Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Solution of Nonlinear Equations: Lecture (III) : Dr. Jie Zou PHY 3320 1
Solution of Nonlinear Equations: Lecture (III) : Dr. Jie Zou PHY 3320 1
Uploaded by
Jasminee son0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
24 views5 pagesThe document discusses the secant method for solving nonlinear equations numerically. It provides:
1) An outline of the secant method algorithm which uses a backward finite difference approximation for the derivative and finds successive approximations starting from two initial guesses.
2) Details of the secant method algorithm including computing the next approximation and checking for convergence.
3) Notes that the secant method is similar to Newton's method but uses a backward difference for the derivative, and may not always converge.
4) An example of applying the secant method to find the root of a given equation, starting from two initial guesses.
Original Description:
Original Title
Secant.ppt
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses the secant method for solving nonlinear equations numerically. It provides:
1) An outline of the secant method algorithm which uses a backward finite difference approximation for the derivative and finds successive approximations starting from two initial guesses.
2) Details of the secant method algorithm including computing the next approximation and checking for convergence.
3) Notes that the secant method is similar to Newton's method but uses a backward difference for the derivative, and may not always converge.
4) An example of applying the secant method to find the root of a given equation, starting from two initial guesses.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as ppt, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
24 views5 pagesSolution of Nonlinear Equations: Lecture (III) : Dr. Jie Zou PHY 3320 1
Solution of Nonlinear Equations: Lecture (III) : Dr. Jie Zou PHY 3320 1
Uploaded by
Jasminee sonThe document discusses the secant method for solving nonlinear equations numerically. It provides:
1) An outline of the secant method algorithm which uses a backward finite difference approximation for the derivative and finds successive approximations starting from two initial guesses.
2) Details of the secant method algorithm including computing the next approximation and checking for convergence.
3) Notes that the secant method is similar to Newton's method but uses a backward difference for the derivative, and may not always converge.
4) An example of applying the secant method to find the root of a given equation, starting from two initial guesses.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as ppt, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 5
Chapter 2
Solution of Nonlinear Equations:
Lecture (III)
Dr. Jie Zou PHY 3320 1
Outline
Numerical methods
(3) Secant method
Dr. Jie Zou PHY 3320 2
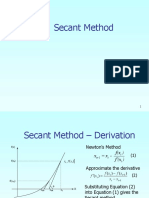
Secant method
f xi f xi 1 Secant method algorithm: An
f xi approximation to the derivative:
xi xi 1
f xi xi xi 1
xi 1 xi xi f xi , i 2, 3, 4
f xi f xi f xi 1
1. Start with two initial guesses x1
and x2 and . set i = 2.
2. Find the new approximation, xi+1.
xi xi 1
xi 1 xi f xi
f xi f x
i 1
3. Verify the convergence. If |
f(xi+1)|, stop the process by
taking xi+1 as the root.
Otherwise, set i=i+1 and go to
Dr. Jie Zou PHY 3320 step 2. 3
Notes on Secant method
Secant method is
similar to Newton’s
method but uses a
back-ward finite-
difference
approximation for the
derivative, f’(x).
Secant method may
not converge (see an
example on the left).
Dr. Jie Zou PHY 3320 4
Example: Secant method
Example 2.14: Find the root of the
equation
1.5 x 1 0.65 x
f x 1
0.65 tan 0
1 x
2 2
x 1 x
2
using Secant method with two initial
guesses xl = 0.0 and x2 = 0.5 and the
convergence criterion, |f(xi)| with
= 10-5.
Dr. Jie Zou PHY 3320 5
You might also like
- FGRGHDocument15 pagesFGRGHMiles100% (1)
- The Newton Raphson Method - 2017Document61 pagesThe Newton Raphson Method - 2017Aril PurnomoNo ratings yet
- The Newton Raphson Method - 2017Document61 pagesThe Newton Raphson Method - 2017NajwaAinayaZawaidNo ratings yet
- Secant MethodDocument22 pagesSecant Methodjeffrey marapiaNo ratings yet
- Secant MethodDocument24 pagesSecant Methodsoran najebNo ratings yet
- Numerical Methods With ApplicationsDocument49 pagesNumerical Methods With Applicationsrazlan ghazaliNo ratings yet
- GEM 803 Chapter 2 (3rd Term) PDFDocument11 pagesGEM 803 Chapter 2 (3rd Term) PDFRalph Justine GuintoNo ratings yet
- Week03 Open MethodsDocument23 pagesWeek03 Open MethodsFatinnnnnnNo ratings yet
- 4 SecantDocument22 pages4 SecantTerrell LasamNo ratings yet
- Secant Method: Major: All Engineering Majors Authors: Autar Kaw, Jai PaulDocument24 pagesSecant Method: Major: All Engineering Majors Authors: Autar Kaw, Jai PaulShivam PatilNo ratings yet
- EEE212 Week4Document31 pagesEEE212 Week4melikeNo ratings yet
- The Bisection MethodsDocument5 pagesThe Bisection MethodsyacobNo ratings yet
- Métodos NuméricosDocument1 pageMétodos Numéricossantosdalila227No ratings yet
- It Can Be Generalized For F: R RDocument1 pageIt Can Be Generalized For F: R RVasea GurduzaNo ratings yet
- NewtonDocument48 pagesNewtonArsene MawejaNo ratings yet
- Roots of Equations: Open MethodsDocument53 pagesRoots of Equations: Open MethodsGary BlakeNo ratings yet
- Newton-Raphson Method: Numerical AnalysisDocument14 pagesNewton-Raphson Method: Numerical Analysisنورالهدى سعيد عبدNo ratings yet
- Numerical AnalysisDocument21 pagesNumerical AnalysisMeiva Marthaulina LestariNo ratings yet
- Prof. Muhammad Saeed: 1. Nonlinear Equations 2. System of Linear EquationsDocument15 pagesProf. Muhammad Saeed: 1. Nonlinear Equations 2. System of Linear Equationsumarjavaid99No ratings yet
- Lecture 7 Secant Method With You 240304 130541 2Document10 pagesLecture 7 Secant Method With You 240304 130541 2muida4008No ratings yet
- 3 Numerical OptimizationDocument17 pages3 Numerical Optimization공명형No ratings yet
- KIL1005: Numerical Methods For EngineeringDocument36 pagesKIL1005: Numerical Methods For EngineeringSafayet AzizNo ratings yet
- CH 4 Solution of Systems of Non Linear EquationDocument6 pagesCH 4 Solution of Systems of Non Linear EquationAddisu Safo Bosera0% (1)
- NM Lect2Document55 pagesNM Lect2خيري سمير كمالNo ratings yet
- 2.2 Nonlinear Equs - Newton - SecantDocument46 pages2.2 Nonlinear Equs - Newton - SecantIbrahim AbadiNo ratings yet
- Newton Raphson, Secant and Multiple RootsDocument44 pagesNewton Raphson, Secant and Multiple RootsGeorge PrimatoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Solution of Nonlinear Equation PDFDocument3 pagesChapter 2 - Solution of Nonlinear Equation PDFsam19961No ratings yet
- Algorithm For UnconstrainedDocument30 pagesAlgorithm For UnconstrainedHassanZameerNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9Document5 pagesChapter 9Dhynelle MuycoNo ratings yet
- Ea 19Document18 pagesEa 19ArsalanNo ratings yet
- Lab 1Document31 pagesLab 1kruthi_dhoriaNo ratings yet
- Numerical MethodsDocument35 pagesNumerical MethodsNiharika Gupta100% (1)
- Hampiran Numerik Solusi Persamaan Nirlanjar: Pertemuan 3Document29 pagesHampiran Numerik Solusi Persamaan Nirlanjar: Pertemuan 3dikiNo ratings yet
- Path Following Methods: Prof. Dr. Eleni Chatzi, Dr. Konstantinos Agathos Lecture 4 - 10 October, 2019Document44 pagesPath Following Methods: Prof. Dr. Eleni Chatzi, Dr. Konstantinos Agathos Lecture 4 - 10 October, 2019Sudip ShresthaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 23Document5 pagesLecture 23The tricksterNo ratings yet
- Secant MethodDocument24 pagesSecant MethodSO R ANNo ratings yet
- 02A - RootBracketing Komp Num 01Document23 pages02A - RootBracketing Komp Num 01Mess YeahNo ratings yet
- Equation-Solving This One Is The KeyDocument8 pagesEquation-Solving This One Is The KeyAimen AouniNo ratings yet
- Convergence of NM and Modified Newton Ralphon MethodDocument15 pagesConvergence of NM and Modified Newton Ralphon MethodkmprabhaNo ratings yet
- Ch6 Open - Methods 10 10 2010Document47 pagesCh6 Open - Methods 10 10 2010No RaimaNo ratings yet
- Derivatives and Its Applications Lecture NotesDocument4 pagesDerivatives and Its Applications Lecture NotesS.m. ChandrashekarNo ratings yet
- Btech 4 Sem Engineering Mathematics 3 Ras401 2019Document2 pagesBtech 4 Sem Engineering Mathematics 3 Ras401 2019priyanshu guptaNo ratings yet
- mth603 Sol Subjective Final 2014bysyedaDocument42 pagesmth603 Sol Subjective Final 2014bysyedabc170401540 MUHAMMAD SHAHIDNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 1Document2 pagesAssignment 1 1KARTHICK MNo ratings yet
- Numerical Analysis - Roots of EquationsDocument19 pagesNumerical Analysis - Roots of EquationsR SetiawanNo ratings yet
- Secant Method (Sauer)Document6 pagesSecant Method (Sauer)Ismael LinsNo ratings yet
- Semester Project NCDocument66 pagesSemester Project NCIqra ArshadNo ratings yet
- Secant MethodDocument6 pagesSecant Methodcomunidad enkollNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 - Differentiation ApplicationsDocument18 pagesLecture 3 - Differentiation ApplicationsHannah Du toitNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4Document48 pagesLecture 4Fareh IqbalNo ratings yet
- Z I W I Z I Wi I: Assignment-List of ExamplesDocument2 pagesZ I W I Z I Wi I: Assignment-List of Examplesηιяαν ραтєlNo ratings yet
- University of Palestine Gaza Strip Civil Engineering College Numerical Analysis CIVL 3309 Dr. Suhail LubbadDocument23 pagesUniversity of Palestine Gaza Strip Civil Engineering College Numerical Analysis CIVL 3309 Dr. Suhail LubbadHazem AlmasryNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5Document26 pagesLecture 5Nanditha ANo ratings yet
- Mth603 Finalterm Subjective: Question No: 50 (Marks: 5)Document43 pagesMth603 Finalterm Subjective: Question No: 50 (Marks: 5)Taha ChuhdaryNo ratings yet
- Poisson Equation: by Li ChenDocument18 pagesPoisson Equation: by Li ChenCristofer TejedaNo ratings yet
- MAE C5 6 IntegralsDocument56 pagesMAE C5 6 Integralsphongkhiem.wasecoNo ratings yet
- TALectureNotes W6Document18 pagesTALectureNotes W6簡千翔No ratings yet
- Assignment ExamDocument1 pageAssignment ExamHarish KumarNo ratings yet
- Department of Mathematics: Babu Banarasi Das National Institute of Technology & Management, LucknowDocument1 pageDepartment of Mathematics: Babu Banarasi Das National Institute of Technology & Management, Lucknowharish nigamNo ratings yet
- Functional Operators (AM-22), Volume 2: The Geometry of Orthogonal Spaces. (AM-22)From EverandFunctional Operators (AM-22), Volume 2: The Geometry of Orthogonal Spaces. (AM-22)No ratings yet
- Green's Function Estimates for Lattice Schrödinger Operators and Applications. (AM-158)From EverandGreen's Function Estimates for Lattice Schrödinger Operators and Applications. (AM-158)No ratings yet
- Section A-Very Short Questions (1M 20) : Compiled by:ULKA SHAH No. 97240 64249Document4 pagesSection A-Very Short Questions (1M 20) : Compiled by:ULKA SHAH No. 97240 64249DhyeayaNo ratings yet
- CH 8 - Trigonometry Class XDocument2 pagesCH 8 - Trigonometry Class XCRPF SchoolNo ratings yet
- S VD ChapterDocument12 pagesS VD Chapterhaji sahebNo ratings yet
- Pre Mfe Nla Feb2020 SyllabusDocument4 pagesPre Mfe Nla Feb2020 Syllabustravel PassionNo ratings yet
- Equations of Straight Lines Practice - MathBitsNotebook (A1 - CCSS Math)Document5 pagesEquations of Straight Lines Practice - MathBitsNotebook (A1 - CCSS Math)agus agusNo ratings yet
- Chapt 6Document12 pagesChapt 6NewtoniXNo ratings yet
- Binary Search TreeDocument85 pagesBinary Search TreeanandNo ratings yet
- Class 12 Revised Syllabus For 2023 Board Examination-1Document14 pagesClass 12 Revised Syllabus For 2023 Board Examination-1Arkin DixitNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 Computational Methods For EngineersDocument14 pagesLecture 2 Computational Methods For EngineersJan Michael BatiloNo ratings yet
- Clec 301 Engg Maths IIDocument3 pagesClec 301 Engg Maths IISumathi RajuNo ratings yet
- 17 Evaluation of Improper IntegralsDocument74 pages17 Evaluation of Improper Integralsalienxx0% (1)
- Solving Systems of Algebraic Equations: Daniel LazardDocument27 pagesSolving Systems of Algebraic Equations: Daniel LazardErwan Christo Shui 廖No ratings yet
- Inverse Trig Worksheet 1. Find The EXACT Value of The FollowingDocument3 pagesInverse Trig Worksheet 1. Find The EXACT Value of The FollowingDane AgoyaoyNo ratings yet
- 7.assignment2 DAA Answers Dsatm PDFDocument19 pages7.assignment2 DAA Answers Dsatm PDFM.A rajaNo ratings yet
- Kernel Methodsfor Machine Learningwith Mathand PythoDocument215 pagesKernel Methodsfor Machine Learningwith Mathand PythoKabir WestNo ratings yet
- Question Bank Inverse Laplace TransformDocument4 pagesQuestion Bank Inverse Laplace Transformketaki.mahajanNo ratings yet
- S6 Assignment I On CH 1 To 3Document3 pagesS6 Assignment I On CH 1 To 3rehankatyal05No ratings yet
- Introduction To Exponential & Logarithmic FunctionsDocument3 pagesIntroduction To Exponential & Logarithmic FunctionsnooluoitNo ratings yet
- Lab Report#5: Digital Signal Processing EEE-324Document11 pagesLab Report#5: Digital Signal Processing EEE-324Abdul BasitNo ratings yet
- 2.0 Jee (Main) Sets Relations Functions (New Syllabus)Document255 pages2.0 Jee (Main) Sets Relations Functions (New Syllabus)dahaleswaroopNo ratings yet
- Techniques To DervitivesDocument2 pagesTechniques To DervitivesM Farooq DilshadNo ratings yet
- APCalc 1969 To 2005Document74 pagesAPCalc 1969 To 2005Amy Wong0% (1)
- Fibonacci HeapsDocument17 pagesFibonacci HeapsvjykmrNo ratings yet
- Intermediate Value TheoremDocument7 pagesIntermediate Value TheoremPriyanka ShawNo ratings yet
- 4 Integral Equations by D.C. Sharma M.C. GoyalDocument200 pages4 Integral Equations by D.C. Sharma M.C. GoyalManas Ranjan MishraNo ratings yet
- Handbook Math FunctionsDocument131 pagesHandbook Math FunctionsAmutha Narainasamy100% (1)
- Simpsons 1-3rd & 3-8th RuleDocument12 pagesSimpsons 1-3rd & 3-8th RuleVikas RathodNo ratings yet
- Matlab by Rajesh Bandari YadavDocument55 pagesMatlab by Rajesh Bandari Yadavhyma kadakatla100% (2)
- Mathematics B.A, B.Sc. Syllabus Final PDFDocument27 pagesMathematics B.A, B.Sc. Syllabus Final PDFVishal Kumar SinghNo ratings yet