Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Banking and Insurance
Banking and Insurance
Uploaded by
yaminshaikh0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 views12 pagesThe document provides a history of banking in India including:
1) Banking originated in the 18th century with the oldest bank being the State Bank of India.
2) Currently there are 96 scheduled commercial banks comprising of 27 public sector banks, 31 private banks, and 38 foreign banks operating over 53,000 branches and 17,000 ATMs across India.
3) Cooperative banks and Regional Rural Banks (RRBs) were also established to better serve rural communities and provide credit to weaker sections. RRBs in particular aim to promote access to institutional credit for agriculture and rural sectors.
Original Description:
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document provides a history of banking in India including:
1) Banking originated in the 18th century with the oldest bank being the State Bank of India.
2) Currently there are 96 scheduled commercial banks comprising of 27 public sector banks, 31 private banks, and 38 foreign banks operating over 53,000 branches and 17,000 ATMs across India.
3) Cooperative banks and Regional Rural Banks (RRBs) were also established to better serve rural communities and provide credit to weaker sections. RRBs in particular aim to promote access to institutional credit for agriculture and rural sectors.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 views12 pagesBanking and Insurance
Banking and Insurance
Uploaded by
yaminshaikhThe document provides a history of banking in India including:
1) Banking originated in the 18th century with the oldest bank being the State Bank of India.
2) Currently there are 96 scheduled commercial banks comprising of 27 public sector banks, 31 private banks, and 38 foreign banks operating over 53,000 branches and 17,000 ATMs across India.
3) Cooperative banks and Regional Rural Banks (RRBs) were also established to better serve rural communities and provide credit to weaker sections. RRBs in particular aim to promote access to institutional credit for agriculture and rural sectors.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 12
History of banks in India
• Banking in India originated in 18th century
• State bank – the oldest bank in India
• Currently India has
96 scheduled commercial banks
27 public sector banks
31 private banks
38 foreign banks
And…. The HISTORY continues
• The total banks in India have combined
Over 53,000 BRANCHES
17,000 ATM’s
COMPARISON OF TOTAL ASSETS OF BANKING INDUSTRY
Public sector banks – 75%
Private sector – 18.2%
Foreign banks – 6.5%
CO-OPERATIVE BANKS
• An important constituent of INDIAN FINANCIAL
SYSTEM
• Started functioning in India 100 years ago
• It is regulated by the RBI
• Coperative Banks governed by Banking Regulations
Act 1949 and Banking Laws (Co-operative Societies)
Act 1965
Co- operative Banks in India Co-operative Banks in India
finance rural areas as under finance urban area as under
•Farming •Self-employment
•Cattle •Industries
•Milk •Small scale units
•Hatchery •Home finance
•Personal Finance •Consumer finance
•Personal finance
Few Co-operative Banks in India
• Suco Bank
• New India Co-Op Bank
• Panchkula Cooperative Bank
• Sangli Cooperative Bank
REGIONAL RURAL BANKS (RRB’s)
• Established on 2nd October, 1975.
• Provides credit to weaker sections of the rural areas
• Started with 5 RRB’s, now it has 30 RRB’s
• Concessions enjoyed like lower interest rates .
Few RRB’s in India
• Andhra Pradesh Grameena Vikas Bank
• Jammu Rural Bank
• Punjab Gramin Bank
Objectives of RRB’s
RRBs are oriented towards meeting the needs of the
weaker sections of the rural population consisting of:
- Small and marginal farmers
- Agricultural laborers
- Artisans
- Small entrepreneurs
- Mobilize deposits from rural households
RRBs are expected to make credit available to rural
households besides inspiring carefulness
Put it simple to ensure sufficient institutional credit for
agriculture and other rural sectors
Key Performance Indicators : RRBs (Rs. Crore)
Indicator 31.03.2004 31.03.2005 31.03.2006
No. of RRBs 196 196 133
No. of districts covered 518 523 525
No. of branches 14446 14484 14494
No. of Staff 69249 68912 68629
Owned funds 5438 6181 6647
Deposits 56350 62143 71329
Borrowings 4595 5524 7303
Investments 36135 36761 41182
Loans outstanding 26114 32870 39713
Credit-deposit (CD) ratio 46% 53% 56%
Loans issued 15579 21082 25427
No. of RRBs having accumulated losses 90 83 58
Accumulated losses 2725 2715 2637
No. of RRBs in profit 163 166 111
Net NPA (%) 8.55% 4.84% 3.99%
Recovery (%) (as on 30 June) 73% 78% 80%
Per branch productivity 5.71 6.56 7.66
Per staff productivity 1.19 1.38 1.62
Population Group and Bank Group-wise (March 2005)
Bank Group Rural Offices Semi-urban Urban / Total
Offices Metro
Offices
No % to No % to No % to No % to
Total Total Total Total
RRBs 11824 37 2284 15 537 02 1464 21
5
SCBs other than 20143 63 1333 85 2184 98 5532 79
RRBs 5 6 4
Total 31967 100 1561 100 2238 100 6996 100
9 3 9
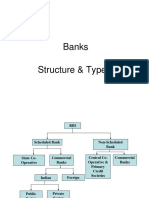
Commercial Bank
• It is a type of financial intermediary
• It is also known as business banking
• Provides checking accounts, savings accounts,
and money market accounts
Commercial Bank
Scheduled
Bank Unscheduled Bank
Union Bank HDFC Bank Ltd.
ICICI Bank Ltd.
Vijaya Bank
IndusInd Bank
Dena Bank Kotak Mahindra
SBI UTI Bank
You might also like
- Evagrius Talking Back PDFDocument2 pagesEvagrius Talking Back PDFAnthonyNo ratings yet
- Regional Rural Banks of India: Evolution, Performance and ManagementFrom EverandRegional Rural Banks of India: Evolution, Performance and ManagementNo ratings yet
- Experiential MarketingDocument22 pagesExperiential Marketingjatin_met1No ratings yet
- Regional Rural BanksDocument11 pagesRegional Rural BanksIndermohan Singh80% (5)
- Regional Rural BanksDocument13 pagesRegional Rural Banksshivakumar N100% (1)
- Chapter - 5 Regional Rural BanksDocument11 pagesChapter - 5 Regional Rural Banksbaby0310No ratings yet
- 3 Best Practices Corporate Governance Sindhudurg DCCB National Seminar STCCSDocument32 pages3 Best Practices Corporate Governance Sindhudurg DCCB National Seminar STCCSGauresh NaikNo ratings yet
- Chapeter 2: Introduction of Pubali Bank LTDDocument16 pagesChapeter 2: Introduction of Pubali Bank LTDMuhammad Hayath ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- Bank Management: PGDM Iimc 2020 Praloy MajumderDocument40 pagesBank Management: PGDM Iimc 2020 Praloy MajumderLiontiniNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Private Sector Banks - Investor'S PerspectiveDocument55 pagesAnalysis of Private Sector Banks - Investor'S Perspectivemonal_bhattadNo ratings yet
- Rural Banking: (In India)Document35 pagesRural Banking: (In India)nuro smartNo ratings yet
- Rural Banking in IndiaDocument15 pagesRural Banking in IndiaSant KumarNo ratings yet
- Data Analysis: Pradhan Mantri Jan-Dhan Yojana (Pmjdy)Document13 pagesData Analysis: Pradhan Mantri Jan-Dhan Yojana (Pmjdy)vivek adkineNo ratings yet
- Determinants of Profitability of Banks in India: A Multivariate AnalysisDocument19 pagesDeterminants of Profitability of Banks in India: A Multivariate AnalysisNeelNo ratings yet
- Micro Finance in IndiaDocument16 pagesMicro Finance in Indiagouravsaikia24No ratings yet
- Bangladesh Krishi Bank Overall Performance Recent 5yrs PDFDocument15 pagesBangladesh Krishi Bank Overall Performance Recent 5yrs PDFAnimesh DharNo ratings yet
- ICICI Bank ReportDocument6 pagesICICI Bank Reportsuhail_thakurNo ratings yet
- Mercial Banks1Document16 pagesMercial Banks1kanna1808No ratings yet
- POs Pre Joining Study Material PDFDocument152 pagesPOs Pre Joining Study Material PDFKushagra Pratap SinghNo ratings yet
- Provisioning Coverage Ratio - Part IIDocument4 pagesProvisioning Coverage Ratio - Part IIJayakrishnaraj AJDNo ratings yet
- IJCRT2204055Document5 pagesIJCRT2204055Jay statusNo ratings yet
- Best Practices 2 Sindhu Durg DCCB PDFDocument13 pagesBest Practices 2 Sindhu Durg DCCB PDFPRALHADNo ratings yet
- Research Analysis: Prepared by Darshan PatiraDocument7 pagesResearch Analysis: Prepared by Darshan Patiradarshan jainNo ratings yet
- Comprehensive Study About Banking Sector: State Bank of India Bank of BarodaDocument13 pagesComprehensive Study About Banking Sector: State Bank of India Bank of BarodaKapil KumarNo ratings yet
- GROUP 16-Financial Sector After NationalisationDocument18 pagesGROUP 16-Financial Sector After NationalisationBahawal Shahryar KhanNo ratings yet
- Press Meet 31 March 2006Document23 pagesPress Meet 31 March 2006pranav_pk88No ratings yet
- BTL Presentations, Below The Line BTL PPT - RC&M India Experiential Marketing FirmDocument22 pagesBTL Presentations, Below The Line BTL PPT - RC&M India Experiential Marketing Firmrcmindia_videoNo ratings yet
- Financial InclusionDocument42 pagesFinancial InclusionNeeta PaiNo ratings yet
- Project Report On "Credit Risk Management in State Bank of India"Document22 pagesProject Report On "Credit Risk Management in State Bank of India"Sandeep YadavNo ratings yet
- Financial Aspects of Kotak Mahindra BankDocument6 pagesFinancial Aspects of Kotak Mahindra Bankajeetkumarverma 2k21dmba20No ratings yet
- Merger of State Bank of India WITH StateDocument20 pagesMerger of State Bank of India WITH StateShilpa WasnikNo ratings yet
- Internship Arif FinalDocument58 pagesInternship Arif Finalটিটন চাকমাNo ratings yet
- Banking Sector Developments in India, 1980-2005: What The Annual Accounts Speak?Document29 pagesBanking Sector Developments in India, 1980-2005: What The Annual Accounts Speak?sg31No ratings yet
- Financial System in BD 08.10.2020 - UpdateDocument39 pagesFinancial System in BD 08.10.2020 - UpdateShamim IqbalNo ratings yet
- Banking: Regional Rural Bank, Cooperative Bank, Commercial BankDocument24 pagesBanking: Regional Rural Bank, Cooperative Bank, Commercial BankMayank Sharan GargNo ratings yet
- Nestle and Britannia RatiosDocument21 pagesNestle and Britannia RatiosKartik RawatNo ratings yet
- BankingDocument48 pagesBankingHARIKA KURRANo ratings yet
- Credit Management and Investment of Uttara Bank LimitedDocument61 pagesCredit Management and Investment of Uttara Bank LimitedSaikat DuttaNo ratings yet
- Punjab National Bank Project ReportDocument40 pagesPunjab National Bank Project ReportVarun100% (40)
- 09p165 Mbfi Swot AnalysisDocument9 pages09p165 Mbfi Swot AnalysisrudranilsterNo ratings yet
- Axis Bank: One Solution For All Your Financial NeedsDocument46 pagesAxis Bank: One Solution For All Your Financial NeedsInderpreet SinghNo ratings yet
- AxisDocument71 pagesAxisanu_1987No ratings yet
- General BankingDocument167 pagesGeneral BankingSuvasish DasguptaNo ratings yet
- Introduction: Financial Inclusion and PMJDYDocument4 pagesIntroduction: Financial Inclusion and PMJDYNakshtra DasNo ratings yet
- Kumar Sachin Deo Kumar Sachin Deo Heena Praveen Heena PraveenDocument15 pagesKumar Sachin Deo Kumar Sachin Deo Heena Praveen Heena Praveenkumar sachin deoNo ratings yet
- Profitability of Co-Operative Banks, Regional Rural Banks and Commercial BanksDocument12 pagesProfitability of Co-Operative Banks, Regional Rural Banks and Commercial BanksYogesh MandhaniNo ratings yet
- Role of Commercial Banks in IndiaDocument24 pagesRole of Commercial Banks in IndiakanikaNo ratings yet
- Banking IndustryDocument6 pagesBanking IndustryRaiyan KhanNo ratings yet
- IB CA 1 Shaik MasthanDocument17 pagesIB CA 1 Shaik Masthanmasthan shaikNo ratings yet
- Banking Sector - UCO Bank: Presented by - Sajal MondalDocument24 pagesBanking Sector - UCO Bank: Presented by - Sajal MondalGok L TunaNo ratings yet
- Chaitanya India Fin Credit Private LimitedDocument22 pagesChaitanya India Fin Credit Private LimitedAditi SharmaNo ratings yet
- Origin and Performance of Regional Rural Bank of IndiaDocument13 pagesOrigin and Performance of Regional Rural Bank of IndiaHetvi TankNo ratings yet
- Andhra Bank: Welcomes Press MeetDocument23 pagesAndhra Bank: Welcomes Press Meetrahul3678No ratings yet
- FIM Final PresentationDocument50 pagesFIM Final Presentationavii boutiqueNo ratings yet
- Arthneeti: All The Best!Document10 pagesArthneeti: All The Best!Kanav GuptaNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 5: E-Banking Services Offered by BanksDocument33 pagesChapter - 5: E-Banking Services Offered by BanksnofaNo ratings yet
- Small Money Big Impact: Fighting Poverty with MicrofinanceFrom EverandSmall Money Big Impact: Fighting Poverty with MicrofinanceNo ratings yet
- Understanding the Mathematics of Personal Finance: An Introduction to Financial LiteracyFrom EverandUnderstanding the Mathematics of Personal Finance: An Introduction to Financial LiteracyNo ratings yet
- The Design of Micro Credit Contracts and Micro Enterprise Finance in UgandaFrom EverandThe Design of Micro Credit Contracts and Micro Enterprise Finance in UgandaNo ratings yet
- Cover PageDocument1 pageCover PageyaminshaikhNo ratings yet
- HULDocument10 pagesHUL..sravana karthikNo ratings yet
- Van HeusenDocument2 pagesVan HeusenyaminshaikhNo ratings yet
- The Customer Is Not Always RightDocument11 pagesThe Customer Is Not Always RightyaminshaikhNo ratings yet
- NRI Investments in IndiaDocument7 pagesNRI Investments in Indiabhavnesh_muthaNo ratings yet
- FW 8 BenDocument1 pageFW 8 BenELNo ratings yet
- Rajkot N-Equity QuotationDocument3 pagesRajkot N-Equity QuotationanilravraniNo ratings yet
- Leadership Programs in Healthcare - INSEAD Healthcare ClubDocument14 pagesLeadership Programs in Healthcare - INSEAD Healthcare ClubkennyNo ratings yet
- Recruitment and SelectionDocument75 pagesRecruitment and SelectionVishal SainiNo ratings yet
- COPPERMASK - FAQsDocument28 pagesCOPPERMASK - FAQsvernalbelasonNo ratings yet
- ReceiptDocument3 pagesReceiptAhsan KhanNo ratings yet
- Midterm Module in SocSci2Document10 pagesMidterm Module in SocSci2Alvin Kris AlicNo ratings yet
- Halfling Rogue BackstoryDocument2 pagesHalfling Rogue BackstoryalexNo ratings yet
- Pages From Model Financial Statements 2018 - Final - Pg. 3Document1 pagePages From Model Financial Statements 2018 - Final - Pg. 3Ahsan TariqNo ratings yet
- Dayao v. ComelecDocument15 pagesDayao v. ComelecRichelle CartinNo ratings yet
- Users Story of HR Leave and Attendence SystemDocument5 pagesUsers Story of HR Leave and Attendence SystemThivya RameshNo ratings yet
- Pr1C Procedure For Suspension and Reinstatement or Withdrawal of Class in Case of Surveys, Conditions of Class or Recommendations Going OverdueDocument7 pagesPr1C Procedure For Suspension and Reinstatement or Withdrawal of Class in Case of Surveys, Conditions of Class or Recommendations Going OverdueOlympia HellasNo ratings yet
- Practice- mệnh đề quan hệDocument2 pagesPractice- mệnh đề quan hệHuyen Trang NguyenNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Managerial Accounting 9th Edition CrossonDocument36 pagesTest Bank For Managerial Accounting 9th Edition Crossonfloatsedlitzww63v100% (53)
- ICTAD Specifications For WorksDocument12 pagesICTAD Specifications For Workssanojani50% (8)
- MilleniumDocument2 pagesMilleniumrahul_dua111100% (1)
- Beginner's Guide by Vikas RanjanDocument42 pagesBeginner's Guide by Vikas Ranjanyociped339No ratings yet
- Sch-Memo-No 44 - SLCP and Aip WorkshopDocument5 pagesSch-Memo-No 44 - SLCP and Aip WorkshopVan Russel Robles0% (1)
- Cockfighting Is Constantly Under Attack by AnimalDocument16 pagesCockfighting Is Constantly Under Attack by AnimalZyrah Mae ValdezNo ratings yet
- Narrative Report On Voter's Ed DisseminationDocument4 pagesNarrative Report On Voter's Ed DisseminationLhea ClomaNo ratings yet
- Miriam Tillinger CVDocument6 pagesMiriam Tillinger CVapi-222275167No ratings yet
- 4 Lives, New IntroductionDocument10 pages4 Lives, New IntroductionSaraNo ratings yet
- Communicate With Customer Using Technologies PDF Teaching MaterialDocument25 pagesCommunicate With Customer Using Technologies PDF Teaching MaterialAzarya DamtewNo ratings yet
- Kubota (2021) - Critical Antiracist Pedagogy in ELT - 1Document10 pagesKubota (2021) - Critical Antiracist Pedagogy in ELT - 1Znd BNo ratings yet
- Coulee Roots BujinkanDocument19 pagesCoulee Roots BujinkanGodsniper100% (2)
- BofA - The EEMEA FX Strategist Higher Oil More EEMEA FX Weakness - 20230926Document19 pagesBofA - The EEMEA FX Strategist Higher Oil More EEMEA FX Weakness - 20230926Sofia Franco100% (1)
- AQA Sociology Media Topic Ten MarkersDocument26 pagesAQA Sociology Media Topic Ten MarkersRostifer rundaleNo ratings yet
- Actuarial 68 Answer KeyDocument1 pageActuarial 68 Answer KeyAkirah McEwenNo ratings yet