Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Alkane 1
Alkane 1
Uploaded by
Dr Said Hassan0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views15 pagesAlkanes are saturated hydrocarbons that contain only carbon and hydrogen. The IUPAC naming system identifies alkanes by determining the parent chain, numbering the carbons in the chain, and noting any substituents and their locations. This systematic approach allows unique names for each alkane molecule.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentAlkanes are saturated hydrocarbons that contain only carbon and hydrogen. The IUPAC naming system identifies alkanes by determining the parent chain, numbering the carbons in the chain, and noting any substituents and their locations. This systematic approach allows unique names for each alkane molecule.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views15 pagesAlkane 1
Alkane 1
Uploaded by
Dr Said HassanAlkanes are saturated hydrocarbons that contain only carbon and hydrogen. The IUPAC naming system identifies alkanes by determining the parent chain, numbering the carbons in the chain, and noting any substituents and their locations. This systematic approach allows unique names for each alkane molecule.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 15
Alkanes
• Hydrocarbons are compounds that are only composed
of hydrogen and carbon.
Alkanes
• Saturated hydrocarbons do NOT contain any pi bonds.
• When communicating about molecules, each unique
molecule must have a unique name.
– The suffix ane is used for saturated hydrocarbons.
Naming Compounds – Alkanes
• In 1892, as the number of known molecules grew,
chemists decided that a SYSTEMATIC naming system
was needed.
– IUPAC (International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry)
system
• We can learn the IUPAC system instead of having to
memorize a common name for every molecule.
Naming Compounds – Alkanes
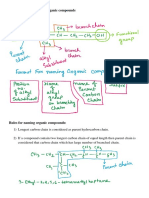
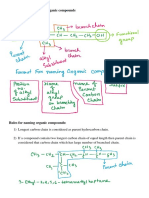
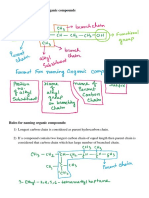
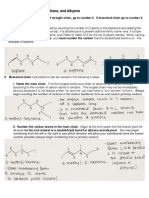
Finding The Parent Chain
• The IUPAC system:
1. Find the parent chain, the longest consecutive chain of
carbons.
Naming Compounds – Alkanes
Finding The Parent Chain
1. Find the parent chain, the longest consecutive chain of
carbons.
Naming Compounds – Alkanes
Finding The Parent Chain
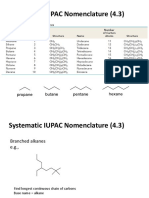
• Use Table 4.1 to look up the prefix that corresponds
to the number of carbons in the parent chain.
Naming Compounds – Alkanes
Finding The Parent Chain
1. Find the parent chain, the
longest consecutive chain of
carbons.
– If the parent chain has 9
carbons, the parent name is
nonane.
– It would be smart to memorize
the names for chains 1 to 10
carbons in length.
Naming Compounds – Alkanes
Finding The Parent Chain
1. Find the parent chain, the longest consecutive chain of
carbons.
– If there is more than one possible parent chain, choose the
one with the most substituents (side chains) attached .
Naming Compounds – Alkanes
Numbering the Parent Chain
3. Number in sequence the consecutive carbons in the
parent chain and assign a locant to each substituent.
– The number or LOCANT is used to communicate where each
substituent is attached to the parent chain.
• The molecules above are isomers, and they have the
same parent name. Their full name must
differ though, because they are not identical.
Naming Compounds – Alkanes
Numbering the Parent Chain
• Guidelines to follow when numbering the parent
chain:
1. If ONE substituent is present, number the parent chain so
that the substituent has the lowest number possible.
Naming Compounds – Alkanes
Numbering the Parent Chain
• Guidelines to follow when numbering the parent
chain:
2. When multiple substituents are present, number the parent
chain to give the first substituent the lowest number
possible.
Naming Compounds – Alkanes
Numbering the Parent Chain
• Guidelines to follow when numbering the parent
chain:
3. If there is a tie, then number the parent chain so that the
second locant gets the lowest number possible.
Naming Compounds – Alkanes
Numbering the Parent Chain
• Guidelines to follow when numbering the parent
chain:
– The same rules apply for cycloalkanes.
Naming Compounds – Alkanes
Assembling The Entire Name
• Guidelines to follow when numbering the parent chain
4. To assemble the complete name, assign a locant to each
substituent, and list them before the parent chain name in
alphabetical order
5. A prefix is used (di, tri, terta, penta, etc.) if multiple
substituents are identical
6. Prefixes are NOT used for alphabetical purposes, except for
the prefix “iso”
• Name the cycloalkanes:
Naming Compounds – Alkanes
Summary
1. Identify the parent chain, the longest consecutive
chain of carbons.
2. Identify and name substituents (side chains).
3. Number the parent chain and assign a locant (and
prefix if necessary) to each substituent.
– Give the first substituent the lowest number possible.
4. List the numbered substituents before the parent chain
name in alphabetical order.
– .
You might also like
- CCR Operating Manual DraftDocument271 pagesCCR Operating Manual Draftsathya perumal100% (5)
- Saturated HydrocarbonDocument60 pagesSaturated HydrocarbonMarvin K. Candor100% (1)
- Nmat Reviewer Orgchem PDFDocument15 pagesNmat Reviewer Orgchem PDFAlice Katrina100% (1)
- Science 20 Unit ADocument133 pagesScience 20 Unit Aapi-2079572300% (1)
- Isomers - All PDFDocument19 pagesIsomers - All PDFbencleeseNo ratings yet
- Alkane NomenclatureDocument1 pageAlkane NomenclatureRhian Geena VelasquezNo ratings yet
- Week 3.1 Slide DitaDocument32 pagesWeek 3.1 Slide DitaAnnisah MardiyyahNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 4 Alkanes and Cycloalkanes - HJMDocument78 pagesChapter - 4 Alkanes and Cycloalkanes - HJMMarisol AcostaNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry Alkynes PDFDocument4 pagesOrganic Chemistry Alkynes PDFDyaharra AgangNo ratings yet
- DENT1002-Lecture4-Alkanes and Cycloalkanes-I-BDoganDocument23 pagesDENT1002-Lecture4-Alkanes and Cycloalkanes-I-BDoganzlarsson127No ratings yet
- CA Lesson 2 AlkanesDocument31 pagesCA Lesson 2 AlkanesAlbaraaAliNo ratings yet
- Unit III Nomenclature of Organic CompondsDocument13 pagesUnit III Nomenclature of Organic CompondsdharaniNo ratings yet
- Organic-Chemistry HydrocarbonsDocument4 pagesOrganic-Chemistry Hydrocarbonsxyrruschloe06No ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Functional Groups in Organic ChemistryDocument115 pagesChapter 1 Functional Groups in Organic ChemistryZedo AnberbirNo ratings yet
- Hydrocarbons - AlkanesDocument16 pagesHydrocarbons - Alkanesdichosohubert548No ratings yet
- Hydrocarbons: ObjectivesDocument29 pagesHydrocarbons: Objectivesjohn ryan piolNo ratings yet
- AlkenaDocument21 pagesAlkenaIsmatul IzzatiNo ratings yet
- 14-04-20 - Nomenclature - Alkanes, AlkenesmamDocument21 pages14-04-20 - Nomenclature - Alkanes, AlkenesmamArthiNo ratings yet
- Systematic IUPAC Nomenclature (4.3)Document22 pagesSystematic IUPAC Nomenclature (4.3)Jennifer PatrickNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Organic Compounds (For Demo)Document36 pagesIntroduction To Organic Compounds (For Demo)Shalou Beth FlorendoNo ratings yet
- PHARM 122 6 AlkanesDocument38 pagesPHARM 122 6 AlkanesTrixie Anne FelicitasNo ratings yet
- Alkanes - Saturated Hydrocarbons: How To Name Organic Compounds Using The IUPAC RulesDocument6 pagesAlkanes - Saturated Hydrocarbons: How To Name Organic Compounds Using The IUPAC RulesK S RayuduNo ratings yet
- Alkanes - Saturated HydrocarbonsDocument9 pagesAlkanes - Saturated HydrocarbonsLâm Quách Trâm AnhNo ratings yet
- 2 Acid & Bases & Introduction To Organic ReactionsDocument59 pages2 Acid & Bases & Introduction To Organic ReactionsCesar CalderonNo ratings yet
- Naming of Alkanes, Alkenes and AlkynesDocument34 pagesNaming of Alkanes, Alkenes and AlkynesArt Caresosa-FernandoNo ratings yet
- HydrocarbonsDocument35 pagesHydrocarbonsCherine NoueihedNo ratings yet
- Topic 2Document20 pagesTopic 2acatcomelNo ratings yet
- ALKANESDocument4 pagesALKANESLiezel VillaruzNo ratings yet
- Alkanes and Cycloalkanes - PPTX 2Document57 pagesAlkanes and Cycloalkanes - PPTX 2eysabelagwenNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry: (Part One)Document104 pagesOrganic Chemistry: (Part One)eltoumNo ratings yet
- IUPAC Nomenclature of Organic CompoundsDocument2 pagesIUPAC Nomenclature of Organic CompoundsSimanta SharmaNo ratings yet
- IUPAC Nomenclature of Organic CompoundsDocument2 pagesIUPAC Nomenclature of Organic CompoundsSimanta SharmaNo ratings yet
- IUPAC Nomenclature of Organic CompoundsDocument2 pagesIUPAC Nomenclature of Organic CompoundsSimanta SharmaNo ratings yet
- Organic ChemistryDocument55 pagesOrganic ChemistryKim Taeha BTSNo ratings yet
- Hydrocarbons.2Document45 pagesHydrocarbons.2pasatiemporoseanneNo ratings yet
- Classification and Nomenclature of Organic CompoundsDocument15 pagesClassification and Nomenclature of Organic CompoundsМария МановаNo ratings yet
- CH 22: Organic ChemistryDocument35 pagesCH 22: Organic ChemistryRENE N. RAMILONo ratings yet
- Structural Theory in Organic Chemistry: Functional Groups and Chemical BondingDocument49 pagesStructural Theory in Organic Chemistry: Functional Groups and Chemical BondingMaria Claudia MartinezNo ratings yet
- Akanes Alkenes Alkynes Aromatic Systematic Nomenclature (IUPAC) ofDocument2 pagesAkanes Alkenes Alkynes Aromatic Systematic Nomenclature (IUPAC) ofJuaNn CarloSsNo ratings yet
- Nomenclature Organic IUPAC RulesDocument9 pagesNomenclature Organic IUPAC RulesSkyla DavisNo ratings yet
- IUPAC NomenclatureDocument4 pagesIUPAC NomenclatureNitesha MadhuNo ratings yet
- Chem Assignment 1Document4 pagesChem Assignment 1Protikal GamerNo ratings yet
- 02 - Detailed Naming Hydrocarbons PowerpointDocument24 pages02 - Detailed Naming Hydrocarbons Powerpoint1jerryzhouNo ratings yet
- Nomenclature JDDocument4 pagesNomenclature JDBose LogoNo ratings yet
- Nomenclature 1Document35 pagesNomenclature 1Anchal ChadhaNo ratings yet
- AlkenesAlkynes-nomenclature-and-properties-for - College-Bio StudentsDocument23 pagesAlkenesAlkynes-nomenclature-and-properties-for - College-Bio Studentshixevab276No ratings yet
- Hydrocarbon S: Group 3: Leader: Angela Dela Cruz Daphne Sy Sofia Anne Caoagas Alen Gem Red Christian Faith ColisDocument16 pagesHydrocarbon S: Group 3: Leader: Angela Dela Cruz Daphne Sy Sofia Anne Caoagas Alen Gem Red Christian Faith ColisDaphne SyNo ratings yet
- Mike's Videos - Organic Chemistry Lesson OutlineDocument64 pagesMike's Videos - Organic Chemistry Lesson Outlinekjk khkNo ratings yet
- (8.1) Learning MaterialDocument41 pages(8.1) Learning MaterialLuna VasquezNo ratings yet
- Nomenclature of Organic CompoundsDocument17 pagesNomenclature of Organic Compoundsubonge822No ratings yet
- IUPAC RulesDocument14 pagesIUPAC RulesIce BoyNo ratings yet
- Chem 1814 Review SheetsDocument14 pagesChem 1814 Review SheetsLinda Appiah OfosuheneNo ratings yet
- 4.1 Basic Concepts and HydrocarbonsDocument13 pages4.1 Basic Concepts and HydrocarbonsMariam BanoNo ratings yet
- Alkenes and AlkynesDocument20 pagesAlkenes and AlkynesABDULRAHMAN MOUSLLINo ratings yet
- EGF2042 Chapter 2 (Naming Organic Compound) ORIGINALDocument75 pagesEGF2042 Chapter 2 (Naming Organic Compound) ORIGINALhanis izzatiNo ratings yet
- Alkanes and Their StereochemistryDocument75 pagesAlkanes and Their Stereochemistry110003551 110ANo ratings yet
- 3.2 Unsaturated HydrocarbonsDocument20 pages3.2 Unsaturated HydrocarbonsVergil HashimotoNo ratings yet
- Alkanes and CycloalkanesDocument14 pagesAlkanes and Cycloalkaneskurdish movieNo ratings yet
- Alkenes and Alkynes: Lesson 3Document21 pagesAlkenes and Alkynes: Lesson 3AlbaraaAliNo ratings yet
- Intro To Organic Chemistry 2022 Sep 9Document59 pagesIntro To Organic Chemistry 2022 Sep 9SanaaNo ratings yet
- KC A4 Hydrocarbons Part 3 - AlkenesDocument13 pagesKC A4 Hydrocarbons Part 3 - Alkenesfmukuka12No ratings yet
- Al KynesDocument18 pagesAl KynesPrincess NavarroNo ratings yet
- Heterocyclic Systems with Bridgehead Nitrogen Atoms, Part 1From EverandHeterocyclic Systems with Bridgehead Nitrogen Atoms, Part 1William L. MosbyNo ratings yet
- What is Organic Chemistry? Chemistry Book 4th Grade | Children's Chemistry BooksFrom EverandWhat is Organic Chemistry? Chemistry Book 4th Grade | Children's Chemistry BooksNo ratings yet
- Carbon and Its CompoundsDocument10 pagesCarbon and Its CompoundsDr Said HassanNo ratings yet
- (Inter Between) Between Molecules: Intermolecular ForcesDocument42 pages(Inter Between) Between Molecules: Intermolecular ForcesDr Said HassanNo ratings yet
- Lec Aldehyde and KetoneDocument18 pagesLec Aldehyde and KetoneDr Said HassanNo ratings yet
- Allotropes of Carbon: Graphite Buckminsterfullerene DiamondDocument9 pagesAllotropes of Carbon: Graphite Buckminsterfullerene DiamondDr Said HassanNo ratings yet
- Chemistry of AminesDocument35 pagesChemistry of AminesDr Said HassanNo ratings yet
- Chapt20 LectureDocument53 pagesChapt20 LectureDr Said HassanNo ratings yet
- Petroleun Refinery Enforcement Manual PDFDocument661 pagesPetroleun Refinery Enforcement Manual PDFiperaltatorres100% (1)
- 4 AllDocument28 pages4 AllEtwo Xiao0% (1)
- Praktikum Kimia Organik 1 Uin Jakarta PkimDocument31 pagesPraktikum Kimia Organik 1 Uin Jakarta PkimNur BillahNo ratings yet
- Degree of Unsaturation.: Prepared By: Efefany Jane H. JumaritoDocument10 pagesDegree of Unsaturation.: Prepared By: Efefany Jane H. JumaritoJodie Mer DayamaNo ratings yet
- Applied Energy: Contents Lists Available atDocument17 pagesApplied Energy: Contents Lists Available atMohamed aliNo ratings yet
- Organic ChemistryDocument864 pagesOrganic Chemistryforumchemitry100% (1)
- Formal Report 1Document6 pagesFormal Report 1Patricia Denise OrquiaNo ratings yet
- Pyridine Improves Aluminum Triiodide Induced Selective Cleavage of Alkyl O-Hydroxyphenyl Ethers A Practical and EfficientDocument5 pagesPyridine Improves Aluminum Triiodide Induced Selective Cleavage of Alkyl O-Hydroxyphenyl Ethers A Practical and EfficientthegreatgbrothersNo ratings yet
- UNIT 10 Organic ChemistryDocument51 pagesUNIT 10 Organic ChemistryTristan PereyNo ratings yet
- Hasan Sayginel: Edexcel A Level Organic ChemistryDocument41 pagesHasan Sayginel: Edexcel A Level Organic ChemistryDEEBANNo ratings yet
- Final LD Correctons DoneeeDocument67 pagesFinal LD Correctons Doneeebarath sundarNo ratings yet
- Revision 2 Chapter 4-5Document125 pagesRevision 2 Chapter 4-5Siti NuraqidahNo ratings yet
- 1.4 Energetics Revision QuestionsDocument88 pages1.4 Energetics Revision QuestionsTheMagicCarpet0% (1)
- 2021 Uses of Organic Compounds Part1Document35 pages2021 Uses of Organic Compounds Part1Rachelle Anne VistalNo ratings yet
- Abu Dhabi University Mohammed Abdullah, 1054540 Dr. Jolly Jacob, Associate Professor of Chemistry, College of Arts and Science, Abu Dhabi UniversityDocument8 pagesAbu Dhabi University Mohammed Abdullah, 1054540 Dr. Jolly Jacob, Associate Professor of Chemistry, College of Arts and Science, Abu Dhabi UniversityCosmescu Mario FlorinNo ratings yet
- Organic Chem 2010Document107 pagesOrganic Chem 2010张浩天No ratings yet
- Hydrocarbon NotesDocument4 pagesHydrocarbon NotesSaumiaDevadasNo ratings yet
- Tablas Elucidacion Estructural (Protoì - N y Carbono)Document54 pagesTablas Elucidacion Estructural (Protoì - N y Carbono)Álex Martínez AriasNo ratings yet
- Preservation, Degradation, andDocument11 pagesPreservation, Degradation, andزهر البنفسج أحمدNo ratings yet
- Grade 9 (Outline Week 5) - 2ND QTRDocument10 pagesGrade 9 (Outline Week 5) - 2ND QTRJochelleNo ratings yet
- Alkane Theory Eng. Module-4Document16 pagesAlkane Theory Eng. Module-4Raju SinghNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry IgcseDocument31 pagesOrganic Chemistry Igcsenkoan12No ratings yet
- The Influence of Various Oxygenated Functional Groups in Carbonyl and Ether Compounds On Compression Ignition and Exhaust Gas EmissionsDocument15 pagesThe Influence of Various Oxygenated Functional Groups in Carbonyl and Ether Compounds On Compression Ignition and Exhaust Gas Emissionschris21091No ratings yet
- Metron Fuel Quality Final PDFDocument67 pagesMetron Fuel Quality Final PDFpersadanusantara100% (1)
- Test 1 Chem 3 c1-c3 Online 1Document17 pagesTest 1 Chem 3 c1-c3 Online 1HanaOmarNo ratings yet
- Aluminum-Promoted Tungstated Zirconia CatalystDocument12 pagesAluminum-Promoted Tungstated Zirconia CatalystzahiraNo ratings yet