Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Hepatic Cirrhosis: de Los Santos, Kristine Bernadette R. Usana, Noah Billy D.R
Hepatic Cirrhosis: de Los Santos, Kristine Bernadette R. Usana, Noah Billy D.R
Uploaded by
Bernadette De Los Santos0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
70 views26 pagesHepatic cirrhosis is a chronic disease where normal liver tissue is replaced by fibrosis, disrupting liver structure and function. It has three main types: alcoholic, postnecrotic, and biliary. Risk factors include alcoholism, viral infections, and toxins. Medical management focuses on treating symptoms, improving nutrition, and potentially liver transplantation. Nursing management priorities include rest, skin care, injury prevention, and monitoring for complications like bleeding, encephalopathy, and fluid imbalance.
Original Description:
Original Title
Cirrhosis
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentHepatic cirrhosis is a chronic disease where normal liver tissue is replaced by fibrosis, disrupting liver structure and function. It has three main types: alcoholic, postnecrotic, and biliary. Risk factors include alcoholism, viral infections, and toxins. Medical management focuses on treating symptoms, improving nutrition, and potentially liver transplantation. Nursing management priorities include rest, skin care, injury prevention, and monitoring for complications like bleeding, encephalopathy, and fluid imbalance.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
70 views26 pagesHepatic Cirrhosis: de Los Santos, Kristine Bernadette R. Usana, Noah Billy D.R
Hepatic Cirrhosis: de Los Santos, Kristine Bernadette R. Usana, Noah Billy D.R
Uploaded by
Bernadette De Los SantosHepatic cirrhosis is a chronic disease where normal liver tissue is replaced by fibrosis, disrupting liver structure and function. It has three main types: alcoholic, postnecrotic, and biliary. Risk factors include alcoholism, viral infections, and toxins. Medical management focuses on treating symptoms, improving nutrition, and potentially liver transplantation. Nursing management priorities include rest, skin care, injury prevention, and monitoring for complications like bleeding, encephalopathy, and fluid imbalance.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 26
HEPATIC CIRRHOSIS
DE LOS SANTOS, KRISTINE
BERNADETTE R.
USANA, NOAH BILLY D.R.
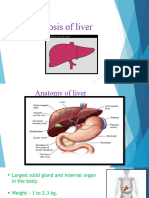
The LIVER is the largest gland in the
body…
Regulates glucose and protein metabolism
Produces and secretes bile for the digestion and
absorption of fat
Removes waste products from the bloodstream
and secretes them into the bile
HEALTHY LIVER
LIVER CIRRHOSIS
Hepatic Cirrhosis
Chronic disease where the normal liver tissue
is replaced by diffuse fibrosis which then
disrupts the structure and function of the liver
THREE TYPES OF CIRRHOSIS
ALCOHOLIC cirrhosis
Scar tissue surrounds the portal area
Caused by chronic alcoholism
Most common type
POSTNECROTIC cirrhosis
Presence of broad bands of scar tissue
Late result of acute viral hepatitis
BILIARY cirrhosis
Scarring in the liver around bile ducts
Results from chronic biliary obstruction and cholangitis
RISK FACTORS
Exposure to carbon tetrachloride, chlorinated
naphthalene, arsenic, or phosphorus
Infectious schistosomiasis
Men are affected more often
Women are at greater risk of developing
alcoholic cirrhosis
40 to 60 years of age
CLINICAL MANIFESTATIONS
COMPENSATED DECOMPENSATED
Intermittent mild fever Ascites
Jaundice
Vascular spiders Weakness
Palmar erythema Muscle wasting
Unexplained epistaxis Weight loss
Continuous mild fever
Ankle edema Purpura (decreased platelet)
Vague morning Spontaneous bruising
indigestion Epistaxis
Flatulent dyspepsia Hypotension
Sparse body hair
Firm, enlarged liver White nails
Splenomegaly Gonadal atrophy
DIAGNOSTIC METHODS
Laparoscopy in conjunction with biopsy
Also called minimally invasive surgery (MIS),
bandaid surgery, keyhole surgery
Biopsy confirms diagnosis
Ultrasound scanning
Measures the difference in density of parenchymal
cells and scar tissue
CT scan, MRI, radioisotope liver scans
Give information about liver size and hepatic blood
flow and obstruction
DIAGNOSTIC METHODS
Liver Function Test (serum AP, AST, ALT,
GGT and serum cholinesterase levels)
Enzyme tests indicate liver cell damage
Bilirubin Test
Measures bile excretion or retention
DIAGNOSTIC FINDINGS
↓ serum albumin level
↑ serum globulin level
↑ serum AP, AST, ALT, GGT levels
↓ serum cholinesterase levels
↑ bilirubin levels
Prolonged PT
Ventilation-perfusion imbalance and hypoxia
MEDICAL MANAGEMENT
Based on presenting symptoms
Antacids or histamine-2 antagonists to decrease
gastric distress and minimize possibility of GI
bleeding
Vitamins and nutritional supplements promote
healing of damaged liver cells and promote client’s
general nutritional status
Spironolactone to decrease ascites; salt restriction
MEDICAL MANAGEMENT
Colchicine (anti-gout) may increase survival time in
clients with mild to moderate cirrhosis
Angiotensin system inhibitors, statins, diuretics,
immunosuppressants, glitazones have been shown to
possess antifibrotic activity for the treatment of
cirrhosis
Clients with ESLD and cirrhosis use the herb milk
thistle (Silybum marianum) to treat jaundice and other
symptoms
Silymarin has anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties
Ursodeoxycholic acid improves liver function in
clients with primary biliary cirrhosis
MEDICAL MANAGEMENT
Hepatitis-related cirrhosis: interferon for viral and
corticosteroids for autoimmune
Wilson's disease-caused cirrhosis: copper chelation
therapy
Portal hypertension: Propranolol to lower BP on portal
system
Transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunting is
occasionally indicated to relieve pressure on the portal
vein in severe complications from portal hypertension
Alcohol and paracetamol, as well as other potentially
damaging substances, are discouraged
If complications cannot be controlled or when the liver
ceases functioning, liver transplantation is necessary
NURSING MANAGEMENT
Promote rest to permit reestablishment of
liver’s functional ability
Monitor I&O and weight daily
Elevate HOB for maximal respiratory efficiency
especially if with marked ascites
O2 therapy to oxygenate damaged cells and prevent
further destruction
Increase activity after improvement in nutrition and
strength
NURSING MANAGEMENT
Improve nutritional status
Provide high CHON diet if without ascites, edema, or signs of
impeding hepatic coma
Administer vit B complex, A, C, and K supplements
If ascites is present, small, frequent meals to minimize abdominal
pressure
Consider client’s preferences
With steatorrhea, administer vit A, D, E, and K
Administer folic acid and iron to prevent anemia
Decrease CHON in diet for client’s showing signs of impending or
advancing coma
Restrict CHON if encephalopathy develops
Incorporate vegetable protein to meet protein needs and decrease risk
of encephalopathy
Restrict sodium to prevent ascites
Avoid consumption of raw shellfish
NURSING MANAGEMENT
Provide skin care
Change positions frequently to prevent pressure
ulcers
Avoid using irritating soaps and adhesive tapes t
prevent trauma to the skin
Apply lotion to soothe irritated skin
Minimize scratching
NURSING MANAGEMENT
Reduce risk for injury
Make sure the side rails are in place and are padded
in case the client becomes restless
Explain all procedures to the client to prevent
agitation
Always assist client when getting out of bed
Evaluate injury properly (internal bleeding tendency)
Instruct client to use an electric razor, soft-bristled
toothbrush
Apply pressure to venipuncture sites to minimize
bleeding
NURSING MANAGEMENT
Monitor and manage potential complications
BLEEDING AND HEMORRHAGE
HEPATIC ENCEPHALOPATHY AND COMA
May manifest as deteriorating mental status and
dementia or abnormal voluntary and involuntary
movements
Serum electrolyte levels are carefully monitored and
corrected if abnormal
O2 is administered if oxygen desaturation occurs
Monitor for fever and abdominal pain (infection,
bacterial peritonitis)
NURSING MANAGEMENT
Monitor and manage potential complications
Excess fluid volume
Administer diuretics, limit fluid intake, enhance client
positioning to optimize pulmonary function
Monitor I&O, daily weight changes, abdominal girth
changes, edema formation
Monitor for nocturia and oliguria
NURSING MANAGEMENT
ENCOURAGE CLIENT TO EXCLUDE
ALCOHOL FROM THE DIET
You might also like
- Answer To Amended Complaint CounterclaimDocument18 pagesAnswer To Amended Complaint CounterclaimMcKenzie StaufferNo ratings yet
- Old Yang Tai Chi Edition OfferDocument23 pagesOld Yang Tai Chi Edition Offerdimmo100% (1)
- Fluid Electrolyte Balances and ImbalanceDocument157 pagesFluid Electrolyte Balances and ImbalanceManisha Shakya0% (1)
- Disorders of Accesssory Organs in GI SystemDocument29 pagesDisorders of Accesssory Organs in GI SystemY. Beatrice AbigailNo ratings yet
- Cirrhosis of Liver, Liver Cancer, HepatitisDocument72 pagesCirrhosis of Liver, Liver Cancer, HepatitisBabita DhruwNo ratings yet
- Biliary Disorder S: Erick Sioco Inserto, RNDocument59 pagesBiliary Disorder S: Erick Sioco Inserto, RNErick Sioco InsertoNo ratings yet
- Seminar On Cirrhosis of LiverDocument9 pagesSeminar On Cirrhosis of Liverrufusprasanth_rachaproluNo ratings yet
- Liver CirrhosisDocument8 pagesLiver CirrhosisgoyaNo ratings yet
- 1 PancreatitisDocument56 pages1 PancreatitisJoemay Belle CabanelaNo ratings yet
- PancreatitisDocument18 pagesPancreatitisMihir PatelNo ratings yet
- Cirrhosis of LiverDocument22 pagesCirrhosis of LiverKrini Tandel50% (2)
- Acute Renal FailureDocument30 pagesAcute Renal FailureJerinNo ratings yet
- Esophageal-Varices 20240201 124908 0000Document25 pagesEsophageal-Varices 20240201 124908 0000Eurika P OrolfoNo ratings yet
- Renal Colic: Prepared By: Regine Anne B. PanganibanDocument19 pagesRenal Colic: Prepared By: Regine Anne B. PanganibanRej PanganibanNo ratings yet
- Definition and Etiology: PancreatitisDocument24 pagesDefinition and Etiology: PancreatitisAliyah Tofani PawelloiNo ratings yet
- PANCREATITISDocument38 pagesPANCREATITISVEDHIKAVIJAYANNo ratings yet
- Presentation On Cirrhosis of LiverDocument34 pagesPresentation On Cirrhosis of LiverAnshu kumariNo ratings yet
- Liver CirrhosisDocument5 pagesLiver CirrhosisRLLTNo ratings yet
- Nursing Patho CardsDocument195 pagesNursing Patho Cardsgiogmail100% (1)
- Acute Renal Failure & Chronic Renal FailureDocument38 pagesAcute Renal Failure & Chronic Renal FailureArti GondNo ratings yet
- Liver FailureDocument22 pagesLiver FailureShriram SinghNo ratings yet
- Activity 8-Liver Cirrhosis-DonghitDocument8 pagesActivity 8-Liver Cirrhosis-DonghitAllona Jane Beatrice DonghitNo ratings yet
- Management and Care of Patients With Ascites: Prepared by Nisha Thomas MspuDocument12 pagesManagement and Care of Patients With Ascites: Prepared by Nisha Thomas MspuShilpaNo ratings yet
- Hepatic Dysfunction: Nursing Disease AnalysisDocument74 pagesHepatic Dysfunction: Nursing Disease AnalysisAisha Valles MalintadNo ratings yet
- Sirrhosis HatiDocument6 pagesSirrhosis HatikimokberusungNo ratings yet
- Cirrhosis of LiverDocument106 pagesCirrhosis of LiveraahadNo ratings yet
- Acute Renal Failure8Document35 pagesAcute Renal Failure8Andrew MidaNo ratings yet
- Chronic Liver FailureDocument4 pagesChronic Liver FailureJasmine Faith SilvaNo ratings yet
- Liver Cirrhosis (VD)Document56 pagesLiver Cirrhosis (VD)HannaTashiaClaudiaNo ratings yet
- Genito Urinary SystemDocument106 pagesGenito Urinary Systemnursereview88% (8)
- Nursing MGT of PT With Lower Git DisordersDocument65 pagesNursing MGT of PT With Lower Git DisordersCarlos LorenzoNo ratings yet
- Alteration in Urinary System - ppt22222Document117 pagesAlteration in Urinary System - ppt22222yen1988No ratings yet
- Acute Renal FailureDocument20 pagesAcute Renal FailureRufus RajNo ratings yet
- Cirrhosis AndrewDocument33 pagesCirrhosis Andrewlionel andreaNo ratings yet
- Renal Disorders, Renal Failure, & Renal Dialysis: Remerose C. Ragasa, R.NDocument41 pagesRenal Disorders, Renal Failure, & Renal Dialysis: Remerose C. Ragasa, R.NremeroseNo ratings yet
- Kidney: Disorders of TheDocument52 pagesKidney: Disorders of ThejuliusromatolentinoNo ratings yet
- Fulminant Hepatic FailureDocument10 pagesFulminant Hepatic FailureAira Anne Tonee VillaminNo ratings yet
- Achalasia, Gerd and Hital HerniaDocument60 pagesAchalasia, Gerd and Hital HerniaMonika MaanNo ratings yet
- ASCITESDocument25 pagesASCITESGanesh BabuNo ratings yet
- Acute Renal Failure & Chronic Renal FailureDocument39 pagesAcute Renal Failure & Chronic Renal FailureMarie MayNo ratings yet
- Pancreatitispptnitinm1st 181229090413Document58 pagesPancreatitispptnitinm1st 181229090413enam professorNo ratings yet
- Biliary DisoderDocument50 pagesBiliary DisoderZanida ZainonNo ratings yet
- Chronic Renal FailureDocument3 pagesChronic Renal FailureNurol-Ainah Hafizah U. PimpingNo ratings yet
- NCM Lecture (Liver and Gallbladder)Document76 pagesNCM Lecture (Liver and Gallbladder)beer_ettaaNo ratings yet
- Chronic Renal FailureDocument3 pagesChronic Renal FailureirismgallNo ratings yet
- Nursing Management of AKIDocument24 pagesNursing Management of AKIheenamaharjanNo ratings yet
- Common Bile DuctDocument28 pagesCommon Bile DuctAmanda ScarletNo ratings yet
- Share GENITO-URINARYDocument69 pagesShare GENITO-URINARYRomer RiveraNo ratings yet
- Ms Reviewer Renal UrinaryDocument5 pagesMs Reviewer Renal UrinaryAlyssa Nicole CajayonNo ratings yet
- ATI Med Surg TipsDocument17 pagesATI Med Surg Tipsmike Gee100% (5)
- Risk Factors: CholelithiasisDocument10 pagesRisk Factors: CholelithiasisRoyster CabralNo ratings yet
- Gall Bladder Diseases by - DR Arun Aggarwal GastroenterologistDocument53 pagesGall Bladder Diseases by - DR Arun Aggarwal GastroenterologistDr. Arun Aggarwal GastroenterologistNo ratings yet
- Gastric UlcerDocument31 pagesGastric UlcerMuhammadNo ratings yet
- Constipation: Ekaterine Labadze MDDocument24 pagesConstipation: Ekaterine Labadze MDsushant jainNo ratings yet
- Assessment and Management of Patients With Hepatic DisordersDocument31 pagesAssessment and Management of Patients With Hepatic DisordersNoor MajaliNo ratings yet
- Liver Cirrhosis: By: Bandna Kumari M.SC (N) 1 YRDocument66 pagesLiver Cirrhosis: By: Bandna Kumari M.SC (N) 1 YRrSNo ratings yet
- Week 13 - Obesity and HepaticDocument91 pagesWeek 13 - Obesity and HepaticEditha LucasNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 2 - C - II Liver CirrhosisDocument39 pagesChapter - 2 - C - II Liver CirrhosisEmmaNo ratings yet
- Electrolyte ImbalancesDocument8 pagesElectrolyte Imbalancesdonna mae junioNo ratings yet
- Ascites, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandAscites, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Liver Cirrhosis, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related DiseasesFrom EverandLiver Cirrhosis, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related DiseasesNo ratings yet
- m106 Report Competencies of Midwifery PracticeDocument71 pagesm106 Report Competencies of Midwifery PracticeTresiah LozanoNo ratings yet
- 113 Najm Course ReportDocument8 pages113 Najm Course ReportA. A. SuleimanNo ratings yet
- Stock 01 Des 22Document70 pagesStock 01 Des 22kaprodiS1 stikesalfatahNo ratings yet
- HSG THỊ ANH 9 (2018- 2019)Document9 pagesHSG THỊ ANH 9 (2018- 2019)Bảo HoàngNo ratings yet
- Teens Your Brain Needs Real FoodDocument4 pagesTeens Your Brain Needs Real FoodGiovana NavaNo ratings yet
- Rehabilitation Protocol For Rotator Cuff Tear Large To Massive TearDocument5 pagesRehabilitation Protocol For Rotator Cuff Tear Large To Massive TearRa RNo ratings yet
- Worksheet in Clarivate MultichannelPortfolio InternAssessment 2022Document612 pagesWorksheet in Clarivate MultichannelPortfolio InternAssessment 20221DS19AU006 AJITH KUMAR S NNo ratings yet
- Rabies VaccineDocument2 pagesRabies VaccineMichael DharshwinNo ratings yet
- Hindustan Times Delhi 21 - 6Document44 pagesHindustan Times Delhi 21 - 6Hmbe hmbeNo ratings yet
- Physical Therapy For A Child With Encopresis: A Case ReportDocument8 pagesPhysical Therapy For A Child With Encopresis: A Case ReportChiara GaleazziNo ratings yet
- How To FingerDocument18 pagesHow To FingerAgiabAbera100% (1)
- Fosfomycin: Review and Use Criteria BackgroundDocument12 pagesFosfomycin: Review and Use Criteria BackgroundAbu Azzam Al-Hadi100% (1)
- A Case Report of HELLP SyndromeDocument4 pagesA Case Report of HELLP SyndromeEditor_IAIMNo ratings yet
- The Ethics of Veracity and It Is Importance in The Medical EthicsDocument5 pagesThe Ethics of Veracity and It Is Importance in The Medical EthicsDalene EvangelioNo ratings yet
- ECT Electroconvulsive Therapy Fact SheetDocument4 pagesECT Electroconvulsive Therapy Fact SheetSonali DakhoreNo ratings yet
- NO Facts Ideas Learning Issues Action PlanDocument2 pagesNO Facts Ideas Learning Issues Action PlandharwinNo ratings yet
- Coronavirus Self-Declaration Form: First Name: Last Name: Appointment Date & Time: Contact Person in SMCDocument3 pagesCoronavirus Self-Declaration Form: First Name: Last Name: Appointment Date & Time: Contact Person in SMCswati durejaNo ratings yet
- Outpatient ClaimDocument1 pageOutpatient Claimtajuddin8No ratings yet
- Laser Scar Removal Service in NepalDocument2 pagesLaser Scar Removal Service in NepalHealthy Choice ClinicNo ratings yet
- Journal Pre-Proof: The Annals of Thoracic SurgeryDocument4 pagesJournal Pre-Proof: The Annals of Thoracic SurgeryJulietaNo ratings yet
- How Did JoeDocument2 pagesHow Did JoeIvanNo ratings yet
- Cle2018 Industrial-wastes-treatment-And-disposalDocument2 pagesCle2018 Industrial-wastes-treatment-And-disposalSuraj SainiNo ratings yet
- To What Extent Were The World War II Internment Camps On The Isle of Man Total Institutions'? A Case Study of Onchan Camp 1940-41Document46 pagesTo What Extent Were The World War II Internment Camps On The Isle of Man Total Institutions'? A Case Study of Onchan Camp 1940-41thomiddonNo ratings yet
- Cancer LungDocument95 pagesCancer LungAnonymous ylMpcDqNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document49 pagesChapter 1Veshal Purshothama SeelanNo ratings yet
- ChecklistDocument4 pagesChecklistJASMINE BRITTANY MONTOYANo ratings yet
- Paper Seminario Jose EpulefDocument11 pagesPaper Seminario Jose EpulefJL EulefiNo ratings yet
- Pit AstidDocument12 pagesPit AstidAstidya GobelNo ratings yet