Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
32 viewsSteam Turbine
Steam Turbine
Uploaded by
Abhas AgarwalThe document discusses steam turbines. It begins by defining a turbine as a device that extracts mechanical energy from a fluid. It then discusses steam turbines specifically, noting that steam from a boiler spins the turbine blades on a shaft. The document goes on to classify steam turbines based on their construction, pressure stages, steam flow direction, number of cylinders, governing method, steam action principle, heat drop process, steam conditions, and industrial usage. It provides examples such as single-stage vs. multistage turbines and impulse vs. reaction turbines. It also includes diagrams of typical turbine layouts and components.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- LAB3Document4 pagesLAB3Juan Camilo Guarnizo Bermudez100% (1)
- Steam Turbines: Dr. Hitendra ShahDocument161 pagesSteam Turbines: Dr. Hitendra ShahNitish Tole100% (1)
- 1 ST - Thermic Turbo Machines-IntroductionDocument30 pages1 ST - Thermic Turbo Machines-IntroductionHakouma HourNo ratings yet
- Steam TurbineDocument3 pagesSteam TurbineErAbdulRehmanNo ratings yet
- PROJECT DushyanthDocument85 pagesPROJECT DushyanthHari KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Steam TurbineDocument58 pagesSteam TurbineJoy Prokash RoyNo ratings yet
- Steam Turbine: Ella Jane B. Cabanag BSME - 4Document11 pagesSteam Turbine: Ella Jane B. Cabanag BSME - 4Ella Jane CabanagNo ratings yet
- Turbines and Its TypesDocument25 pagesTurbines and Its TypesCh ArsalanNo ratings yet
- Unit 4steamturbine 160705174835Document48 pagesUnit 4steamturbine 160705174835Ruby ShajiNo ratings yet
- Steam TurbineDocument19 pagesSteam TurbineAnanya Srivastava100% (1)
- Turbo Machines: Hydraulic TurbinesDocument38 pagesTurbo Machines: Hydraulic TurbinesMahar Mamoon RasheedNo ratings yet
- ME8595 - Thermal Engineering II - Unit IIIDocument50 pagesME8595 - Thermal Engineering II - Unit IIIommech2020No ratings yet
- EE16104 L10 Steam Turbines1Document44 pagesEE16104 L10 Steam Turbines1Pratiksha AnuragiNo ratings yet
- Steam TurbineDocument17 pagesSteam TurbineDicky Nicky November100% (1)
- Steam Turbine 2Document5 pagesSteam Turbine 2Pratibha PatelNo ratings yet
- PROJECT F2 (Dushyanth)Document85 pagesPROJECT F2 (Dushyanth)saiNo ratings yet
- MCE552 Lecture 4aDocument227 pagesMCE552 Lecture 4aOloyede JeremiahNo ratings yet
- Reaction To An Impulse: A Hero'S TakeDocument4 pagesReaction To An Impulse: A Hero'S Takepariskos100% (1)
- Turbine Governing Syatem in Power PlantDocument113 pagesTurbine Governing Syatem in Power Plantnetygen1100% (2)
- Training Module On Turbine, Lub Oil, Gland Steam SystemDocument228 pagesTraining Module On Turbine, Lub Oil, Gland Steam Systemdinesh7136100% (4)
- Chapter 4 - Steam TurbinesiDocument36 pagesChapter 4 - Steam Turbinesismisosphamandla30No ratings yet
- DPDocument21 pagesDPDivya Prakash SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Steam TurbineDocument69 pagesSteam TurbineNgo Van Tan100% (2)
- Steam TurbineDocument10 pagesSteam TurbineBilal Qasim50% (2)
- Turbines (Part of Prof Oza Syllabus) : Compiled by Prof Shivam Shrivastava Ap-Ee, ItnuDocument6 pagesTurbines (Part of Prof Oza Syllabus) : Compiled by Prof Shivam Shrivastava Ap-Ee, ItnuShivam ShrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Thermal Power PlantDocument29 pagesThermal Power Plantshamna AbdullaNo ratings yet
- Meg 5-LF-37 Aux Steam TurbinesDocument36 pagesMeg 5-LF-37 Aux Steam TurbinesAkash KandwalNo ratings yet
- pptPPE (15&17)Document22 pagespptPPE (15&17)HarshitNo ratings yet
- Steam Turbine IIDocument11 pagesSteam Turbine IIg9958306No ratings yet
- Steam Turbine: A Rotor of A Modern Steam Turbine, Used in ADocument13 pagesSteam Turbine: A Rotor of A Modern Steam Turbine, Used in AAnil Tandon100% (1)
- Turbine Control SystemDocument9 pagesTurbine Control SystemAshutosh KumarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document35 pagesChapter 1Divya Prakash SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Steam Turbine 10 OctDocument118 pagesSteam Turbine 10 OctPinak Vadher100% (3)
- Steam Turbine fDocument23 pagesSteam Turbine fdasbidhan089No ratings yet
- Steam Turbine: Prepared byDocument32 pagesSteam Turbine: Prepared byMahiNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 (Steam Turbines)Document29 pagesUnit 3 (Steam Turbines)amarparimiNo ratings yet
- Thermal Energy Steam Sir Charles ParsonsDocument18 pagesThermal Energy Steam Sir Charles ParsonsgauravNo ratings yet
- Types of Steam Turbines ReportDocument6 pagesTypes of Steam Turbines Reportalaa zahranNo ratings yet
- Codes and StandardsDocument82 pagesCodes and StandardsmanojNo ratings yet
- Dr. Mohamed A. Qassem: Heat Transfer BranchDocument19 pagesDr. Mohamed A. Qassem: Heat Transfer BranchMohamed ElfekyNo ratings yet
- I Year (Ii Sem) SESSION-2020-2021: UNIT-1Document26 pagesI Year (Ii Sem) SESSION-2020-2021: UNIT-1Kushagra SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Steam TurbineDocument24 pagesSteam TurbinePujara ManishNo ratings yet
- A Thermal Power Station Comprises All of TheDocument24 pagesA Thermal Power Station Comprises All of TheAnirban BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- TurbineDocument19 pagesTurbineom prakash yadavNo ratings yet
- Chapter-1: HistoryDocument19 pagesChapter-1: HistoryraisNo ratings yet
- Steam Turbine: HistoryDocument9 pagesSteam Turbine: HistoryrikumohanNo ratings yet
- NNM Sir SlideDocument34 pagesNNM Sir SlideAbtahee RUETNo ratings yet
- Steam Power PlantDocument7 pagesSteam Power PlantNav Mehra50% (2)
- Marine Steam TurbinesDocument23 pagesMarine Steam TurbinesBlix KaneNo ratings yet
- Saidi CertificatesDocument17 pagesSaidi Certificatesshiva saiNo ratings yet
- UNIT-I & II Hydraulic Machine. Up Dated. PPT - By. Dr. Subhash KamalDocument80 pagesUNIT-I & II Hydraulic Machine. Up Dated. PPT - By. Dr. Subhash KamalNagendra Manral100% (3)
- Turbine: Navigation SearchDocument9 pagesTurbine: Navigation SearchsyamsundariitmNo ratings yet
- Steam TurbinesDocument14 pagesSteam TurbinesArvindPasuparthy100% (1)
- Title of Project-: Preliminary Study On Thermal Power Plant and Detail Study On Coal Handling PlantDocument98 pagesTitle of Project-: Preliminary Study On Thermal Power Plant and Detail Study On Coal Handling PlantAbir MukherjeeNo ratings yet
- ME LAB 2 - Steam TurbineDocument27 pagesME LAB 2 - Steam TurbineMichael LopezNo ratings yet
- Steam TurbinesDocument76 pagesSteam Turbinesgunawan eko wardoyo100% (1)
- Turning and Boring A specialized treatise for machinists, students in the industrial and engineering schools, and apprentices, on turning and boring methods, etc.From EverandTurning and Boring A specialized treatise for machinists, students in the industrial and engineering schools, and apprentices, on turning and boring methods, etc.No ratings yet
- Collection Development and Acquisition in ASIAN ACADEMIC LIBRARIES: Some Current IssuesDocument8 pagesCollection Development and Acquisition in ASIAN ACADEMIC LIBRARIES: Some Current IssuesKrish ViliranNo ratings yet
- Numeral System Indian and InternationalDocument4 pagesNumeral System Indian and Internationalsatya 1No ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Equivalence Above Word LevelDocument23 pagesChapter 2 - Equivalence Above Word LevelNoo NooNo ratings yet
- CookiesDocument130 pagesCookiesNinjamuppetNo ratings yet
- Practice Test (2020) - 3Document2 pagesPractice Test (2020) - 3Duy HảiNo ratings yet
- DISS Q2 Week1 Learning-Activity-SheetDocument2 pagesDISS Q2 Week1 Learning-Activity-SheetBryanNo ratings yet
- Ecm 9Document1 pageEcm 9Misa GamezNo ratings yet
- PT RatioDocument5 pagesPT RatioMazidul Islam MahfujNo ratings yet
- Air Equipment Compressors Compressor 250 300CFM D XAS 125DD Operation ManualDocument34 pagesAir Equipment Compressors Compressor 250 300CFM D XAS 125DD Operation ManualFloyd MG100% (1)
- Nynas Transformer Oil - Nytro 10GBN: Naphthenics Product Data SheetDocument1 pageNynas Transformer Oil - Nytro 10GBN: Naphthenics Product Data SheetAnonymous S29FwnFNo ratings yet
- Assignment - 6 SolutionsDocument7 pagesAssignment - 6 SolutionsGopal Iswarpur Ghosh100% (1)
- Case Study 148 169Document22 pagesCase Study 148 169Vonn GuintoNo ratings yet
- Personal Workbook For Breaking The Chain of Low Self EsteemDocument308 pagesPersonal Workbook For Breaking The Chain of Low Self EsteemPragyan Nanda100% (1)
- Bandstop Filters and The Bainter Topology: by Bonnie C. BakerDocument5 pagesBandstop Filters and The Bainter Topology: by Bonnie C. Bakerpaoki01No ratings yet
- NK 3 Final With DataDocument20 pagesNK 3 Final With DataАлексейNo ratings yet
- Sika RainTiteDocument2 pagesSika RainTiteRialno TambunanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 03 - Louwers 5eDocument23 pagesChapter 03 - Louwers 5eMonique GordonNo ratings yet
- 2022 Cloud Native Security and Usage ReportDocument30 pages2022 Cloud Native Security and Usage ReportAnand SarmaNo ratings yet
- ADT Service ManualDocument152 pagesADT Service ManualZakhele MpofuNo ratings yet
- SYNTHESIS Filipino 1Document6 pagesSYNTHESIS Filipino 1DhanNo ratings yet
- NHPC Dulhasti 1Document2 pagesNHPC Dulhasti 1Sherry SherNo ratings yet
- 2.High-Confidence Behavior at Work The Exec SkillsDocument27 pages2.High-Confidence Behavior at Work The Exec SkillsRamiro BernalesNo ratings yet
- DLP in IctDocument3 pagesDLP in Ictreyna.sazon001No ratings yet
- Schema Refinement and Normal Forms: Database Management Systems, 3ed, R. Ramakrishnan and J. Gehrke 1Document19 pagesSchema Refinement and Normal Forms: Database Management Systems, 3ed, R. Ramakrishnan and J. Gehrke 1PRADNYA KASHIKARNo ratings yet
- Final ProjectDocument6 pagesFinal ProjectAmmar HussainNo ratings yet
- 320DLRR GMX ELE SchematicDocument14 pages320DLRR GMX ELE Schematicthaw3tar3minNo ratings yet
- الاستدامة في العمارةDocument17 pagesالاستدامة في العمارةkhawla zanganaNo ratings yet
- String/Arrays in JavaDocument7 pagesString/Arrays in JavaSaif HassanNo ratings yet
- Classroom Program 10B 2023 2024Document2 pagesClassroom Program 10B 2023 2024jester18 bordersyoNo ratings yet
Steam Turbine
Steam Turbine
Uploaded by
Abhas Agarwal0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
32 views21 pagesThe document discusses steam turbines. It begins by defining a turbine as a device that extracts mechanical energy from a fluid. It then discusses steam turbines specifically, noting that steam from a boiler spins the turbine blades on a shaft. The document goes on to classify steam turbines based on their construction, pressure stages, steam flow direction, number of cylinders, governing method, steam action principle, heat drop process, steam conditions, and industrial usage. It provides examples such as single-stage vs. multistage turbines and impulse vs. reaction turbines. It also includes diagrams of typical turbine layouts and components.
Original Description:
Details of various types of Steam Turbine and its operating principle.
Original Title
Steam Turbine-
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses steam turbines. It begins by defining a turbine as a device that extracts mechanical energy from a fluid. It then discusses steam turbines specifically, noting that steam from a boiler spins the turbine blades on a shaft. The document goes on to classify steam turbines based on their construction, pressure stages, steam flow direction, number of cylinders, governing method, steam action principle, heat drop process, steam conditions, and industrial usage. It provides examples such as single-stage vs. multistage turbines and impulse vs. reaction turbines. It also includes diagrams of typical turbine layouts and components.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
32 views21 pagesSteam Turbine
Steam Turbine
Uploaded by
Abhas AgarwalThe document discusses steam turbines. It begins by defining a turbine as a device that extracts mechanical energy from a fluid. It then discusses steam turbines specifically, noting that steam from a boiler spins the turbine blades on a shaft. The document goes on to classify steam turbines based on their construction, pressure stages, steam flow direction, number of cylinders, governing method, steam action principle, heat drop process, steam conditions, and industrial usage. It provides examples such as single-stage vs. multistage turbines and impulse vs. reaction turbines. It also includes diagrams of typical turbine layouts and components.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 21
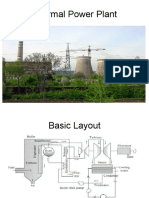
STEAM TURBINE
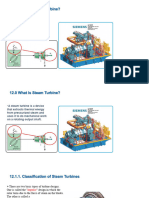
• What is Turbine
• “Turbine” is a general term for any device that extracts mechanical
energy from a fluid – generally converting it to rotating energy of a
turbine wheel.
• For liquids, we usually call them “hydraulic turbines” or “hydro-
turbines”.
• For gases, we usually call them “wind turbines”, “gas turbines”, or
“steam turbines”, depending on the type of gas being used.
• In steam turbine, steam from the steam generator / boiler is pushed
into the turbine through nozzles, which spins the blades mounted on a
shaft. The steam turbine consists of a casing to which stationary
blades are fixed inside and a rotor has moving blades on the periphery.
Classification of Turbines
Steam turbines may be classified into different categories depending on their construction, the
process by which heat drop is achieved, the initial and final conditions of steam used and their
industrial usage.
According to the number of pressure stages:
· Single-stage
· Multistage impulse and reaction turbines; they are made in a wide range of power capacities
varying from small to large.
According to the direction of steam flow:
· Axial turbines in which the steam flows in a direction parallel to the axis of the turbine;
· Radial turbines in which the steam flows in a direction perpendicular to the axis of the turbine
with one or more low pressure stages in such turbines being axial.
According to the number of cylinder:
· Single-cylinder turbines.
· Double-cylinder turbines.
· Three-Cylinder turbines and
Multi-Cylinder turbines
According to the method of governing:
· Turbines with throttle governing
· Turbine with bypass governing
According to the principle of action of steam:
· Impulse turbines.
· Axial reaction turbines.
· Radial reaction turbines with stationary guide blades.
· Radial reaction turbines without any stationary blades.
According to the heat drop process:
· Condensing turbines with regeneration;
· Back pressure turbines:
· Mixed pressure turbines
According to the steam conditions at inlet to turbines:
· Low-pressure turbines, using steam at pressure of 1.2 to 2 ata.
· Medium-pressure turbines, using steam at pressure of upto. 40 ata.
· High-pressure turbines, utilising steam at pressure above 40 ata.
· Turbines of very high pressures, utilising steam at pressures of 170 ata and
higher and temperature of 535 deg. C and higher.
· Turbines of supercritical pressures, using steam at pressure of 255 ata and
above.
According to their usage in industry
TURBINE SYSTEM
Typical Turbine Layout
Turbine Section View Double Flow Turbine
Convergent-Divergent model
Range of turbine Design Parameter
High Pressure Gas Turbine:
Maximum AN2 : 2.5×107 – 3.3 ×107 m2.rpm2.
Stage loading coefficient: 1.4 – 2.0
Stage Exit Mach Number: 0.4 – 0.5
Low Pressure Gas Turbine:
Inlet mass flow rate: 195 – 215 kg/m2.s
Hub/tip ratio: .35-.5
Max. Stage loading (based on hub): 2.4
Exit Mach Number: 0.4 – 0.5
Flow through impulse blades
Moving Blade
You might also like
- LAB3Document4 pagesLAB3Juan Camilo Guarnizo Bermudez100% (1)
- Steam Turbines: Dr. Hitendra ShahDocument161 pagesSteam Turbines: Dr. Hitendra ShahNitish Tole100% (1)
- 1 ST - Thermic Turbo Machines-IntroductionDocument30 pages1 ST - Thermic Turbo Machines-IntroductionHakouma HourNo ratings yet
- Steam TurbineDocument3 pagesSteam TurbineErAbdulRehmanNo ratings yet
- PROJECT DushyanthDocument85 pagesPROJECT DushyanthHari KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Steam TurbineDocument58 pagesSteam TurbineJoy Prokash RoyNo ratings yet
- Steam Turbine: Ella Jane B. Cabanag BSME - 4Document11 pagesSteam Turbine: Ella Jane B. Cabanag BSME - 4Ella Jane CabanagNo ratings yet
- Turbines and Its TypesDocument25 pagesTurbines and Its TypesCh ArsalanNo ratings yet
- Unit 4steamturbine 160705174835Document48 pagesUnit 4steamturbine 160705174835Ruby ShajiNo ratings yet
- Steam TurbineDocument19 pagesSteam TurbineAnanya Srivastava100% (1)
- Turbo Machines: Hydraulic TurbinesDocument38 pagesTurbo Machines: Hydraulic TurbinesMahar Mamoon RasheedNo ratings yet
- ME8595 - Thermal Engineering II - Unit IIIDocument50 pagesME8595 - Thermal Engineering II - Unit IIIommech2020No ratings yet
- EE16104 L10 Steam Turbines1Document44 pagesEE16104 L10 Steam Turbines1Pratiksha AnuragiNo ratings yet
- Steam TurbineDocument17 pagesSteam TurbineDicky Nicky November100% (1)
- Steam Turbine 2Document5 pagesSteam Turbine 2Pratibha PatelNo ratings yet
- PROJECT F2 (Dushyanth)Document85 pagesPROJECT F2 (Dushyanth)saiNo ratings yet
- MCE552 Lecture 4aDocument227 pagesMCE552 Lecture 4aOloyede JeremiahNo ratings yet
- Reaction To An Impulse: A Hero'S TakeDocument4 pagesReaction To An Impulse: A Hero'S Takepariskos100% (1)
- Turbine Governing Syatem in Power PlantDocument113 pagesTurbine Governing Syatem in Power Plantnetygen1100% (2)
- Training Module On Turbine, Lub Oil, Gland Steam SystemDocument228 pagesTraining Module On Turbine, Lub Oil, Gland Steam Systemdinesh7136100% (4)
- Chapter 4 - Steam TurbinesiDocument36 pagesChapter 4 - Steam Turbinesismisosphamandla30No ratings yet
- DPDocument21 pagesDPDivya Prakash SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Steam TurbineDocument69 pagesSteam TurbineNgo Van Tan100% (2)
- Steam TurbineDocument10 pagesSteam TurbineBilal Qasim50% (2)
- Turbines (Part of Prof Oza Syllabus) : Compiled by Prof Shivam Shrivastava Ap-Ee, ItnuDocument6 pagesTurbines (Part of Prof Oza Syllabus) : Compiled by Prof Shivam Shrivastava Ap-Ee, ItnuShivam ShrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Thermal Power PlantDocument29 pagesThermal Power Plantshamna AbdullaNo ratings yet
- Meg 5-LF-37 Aux Steam TurbinesDocument36 pagesMeg 5-LF-37 Aux Steam TurbinesAkash KandwalNo ratings yet
- pptPPE (15&17)Document22 pagespptPPE (15&17)HarshitNo ratings yet
- Steam Turbine IIDocument11 pagesSteam Turbine IIg9958306No ratings yet
- Steam Turbine: A Rotor of A Modern Steam Turbine, Used in ADocument13 pagesSteam Turbine: A Rotor of A Modern Steam Turbine, Used in AAnil Tandon100% (1)
- Turbine Control SystemDocument9 pagesTurbine Control SystemAshutosh KumarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document35 pagesChapter 1Divya Prakash SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Steam Turbine 10 OctDocument118 pagesSteam Turbine 10 OctPinak Vadher100% (3)
- Steam Turbine fDocument23 pagesSteam Turbine fdasbidhan089No ratings yet
- Steam Turbine: Prepared byDocument32 pagesSteam Turbine: Prepared byMahiNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 (Steam Turbines)Document29 pagesUnit 3 (Steam Turbines)amarparimiNo ratings yet
- Thermal Energy Steam Sir Charles ParsonsDocument18 pagesThermal Energy Steam Sir Charles ParsonsgauravNo ratings yet
- Types of Steam Turbines ReportDocument6 pagesTypes of Steam Turbines Reportalaa zahranNo ratings yet
- Codes and StandardsDocument82 pagesCodes and StandardsmanojNo ratings yet
- Dr. Mohamed A. Qassem: Heat Transfer BranchDocument19 pagesDr. Mohamed A. Qassem: Heat Transfer BranchMohamed ElfekyNo ratings yet
- I Year (Ii Sem) SESSION-2020-2021: UNIT-1Document26 pagesI Year (Ii Sem) SESSION-2020-2021: UNIT-1Kushagra SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Steam TurbineDocument24 pagesSteam TurbinePujara ManishNo ratings yet
- A Thermal Power Station Comprises All of TheDocument24 pagesA Thermal Power Station Comprises All of TheAnirban BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- TurbineDocument19 pagesTurbineom prakash yadavNo ratings yet
- Chapter-1: HistoryDocument19 pagesChapter-1: HistoryraisNo ratings yet
- Steam Turbine: HistoryDocument9 pagesSteam Turbine: HistoryrikumohanNo ratings yet
- NNM Sir SlideDocument34 pagesNNM Sir SlideAbtahee RUETNo ratings yet
- Steam Power PlantDocument7 pagesSteam Power PlantNav Mehra50% (2)
- Marine Steam TurbinesDocument23 pagesMarine Steam TurbinesBlix KaneNo ratings yet
- Saidi CertificatesDocument17 pagesSaidi Certificatesshiva saiNo ratings yet
- UNIT-I & II Hydraulic Machine. Up Dated. PPT - By. Dr. Subhash KamalDocument80 pagesUNIT-I & II Hydraulic Machine. Up Dated. PPT - By. Dr. Subhash KamalNagendra Manral100% (3)
- Turbine: Navigation SearchDocument9 pagesTurbine: Navigation SearchsyamsundariitmNo ratings yet
- Steam TurbinesDocument14 pagesSteam TurbinesArvindPasuparthy100% (1)
- Title of Project-: Preliminary Study On Thermal Power Plant and Detail Study On Coal Handling PlantDocument98 pagesTitle of Project-: Preliminary Study On Thermal Power Plant and Detail Study On Coal Handling PlantAbir MukherjeeNo ratings yet
- ME LAB 2 - Steam TurbineDocument27 pagesME LAB 2 - Steam TurbineMichael LopezNo ratings yet
- Steam TurbinesDocument76 pagesSteam Turbinesgunawan eko wardoyo100% (1)
- Turning and Boring A specialized treatise for machinists, students in the industrial and engineering schools, and apprentices, on turning and boring methods, etc.From EverandTurning and Boring A specialized treatise for machinists, students in the industrial and engineering schools, and apprentices, on turning and boring methods, etc.No ratings yet
- Collection Development and Acquisition in ASIAN ACADEMIC LIBRARIES: Some Current IssuesDocument8 pagesCollection Development and Acquisition in ASIAN ACADEMIC LIBRARIES: Some Current IssuesKrish ViliranNo ratings yet
- Numeral System Indian and InternationalDocument4 pagesNumeral System Indian and Internationalsatya 1No ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Equivalence Above Word LevelDocument23 pagesChapter 2 - Equivalence Above Word LevelNoo NooNo ratings yet
- CookiesDocument130 pagesCookiesNinjamuppetNo ratings yet
- Practice Test (2020) - 3Document2 pagesPractice Test (2020) - 3Duy HảiNo ratings yet
- DISS Q2 Week1 Learning-Activity-SheetDocument2 pagesDISS Q2 Week1 Learning-Activity-SheetBryanNo ratings yet
- Ecm 9Document1 pageEcm 9Misa GamezNo ratings yet
- PT RatioDocument5 pagesPT RatioMazidul Islam MahfujNo ratings yet
- Air Equipment Compressors Compressor 250 300CFM D XAS 125DD Operation ManualDocument34 pagesAir Equipment Compressors Compressor 250 300CFM D XAS 125DD Operation ManualFloyd MG100% (1)
- Nynas Transformer Oil - Nytro 10GBN: Naphthenics Product Data SheetDocument1 pageNynas Transformer Oil - Nytro 10GBN: Naphthenics Product Data SheetAnonymous S29FwnFNo ratings yet
- Assignment - 6 SolutionsDocument7 pagesAssignment - 6 SolutionsGopal Iswarpur Ghosh100% (1)
- Case Study 148 169Document22 pagesCase Study 148 169Vonn GuintoNo ratings yet
- Personal Workbook For Breaking The Chain of Low Self EsteemDocument308 pagesPersonal Workbook For Breaking The Chain of Low Self EsteemPragyan Nanda100% (1)
- Bandstop Filters and The Bainter Topology: by Bonnie C. BakerDocument5 pagesBandstop Filters and The Bainter Topology: by Bonnie C. Bakerpaoki01No ratings yet
- NK 3 Final With DataDocument20 pagesNK 3 Final With DataАлексейNo ratings yet
- Sika RainTiteDocument2 pagesSika RainTiteRialno TambunanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 03 - Louwers 5eDocument23 pagesChapter 03 - Louwers 5eMonique GordonNo ratings yet
- 2022 Cloud Native Security and Usage ReportDocument30 pages2022 Cloud Native Security and Usage ReportAnand SarmaNo ratings yet
- ADT Service ManualDocument152 pagesADT Service ManualZakhele MpofuNo ratings yet
- SYNTHESIS Filipino 1Document6 pagesSYNTHESIS Filipino 1DhanNo ratings yet
- NHPC Dulhasti 1Document2 pagesNHPC Dulhasti 1Sherry SherNo ratings yet
- 2.High-Confidence Behavior at Work The Exec SkillsDocument27 pages2.High-Confidence Behavior at Work The Exec SkillsRamiro BernalesNo ratings yet
- DLP in IctDocument3 pagesDLP in Ictreyna.sazon001No ratings yet
- Schema Refinement and Normal Forms: Database Management Systems, 3ed, R. Ramakrishnan and J. Gehrke 1Document19 pagesSchema Refinement and Normal Forms: Database Management Systems, 3ed, R. Ramakrishnan and J. Gehrke 1PRADNYA KASHIKARNo ratings yet
- Final ProjectDocument6 pagesFinal ProjectAmmar HussainNo ratings yet
- 320DLRR GMX ELE SchematicDocument14 pages320DLRR GMX ELE Schematicthaw3tar3minNo ratings yet
- الاستدامة في العمارةDocument17 pagesالاستدامة في العمارةkhawla zanganaNo ratings yet
- String/Arrays in JavaDocument7 pagesString/Arrays in JavaSaif HassanNo ratings yet
- Classroom Program 10B 2023 2024Document2 pagesClassroom Program 10B 2023 2024jester18 bordersyoNo ratings yet