Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Adiabatic Saturation Temperature
Adiabatic Saturation Temperature
Uploaded by
Nuzhat Amber0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
20 views4 pagesThis document discusses adiabatic saturation temperature and the Lewis relation for air-water systems. It provides equations showing that the wet-bulb temperature equals the adiabatic saturation temperature when the psychrometric ratio is 1. For low humidity air, the psychrometric ratio is approximately 1, so the wet-bulb and adiabatic saturation temperatures are also approximately equal. The Lewis relation can be derived from both the Reynolds and Chilton-Colburn analogies for heat and mass transfer and is valid for air-water systems even when Prandtl and Schmidt numbers are not equal to 1.
Original Description:
Original Title
Lecture-2B.pptx
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document discusses adiabatic saturation temperature and the Lewis relation for air-water systems. It provides equations showing that the wet-bulb temperature equals the adiabatic saturation temperature when the psychrometric ratio is 1. For low humidity air, the psychrometric ratio is approximately 1, so the wet-bulb and adiabatic saturation temperatures are also approximately equal. The Lewis relation can be derived from both the Reynolds and Chilton-Colburn analogies for heat and mass transfer and is valid for air-water systems even when Prandtl and Schmidt numbers are not equal to 1.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
20 views4 pagesAdiabatic Saturation Temperature
Adiabatic Saturation Temperature
Uploaded by
Nuzhat AmberThis document discusses adiabatic saturation temperature and the Lewis relation for air-water systems. It provides equations showing that the wet-bulb temperature equals the adiabatic saturation temperature when the psychrometric ratio is 1. For low humidity air, the psychrometric ratio is approximately 1, so the wet-bulb and adiabatic saturation temperatures are also approximately equal. The Lewis relation can be derived from both the Reynolds and Chilton-Colburn analogies for heat and mass transfer and is valid for air-water systems even when Prandtl and Schmidt numbers are not equal to 1.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 4
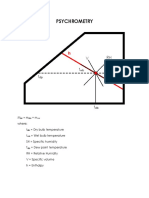
Adiabatic Saturation Temperature
Thus, following are relations for wet-bulb temp
and adiabatic saturation temps. respectively:
(1)
(2)
Thus wet-bulb temp is equal to adiabatic saturation
temp when s=h/(hDρA)
h/(hDρAs)=b is called the psychrometric ratio. Eq (2)
above can also be called as eq. of adiabatic cooling
line)
Adiabatic Saturation Temperature
For most air and organic liquids b=1.3-2.5 i.e. wet-
bulb temp is higher than the adiabatic saturation
temp.
If
Pr=Sc=1 for any system, then from Lewis
relation,
(3)
Where Cp and density are of vapor phase (air
including water vapors).
Adiabatic Saturation Temperature
For
low humidity, C ≃s and ≃
p A, So, we can write
from above equation
(4)
⇒
. For low humidity, Cp≃s and b=1 i.e. for air-
water system, wet-bulb temp. equals the
adiabatic saturation temp.
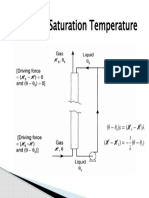
Lewis Relation Revisit
Lewis relation can be obtained from both the Reynold
and Chilton Colburn analogy. From Chilton-Colburn
analogy, see Cengel article 14-9 for air water system
In Reynold Analogy when ʋ=DAB=α. So, Pr=Sc=Le=1
We can prove that
Nu=Sh i.e.
hL/k=hDL/DAB=hDL/ α =hDL/(k/ρCp)
⇒h=hDρCp
By Chilton-Colburn Analogy, above relation is valid
for air-water system even if Pr≠Sc ≠1since then
(α/DAB)2/3⋍1
You might also like
- The Relationship Between Relative Humidity and The Dewpoint Temp in Moist Air PDFDocument9 pagesThe Relationship Between Relative Humidity and The Dewpoint Temp in Moist Air PDFniqutomoNo ratings yet
- Qpedia Nov08 Estimating The Effect of Moist Air On Natural Convection Heat TransferDocument7 pagesQpedia Nov08 Estimating The Effect of Moist Air On Natural Convection Heat TransferGe YemoNo ratings yet
- 02 Psychrometric CalculationDocument25 pages02 Psychrometric Calculationmarkjosephserrano0418No ratings yet
- Lesson 7-Properties of Gas and Vapor MixturesDocument5 pagesLesson 7-Properties of Gas and Vapor MixturesOrley G Fadriquel0% (1)
- Psychrometry: H MH MH MH Etc P P P P EtcDocument9 pagesPsychrometry: H MH MH MH Etc P P P P EtcAhmed EldalyNo ratings yet
- Unit 1.a Dynamic Equations For Moist ConvectionDocument46 pagesUnit 1.a Dynamic Equations For Moist Convectionruth ranselNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 StudentDocument25 pagesChapter 1 StudentAbdalhady JoharjiNo ratings yet
- The Relationship Between Relative Humidity and The Dewpoint Temperature in Moist AirDocument9 pagesThe Relationship Between Relative Humidity and The Dewpoint Temperature in Moist AirValentinus GalihNo ratings yet
- Drying 2Document17 pagesDrying 2jY-renNo ratings yet
- Week 4Document26 pagesWeek 4abdullahghaya124No ratings yet
- PsychrometricesDocument9 pagesPsychrometriceskawsar_002No ratings yet
- Saturated Adiabatic Processes: JA Curry, Georgia Institute of Technology, Atlanta, GA, USADocument4 pagesSaturated Adiabatic Processes: JA Curry, Georgia Institute of Technology, Atlanta, GA, USAJean-Christophe RautNo ratings yet
- (Class 1-5) Lectures-1Document38 pages(Class 1-5) Lectures-1Aniruddha BagchiNo ratings yet
- ETD Chapter 5Document14 pagesETD Chapter 5Vasantha SeelanNo ratings yet
- Lecture # 13: Dr. Muzaffar AliDocument41 pagesLecture # 13: Dr. Muzaffar Alikamran bhatNo ratings yet
- Cooling TowerDocument11 pagesCooling TowerinstrutechNo ratings yet
- Antoine'sDocument3 pagesAntoine'sGarcia RaphNo ratings yet
- 11 PsychrometricsDocument13 pages11 PsychrometricsImranAtheeqNo ratings yet
- Slides MIN 106 Air ConditioningDocument55 pagesSlides MIN 106 Air ConditioningaagrawalNo ratings yet
- CATAPANG, Jamiel S. - Experiment 4 (Air Properties - A4)Document25 pagesCATAPANG, Jamiel S. - Experiment 4 (Air Properties - A4)Jamiel CatapangNo ratings yet
- 01-Handout-High Speed FundamentalsDocument4 pages01-Handout-High Speed FundamentalsMesum IrfaniNo ratings yet
- 02 Thermodynamics of Moist AirDocument7 pages02 Thermodynamics of Moist AirGonzalo MartinezNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 General ConceptsDocument9 pagesLecture 1 General ConceptsemresiNo ratings yet
- Santillan LBYME3B Laboratory Report 03Document14 pagesSantillan LBYME3B Laboratory Report 03Nygel Gian SantillanNo ratings yet
- Absolute and Specific Humidity: Air Dry of Mass Vapor Water of Mass R Ratio MixingDocument12 pagesAbsolute and Specific Humidity: Air Dry of Mass Vapor Water of Mass R Ratio MixingguloNo ratings yet
- Engineering Mathematics by K.A. StroudDocument16 pagesEngineering Mathematics by K.A. Stroudharrisondaniel0415No ratings yet
- 8.1 Psychrometry and Thermodynamic Properties of Moist AirDocument6 pages8.1 Psychrometry and Thermodynamic Properties of Moist AirJayr bangalaoNo ratings yet
- Humidification and DryingDocument45 pagesHumidification and DryingNegese TeklearegayNo ratings yet
- Compressible Flow ReviewDocument8 pagesCompressible Flow Reviewthehighlife1080No ratings yet
- 2 Psychrometry PDFDocument24 pages2 Psychrometry PDFFaiz FauziNo ratings yet
- Psychrometrics Psychrometrics, Psychrometry, and Hygrometry Are Names For The Field ofDocument8 pagesPsychrometrics Psychrometrics, Psychrometry, and Hygrometry Are Names For The Field ofFaruk HosenNo ratings yet
- Lecture 7. HumidificationDocument29 pagesLecture 7. HumidificationNOBLEMAN100% (1)
- Psychrometry: V RH T T SHDocument13 pagesPsychrometry: V RH T T SHKAL ELNo ratings yet
- 01 - Lecture (August 4)Document15 pages01 - Lecture (August 4)Samarth RawatNo ratings yet
- PsicrometriaDocument68 pagesPsicrometriaEddy FarfanNo ratings yet
- Esci241 Lesson06 HumidityDocument8 pagesEsci241 Lesson06 HumiditySteven ScottNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 2 Psychrometry and Air-ConditioningDocument14 pagesCHAPTER 2 Psychrometry and Air-ConditioningMdnor Rahim0% (1)
- Rac 6-10 Week Lecture SlidesDocument82 pagesRac 6-10 Week Lecture Slidesmfnzk1980No ratings yet
- Lecture11 PDFDocument12 pagesLecture11 PDFEleuterio MontaNo ratings yet
- L8 PsychrometryDocument51 pagesL8 PsychrometrylasldnjNo ratings yet
- L11 (Psychrometry)Document25 pagesL11 (Psychrometry)Kavin KabilanNo ratings yet
- Lec 1. Gas-Vapor - MixtureDocument38 pagesLec 1. Gas-Vapor - MixtureYonatan NegusuNo ratings yet
- The Earth-Atmosphere System: Atmospheric CompositionDocument11 pagesThe Earth-Atmosphere System: Atmospheric CompositionDarianys MirandaNo ratings yet
- PSIKROMETRIDocument34 pagesPSIKROMETRIrikibinNo ratings yet
- Version: 008 Date: Nov. 12, 1998 UpdatedDocument22 pagesVersion: 008 Date: Nov. 12, 1998 UpdatedDavidTauNo ratings yet
- ME 331 Refrigeration & Air Conditioning: M AsfandyarDocument30 pagesME 331 Refrigeration & Air Conditioning: M AsfandyarSuaid Tariq BalghariNo ratings yet
- BTD Module 5 PDFDocument20 pagesBTD Module 5 PDFAkshay ShettyNo ratings yet
- PM Chap3 Thermodynamic Lecture6Document34 pagesPM Chap3 Thermodynamic Lecture6nisAfiqahNo ratings yet
- Gas-Vapor Mixtures: Diah Susanti, PH.DDocument26 pagesGas-Vapor Mixtures: Diah Susanti, PH.DDiana KamaliyahNo ratings yet
- PsychrometryDocument16 pagesPsychrometryMuhammad Saad Shaukat AhmadNo ratings yet
- School of Physics and Astronomy Junior Honours Thermodynamics GJA 2013-2014Document4 pagesSchool of Physics and Astronomy Junior Honours Thermodynamics GJA 2013-2014Babu AravindNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 (Humidity and Solubility)Document39 pagesChapter 3 (Humidity and Solubility)Riham Fuad Bazkhan Al ZadjaliNo ratings yet
- Compressible FlowDocument4 pagesCompressible Flowcmraj2020No ratings yet
- Water VaporDocument2 pagesWater VaporNagarjuna Reddy NukalaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 19 (Humidification Operations)Document25 pagesChapter 19 (Humidification Operations)adekNo ratings yet
- Energies 12 03266Document14 pagesEnergies 12 03266BillyNo ratings yet
- Mech1442851738363 PDFDocument57 pagesMech1442851738363 PDFMonevNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Gas Vapor MixtureDocument47 pagesChapter 2 - Gas Vapor MixturenunuNo ratings yet
- How To Add A CITI Course v2Document2 pagesHow To Add A CITI Course v2Nuzhat AmberNo ratings yet
- ME7310 W21 SyllabusDocument4 pagesME7310 W21 SyllabusNuzhat AmberNo ratings yet
- ME7310 Course Learning ObjectivesDocument28 pagesME7310 Course Learning ObjectivesNuzhat AmberNo ratings yet
- Application For Admission 2020-2021 Academic Year Master ProgramsDocument6 pagesApplication For Admission 2020-2021 Academic Year Master ProgramsNuzhat AmberNo ratings yet
- Deadline: 18:00 (6:00 PM) Baku Time On Wednesday, April 15, 2020Document2 pagesDeadline: 18:00 (6:00 PM) Baku Time On Wednesday, April 15, 2020Nuzhat AmberNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2ADocument1 pageLecture 2ANuzhat AmberNo ratings yet
- Electrochemical Machining of Metal Plates: J. F. Cooper, M. C. EvansDocument22 pagesElectrochemical Machining of Metal Plates: J. F. Cooper, M. C. EvansNuzhat AmberNo ratings yet