Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Dep Solvent Extraction
Dep Solvent Extraction
Uploaded by
Mr'RomdonFoxJr.0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
131 views10 pagesThe document discusses solvent extraction techniques for recovering and preconcentrating metals. Solvent extraction can be classified as either discontinuous batch methods using separating funnels or continuous methods using solvent recirculation, extraction chromatography, or countercurrent chromatography. Extraction reagents used include acidic, basic, and neutral extractants like carboxylic acids, phosphoric acids, and hydroxyoximes which transfer metal cations into the organic phase as neutral complexes. The distribution ratio of metal ions between the aqueous and organic phases depends on the reagent concentration and equilibrium pH.
Original Description:
Original Title
DEP SOLVENT EXTRACTION
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses solvent extraction techniques for recovering and preconcentrating metals. Solvent extraction can be classified as either discontinuous batch methods using separating funnels or continuous methods using solvent recirculation, extraction chromatography, or countercurrent chromatography. Extraction reagents used include acidic, basic, and neutral extractants like carboxylic acids, phosphoric acids, and hydroxyoximes which transfer metal cations into the organic phase as neutral complexes. The distribution ratio of metal ions between the aqueous and organic phases depends on the reagent concentration and equilibrium pH.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as ppt, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
131 views10 pagesDep Solvent Extraction
Dep Solvent Extraction
Uploaded by
Mr'RomdonFoxJr.The document discusses solvent extraction techniques for recovering and preconcentrating metals. Solvent extraction can be classified as either discontinuous batch methods using separating funnels or continuous methods using solvent recirculation, extraction chromatography, or countercurrent chromatography. Extraction reagents used include acidic, basic, and neutral extractants like carboxylic acids, phosphoric acids, and hydroxyoximes which transfer metal cations into the organic phase as neutral complexes. The distribution ratio of metal ions between the aqueous and organic phases depends on the reagent concentration and equilibrium pH.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as ppt, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 10
SOLVENT EXTRACTION
The application of extractions
( cloud point extraction, for recovery and
extraction to ionic liquids, preconcentration
supercritical fluid extraction,
and membrane extraction )
The extraction can be classified into two general types.
1). Discontinuous methods (“batch”)
performed in conventional separating funnels.
2). Continuous methods
performed by different procedures, such as solvent
recirculation, extraction chromatographic techniques or
countercurrent chromatography.
Extraction reagents are normally used :
The acidic, basic and solvating (neutral) extractants.
Acidic extractants can be divided into simple organic acids,
e.g., carboxylic acids, phosphoric acids, phosphonic acids,
phosphinic acids, thiophosphorus acids and sulfonic acids,
and chelating reagents, e.g., hydroxyoximes, 8-hydroxy(thio)
quinolines,b-diketones, nitrosophenols, pyridylazonaphthols.
These reagents transfer metal cations into the organic phase
in the form of neutral complexes, e.g., copper(II) with
hydroxyoximes (HL) :
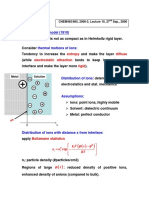
The distribution ratio ( D = Co/Cw ) is a function of reagent
concentration and equilibrium pH :
the possible extraction pathways in typical extraction
for metal recovery with an acidic extractant
In general case reaction proceeds simultaneously both in the
bulk of the aqueous phase and at the interface
Reaction scheme of metal complexing from acidic sulfate solutions
with hydroxyoxime extractants.
Solvent for extraction
Pengaruh pH dan n kali ekstraksi
The extraction of metal dithizonate in chloroform
You might also like
- Extraction of MetalDocument17 pagesExtraction of MetalSyahmi RodziNo ratings yet
- The Diels-Alder ReactionDocument351 pagesThe Diels-Alder ReactionRay Frausto100% (1)
- Peroxo Compounds, InorganicDocument32 pagesPeroxo Compounds, InorganicKilsys AlvaradoNo ratings yet
- Process Description DmeDocument3 pagesProcess Description DmeFirdaus YahyaNo ratings yet
- Dielectric Constant ValuesDocument42 pagesDielectric Constant Valuesmarcomaciel3061No ratings yet
- Centrifugal Force Is Used in Industry & LaboratoryDocument64 pagesCentrifugal Force Is Used in Industry & LaboratoryRoshan jaiswalNo ratings yet
- Liquid Liquid ExtractionDocument15 pagesLiquid Liquid ExtractionDrAlok GargNo ratings yet
- CHEM 102 Instructional Objectives: - Additional Aqueous EquilibriaDocument29 pagesCHEM 102 Instructional Objectives: - Additional Aqueous EquilibriarajNo ratings yet
- Azipine PDFDocument58 pagesAzipine PDFGanesamoorthy Thirunarayanan67% (3)
- ChromatographyDocument18 pagesChromatographyyoga nayagi punichelvanaNo ratings yet
- 7-Liquid Liquid Extraction - COMPLETEDocument39 pages7-Liquid Liquid Extraction - COMPLETERickyWisaksonoNo ratings yet
- Unit 1Document24 pagesUnit 1yashrajNo ratings yet
- Ionic Liquid: Green Chemistry PresentationDocument29 pagesIonic Liquid: Green Chemistry PresentationBaloch SamNo ratings yet
- Review Impurezas PDFDocument7 pagesReview Impurezas PDFGeral RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Acyl ChlorideDocument11 pagesAcyl ChlorideEbby NisaNo ratings yet
- Sigmatropic Rearrangement ReactionDocument18 pagesSigmatropic Rearrangement ReactionSuman ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Arc Discharge ApplicationDocument15 pagesArc Discharge ApplicationHong Chun LeeNo ratings yet
- B.sc. Industrial ChemistryDocument79 pagesB.sc. Industrial ChemistryOmar Abd Elsalam0% (1)
- Chapter15Quality AssuranceDocument26 pagesChapter15Quality Assurancejljimenez1969No ratings yet
- Hexamine PDFDocument86 pagesHexamine PDFmanoranjan singh100% (1)
- Elimination ReactionsDocument7 pagesElimination ReactionsIrfan IslamyNo ratings yet
- Experiment 6Document4 pagesExperiment 6Joao DinizNo ratings yet
- Production of Diethyl EthereDocument163 pagesProduction of Diethyl Ethereيزيد العزانيNo ratings yet
- Gravimetric Analysis and Precipitation - TitrationsDocument34 pagesGravimetric Analysis and Precipitation - TitrationsElvinNo ratings yet
- Ester LabDocument5 pagesEster LabDea YusufNo ratings yet
- SCYA2101 Engineering Chemistry Lab Manual Final Copy For WebsiteDocument41 pagesSCYA2101 Engineering Chemistry Lab Manual Final Copy For WebsiteSivaSaiNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Trace Metals in Honey Using Atomic Absorption Spectroscop-Power PointDocument16 pagesAnalysis of Trace Metals in Honey Using Atomic Absorption Spectroscop-Power PointTANKO BAKONo ratings yet
- Protection Groups in Organic PDFDocument67 pagesProtection Groups in Organic PDFToàn MinhNo ratings yet
- Green Chemistry Kimia FisikDocument16 pagesGreen Chemistry Kimia FisikRinaldi SatriaNo ratings yet
- t2 Chem Revision Ex 15 MSDocument29 pagest2 Chem Revision Ex 15 MSvieronic_princeNo ratings yet
- Lab 2 Hysys Distillation ColumnDocument8 pagesLab 2 Hysys Distillation ColumnAl FatahNo ratings yet
- Systematic Qualitative Organic AnalysisDocument17 pagesSystematic Qualitative Organic Analysisravi@laviNo ratings yet
- Modern Aldol Reactions, Part2Document346 pagesModern Aldol Reactions, Part2Kybernetikum100% (1)
- Liquid Urea-Formaldehyde Resin Manufacturing Industry-217599 - 4Document65 pagesLiquid Urea-Formaldehyde Resin Manufacturing Industry-217599 - 4Sanzar Rahman 1621555030No ratings yet
- Chapter 18 - Carbonyl CompoundsDocument9 pagesChapter 18 - Carbonyl CompoundsNabindra RuwaliNo ratings yet
- FTIRDocument6 pagesFTIRAnubhav ShuklaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1501 - Introduction To Chemical EquilibriumDocument15 pagesLecture 1501 - Introduction To Chemical Equilibriumapi-196433526No ratings yet
- Literature Survey - DR - KS PDFDocument26 pagesLiterature Survey - DR - KS PDFdabrevipulNo ratings yet
- Industrial ChemistryDocument168 pagesIndustrial ChemistryAbdullah Sabry AzzamNo ratings yet
- Imine ReductionDocument4 pagesImine ReductionRatna Siti KhodijahNo ratings yet
- Unit - II Process in Organic Chemical manufacture-II HydrogenationDocument15 pagesUnit - II Process in Organic Chemical manufacture-II HydrogenationMaahir AppNo ratings yet
- Alcohols LabDocument7 pagesAlcohols Lab7sky7harveyNo ratings yet
- Clay Catalysts in Organic SynthesisDocument21 pagesClay Catalysts in Organic Synthesisbvk1976No ratings yet
- 7Document19 pages7Shibu KumardNo ratings yet
- Green Chemistry Lecture 1 & 2Document25 pagesGreen Chemistry Lecture 1 & 2Muhammad IrshadNo ratings yet
- SulfonationDocument29 pagesSulfonationamona2020100% (1)
- Spent Acid From Nitration of TolueneDocument2 pagesSpent Acid From Nitration of TolueneacckypenrynNo ratings yet
- Syllabus For Master of Science in Chemistry: The Assam Kaziranga University, JorhatDocument52 pagesSyllabus For Master of Science in Chemistry: The Assam Kaziranga University, JorhatDibyajyoti SaikiaNo ratings yet
- HPLC NotesDocument50 pagesHPLC NotesEmmanuella Offiong100% (1)
- Chemistry in Everyday Life One Shot BouncebackDocument136 pagesChemistry in Everyday Life One Shot BouncebackPratik RanjanNo ratings yet
- 03 NitrationDocument50 pages03 NitrationShary Rafaqat100% (1)
- Lab 3Document16 pagesLab 3Paen Zulkifli100% (1)
- Daftar Nama Praktikan Fisika II Jurusan KimiaDocument3 pagesDaftar Nama Praktikan Fisika II Jurusan KimiaMr'RomdonFoxJr.No ratings yet
- Eugenol-Loaded Chitosan Nanoparticles: I. Thermal Stability Improvement of Eugenol Through EncapsulationDocument8 pagesEugenol-Loaded Chitosan Nanoparticles: I. Thermal Stability Improvement of Eugenol Through EncapsulationMr'RomdonFoxJr.No ratings yet
- Lecture10 PDFDocument13 pagesLecture10 PDFMr'RomdonFoxJr.No ratings yet
- Dep Solvent ExtractionDocument10 pagesDep Solvent ExtractionMr'RomdonFoxJr.No ratings yet