Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Contemporary World 3
Contemporary World 3
Uploaded by
Ciedelle Honey Lou Dimalig0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
32 views12 pagesGlobalization refers to the increased integration and interdependence of economies, technologies, and cultures across the world. It is driven by advances in transportation and communication technologies and involves three main types: economic, political, and cultural. Globalization affects individuals, communities, and institutions both locally and globally. While proponents argue it promotes growth and development, critics say it can increase inequality and undermine national policies and cultures.
Original Description:
Original Title
contemporary world 3.pptx
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentGlobalization refers to the increased integration and interdependence of economies, technologies, and cultures across the world. It is driven by advances in transportation and communication technologies and involves three main types: economic, political, and cultural. Globalization affects individuals, communities, and institutions both locally and globally. While proponents argue it promotes growth and development, critics say it can increase inequality and undermine national policies and cultures.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
32 views12 pagesContemporary World 3
Contemporary World 3
Uploaded by
Ciedelle Honey Lou DimaligGlobalization refers to the increased integration and interdependence of economies, technologies, and cultures across the world. It is driven by advances in transportation and communication technologies and involves three main types: economic, political, and cultural. Globalization affects individuals, communities, and institutions both locally and globally. While proponents argue it promotes growth and development, critics say it can increase inequality and undermine national policies and cultures.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 12
WORKING
DEFINITION OF
GLOBALIZATIO
N
CAMALLERE , DANELYN BSCE 1-B
What is GLOBALIZATION?
Globalization is a term used to describe
the changes in socities and the world
economy that are the result of dramatically
increased trade and cultural exchange. In
specifically economic contexts, it refers
almost exclusively to the effects of trade,
particularly trade liberalization or “free
trade”.
GLOBALIZATION
In business, the term globalization is
often used in an economic context to
describe an integrated economy
marked by free trade, the free flow of
capital and corporate use of foreign
labor markets to maximize returns
and benefit the common good.
HOW Globalization works:
Globalization is driven by the convergence
of political, cultural and economic systems
that ultimately promote ---and often
necessitate ---increased interaction,
integration and dependency amongst
nations.
The more that disparate regions of the
world become intertwined politically,
culturally and economically, the more the
globalized the world becomes.
These international interactions and
dependencies are enabled and
accelerated by advances in technology,
especially in transportation and
telecommunications. In general, money,
technology, materials and even people
flow more swiftly across national
boundaries today than they ever have in
the past. The flow of knowledge, ideas
and cultures is expediated through
internet communications.
Three types of
GLOBALIZATION:
ECONOMIC GLOBALIZATION- this type focuses on
the unification and integration of international financial
markets, as well as multinational corporations that
have a significant influence on international markets.
POLITICAL GLOBALIZATION- this type deals mainly
with policies designed to facilitate international trade
and commerce. It also deals with the institutions that
implement these policies, which can include national
governments as well as international institutions, such
as the International Monetary Fund and the World
Trade Organization.
CULTURAL GLOBALIZATION- this type
focuses on the social factors that cause
cultures to converge– such as increased
ease of communication and
transportation, brought about by
technology.
•It’s important to note that all the types
influence each other. For example,
economic globalization is made possible
by certain liberal trade policies that fall
under the category of political
globalization. Cultural globalization is also
affected by policies passed in political
globalization and is affected by policies
passed in political globalization and is
Effects of GLOBALIZATION:
The effects of each type of globalization can be felt both
locally and globally, and can be observed in interactions
at every level of society, from an individual at the micro
level to a society at the macro level.
The individual level includes the way of international
influence affects ordinary people within a nation or region.
The community level includes effects to local or regional
organizations, businesses and economies.
The institutional level includes effects to multinational
corporations, national governments and higher education
institutions that have international students. At this level,
decisions are made at that affect the lower levels.
Advantages of
GLOBALIZATION
Proponents of globalization argue that it can solve
fundamental problems with the global economy,
such as poverty and unemployment, by promoting
a free market that benefits rich and poor nations
alike.
Free trade aims to reduce the amount of trade
barriers between nations. A trade barrier is any
imposed restriction on international, including
tariffs and subsidies. This consequently promotes
economic growth, creates job, makes companies
more competitive and lowers prices for consumers.
It also theoritically gives
poorer countries an
opportunity for economic
development throug
exposure to foreign capital
and tech, resulting in
conditions that foster an
improved standard of
Disadvantages of
GLOBALIZATION:
The biggest advantages of globalization are also its
biggest disadvantages. While many proponents
view globalization as an avenue for solving cire
economic problems, critics see it as worsening
global inequality.
For instance, while some proponents say
globalization creates new markets and wealth – and
promotes greater cultural and social integration by
eliminating barriers – critics blame the elimination
of barriers for undermining national policies and
cultures and destabilizing advanced labor markets
in favor of lower-cost wages elsewhere.
Similarly, some proponents point to
the rising economies of poor
countries benefiting from companies
moving operations there to minimize
costs. Meanwhile, some critics say
such moves could lower living
standards in developed countries by
eliminating jobs.
While proponents focus on the
increased trade benefits and political
cooperation that come from a united
global economy, critics acknowledge
that tightly integrated global
You might also like
- OUMH1603 Learning Skills For 21st Century - Cdec19 PDFDocument240 pagesOUMH1603 Learning Skills For 21st Century - Cdec19 PDFமல்லிகா தேவி100% (3)
- 24assets - Daniel Priestly PDFDocument210 pages24assets - Daniel Priestly PDFKristo Sootalu100% (6)
- Engg7t2 Ems Savings Budgets Income and Expenses Lesson PlanDocument3 pagesEngg7t2 Ems Savings Budgets Income and Expenses Lesson PlanStacey Nefdt100% (5)
- Complete Lectorate Formation TopicsDocument52 pagesComplete Lectorate Formation TopicsCiedelle Honey Lou Dimalig100% (3)
- Rubrics of The IEC MaterialDocument1 pageRubrics of The IEC MaterialCiedelle Honey Lou DimaligNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Types of IndustriesDocument64 pagesChapter 3 - Types of IndustriesIvy Joy Calagunay AmpodiaNo ratings yet
- IGCSE English As A Second Language 0511 - s20 - QP - 22Document16 pagesIGCSE English As A Second Language 0511 - s20 - QP - 22ri.yax3365No ratings yet
- Contemporary World (Anthony Chua Maliwanag) : Defining GlobalizationDocument9 pagesContemporary World (Anthony Chua Maliwanag) : Defining GlobalizationMary Jane PelaezNo ratings yet
- Contemporary WorldDocument4 pagesContemporary WorldHaniya KhanNo ratings yet
- Concept of Globalization - Contemporary ArtsDocument22 pagesConcept of Globalization - Contemporary ArtsEdrickLouise DimayugaNo ratings yet
- GlobalizationDocument5 pagesGlobalizationMuhammad GulfamNo ratings yet
- 1.1 History of GlobalizationDocument8 pages1.1 History of GlobalizationAbdela Aman MtechNo ratings yet
- Group 2 Structure of The GlobalizationDocument35 pagesGroup 2 Structure of The GlobalizationJane Quenie Caera LibrandaNo ratings yet
- Comparative Police System/Comparative Models in Policng: GlobalizationDocument35 pagesComparative Police System/Comparative Models in Policng: Globalizationmusubi purpleNo ratings yet
- GlobalizationDocument12 pagesGlobalizationNeil TalamanNo ratings yet
- GlobalizationDocument28 pagesGlobalizationLee Harvey MaigueNo ratings yet
- International BusinessDocument4 pagesInternational BusinessGhulam MehboobNo ratings yet
- Discussion 1Document27 pagesDiscussion 1kcana.fflNo ratings yet
- GlobalizationDocument32 pagesGlobalizationKRIZZEL CATAMINNo ratings yet
- PPT in Contemporary World SubjectDocument33 pagesPPT in Contemporary World SubjectAsianheart Francisco KhajarNo ratings yet
- The Impact of Globalization in The Developing CountriesDocument10 pagesThe Impact of Globalization in The Developing Countriesهيام الجنيدNo ratings yet
- What Is GlobalizationDocument12 pagesWhat Is GlobalizationVirgelyn Udtohan SerdanNo ratings yet
- Module-1 Contemporary WorldDocument7 pagesModule-1 Contemporary WorldRaniel Galindo0% (1)
- Chapter 2 Global Structures and FlowsDocument22 pagesChapter 2 Global Structures and FlowsJela Jane ArcalNo ratings yet
- 1 - Unit Activity Cmad2Document3 pages1 - Unit Activity Cmad2MOJAHID CAMADNo ratings yet
- Globalization and SocietyDocument3 pagesGlobalization and SocietyKrupa SamuelNo ratings yet
- Globalization Term PaperDocument8 pagesGlobalization Term PaperHerjay Racho SulapasNo ratings yet
- Globalization - A Brief OverviewDocument8 pagesGlobalization - A Brief OverviewfbonciuNo ratings yet
- in Contemporary World SubjectDocument85 pagesin Contemporary World SubjectZsaira Amber Marfil RabinoNo ratings yet
- Issues Brief - Globalization - A Brief OverviewDocument12 pagesIssues Brief - Globalization - A Brief OverviewVon Rother Celoso DiazNo ratings yet
- What Is GlobalizationDocument9 pagesWhat Is GlobalizationStephanie Dawn CachuelaNo ratings yet
- New Microsoft Word DocumentDocument7 pagesNew Microsoft Word DocumentAyushi SharmaNo ratings yet
- International Trade Investment Information Technology Environment Culture Economic Development Human Physical Well-BeingDocument3 pagesInternational Trade Investment Information Technology Environment Culture Economic Development Human Physical Well-Beingdenisc7No ratings yet
- Economic GlobalizationDocument27 pagesEconomic GlobalizationsaveezaNo ratings yet
- Course - Outcome - #1 - Article Review - IntbusDocument3 pagesCourse - Outcome - #1 - Article Review - IntbusIrel MrazNo ratings yet
- GlobalizationDocument29 pagesGlobalizationWarisha RanaNo ratings yet
- Contemporary World MidtermDocument20 pagesContemporary World MidtermJohn Mhelson SorianoNo ratings yet
- Globalization 2Document5 pagesGlobalization 2lightningmcking2No ratings yet
- Essay: The Causes and Effects of GlobalizationDocument4 pagesEssay: The Causes and Effects of GlobalizationAbdul RahmanNo ratings yet
- The Contemporary WorldDocument23 pagesThe Contemporary WorldGojo SatorinasNo ratings yet
- Q1W4 Lesson 1 Concrete Effects of Globalization and To Ones Daily LifeDocument7 pagesQ1W4 Lesson 1 Concrete Effects of Globalization and To Ones Daily LifeLeslie TabuzoNo ratings yet
- Globalization and StateDocument5 pagesGlobalization and Stateshereen padchongaNo ratings yet
- 1 - GlobalizationDocument9 pages1 - Globalizationjohnpaulsampani2003No ratings yet
- NOTEPADDocument2 pagesNOTEPADtgresultayNo ratings yet
- Introduction To GlobalizationDocument7 pagesIntroduction To Globalizationstephanie serdoncilloNo ratings yet
- New Microsoft Word DocumentDocument22 pagesNew Microsoft Word DocumentAjay PandayNo ratings yet
- ContemporaryDocument28 pagesContemporaryreizgobangco04No ratings yet
- Lorenzo - SOCSCI 1 - ASSIGNMENT 1Document4 pagesLorenzo - SOCSCI 1 - ASSIGNMENT 1Mia Fe Cuaya LorenzoNo ratings yet
- DR Sohail All AssignmentsDocument39 pagesDR Sohail All Assignmentsmouzamkhan76No ratings yet
- The Essence of Defining Globalization: I. Directions: Give Your Answer ConciselyDocument3 pagesThe Essence of Defining Globalization: I. Directions: Give Your Answer ConciselyJannah Mariz ChengNo ratings yet
- Subject: Contemporary World Name: Ferdinand P. Bagni Date: March 20, 2019 Instructor: Mr. James OyandoDocument13 pagesSubject: Contemporary World Name: Ferdinand P. Bagni Date: March 20, 2019 Instructor: Mr. James OyandoEmalyn VelascoNo ratings yet
- The Economics of Globalization - Impacts and ControversiesDocument1 pageThe Economics of Globalization - Impacts and ControversiesJuan BrattiNo ratings yet
- Group 1 - GE 3Document9 pagesGroup 1 - GE 3JuNo ratings yet
- Globalization: Lesson 1 Mr. Jherome Sarona, LPTDocument133 pagesGlobalization: Lesson 1 Mr. Jherome Sarona, LPTRommel estrelladoNo ratings yet
- Globalization and DriversDocument2 pagesGlobalization and DriversChristine FernandezNo ratings yet
- Globalisation AND Psychology: Oindrila PaulDocument34 pagesGlobalisation AND Psychology: Oindrila Paulprerana sahaNo ratings yet
- Globalization Liberalization and PrivatizationDocument7 pagesGlobalization Liberalization and PrivatizationChandra Shekhar PantNo ratings yet
- Economic GlobalizationDocument5 pagesEconomic GlobalizationRebecca TayagNo ratings yet
- Advantages and Disadvantages of GlobalizationDocument4 pagesAdvantages and Disadvantages of GlobalizationPavan Koundinya75% (4)
- Course Description: The Contemporary World Course Code: GE 3Document3 pagesCourse Description: The Contemporary World Course Code: GE 3Belle VillasinNo ratings yet
- Essay On Globalization 1Document6 pagesEssay On Globalization 1Shina khanNo ratings yet
- Defenition and Nature of GlobalizationDocument43 pagesDefenition and Nature of GlobalizationBRILIAN GUMAYAGAY TOMAS100% (4)
- IB Notes - Imp by Vivek SirDocument15 pagesIB Notes - Imp by Vivek SirRohit ThakurNo ratings yet
- Globalization CoverageDocument43 pagesGlobalization CoverageJennifer Maria Suzanne JuanerioNo ratings yet
- Think Piece About GlobalizationDocument3 pagesThink Piece About GlobalizationGweneth EncelaNo ratings yet
- TH e Heavy Price of Globalization: Globalization and Sustainable DevelopmentDocument19 pagesTH e Heavy Price of Globalization: Globalization and Sustainable DevelopmentRajiv KhokherNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 Assessment TaskDocument3 pagesLesson 3 Assessment TaskCiedelle Honey Lou DimaligNo ratings yet
- Controversial Topics in BioethicsDocument1 pageControversial Topics in BioethicsCiedelle Honey Lou DimaligNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 Assessment TaskDocument2 pagesLesson 2 Assessment TaskCiedelle Honey Lou DimaligNo ratings yet
- Let's Talk 9Document10 pagesLet's Talk 9Ciedelle Honey Lou DimaligNo ratings yet
- Let's Talk 5Document5 pagesLet's Talk 5Ciedelle Honey Lou DimaligNo ratings yet
- National Drug Education ProgramDocument1 pageNational Drug Education ProgramCiedelle Honey Lou Dimalig100% (1)
- Let's Talk 4Document6 pagesLet's Talk 4Ciedelle Honey Lou DimaligNo ratings yet
- WORKSHOP 1on Formulation of TPACKDocument2 pagesWORKSHOP 1on Formulation of TPACKCiedelle Honey Lou DimaligNo ratings yet
- Learning How To Live Life Is The Best Thing You Can Give YourselfDocument15 pagesLearning How To Live Life Is The Best Thing You Can Give YourselfCiedelle Honey Lou DimaligNo ratings yet
- QLR Observation GuideDocument2 pagesQLR Observation GuideCiedelle Honey Lou DimaligNo ratings yet
- Transcultural NursingDocument10 pagesTranscultural NursingCiedelle Honey Lou DimaligNo ratings yet
- Personal Stress Management in Embracing Holistic Health DuringDocument23 pagesPersonal Stress Management in Embracing Holistic Health DuringCiedelle Honey Lou DimaligNo ratings yet
- Interprofessional CareDocument1 pageInterprofessional CareCiedelle Honey Lou DimaligNo ratings yet
- About WeatherDocument18 pagesAbout WeatherCiedelle Honey Lou DimaligNo ratings yet
- Free Screen Recorder ToolsDocument8 pagesFree Screen Recorder ToolsCiedelle Honey Lou DimaligNo ratings yet
- Community and Environmental Health 2Document14 pagesCommunity and Environmental Health 2Ciedelle Honey Lou Dimalig100% (1)
- Rubrics of The Recorded Health Teaching With Health PlanDocument2 pagesRubrics of The Recorded Health Teaching With Health PlanCiedelle Honey Lou DimaligNo ratings yet
- Emergency Preparedness PlanDocument10 pagesEmergency Preparedness PlanCiedelle Honey Lou DimaligNo ratings yet
- CE-520 Reinforced Concrete Design: Cor Jesu CollegeDocument15 pagesCE-520 Reinforced Concrete Design: Cor Jesu CollegeTemoteo L. Pupa IIINo ratings yet
- Araneta V Gatmaitan Digest Admin LawsDocument1 pageAraneta V Gatmaitan Digest Admin LawsGracia SullanoNo ratings yet
- The Implementatiof Halal Cosmetic Standard in MalaysiaDocument10 pagesThe Implementatiof Halal Cosmetic Standard in MalaysiaVan AshcrofNo ratings yet
- LS C&S Bangladesh Project Branch Office Page 1 of 6Document6 pagesLS C&S Bangladesh Project Branch Office Page 1 of 6Mushfik ArafatNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Grade 9 MathematicsDocument3 pagesLesson Plan Grade 9 MathematicsPatrick AniroNo ratings yet
- TRANSPO FINAL ANTIPOLO EditedDocument133 pagesTRANSPO FINAL ANTIPOLO EditedGabCruz0% (1)
- Arrest Warrant of 11 April 2000 Congo v. Belgium ICJ Reports 14 February 2002Document12 pagesArrest Warrant of 11 April 2000 Congo v. Belgium ICJ Reports 14 February 2002Alelojo, NikkoNo ratings yet
- CalvetaDocument11 pagesCalvetaAnonymous 3Pk0Oj100% (1)
- Daily Lesson Log: Napolan National High School Tvl-Ict-Css IiDocument1 pageDaily Lesson Log: Napolan National High School Tvl-Ict-Css IiTabata Qbz TawinNo ratings yet
- E-Commerce-SWOT AnalysisDocument6 pagesE-Commerce-SWOT AnalysisShamim HasanNo ratings yet
- Michael Lueck Marine TourismDocument64 pagesMichael Lueck Marine Tourismo.atikNo ratings yet
- Declaration of Honour PTDocument3 pagesDeclaration of Honour PTHugo SilvaNo ratings yet
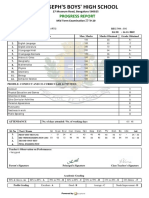
- ST Joseph'S Boys' High School: Progress ReportDocument1 pageST Joseph'S Boys' High School: Progress Reportvanessa martisNo ratings yet
- Constitutionalism My NotesDocument3 pagesConstitutionalism My NotesTrupti GowdaNo ratings yet
- The Canter Model of DisciplineDocument11 pagesThe Canter Model of DisciplineAini NordinNo ratings yet
- Professional Education BulletsDocument9 pagesProfessional Education Bulletsvanessa doteNo ratings yet
- The Analysis of Police Crisis Negotiations - Terry Royce PDFDocument24 pagesThe Analysis of Police Crisis Negotiations - Terry Royce PDFLiviu LiviuNo ratings yet
- Ce-111 - Civil Engineering Orientation Individual Researh Activity No. 02Document9 pagesCe-111 - Civil Engineering Orientation Individual Researh Activity No. 02Jovin BallesterosNo ratings yet
- PWD Budget 2019 - bp18Document76 pagesPWD Budget 2019 - bp18amitNo ratings yet
- Topic: Love and Relationships: Title of The Unit: All You Need Is LoveDocument26 pagesTopic: Love and Relationships: Title of The Unit: All You Need Is LoveNadia Escourido QuintianaNo ratings yet
- ThesisDocument16 pagesThesisthesis10No ratings yet
- Grade 7 English - Budget of LessonDocument8 pagesGrade 7 English - Budget of LessonKeith Pujante100% (2)
- France Legal Deposit LawDocument21 pagesFrance Legal Deposit Lawsteth16No ratings yet
- Human Resource Planning: Vishakha BhattacharyaDocument9 pagesHuman Resource Planning: Vishakha BhattacharyaVishakha BhattacharyaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 (Entrepreneurial Marketing)Document19 pagesChapter 4 (Entrepreneurial Marketing)CathNo ratings yet