Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Topic:: Participation of U.S. in Pta'S
Topic:: Participation of U.S. in Pta'S
Uploaded by
Pranay0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views15 pagesThe document discusses the United States' participation in preferential trade agreements (PTAs). It provides three key points:
1) As of 2016, the United States had established 14 PTAs with 20 trading partners to remove trade barriers and set commerce rules between countries.
2) PTAs facilitate trade and investment among member countries by reducing tariffs and restrictions, easing foreign investment rules, and establishing dispute resolution.
3) The United States enters PTAs for both economic reasons like increased trade, and non-economic reasons like achieving foreign policy goals and supporting allies.
Original Description:
Original Title
foreign t22546575
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses the United States' participation in preferential trade agreements (PTAs). It provides three key points:
1) As of 2016, the United States had established 14 PTAs with 20 trading partners to remove trade barriers and set commerce rules between countries.
2) PTAs facilitate trade and investment among member countries by reducing tariffs and restrictions, easing foreign investment rules, and establishing dispute resolution.
3) The United States enters PTAs for both economic reasons like increased trade, and non-economic reasons like achieving foreign policy goals and supporting allies.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views15 pagesTopic:: Participation of U.S. in Pta'S
Topic:: Participation of U.S. in Pta'S
Uploaded by
PranayThe document discusses the United States' participation in preferential trade agreements (PTAs). It provides three key points:
1) As of 2016, the United States had established 14 PTAs with 20 trading partners to remove trade barriers and set commerce rules between countries.
2) PTAs facilitate trade and investment among member countries by reducing tariffs and restrictions, easing foreign investment rules, and establishing dispute resolution.
3) The United States enters PTAs for both economic reasons like increased trade, and non-economic reasons like achieving foreign policy goals and supporting allies.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 15
TOPIC:
PARTICIPATION OF U.S. IN PTA’s
PRESENTED BY:PRANAY GUPTA
ROLL NO.: 07
PRESENTED TO: Dr. NEHA GUPTA
PREFERENTIAL TRADE AGREEMENTS (PTAs)
Preferential trade agreements (PTAs) are treaties
that remove barriers to trade and set rules for
international commerce between two countries or
among a small group of countries.As of August 2016,
the United States had established 14 PTAs with 20 of
its trading partners.
How Does Trade Affect the U.S. Economy?
International trade yields several benefits for the U.S.
economy.
•Trade increases competition between foreign
and domestic producers.
•It enables the most productive businesses
and industries in the United States to expand to
take advantage of profitable new opportunities.
•trade can boost economic output and
workers’ average real (inflation adjusted) wage.
•U.S. consumers and businesses benefit because
trade lowers prices for some goods and services
and increases the variety of products available
for purchase.
•Not everyone benefits from trade expansion,
however.
Although increases in trade probably do not
significantly affect total employment, trade can
affect different workers in different ways.
oWorkers in occupations, businesses, and
industries that expand because of trade may
make more money,
whereas workers in occupations,
businesses, and industries that shrink may make
less money or experience longer-than-
average unemployment.
Such losses can be temporary or permanent.
Why Does the United States Establish Preferential
Trade Agreements?
The United States establishes preferential trade agreements
for economic and noneconomic reasons.
•It enable the United States and its partner
countries to realize the economic benefits of
increased trade and investment.
•In addition, the agreements sometimes
harmonize laws and regulations which, among
other effects, make the costs of operating
businesses in other countries more similar to
those costs in the United States.
•An important noneconomic reason for
establishing PTAs is to achieve foreign
policy goals.
Those goals include supporting
the economies of U.S. allies
and promoting the adoption of preferred domes
policies,such as environmental
conservation or stronger workers’ rights.
Preferential trade Trade
How Do Preferential agreements facilitate
Agreements Work? trade
and investment among member countries. To
encourage member countries to trade
•PTAs reduce or eliminate barriers to trade, such
as import tariffs (taxes that countries impose on
foreign-made goods)
•Restrictions on trade in services, and other
commercial rules that impede the flow of trade.
•In addition, PTAs facilitate investment
among member countries by easing
regulations on foreign investment and
providing improved legal protections for
foreign investors.
•Preferential trade agreements also set
commercial rules that, among other
effects, narrow differences in the costs of
operations among member countries
•To ensure that member countries comply with
the provisions of an agreement
PTAs establish dispute resolution
mechanisms.
Those mechanisms can take two forms:
oOne provides a legal platform for countries to
make claims against other member countries;
othe other enables investors in member
countries to make claims against the
governments of other member countries
Provisions of U.S. Preferential Trade
Agreements
PTAs generally include three types of provisions.
•first type facilitates trade and investment by
lowering import tariffs, easing quotas, and
improving market access for service providers and
investors.
•The second type sets commercial rules and
standards. Although that type of provision also
often stimulates trade and cross border
investment, its costs of compliance (if they are
high) can impede trade among partners.
Characteristics of Partner Countries of U.S. Trade Agreements
Before the Year of Implementation.
Characteristics of Partner Countries of U.S. Trade Agreements
Before the Year of Implementation.
CAFTA-DR = Costa Rica, El Salvador, Guatemala, Honduras, Nicaragua, and
the Dominican Republic; GDP = gross domestic product; MFN = most-favored
nation; NAFTA = North American Free Trade Agreement; n.a. = not applicable;
* = between zero and 0.05 percent.
a. Includes only trade in goods; does not include trade in services.
b. Data for average trade-weighted MFN import tariffs for Canada are only
available starting in 1989.
c. Includes Canada and Mexico. In 1994, NAFTA superseded the 1989
agreement between the United States and Canada.
d. CAFTA-DR was implemented by the United States, El Salvador, Guatemala,
Honduras, and Nicaragua in 2006. Implementation of the agreement by
the Dominican Republic and Costa Rica did not occur until 2007 and 2009,
respectively. This table presents data for CAFTA-DR countries in 2005, the
year before the agreement’s initial implementation.
Potential U.S. Preferential Trade Agreements
The European Union comprises Austria, Belgium, Bulgaria, Croatia, Republic
of Cyprus, Czech Republic, Denmark, Estonia, Finland, France, Germany,
Greece, Hungary, Ireland, Italy, Latvia, Lithuania, Luxembourg, Malta,
Netherlands, Poland, Portugal, Romania, Slovakia, Slovenia, Spain, Sweden,
and the United Kingdom.
THANK YOU!!
You might also like
- Textbook Principles of International Economic Law Matthias Herdegen Ebook All Chapter PDFDocument53 pagesTextbook Principles of International Economic Law Matthias Herdegen Ebook All Chapter PDFdaniel.healy770100% (7)
- Final GATT & WTO ProjectDocument47 pagesFinal GATT & WTO Projectmsms_khatri100% (7)
- The Fundamentals of Trade Finance: 1st EditionFrom EverandThe Fundamentals of Trade Finance: 1st EditionRating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- Import and Export Markets in IndiaDocument21 pagesImport and Export Markets in IndiaAnant Bajaj50% (2)
- Preferential Trade Agreements: (Ptas)Document14 pagesPreferential Trade Agreements: (Ptas)PranayNo ratings yet
- CH - 09 (Regional Economic Integration)Document33 pagesCH - 09 (Regional Economic Integration)AhanafNo ratings yet
- Project On Free Trade AgreementDocument19 pagesProject On Free Trade Agreementprashant_addi05100% (3)
- Lesson Seven International Trade AgreementsDocument5 pagesLesson Seven International Trade AgreementsBen Wekesa100% (2)
- ITL Important TopicsDocument11 pagesITL Important TopicsTushar GuptaNo ratings yet
- Trade Agrement Unit 2 Lec 6Document13 pagesTrade Agrement Unit 2 Lec 6Jahangir BalochNo ratings yet
- U.S. Free Trade AgreementsDocument2 pagesU.S. Free Trade Agreementstpowell55No ratings yet
- IF10156Document3 pagesIF10156kashiram30475No ratings yet
- 171 IbDocument16 pages171 Ibgadhanalvez123No ratings yet
- India and Ftas: Weekly FocusDocument8 pagesIndia and Ftas: Weekly FocusBharatNo ratings yet
- Trade Regulations and Industrial PoliciesDocument23 pagesTrade Regulations and Industrial PoliciesAbraham MoralesNo ratings yet
- Week 3 SlideDocument12 pagesWeek 3 Slideshriabhatia19No ratings yet
- Regional Integration Functions and FormsDocument26 pagesRegional Integration Functions and FormsTafwaza JereNo ratings yet
- UNIT-2: Overview of India & World Trade - EXIM PolicyDocument16 pagesUNIT-2: Overview of India & World Trade - EXIM PolicyNandhu SanthoshNo ratings yet
- International Trade Polic2 - GATTDocument5 pagesInternational Trade Polic2 - GATTEmmanuel BongayNo ratings yet
- The Wealth of Nations: DAM Mith Free TradeDocument6 pagesThe Wealth of Nations: DAM Mith Free Tradegirish_gupta509575No ratings yet
- The Association Agreement Between The European Union and Central America: Annexes To Final ReportDocument18 pagesThe Association Agreement Between The European Union and Central America: Annexes To Final ReportCAWNetworkNo ratings yet
- General Agreement On Tariff and Trade and World Trade OrganisationDocument17 pagesGeneral Agreement On Tariff and Trade and World Trade OrganisationAasthaNo ratings yet
- 2021 Short Version US PolicyDocument4 pages2021 Short Version US Policyirolines kolaplNo ratings yet
- Most Favoured NationDocument1 pageMost Favoured NationPratyay KunduNo ratings yet
- Political EcoDocument4 pagesPolitical Ecoenamulbari56No ratings yet
- ECOMACDocument3 pagesECOMACquennieguanco22No ratings yet
- Regional Trade AgreementsDocument8 pagesRegional Trade AgreementsAditya SharmaNo ratings yet
- Feenstra Taylor Chapter 11Document26 pagesFeenstra Taylor Chapter 11f20213040No ratings yet
- Lesson 4 Notes V2Document5 pagesLesson 4 Notes V2satria.jfaustinoNo ratings yet
- RTB-MBA-GE-IB-01 Unit-Iii: Proliferation of RTA's and The Underlying ReasonsDocument27 pagesRTB-MBA-GE-IB-01 Unit-Iii: Proliferation of RTA's and The Underlying ReasonsAnwar KhanNo ratings yet
- 01 - Global and Regional Economic Cooperation and Integration and The United Nations Impact On TradeDocument40 pages01 - Global and Regional Economic Cooperation and Integration and The United Nations Impact On TradeAmaranthine Angel HarpNo ratings yet
- Regional Trade Agreements-FinalDocument11 pagesRegional Trade Agreements-FinalSwetha VasuNo ratings yet
- The Basics of Non-Discrimination Principle WTODocument5 pagesThe Basics of Non-Discrimination Principle WTOFirman HamdanNo ratings yet
- Case Summary-IM-1-GroupDocument4 pagesCase Summary-IM-1-GroupDivam AroraNo ratings yet
- General Agreement On Tariff and Trade and World Trade OrganisationDocument17 pagesGeneral Agreement On Tariff and Trade and World Trade OrganisationHarvinder SinghNo ratings yet
- INTMKT Chapter 03 The Global Trade EnvironmentDocument36 pagesINTMKT Chapter 03 The Global Trade EnvironmentPhương Yến Nguyễn ThịNo ratings yet
- General Agreement On Tariffs and TradeDocument34 pagesGeneral Agreement On Tariffs and Tradeprabha.v2018No ratings yet
- Trade Policies and Agreements PDFDocument29 pagesTrade Policies and Agreements PDFKueency RoniNo ratings yet
- Principles of The Trading System: Trade Without DiscriminationDocument5 pagesPrinciples of The Trading System: Trade Without DiscriminationVIJAYADARSHINI VIDJEANNo ratings yet
- Bilateral and Multilateral Trade LawsDocument4 pagesBilateral and Multilateral Trade LawsVera CalusinNo ratings yet
- 7 Traditional Trade Policy Multilateralism and The WTODocument6 pages7 Traditional Trade Policy Multilateralism and The WTOOlga LiNo ratings yet
- Understanding The WtoDocument7 pagesUnderstanding The WtoNabinSundar NayakNo ratings yet
- Trade AgreementsDocument9 pagesTrade AgreementsHammad NaeemNo ratings yet
- General Agreement On Tariff and Trade and World Trade OrganisationDocument19 pagesGeneral Agreement On Tariff and Trade and World Trade Organisationakhil91_91No ratings yet
- Bilateral & Commodity AgreementsDocument19 pagesBilateral & Commodity AgreementsDevyani GamitNo ratings yet
- Competition Law and International TradeDocument17 pagesCompetition Law and International Tradevainygoel100% (2)
- Tariff and NonDocument38 pagesTariff and Non14mastermo100% (1)
- Gatt, WTO and GlobalizationDocument29 pagesGatt, WTO and GlobalizationGaurav NavaleNo ratings yet
- TERMppr US Trade PolicyDocument33 pagesTERMppr US Trade Policysampada13No ratings yet
- Assignment 3Document4 pagesAssignment 3Cát ThùyNo ratings yet
- Trade RestrictionsDocument19 pagesTrade RestrictionsAna-Maria NicolescuNo ratings yet
- BTPC-402 Lec-25Document24 pagesBTPC-402 Lec-25Harman MeehnianNo ratings yet
- NaftaDocument20 pagesNaftavijay aravapalliNo ratings yet
- New Issues in World TradeDocument10 pagesNew Issues in World Tradesush_lukeNo ratings yet
- FIRST READING International Trade AgreementsDocument7 pagesFIRST READING International Trade AgreementsRena MabinseNo ratings yet
- Congressionnal Resaerch Service - U.S. Trade Policy - Background and Current IssuesDocument3 pagesCongressionnal Resaerch Service - U.S. Trade Policy - Background and Current IssuesWilliam WulffNo ratings yet
- Regional Trade AgreementsDocument22 pagesRegional Trade AgreementsRishabh Suman100% (1)
- Theory of Economic IntegrationDocument39 pagesTheory of Economic IntegrationJustin Lim100% (1)
- Free Trade AgreementsDocument5 pagesFree Trade AgreementsNarasimha NaruNo ratings yet
- For TradeDocument4 pagesFor Tradechristinayramos24No ratings yet
- Solution Manual For International Business A Managerial Perspective 8 e 8th Edition 0133506290Document26 pagesSolution Manual For International Business A Managerial Perspective 8 e 8th Edition 0133506290BethRowenfed100% (41)
- Challenges of Global Logistics, Costing and Pricing in International SetupDocument23 pagesChallenges of Global Logistics, Costing and Pricing in International SetupPranayNo ratings yet
- Industrial Visit To Uflex Report-PranayDocument12 pagesIndustrial Visit To Uflex Report-PranayPranayNo ratings yet
- Consumer BehaviourDocument10 pagesConsumer BehaviourPranayNo ratings yet
- Tata Steel Q1 Results: Third Straight Loss As Pandemic Hits: Case StudyDocument8 pagesTata Steel Q1 Results: Third Straight Loss As Pandemic Hits: Case StudyPranayNo ratings yet
- Foreign TradeDocument34 pagesForeign TradePranayNo ratings yet
- Preferential Trade Agreements: (Ptas)Document14 pagesPreferential Trade Agreements: (Ptas)PranayNo ratings yet
- Regional Economic IntegrationDocument18 pagesRegional Economic IntegrationPranayNo ratings yet
- Business Analysis and Its Socio-Economic Impact: Senior High SchoolDocument41 pagesBusiness Analysis and Its Socio-Economic Impact: Senior High SchoolKishly Concepcion100% (1)
- International Trade - Types, Importance, Advantages and DisadvantagesDocument4 pagesInternational Trade - Types, Importance, Advantages and DisadvantagesYEIMI ORTEGA ACUÑANo ratings yet
- Full Download International Financial Management Canadian Perspectives 2nd Edition Eun Test BankDocument8 pagesFull Download International Financial Management Canadian Perspectives 2nd Edition Eun Test Bankdanielmoreno72d100% (32)
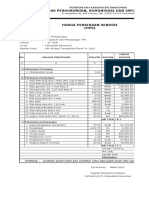
- Dinas Perhubungan, Komunikasi Dan Informatika: NO. Uraian Pekerjaan Volume Satuan Harga Satuan (RP.)Document11 pagesDinas Perhubungan, Komunikasi Dan Informatika: NO. Uraian Pekerjaan Volume Satuan Harga Satuan (RP.)Rah Panji DamarsidhiNo ratings yet
- Regional Economic IntegrationDocument1 pageRegional Economic IntegrationSale BrankovicNo ratings yet
- Jurnal Analisis HukumDocument17 pagesJurnal Analisis HukumChusna RofiqohNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - International TradeDocument70 pagesChapter 3 - International TradeHay JirenyaaNo ratings yet
- International Economics - Midterm NotesDocument18 pagesInternational Economics - Midterm NotesLonerStrelokNo ratings yet
- REVIEWER AE m8.1Document4 pagesREVIEWER AE m8.1Kenma KozumeNo ratings yet
- 500 USD To EUR - US Dollars To Euros Exchange RateDocument1 page500 USD To EUR - US Dollars To Euros Exchange RateYovanna VenturaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7Document12 pagesChapter 7Annie DuolingoNo ratings yet
- International FinanceDocument18 pagesInternational FinanceQuansimah BonsuNo ratings yet
- Glossary International Business Final PDFDocument39 pagesGlossary International Business Final PDFSumant SharmaNo ratings yet
- North American Free Trade Agreement: NaftaDocument5 pagesNorth American Free Trade Agreement: NaftaDrPinky ShrivastavaNo ratings yet
- 11 Actividad #4 Crucigrama Contabilidad VDocument3 pages11 Actividad #4 Crucigrama Contabilidad VMaria F OrtizNo ratings yet
- Lec 6 FX ArbitrageDocument31 pagesLec 6 FX ArbitrageAprilNo ratings yet
- Most Favoured Nation Concept in WtoDocument23 pagesMost Favoured Nation Concept in Wtorishabhsingh261100% (1)
- Form AK - Additional PageDocument3 pagesForm AK - Additional PagekatacumiNo ratings yet
- CORE Finance Project Term 1Document4 pagesCORE Finance Project Term 1ashbornsfragmentNo ratings yet
- Lecture 12 - 14Document29 pagesLecture 12 - 14Ashish kumar ThapaNo ratings yet
- Midterm AnswerDocument4 pagesMidterm AnswerMary Ivy PunzalanNo ratings yet
- Evaluacion Final - Escenario 8 - PRIMER BLOQUE-TEORICO - PRACTICO - VIRTUAL - CULTURA Y ECONOMÍA REGIONAL DE AMÉRICADocument12 pagesEvaluacion Final - Escenario 8 - PRIMER BLOQUE-TEORICO - PRACTICO - VIRTUAL - CULTURA Y ECONOMÍA REGIONAL DE AMÉRICAKWOZNo ratings yet
- Chapter 19Document60 pagesChapter 19JoreseNo ratings yet
- Nickels10ce Enhanced PPT Ch03Document39 pagesNickels10ce Enhanced PPT Ch03Ishaan NasitNo ratings yet
- Kyrghyzstan FreeZones AtlasDocument6 pagesKyrghyzstan FreeZones AtlasAmiranNo ratings yet
- Economic integr-WPS OfficeDocument3 pagesEconomic integr-WPS OfficeJohnNo ratings yet
- A187844 Aiman Zakwan Tutorial 4Document1 pageA187844 Aiman Zakwan Tutorial 4aiman ZakwanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 The Global Trade Environment: Global Marketing, 9e (Keegan)Document25 pagesChapter 3 The Global Trade Environment: Global Marketing, 9e (Keegan)miranjdNo ratings yet