Professional Documents
Culture Documents
TOPIK 4 Subjunctive Verb (Wish)
TOPIK 4 Subjunctive Verb (Wish)
Uploaded by
Dzaky Today0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views7 pagesThe document discusses the use of subjunctive verbs after "wish". It states that for wishes about the present or future, use the past subjunctive form, which is like the past simple form except "were" is used for all subjects. For wishes about the past, use the past perfect form. It then provides examples of using wish to express something impossible, wishing for something, and wishing someone something good.
Original Description:
Original Title
TOPIK 4 Subjunctive verb (wish)
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses the use of subjunctive verbs after "wish". It states that for wishes about the present or future, use the past subjunctive form, which is like the past simple form except "were" is used for all subjects. For wishes about the past, use the past perfect form. It then provides examples of using wish to express something impossible, wishing for something, and wishing someone something good.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views7 pagesTOPIK 4 Subjunctive Verb (Wish)
TOPIK 4 Subjunctive Verb (Wish)
Uploaded by
Dzaky TodayThe document discusses the use of subjunctive verbs after "wish". It states that for wishes about the present or future, use the past subjunctive form, which is like the past simple form except "were" is used for all subjects. For wishes about the past, use the past perfect form. It then provides examples of using wish to express something impossible, wishing for something, and wishing someone something good.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 7
TOPIK 4
Subjunctive verb (wish)
SUBJUNCTIVE VERBS
SUBJUNCTIVE VERBS
What verb forms follow 'wish'?
What verb forms follow 'wish'?
For wishes about the present or future, use the subjunctive. Follow the wish with the past
For wishes about the present or future, use the subjunctive. Follow the wish with the past
subjunctive. The past subjunctive looks like the past simple, except for the verb to be which uses were
subjunctive. The past subjunctive looks like the past simple, except for the verb to be which uses were
for all subjects.
for all subjects.
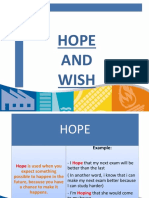
• I wish I had a better job.
• I wish I had a better job.
• I wish I were famous.
• I wish I were famous.
• I wish I didn't spend so much on clothes.
• I wish I didn't spend so much on clothes.
For wishes about the past, use the past perfect.
For wishes about the past, use the past perfect.
• I wish I hadn't drunk so much last night.
• I wish I hadn't drunk so much last night.
• I wish I had accepted the job.
• I wish I had accepted the job.
• Ways of using the verb (wish)
• Ways of using the verb (wish)
1) Wish - something impossible or impossible to be true
1) Wish - something impossible or impossible to be true
We use this pattern when we imagine a different past or present situation which is very impossible or
We use this pattern when we imagine a different past or present situation which is very impossible or
impossible. The clause after wish often uses a past form of the verb, such as was and hadn> t in these
impossible. The clause after wish often uses a past form of the verb, such as was and hadn> t in these
examples:
examples:
• I wish my eyesight was better.
• I wish my eyesight was better.
• I wish I hadn’t told her.
• I wish I hadn’t told her.
2) Wish - for something
2) Wish - for something
This is when you think very hard about something you want to happen - you wish for it to happen. We use
This is when you think very hard about something you want to happen - you wish for it to happen. We use
it with for:
it with for:
• I wish for a happy, peaceful life.
• I wish for a happy, peaceful life.
• She wished for a better job.
• She wished for a better job.
3) Wish – Someone something
3) Wish – Someone something
This is when you tell someone you hope they will experience something good like being safe or happy
This is when you tell someone you hope they will experience something good like being safe or happy
(it's usually something good, but not always!). There is an indirect object (him) and a direct object (a safe
(it's usually something good, but not always!). There is an indirect object (him) and a direct object (a safe
trip) in the example:
trip) in the example:
• I wished him a safe trip!
• I wished him a safe trip!
Here are two more Examples which follow this pattern:
Here are two more Examples which follow this pattern:
• He wished me luck!
• He wished me luck!
• I wish you a happy anniversary!
• I wish you a happy anniversary!
TERIMAKASI
H
You might also like
- Hello, Dear StudentsDocument18 pagesHello, Dear Studentsmairaj2No ratings yet
- Grade 9 English 2nd Quarter Lesson PlanDocument2 pagesGrade 9 English 2nd Quarter Lesson PlanMae Ann Miralles Piorque88% (17)
- Exercícios Sobre o Present PerfectDocument3 pagesExercícios Sobre o Present PerfectAdemilton Rodrigues de Oliveira100% (2)
- Unreal Time and SubjunctivesDocument17 pagesUnreal Time and SubjunctivesMilica StojkovićNo ratings yet
- GuideDocument28 pagesGuideEmmanuel Martínez ApáezNo ratings yet
- Bridges2 Unit04 CW Wish 10 11Document8 pagesBridges2 Unit04 CW Wish 10 11Equipo DirectivoNo ratings yet
- Noun ClausesDocument48 pagesNoun ClausesLili_Hzn_nNo ratings yet
- Verbs3moodsgrade8 150720204028 Lva1 App6892Document14 pagesVerbs3moodsgrade8 150720204028 Lva1 App6892Zeeshan Khan100% (1)
- Indicative vs. SubjunctiveDocument29 pagesIndicative vs. SubjunctiveAnonymous 2MMvcWTNo ratings yet
- Future ContinuousDocument6 pagesFuture Continuous3A EDUARDO ALVAREZNo ratings yet
- Review - Myp 1 - 2020Document35 pagesReview - Myp 1 - 2020JúlioCesarCampagnoloNo ratings yet
- Pertemuan 18 I Wish, If OnlyDocument8 pagesPertemuan 18 I Wish, If OnlyAhmed AliNo ratings yet
- Types of Present Tense: Power Mechanics DepartmentDocument5 pagesTypes of Present Tense: Power Mechanics DepartmentMohammed NoriNo ratings yet
- Subjunctive MoodDocument7 pagesSubjunctive MoodtheseductivecharacterNo ratings yet
- SpeechactDocument14 pagesSpeechactannisa risqaNo ratings yet
- If Only, Wish, Hope 2022Document3 pagesIf Only, Wish, Hope 2022k5fxk7nct4No ratings yet
- Hope and DreamDocument9 pagesHope and DreamriskyyasaNo ratings yet
- Theory Unreal TimeDocument2 pagesTheory Unreal TimeVictoria ColesnicNo ratings yet
- Advanced Grammar & Punctuation ProjectDocument38 pagesAdvanced Grammar & Punctuation ProjectSourav BhowmikNo ratings yet
- B1 Grammar Lessons and Exercises: Present Simple Vs Present Continuous - FormDocument100 pagesB1 Grammar Lessons and Exercises: Present Simple Vs Present Continuous - FormEmilio Mendez DominguezNo ratings yet
- SubjunctiveDocument3 pagesSubjunctivehieroglyphNo ratings yet
- The SubjunctiveDocument10 pagesThe Subjunctivekusikusi100% (1)
- Direct and Indirect Object PronounsDocument27 pagesDirect and Indirect Object Pronounsbq5tt9pyzqNo ratings yet
- Subjunctive: Structure of The SubjunctiveDocument4 pagesSubjunctive: Structure of The SubjunctiveAlin vlNo ratings yet
- ClausesDocument54 pagesClausesjeremiah ocheaNo ratings yet
- Presentacion Tiempo Verbal Will y Going To CorreccionDocument11 pagesPresentacion Tiempo Verbal Will y Going To CorreccionMargy PerezNo ratings yet
- Meeting 4: Intermediate SpeakingDocument37 pagesMeeting 4: Intermediate SpeakingDewi MaryamNo ratings yet
- C1. SubjunctiveDocument9 pagesC1. SubjunctiveLiz WorapsowNo ratings yet
- Partner Share: Describe A Movie Where A Toy Comes To LifeDocument21 pagesPartner Share: Describe A Movie Where A Toy Comes To Lifekashifbutty2kNo ratings yet
- Direct and Indirect Speech-SSDocument21 pagesDirect and Indirect Speech-SSPriyanka GandhiNo ratings yet
- The Subjunctive MoodDocument25 pagesThe Subjunctive MoodBOGDAN-IOAN MACARIENo ratings yet
- SubjunctiveDocument42 pagesSubjunctiveGilang FaqihNo ratings yet
- Future TensesDocument16 pagesFuture Tenses1912922No ratings yet
- Direct, Indirect, Reported SpeechDocument24 pagesDirect, Indirect, Reported SpeechKHALIDOO6No ratings yet
- Noun ClauseDocument33 pagesNoun ClauseJasmin Goot RayosNo ratings yet
- Clase 1Document11 pagesClase 1n6kh2zj2gwNo ratings yet
- Reported SpeechDocument11 pagesReported Speechmis tarbiyatulmubtadiinNo ratings yet
- Language II Module 4 Subjunctive Mood With NumbersDocument23 pagesLanguage II Module 4 Subjunctive Mood With NumbersCostas NovusNo ratings yet
- Direct and Indirect SpeechDocument2 pagesDirect and Indirect SpeechClaudio ColussiNo ratings yet
- Direct and Indirect SpeechDocument2 pagesDirect and Indirect SpeechClaudio ColussiNo ratings yet
- Modal VerbsDocument25 pagesModal VerbsPaulaNo ratings yet
- Past SimpleDocument6 pagesPast SimpleXavier José DomingosNo ratings yet
- Participle and Participial PhraseDocument23 pagesParticiple and Participial Phrasedara rethNo ratings yet
- Simple Future: FORM WillDocument15 pagesSimple Future: FORM WillNatalia SimascoNo ratings yet
- Explanation - Grammar Unit 6 - Reported SpeechDocument6 pagesExplanation - Grammar Unit 6 - Reported SpeechRosa García RomeroNo ratings yet
- Future TensesDocument22 pagesFuture TensesЮлія ГурмакNo ratings yet
- General RevisionDocument20 pagesGeneral RevisionJESuisAhmedNo ratings yet
- Verbs Followed by Ing' or by To + Infinitive'Document7 pagesVerbs Followed by Ing' or by To + Infinitive'baryalNo ratings yet
- Vocatives Kinship PossessionDocument21 pagesVocatives Kinship Possessionapi-240547275No ratings yet
- ConditionalsDocument21 pagesConditionalsHeiiDy LuUNo ratings yet
- Inglés Gramática (Perspective)Document15 pagesInglés Gramática (Perspective)Amanda PascualNo ratings yet
- MPU 3022 Simple Future Tense: Name: Fong Xi Teng Rachelle Lee Xing Mei Ling Pei Wen Lecturer: Madam Nor' Azah Abdul AzizDocument14 pagesMPU 3022 Simple Future Tense: Name: Fong Xi Teng Rachelle Lee Xing Mei Ling Pei Wen Lecturer: Madam Nor' Azah Abdul AzizxitengfongNo ratings yet
- Reported SpeechDocument4 pagesReported SpeechCayetana GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Hypotetical Meaning of Conditional ClausesDocument16 pagesHypotetical Meaning of Conditional ClausesVictoria Del Rosario Maidana100% (1)
- Letrang MMDocument29 pagesLetrang MMPretty Ireen TacacaNo ratings yet
- SHOPAHOLICSDocument15 pagesSHOPAHOLICScmsecundariaNo ratings yet
- Direct and Indirect Speech EditedDocument4 pagesDirect and Indirect Speech EditedAri ZahNo ratings yet
- Simple Past X Pres PerfectDocument28 pagesSimple Past X Pres PerfectAdriano Santos100% (1)
- English CapsulesDocument1 pageEnglish Capsuleseducational ideasNo ratings yet
- French 1Document2 pagesFrench 1Luc BEAL100% (1)
- Narration: Direct and Indirect SpeechDocument5 pagesNarration: Direct and Indirect SpeechInsaf AliNo ratings yet
- Wishes and RegretsDocument15 pagesWishes and RegretsROUTES SURVEYNo ratings yet
- No Mistakes Grammar Bites, Volume XXIV, “If and Whether,” and “Incredible”From EverandNo Mistakes Grammar Bites, Volume XXIV, “If and Whether,” and “Incredible”No ratings yet
- Unit 10Document2 pagesUnit 10Dzaky TodayNo ratings yet
- Journalists' Questions Your Questions To Walt Disney Who?Document2 pagesJournalists' Questions Your Questions To Walt Disney Who?Dzaky TodayNo ratings yet
- JURNAL - Finka Andriani 175 4cDocument18 pagesJURNAL - Finka Andriani 175 4cDzaky TodayNo ratings yet
- TOPIK 5 Conditional Sentence (Type 2)Document5 pagesTOPIK 5 Conditional Sentence (Type 2)Dzaky TodayNo ratings yet
- Finka AndrianiDocument1 pageFinka AndrianiDzaky TodayNo ratings yet
- M.6.5.s.dzaky Haidar MalikDocument2 pagesM.6.5.s.dzaky Haidar MalikDzaky TodayNo ratings yet
- TOPIK 3 Let & AllowDocument6 pagesTOPIK 3 Let & AllowDzaky TodayNo ratings yet
- TOPIK 1 Linking Words of Contras Though, Although, Eventhough, in Spite ofDocument8 pagesTOPIK 1 Linking Words of Contras Though, Although, Eventhough, in Spite ofDzaky TodayNo ratings yet
- TOPIK 2 Narrative Tense Past Simple & Past Continous, Past Simpe & Past Perfect, Past Perfect Continous.Document6 pagesTOPIK 2 Narrative Tense Past Simple & Past Continous, Past Simpe & Past Perfect, Past Perfect Continous.Dzaky TodayNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 Activity 1: Based On The Article, Answer The Following Questions (Type On Word and Submit)Document1 pageUnit 5 Activity 1: Based On The Article, Answer The Following Questions (Type On Word and Submit)Dzaky TodayNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 Finka Andriani (1811020175)Document2 pagesUnit 4 Finka Andriani (1811020175)Dzaky TodayNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 Activity 1: Based On The Article, Answer The Following Questions (Type On Word and Submit)Document1 pageUnit 5 Activity 1: Based On The Article, Answer The Following Questions (Type On Word and Submit)Dzaky TodayNo ratings yet
- Metrologi Industri & Kontrol KualitasDocument29 pagesMetrologi Industri & Kontrol KualitasDzaky TodayNo ratings yet
- UNIT 5 Activity 2Document1 pageUNIT 5 Activity 2Dzaky TodayNo ratings yet
- Gateway ToDocument36 pagesGateway TonisryneNo ratings yet
- Class-IV-week9-Class - IV - Week 1 PDFDocument20 pagesClass-IV-week9-Class - IV - Week 1 PDFHajra UbaidNo ratings yet
- Present and Past SimpleDocument3 pagesPresent and Past SimpleЕвгений МатеровNo ratings yet
- Ielts Foundation - Unit 4 Travel and Holidays (R-W)Document4 pagesIelts Foundation - Unit 4 Travel and Holidays (R-W)Trung NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Textbook Semantics of Evidentials 1St Edition Murray Ebook All Chapter PDFDocument53 pagesTextbook Semantics of Evidentials 1St Edition Murray Ebook All Chapter PDFmelanie.kirchner649100% (3)
- Paul Ziff - AntiaestheticsDocument165 pagesPaul Ziff - Antiaestheticsboursin100% (1)
- Jargon and Its PeculiaritiesDocument14 pagesJargon and Its PeculiaritiesЛілія ПелещакNo ratings yet
- Smart Student Book 1-10Document10 pagesSmart Student Book 1-10Joao AlfandegaNo ratings yet
- Grammar Inversion and Emphasis Part 1Document4 pagesGrammar Inversion and Emphasis Part 1nszaroNo ratings yet
- Learning Contract For Students of Compacted Material 4th Grade - English and Language Arts StandardsDocument3 pagesLearning Contract For Students of Compacted Material 4th Grade - English and Language Arts Standardsapi-284964654No ratings yet
- DLP ENGLISHDocument6 pagesDLP ENGLISHLira TinoNo ratings yet
- Corpus Linguistics A Guide To The Method PDFDocument422 pagesCorpus Linguistics A Guide To The Method PDFFloaa100% (1)
- Haitian Creole Phase1 BKLTDocument32 pagesHaitian Creole Phase1 BKLTTanya Korolov67% (3)
- Reduced Adverb Clauses Online DLADocument5 pagesReduced Adverb Clauses Online DLAAlberto MartínezNo ratings yet
- Good Writing: "It's Not Where You Start That Matters, It's Where You Finish."Document68 pagesGood Writing: "It's Not Where You Start That Matters, It's Where You Finish."Nicole HernandezNo ratings yet
- Personal Pronouns Constructive Pronouns Different PronounsDocument2 pagesPersonal Pronouns Constructive Pronouns Different PronounsCristian JigneaNo ratings yet
- 1000 Verb Forms With Hindi Meaning A To Z: Englishtak Classes by Ranjan Sir Whatsapp For Online Classes - 7827536116Document12 pages1000 Verb Forms With Hindi Meaning A To Z: Englishtak Classes by Ranjan Sir Whatsapp For Online Classes - 7827536116Reena PaalNo ratings yet
- Role Play Grading RubricDocument1 pageRole Play Grading RubricVictoria De Lera AlonsoNo ratings yet
- Listening Skills Practice: Important People - Exercises: 1. Check Your Understanding: MatchingDocument2 pagesListening Skills Practice: Important People - Exercises: 1. Check Your Understanding: MatchingLuis Silva100% (1)
- Bomhard - Review of "Semitic and Indo-European: The Principal Etymologies" by Saul LevinDocument6 pagesBomhard - Review of "Semitic and Indo-European: The Principal Etymologies" by Saul LevinAllan Bomhard100% (1)
- Access US 4b - Teacher's BookDocument88 pagesAccess US 4b - Teacher's BookBò Sốt VangNo ratings yet
- Reading ComprehensionDocument1 pageReading ComprehensionYASSINE ELMALKINo ratings yet
- Uno Dos Tal Vez TresDocument20 pagesUno Dos Tal Vez Tresfarieda yousefNo ratings yet
- Brief History of English For TeachersDocument10 pagesBrief History of English For TeachersBaby YanyanNo ratings yet
- 6th GRADE Unit 3 2023Document2 pages6th GRADE Unit 3 2023Mary Carmen RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Kuis Gerund or InfinitiveDocument2 pagesKuis Gerund or InfinitivekristyNo ratings yet
- Temario de Oposiciones De: InglésDocument25 pagesTemario de Oposiciones De: Inglésvanesa_duque_3100% (1)