Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Review Metals 2
Review Metals 2
Uploaded by
Nicolas Jay0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
32 views12 pagesThe document summarizes the process of extracting iron from its ore, hematite. It discusses that coke is used both to increase heat in the furnace through reaction with oxygen, and to reduce the iron oxide to iron through reaction with carbon monoxide. Limestone is also used, being decomposed to calcium oxide which removes silicon dioxide impurities from the ore. Electrolysis is described as using an electric current to separate ions in an electrolyte, with reduction occurring at the cathode and oxidation at the anode.
Original Description:
Original Title
review metals 2.ppt
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document summarizes the process of extracting iron from its ore, hematite. It discusses that coke is used both to increase heat in the furnace through reaction with oxygen, and to reduce the iron oxide to iron through reaction with carbon monoxide. Limestone is also used, being decomposed to calcium oxide which removes silicon dioxide impurities from the ore. Electrolysis is described as using an electric current to separate ions in an electrolyte, with reduction occurring at the cathode and oxidation at the anode.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as ppt, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
32 views12 pagesReview Metals 2
Review Metals 2
Uploaded by
Nicolas JayThe document summarizes the process of extracting iron from its ore, hematite. It discusses that coke is used both to increase heat in the furnace through reaction with oxygen, and to reduce the iron oxide to iron through reaction with carbon monoxide. Limestone is also used, being decomposed to calcium oxide which removes silicon dioxide impurities from the ore. Electrolysis is described as using an electric current to separate ions in an electrolyte, with reduction occurring at the cathode and oxidation at the anode.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as ppt, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 12
Last review of metals.
• Areas of emphasis today in other words lesson
objectives.
• The name and purpose of all reactions during
extraction of iron
• The products of extraction of iron including the
waste gases.
• What happens during electrolysis (movement of
ions during electrolysis then Reduction and
oxidation as used in electrolysis the)
1 of 26 © Boardworks Ltd 2019
Extraction of iron
• Hematite is the iron ore
• Chemical name of hematite iron oxide
(Fe2O3)
• The main impurity in hematite is sand which
is chemically silicon dioxide (SiO2).
• Materials used to extract iron are Coke
(carbon), Oxygen and limestone.
2 of 26 © Boardworks Ltd 2019
Uses of each raw material
• Coke is used to perform
two roles
1.To increase heat in the furnace
as it reacts with plenty of
oxygen at the bottom of the
furnace.
C(s) + O2(g) → CO2(g)
3 of 26 © Boardworks Ltd 2019
Second function of coke
2. To reduce the iron oxide to iron.
How?
In the middle of the furnace, there is less oxygen so
the coke in the middle of the furnace reacts with
less oxygen forming carbon monoxide.
C+ ½ O2 → CO
It is this carbon monoxide which reduces
the ore (Fe2O3) to iron.
Fe2O3 + CO → Fe + CO2
4 of 26 © Boardworks Ltd 2019
Limestone
• The chemical name of limestone is calcium
carbonate (CaCO3)
• The heat from the bottom of the furnace
breaks down limestone. This is known as a
decomposition reaction.
• Decomposition is when a compound splits
into other compounds without reacting with
any other substance.
• CaCO3 (s) ---> CaO (s) + CO2 (g)
5 of 26 © Boardworks Ltd 2019
So how is limestone used?
• Limestone is not used as limestone during
extraction of iron but rather one of the
products of this reaction is used.
• Which one is it?
• The calcium oxide.
• What does calcium oxide do?
• It removes the acidic impurity in the ore
(silicon dioxide).
• This reaction is a neutralization reaction
because the calcium oxide is basic while the
impurity is acidic
6 of 26 © Boardworks Ltd 2019
How are the impurities removed and
carbon content reduced?
• Iron from the furnace still contains some
impurities.
• To reduce the amount of carbon we use
oxygen which reacts with carbon forming
carbon dioxide.
• The silicon oxide is removed in the same
way as we have just seen (using calcium
oxide)
7 of 26 © Boardworks Ltd 2019
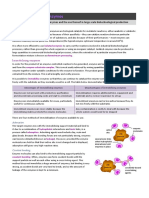
Electrolysis
• Electrolyte. Breaks down when electricity is
passed through it.
• Example Al2O3 Al3+ + O2-
• Cations are the positive ions e.g. Al3+
• Anions are the negative ions e.g. O2-
• Electrode: a point where electrons enter or
leave the electrolyte e.g. graphite
electrodes
• Cathode is negative electrode
• Anode is positive electrode.
8 of 26 © Boardworks Ltd 2019
What happens during electrolysis
• The ions from the electrolyte move to
oppositely charged electrodes.
• Example
• The Al3+ (aluminium ions) move to the
cathode
• The O2- (oxide ions) move to the
anode
9 of 26 © Boardworks Ltd 2019
What happens at the cathode and anode?
• Anode is loss of electrons
• 2O2- -2e O2
• Cathode is gain of electrons
• Al3+ + 3e- Al (reduction
10 of 26 © Boardworks Ltd 2019
Extracting aluminium – redox equations
What redox processes occur at the
electrodes during the electrolysis
of aluminium oxide (Al2O3)?
At the negative electrode:
Al3+ + 3e- Al (reduction)
At the positive electrode:
2O2- O2 + 4e- (oxidation)
What is the overall equation for the extraction of aluminium
by electrolysis?
aluminium oxide aluminium + oxygen
2 Al2O3 (l) 4 Al (l) + 3 O2 (g)
11 of 26 © Boardworks Ltd 2019
If we stay focused and time allows…
• We will do a flame test lab and see the
different colours of flames given out
when different metals burn in air. It is
one way scientists used to distinguish
metals. If not today, we can do it on
Monday
12 of 26 © Boardworks Ltd 2019
You might also like
- Tietz Fundamentals of Clinical Chemistry and Molecular Diagnostics e Book 8th Edition Ebook PDF VersionDocument62 pagesTietz Fundamentals of Clinical Chemistry and Molecular Diagnostics e Book 8th Edition Ebook PDF Versionjack.murgia17598% (40)
- General Organic and Biological Chemistry 3rd EditionDocument550 pagesGeneral Organic and Biological Chemistry 3rd Editionjoanna marie mondejarNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Chemistry - Extraction and Uses of MetalsDocument21 pagesIGCSE Chemistry - Extraction and Uses of MetalsChemistryKlipz90% (10)
- 10.2 MetalsDocument6 pages10.2 MetalshappyproofNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6.3 and 6.4Document16 pagesChapter 6.3 and 6.4jessenia.tutor2010No ratings yet
- Further ElectrochemistryDocument31 pagesFurther ElectrochemistryleanneNo ratings yet
- Extracting MetalsDocument27 pagesExtracting MetalsJojo Hany100% (1)
- Metals KS3 4 Iron and Aluminium Extraction Methods Info SheetDocument5 pagesMetals KS3 4 Iron and Aluminium Extraction Methods Info SheetHappy NthakomwaNo ratings yet
- Extracting MetalsDocument27 pagesExtracting MetalsSơn Minh LươngNo ratings yet
- Extracting MetalsDocument27 pagesExtracting MetalsMadan Yadav100% (2)
- Potassium Sodium Lithium Calcium Magnesium Aluminium Carbon Zinc Iron Tin Lead Hydrogen Copper Silver Gold PlatinumDocument28 pagesPotassium Sodium Lithium Calcium Magnesium Aluminium Carbon Zinc Iron Tin Lead Hydrogen Copper Silver Gold PlatinumsomdattachaudhariNo ratings yet
- Extraction of MetalsDocument5 pagesExtraction of MetalsALVINNo ratings yet
- General PrinciplesDocument14 pagesGeneral PrinciplesRaena SwamiNo ratings yet
- Aluminium MetallurgyDocument3 pagesAluminium MetallurgyShubham ShuklaNo ratings yet
- The Extraction of Metals: Mr. AgachaDocument9 pagesThe Extraction of Metals: Mr. AgachaMasaria LowlandNo ratings yet
- A Levl ChemDocument4 pagesA Levl ChemShah SaqibNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 - Extraction of MetalsDocument24 pagesLesson 1 - Extraction of MetalsKashifNo ratings yet
- Extraction of AluminiunDocument5 pagesExtraction of AluminiunMAKNNIE KPOPNo ratings yet
- Extraction of Aluminium From BauxiteDocument7 pagesExtraction of Aluminium From BauxiteMAKNNIE KPOPNo ratings yet
- PRODUCTION OF STEEL-Lecture 2Document68 pagesPRODUCTION OF STEEL-Lecture 2Nyanda MalashiNo ratings yet
- Extracting Aluminum Using ElectrolysisDocument4 pagesExtracting Aluminum Using ElectrolysisSaed ELkelanyNo ratings yet
- Extracting Aluminum Using ElectrolysisDocument4 pagesExtracting Aluminum Using ElectrolysisSaed ELkelanyNo ratings yet
- Xii em 2022 - 23Document89 pagesXii em 2022 - 23Karan MishraNo ratings yet
- S.4 REDOX REACTIONS Part OneDocument15 pagesS.4 REDOX REACTIONS Part Onearonyosi07No ratings yet
- Metalurgi ProsesDocument29 pagesMetalurgi ProseswisnukawerianNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Extra ClassDocument7 pagesChemistry Extra Classjuan barrettNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1Document21 pagesLesson 1Durairaj RagupathikumarNo ratings yet
- Explanation Text: By: Dwiyanti Octaviani Farrah Nabila F Malik Farhan Nazhara Ardhan Roikhan Azhari Syifa FauziahDocument28 pagesExplanation Text: By: Dwiyanti Octaviani Farrah Nabila F Malik Farhan Nazhara Ardhan Roikhan Azhari Syifa Fauziahsyifa fauziahNo ratings yet
- Metallurgy Notes For IIT JEE PDFDocument17 pagesMetallurgy Notes For IIT JEE PDFADIL RIZVINo ratings yet
- Hall Heroult Process and Hooper ProcessDocument9 pagesHall Heroult Process and Hooper ProcesssaadNo ratings yet
- Extraction of Metals Cambridge OLDocument3 pagesExtraction of Metals Cambridge OLPius VictoriaNo ratings yet
- Metals in SoilDocument12 pagesMetals in SoilHina AftabNo ratings yet
- Extraction of MetalsDocument55 pagesExtraction of MetalsCatriona Chaikin100% (1)
- Reactivity SeriesDocument10 pagesReactivity SeriesZeedan MohammedNo ratings yet
- Topic 9.3Document10 pagesTopic 9.3Yahya ShukurovNo ratings yet
- Extraction of Metals and RecyclingDocument25 pagesExtraction of Metals and Recyclingchong56No ratings yet
- ChemDocument22 pagesChemDivya RajendranNo ratings yet
- Lec 8-12 - Prodution of MetalsDocument183 pagesLec 8-12 - Prodution of MetalsAli HassanNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes in Metals and PolymerDocument14 pagesLecture Notes in Metals and PolymerjoyandreaNo ratings yet
- Sat PalDocument4 pagesSat PalAmit Rashmi MishraNo ratings yet
- Edited Namma Kalvi 12th Chemistry Unit 1267 Study Material em 215233 PDFDocument53 pagesEdited Namma Kalvi 12th Chemistry Unit 1267 Study Material em 215233 PDFAakaash C.K.No ratings yet
- Lecture 8Document42 pagesLecture 8mohammed ramadanNo ratings yet
- Edited Namma Kalvi 12th Chemistry Unit 1267 Study Material em 215233Document53 pagesEdited Namma Kalvi 12th Chemistry Unit 1267 Study Material em 215233Aakaash C.K.No ratings yet
- Oxidation and ReductionDocument8 pagesOxidation and Reductionray469859No ratings yet
- Metallurgy NotesDocument4 pagesMetallurgy Notesrajeevrai692No ratings yet
- 6 - Electrolysis and Its UsesDocument44 pages6 - Electrolysis and Its UsesSubhrajyoti Banerjee0% (1)
- IndustrialchemistryDocument2 pagesIndustrialchemistryKimtuyen TranNo ratings yet
- Electrochemistry Grade 10Document55 pagesElectrochemistry Grade 10ERNESTA JESSANo ratings yet
- Kuliah Metalurgi Ekstraksi 2 Oktober 2020Document108 pagesKuliah Metalurgi Ekstraksi 2 Oktober 2020Benjamin SimarmataNo ratings yet
- Extracting Metals From Their OresDocument7 pagesExtracting Metals From Their OresChuahSiewHoonNo ratings yet
- MetalsDocument10 pagesMetalsPeterNo ratings yet
- b4b13229 14 Metals and Their ExtractionDocument21 pagesb4b13229 14 Metals and Their ExtractionMuhammad UzairNo ratings yet
- Aluminium ExtractionDocument5 pagesAluminium ExtractionMiguel Thaxter100% (1)
- Cambridge IGCSE Chemistry Topic 10: Metals: ExtractionDocument3 pagesCambridge IGCSE Chemistry Topic 10: Metals: Extractionasif shawNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Metal ExtractionDocument15 pagesIntroduction To Metal ExtractionschlemielzNo ratings yet
- Y10T2W2L1Document29 pagesY10T2W2L1sohaila ibrahimNo ratings yet
- 10 Unit 3 PrintDocument10 pages10 Unit 3 PrintClaresse NavarroNo ratings yet
- Metallurgy Theory PDFDocument17 pagesMetallurgy Theory PDFPrajwal TalwalkarNo ratings yet
- 2.6 RedoxDocument41 pages2.6 RedoxSWNCYANIDANo ratings yet
- Science Form 4 Chapter 5Document20 pagesScience Form 4 Chapter 5cellea98rose100% (2)
- C20 Extraction of MetalsDocument31 pagesC20 Extraction of MetalsKris DookharanNo ratings yet
- Extractive Metallurgy 2: Metallurgical Reaction ProcessesFrom EverandExtractive Metallurgy 2: Metallurgical Reaction ProcessesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- 4 Industrial EnzymesDocument2 pages4 Industrial EnzymesNicolas JayNo ratings yet
- Gene Therapy: Using Somatic Cell Therapy and Germline Cell Therapy To Treat Genetic DisordersDocument2 pagesGene Therapy: Using Somatic Cell Therapy and Germline Cell Therapy To Treat Genetic DisordersNicolas JayNo ratings yet
- Sanger Sequencing and The Polymerase Chain ReactionDocument4 pagesSanger Sequencing and The Polymerase Chain ReactionNicolas JayNo ratings yet
- Biotechnology and Batch CulturesDocument3 pagesBiotechnology and Batch CulturesNicolas JayNo ratings yet
- Animal Cloning: Artificial Clones in Animals, and A Comparison of Reproductive and Non-Reproductive CloningDocument2 pagesAnimal Cloning: Artificial Clones in Animals, and A Comparison of Reproductive and Non-Reproductive CloningNicolas JayNo ratings yet
- Why Are Some of Us So Alike, and Others So Different?Document28 pagesWhy Are Some of Us So Alike, and Others So Different?Nicolas JayNo ratings yet
- Cellular Transport Unit Passive TransportDocument23 pagesCellular Transport Unit Passive TransportNicolas JayNo ratings yet
- Lewis TructuresDocument12 pagesLewis TructuresNicolas JayNo ratings yet
- Lewis and VSEPRDocument60 pagesLewis and VSEPRNicolas JayNo ratings yet
- 6A Electrochemistry - AnswerDocument6 pages6A Electrochemistry - AnswerWong Wai Lun100% (1)
- Nursing Care PlanDocument5 pagesNursing Care PlanCharlie AbagonNo ratings yet
- Electrolysis of Aqeous SolutionDocument6 pagesElectrolysis of Aqeous Solutionanon_383714618No ratings yet
- Date Cues Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Basis Goal of Care Nursing Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesDate Cues Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Basis Goal of Care Nursing Intervention Rationale Evaluationkimglaidyl bontuyanNo ratings yet
- NEET AIPMT 2010 Preliminary Original Solved Question PaperDocument48 pagesNEET AIPMT 2010 Preliminary Original Solved Question PaperShaileshNo ratings yet
- Sakthi Sadhana Solutions: Chemicals ListDocument1 pageSakthi Sadhana Solutions: Chemicals ListJagannathan SNo ratings yet
- Development of Electrochemical Micromachining (ECMM) SetupDocument6 pagesDevelopment of Electrochemical Micromachining (ECMM) SetupSilviu BuzeaNo ratings yet
- Maintenance Guide EA-5,3,2Document17 pagesMaintenance Guide EA-5,3,2Wolaé Mathurin Edmond Amegandjin100% (1)
- WRBFS407BDocument100 pagesWRBFS407BIon Logofătu AlbertNo ratings yet
- Electrochemistry-Subjective TesTDocument1 pageElectrochemistry-Subjective TesTKanishq meenaNo ratings yet
- Fluids and Electrolytes Study GuideDocument13 pagesFluids and Electrolytes Study GuideElizabeth McKeeNo ratings yet
- JCI HospitalStandards - 7thedition - FAQ - 120820Document42 pagesJCI HospitalStandards - 7thedition - FAQ - 120820MeilaniBritia100% (2)
- User Guide DO Meter Hanna 9417Document2 pagesUser Guide DO Meter Hanna 9417Rizka Putri Aprilia StundetionNo ratings yet
- Biopotential ElectrodesDocument35 pagesBiopotential ElectrodesakshayNo ratings yet
- Magnesium-Solution Phase Catholyte Seawater Electrochemical SystemDocument5 pagesMagnesium-Solution Phase Catholyte Seawater Electrochemical SystemChemical Ferdi IzzecsonNo ratings yet
- Cathodic Protection Module 1-00Document24 pagesCathodic Protection Module 1-00razoumihineNo ratings yet
- Renin Angiotensin Aldosterone SystemDocument4 pagesRenin Angiotensin Aldosterone SystemYia KyNo ratings yet
- LVP Dan SVPDocument16 pagesLVP Dan SVPLutfia husainNo ratings yet
- Chemical Reaction and EquationDocument15 pagesChemical Reaction and Equationsanjayjoshi.jnvNo ratings yet
- Metal Air Battery - An Overview - ScienceDirect TopicsDocument10 pagesMetal Air Battery - An Overview - ScienceDirect TopicsSenen100% (1)
- Electrolysis of AueqousDocument8 pagesElectrolysis of AueqousSelinawong Win Jing SelinawongNo ratings yet
- Alternative Composite Polymer Electrolyte For SSBDocument10 pagesAlternative Composite Polymer Electrolyte For SSB1DS19CH002 Akash SamantaNo ratings yet
- Conductors: NCERT Notes For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 3: ElectrochemistryDocument12 pagesConductors: NCERT Notes For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 3: ElectrochemistryDev Printing SolutionNo ratings yet
- The Influence of PH On Zeta PotentialDocument24 pagesThe Influence of PH On Zeta PotentialJai MurugeshNo ratings yet
- BSC Bed 2 Year Chemistry SyllabusDocument6 pagesBSC Bed 2 Year Chemistry Syllabuslelico724No ratings yet
- Chapter - 012 Fluid and Electrolytes (Edited) PabrnmanDocument31 pagesChapter - 012 Fluid and Electrolytes (Edited) PabrnmanGian DimayugaNo ratings yet
- Development of Solid-State Reference Electrode Based On Sodium Polyanethol Sulfonate Immobilised On Cellulose AcetateDocument19 pagesDevelopment of Solid-State Reference Electrode Based On Sodium Polyanethol Sulfonate Immobilised On Cellulose AcetateZel Cys CivilEngineeringNo ratings yet
- Electrolytic Polishing of Metallographic Specimens: Standard Guide ForDocument13 pagesElectrolytic Polishing of Metallographic Specimens: Standard Guide ForDhavalNo ratings yet