
- Heat Ventilation and Air Conditioning (HVAC)Document46 pagesHeat Ventilation and Air Conditioning (HVAC)Sagar GoyalNo ratings yet
- Selection Tips For HVAC SystemsDocument41 pagesSelection Tips For HVAC SystemsImtiaz Ahmed100% (1)
- Architectural Building Services: Vedita Bhat Roll No-03Document8 pagesArchitectural Building Services: Vedita Bhat Roll No-03Vedita Bhat100% (1)
- Hvac and Air ConditioningDocument69 pagesHvac and Air ConditioningEtee AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Air Conditioning PPT of EMEDocument24 pagesAir Conditioning PPT of EMEDineshKumar VermaNo ratings yet
- Air and Ref HandoutDocument14 pagesAir and Ref HandoutOba-Elvis IkenyenweNo ratings yet
- Air ConditioningDocument13 pagesAir ConditioningSumedha GuptaNo ratings yet
- Util Finals Reviewer 1Document3 pagesUtil Finals Reviewer 1Angela AlvarezNo ratings yet
- Split Air Conditioning SystemDocument97 pagesSplit Air Conditioning SystemAh Min Ah PuttNo ratings yet
- 1334337428180-Electr - QUESTION - BANK - TL - AC - AND - EM - Final PDFDocument116 pages1334337428180-Electr - QUESTION - BANK - TL - AC - AND - EM - Final PDFPankaj KumarNo ratings yet
- Refrigeration ME 201Document13 pagesRefrigeration ME 201pathan_440No ratings yet
- VAMDocument21 pagesVAMpowergopsNo ratings yet
- Classifications of Air Conditioning System: Based On Major FunctionDocument67 pagesClassifications of Air Conditioning System: Based On Major Functionjet latorreNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 FilesDocument5 pagesUnit 1 FilesAsma Parveen .ANo ratings yet
- Airconditioning Systems Introduction01Document52 pagesAirconditioning Systems Introduction01ajNo ratings yet
- Hvac Notes: Vapor-Compression Absorption Refrigeration Cycle Heat ExchangerDocument36 pagesHvac Notes: Vapor-Compression Absorption Refrigeration Cycle Heat ExchangerMohd Tarique AnwarNo ratings yet
- 12 - Chapter 2 PDFDocument27 pages12 - Chapter 2 PDFMohd SalmanNo ratings yet
- Types of Ac Systems 1Document26 pagesTypes of Ac Systems 1Saul CastroNo ratings yet
- Air CycleDocument30 pagesAir CycleSalokya KhandelwalNo ratings yet
- Architectural Science (HVAC) Lecture 6 & 7Document32 pagesArchitectural Science (HVAC) Lecture 6 & 7ezakbelachewNo ratings yet
- Research 1 - Mechanical System BU2Document17 pagesResearch 1 - Mechanical System BU2Zachary Yassir GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Dasar Teori PendinginDocument64 pagesDasar Teori PendinginsuhandywNo ratings yet
- Vapor Compression CycleDocument14 pagesVapor Compression CycleMir HaziqNo ratings yet
- Residential Building Design Using Prokon SoftwareDocument6 pagesResidential Building Design Using Prokon SoftwareJospin MwemaNo ratings yet
- Refrigeration: "Refrigeration Is The Process of Removing Heat From An Enclosed Space, orDocument16 pagesRefrigeration: "Refrigeration Is The Process of Removing Heat From An Enclosed Space, ordjgondalNo ratings yet
- Selection Tips For Air-Conditioning Cooling Systems PDFDocument10 pagesSelection Tips For Air-Conditioning Cooling Systems PDFlkakeanNo ratings yet
- ADV Refrigeration System Using FlashchamberDocument40 pagesADV Refrigeration System Using FlashchamberAwesm RishuNo ratings yet
- Air Conditioning in Interior Design: Ar. Amit MehtaDocument31 pagesAir Conditioning in Interior Design: Ar. Amit MehtaAr Amit MehtaNo ratings yet
- Air Conditioning EditDocument64 pagesAir Conditioning EditQuratul AiniNo ratings yet
- Carrier Split SystemDocument12 pagesCarrier Split SystemabuMalakNo ratings yet
- UNIT I - Air ConditionDocument62 pagesUNIT I - Air ConditionNeha JojanNo ratings yet
- Ac How It WorksDocument4 pagesAc How It Workshassanain_100No ratings yet
- Notes For Unit Test-1Document7 pagesNotes For Unit Test-1priya dharshiniNo ratings yet
- 8 - Lecture (8) Introduction To ACDocument24 pages8 - Lecture (8) Introduction To ACha3114No ratings yet
- Unit 6 - Refrigeration and Air Conditioning System Need For RefrigerationDocument14 pagesUnit 6 - Refrigeration and Air Conditioning System Need For RefrigerationamitNo ratings yet
- Unit 6 - Refrigeration and Air Conditioning System Need For RefrigerationDocument14 pagesUnit 6 - Refrigeration and Air Conditioning System Need For RefrigerationKiran audinaNo ratings yet
- Refrigration Saving HeatDocument39 pagesRefrigration Saving HeatTanviNo ratings yet
- HVAC Case Study PPT ChanduDocument72 pagesHVAC Case Study PPT Chanduprasahnthrk0775% (4)
- Central AcDocument39 pagesCentral Acmonica singh100% (1)
- Types of Ac SystemsDocument26 pagesTypes of Ac SystemsVarsha PatelNo ratings yet
- Installation and Operation Instructions For Custom Mark III CP Series Oil Fired UnitFrom EverandInstallation and Operation Instructions For Custom Mark III CP Series Oil Fired UnitNo ratings yet
- Oral and Practical Review: Reflections on the Part 147 CourseFrom EverandOral and Practical Review: Reflections on the Part 147 CourseNo ratings yet
- Sdmca: Large Span StructuresDocument31 pagesSdmca: Large Span StructuressampadaNo ratings yet
- External Cladding MaterialDocument11 pagesExternal Cladding Materialsampada100% (1)
- CN Lec 1Document10 pagesCN Lec 1sampadaNo ratings yet
- Case Study SheetDocument3 pagesCase Study SheetsampadaNo ratings yet
- Composition of SoilDocument18 pagesComposition of SoilsampadaNo ratings yet
- Thermal Block: Masonry Block Normal WeightDocument4 pagesThermal Block: Masonry Block Normal WeightEurostar IntNo ratings yet
- K9 Dogs Training Facilities DocumentsDocument85 pagesK9 Dogs Training Facilities DocumentsmahmoudNo ratings yet
- About SawdustDocument1 pageAbout SawdustJennifer DamascoNo ratings yet
- Steps For RCC Design 10.01.08 PDFDocument12 pagesSteps For RCC Design 10.01.08 PDFSACHIDANANDA SNo ratings yet
- Concrete Roof Tiles Technical ManualDocument130 pagesConcrete Roof Tiles Technical ManualNicholas FeatherstonNo ratings yet
- Load Calculation of BeamDocument5 pagesLoad Calculation of BeamNikhilNo ratings yet
- 3 Bed BungalowDocument1 page3 Bed BungalowMichael KiwingaNo ratings yet
- Figure 1, Air Handler (CITATION SOS09 /L 3081)Document5 pagesFigure 1, Air Handler (CITATION SOS09 /L 3081)JadenNo ratings yet
- Sanitary Isometric View Ground Floor Sanitary Layout 2Nd Floor Sanitary LayoutDocument1 pageSanitary Isometric View Ground Floor Sanitary Layout 2Nd Floor Sanitary LayoutChris Gerald CruzNo ratings yet
- PDS Gyproc SoundBloc FDocument2 pagesPDS Gyproc SoundBloc FhartzcarzNo ratings yet
- Grundfosliterature 4609691 PDFDocument120 pagesGrundfosliterature 4609691 PDFLuis MiguelNo ratings yet
- Concrete ClothDocument17 pagesConcrete Clothpandu tejaswiniNo ratings yet
- Shashank B R: A Seminar Report ONDocument25 pagesShashank B R: A Seminar Report ONShashankNo ratings yet
- Pama Guinobatan-P1Document1 pagePama Guinobatan-P1Norvs TVNo ratings yet
- Proposed Vegetable Processing BLDGDocument3 pagesProposed Vegetable Processing BLDGLenvee LosbanesNo ratings yet
- Final Exam: Technical Proposal Retrofitting MethodDocument5 pagesFinal Exam: Technical Proposal Retrofitting Methodjucar fernandezNo ratings yet
- (كشف مدرسة المباهج غير مسعر (كشف 9صف أنكليزي+ عربي 2Document37 pages(كشف مدرسة المباهج غير مسعر (كشف 9صف أنكليزي+ عربي 2ابراهيم الواسطيNo ratings yet
- Polymer Fiber Reinforced Concrete PavementsDocument5 pagesPolymer Fiber Reinforced Concrete PavementsIJRASETPublicationsNo ratings yet
- Polypipe Details PDFDocument1 pagePolypipe Details PDFCire Lop CastroNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals and The ASHRAE Publication HVAC Simplified (Kavanaugh, 2006) - There Is NoDocument13 pagesFundamentals and The ASHRAE Publication HVAC Simplified (Kavanaugh, 2006) - There Is NoCarter RoperNo ratings yet
- Esr-4749 From Icc Report 1Document7 pagesEsr-4749 From Icc Report 1api-46442094No ratings yet
- Basic Plumbing SkillsDocument44 pagesBasic Plumbing Skillsroncekey100% (2)
- Ventilation Fan Pressure OptimizationDocument11 pagesVentilation Fan Pressure OptimizationchoibeNo ratings yet
- Cepex PVCU PipesDocument3 pagesCepex PVCU PipesNima AhvaziNo ratings yet
- Complete Construction Cost of An A Category 10 Marla House in 2020Document14 pagesComplete Construction Cost of An A Category 10 Marla House in 2020Muhammad Taha JilaniNo ratings yet
- Suranga LekamwasamDocument6 pagesSuranga LekamwasamsurangaNo ratings yet
- Boq - Public ToiletDocument5 pagesBoq - Public ToiletAugustine Believe100% (1)
- 1.2 ประมาณราคาศูนย์เด็ก ใส่ ประตู หน้าต่าง อิฐแก้ว แล้วDocument18 pages1.2 ประมาณราคาศูนย์เด็ก ใส่ ประตู หน้าต่าง อิฐแก้ว แล้วsarafan leewan0% (1)
- 051 - Structural Engineer Drawings - 2022.11.18Document3 pages051 - Structural Engineer Drawings - 2022.11.18Flokrida SherifiNo ratings yet
- STA - Timber Frame Construction - Gable Wall Spandrel PanelsDocument7 pagesSTA - Timber Frame Construction - Gable Wall Spandrel Panelsspamalot.yeoNo ratings yet