Professional Documents
Culture Documents
EE428 Industrial Process Control: Slides With Red Background Are Not Included in The Syllabus
EE428 Industrial Process Control: Slides With Red Background Are Not Included in The Syllabus
Uploaded by
Umer ImranOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
EE428 Industrial Process Control: Slides With Red Background Are Not Included in The Syllabus
EE428 Industrial Process Control: Slides With Red Background Are Not Included in The Syllabus
Uploaded by
Umer ImranCopyright:
Available Formats
EE428 Industrial Process Control
Dr. Ammar Hasan
Slides with red background are
not included in the syllabus
Dr. Ammar Hasan SEECS, NUST
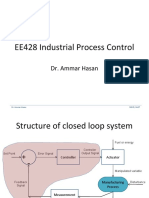
Structure of closed loop system
Fuel or energy
Controller
Set Point Error Signal Output Signal
+ Controller Actuator
-
Manipulated variable
Feedback Manufacturing Disturbance
Signal
Process
Measurement
Devices Measured
variable Output or
controlled variable
Dr. Ammar Hasan SEECS, NUST
Structure of closed loop system
Fuel or energy
Set Point
+ Controller
D to A
converter
filter Actuator
-
Manipulated variable
Feedback Manufacturing Disturbance
Signal
Process
Signal Measure
A to D
conditioning/ ment
converter Measured
amplification Devices
variable Output or
controlled variable
Dr. Ammar Hasan SEECS, NUST
Data acquisition
Dr. Ammar Hasan SEECS, NUST
Data acquisition
Dr. Ammar Hasan SEECS, NUST
Chapter 2: Interfacing Devices
Dr. Ammar Hasan SEECS, NUST
Slides with red background are not included in the syllabus
2.1 OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIERS
• A very versatile amplifier device is the
operational amplifier (op amp).
• The most popular op amp is the μA74l, which is
fabricated inside an 8-pin integrated circuit
package.
• Others are LM301, 558, LM324, TBA221 and
TL071
• There are three important characteristics of op
amps that make them ideal amplifiers:
Dr. Ammar Hasan SEECS, NUST
2.1 OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIERS
• There are three important characteristics of
op amps that make them ideal amplifiers:
1. High input impedance
2. High voltage gain
3. Low output impedance
Dr. Ammar Hasan SEECS, NUST
2.1 OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIERS
Dr. Ammar Hasan SEECS, NUST
2.1 OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIERS
• When external components are connected to
the input and output leads, the op amp is
capable of performing several functions. How
the components are connected determines
which function the op amp performs.
Dr. Ammar Hasan SEECS, NUST
2.1.1 Operational Amplifier
Comparator
• This device compares the voltage applied to
one input to the voltage applied at the other
input.
• Any difference between the volt-ages drives
the op amp output into either a positive or a
negative-volt saturation condition.
Dr. Ammar Hasan SEECS, NUST
2.1.1 Operational Amplifier
Comparator
Dr. Ammar Hasan SEECS, NUST
2.1.1 Operational Amplifier
Comparator
• Saturation is about 80% of the supply voltage.
Therefore, 5 volts is produced if the power
supply is 6.25 volts.
• The polarity of the output is determined by
the polarity of the voltages applied at the
inputs.
Dr. Ammar Hasan SEECS, NUST
2.1.1 Operational Amplifier
Comparator
• When the voltage applied to the inverting input is
more positive than the voltage at the non-inverting
terminals, the output swings to a -5-volt saturation
potential.
• Likewise, when the voltage applied to the inverting
input is more negative than the voltage at the non-
inverting input, the output swings to the +5-volt
saturation potential.
• However, when the input voltages are the same
amplitude, the output is zero.
Dr. Ammar Hasan SEECS, NUST
2.1.2 lnverting Op Amp
• A typical op amp can have a voltage gain of
approximately 200,000.
• However, the output voltage level cannot exceed
approximately 80 percent of the supply voltage.
• For example, the maximum output voltages of the
op amp shown earlier are +5 volts and -5 volts
because the power-supply potentials are +6.25 volts
and 6.25 volts.
Dr. Ammar Hasan SEECS, NUST
2.1.2 lnverting Op Amp
• Therefore, it only takes a 25uV input to result in a
positive or negative 5volt output voltage, depending
on the input-signal polarity and the terminal to which
it is applied.
• However, the op amp is used for many applications
that require a voltage gain less than 200,000.
• A technique called feedback is used to control the
gain of this device, and it is accomplished by
connecting a resistor from the output terminal to an
input lead.
Dr. Ammar Hasan SEECS, NUST
2.1.2 lnverting Op Amp
A negative-feedback circuit is shown below
Dr. Ammar Hasan SEECS, NUST
Summing amplifier
Dr. Ammar Hasan SEECS, NUST
Noninverting amplifier
Dr. Ammar Hasan SEECS, NUST
Difference amplifier
Dr. Ammar Hasan SEECS, NUST
Difference amplifier
• A differential amplifier is a type of electronic
amplifier that amplifies the difference
between two input voltages but suppresses
any voltage common to the two inputs. [1] It is
an analog circuit with two inputs and and one
output in which the output is ideally
proportional to the difference between the
two voltages.
Dr. Ammar Hasan SEECS, NUST
Instrumentation amplifier
• An instrumentation (or instrumentational)
amplifier is a type of differential amplifier
that has been outfitted with input buffer
amplifiers, which eliminate the need for input
impedance matching and thus make the
amplifier particularly suitable for use in
measurement and test equipment.
Dr. Ammar Hasan SEECS, NUST
Instrumentation amplifier
• Additional characteristics include very low DC
offset, low drift, low noise, very high open-
loop gain, very high common-mode rejection
ratio, and very high input impedances.
Instrumentation amplifiers are used where
great accuracy and stability of the circuit both
short and long-term are required
Dr. Ammar Hasan SEECS, NUST
Instrumentation amplifier
Dr. Ammar Hasan SEECS, NUST
Integrating operational amplifier
Dr. Ammar Hasan SEECS, NUST
Integrating operational amplifier
Dr. Ammar Hasan SEECS, NUST
Integrating operational amplifier
Dr. Ammar Hasan SEECS, NUST
Differentiator operational amplifier
Dr. Ammar Hasan SEECS, NUST
Schmitt trigger
• The Schmitt trigger is a device that produces
rectangular wave signals.
• It is often used to convert sine waves or arbitrary
waveforms into crisp square-shaped signals.
• It is also used to restore square waves, which
sometimes become distorted due to electromagnetic
interference (called noise) during transmission, back
to their required square-shaped waveforms.
Dr. Ammar Hasan SEECS, NUST
Schmitt trigger
• The Schmitt trigger uses positive feedback internally
to speed up level transitions.
• It also utilizes an effect called hysteresis, which
means that the switching threshold on a positive-
Dr. Ammar Hasan SEECS, NUST
Schmitt trigger
Dr. Ammar Hasan SEECS, NUST
Schmitt trigger
Dr. Ammar Hasan SEECS, NUST
Schmitt trigger
Dr. Ammar Hasan SEECS, NUST
Optoelectronic Interface Devices
• Applications that require isolation and
safety
Dr. Ammar Hasan SEECS, NUST
Optoelectronic Interface Devices
Photodiodes
• Fast switching detection
• low output current (50-500 uA)
Dr. Ammar Hasan SEECS, NUST
Optoelectronic Interface Devices
Phototransistor
• Amplifies the current therefore higher
output current due to amplification
• Slower response time
Dr. Ammar Hasan SEECS, NUST
Optoelectronic Interface Devices
Photo SCR
• Can be turned on by either or both the
gate or LED
• Can support high currents
Dr. Ammar Hasan SEECS, NUST
Optoelectronic Interface Devices
Photo Triac
• Allows bidirectional current
• Can support high currents but not as
much as SCR
• Turns on by light, turns off when current
is below a threshold
Dr. Ammar Hasan SEECS, NUST
Slides with red background are not included in the syllabus
Digital Comparators
Dr. Ammar Hasan SEECS, NUST
Digital Comparators
Dr. Ammar Hasan SEECS, NUST
Digital Comparators
Dr. Ammar Hasan SEECS, NUST
Digital to analog converters
• Binary weighted D/A converter
Dr. Ammar Hasan SEECS, NUST
Digital to analog converters
• What is the analog output voltage when
a binary 1011 is applied to the binary
weighted D/A converter
Dr. Ammar Hasan SEECS, NUST
Digital to analog converters
• Number of output levels = Vref/2^n-1
Dr. Ammar Hasan SEECS, NUST
Digital to analog converters
Dr. Ammar Hasan SEECS, NUST
Digital to analog converters
Dr. Ammar Hasan SEECS, NUST
Analog to Digital converter
Dr. Ammar Hasan SEECS, NUST
Analog to Digital converter
Dr. Ammar Hasan SEECS, NUST
Analog to Digital converter
Dr. Ammar Hasan SEECS, NUST
Timing Devices
• 555 timer
Dr. Ammar Hasan SEECS, NUST
Timing Devices
• 555 timer
Dr. Ammar Hasan SEECS, NUST
Timing Devices
• 555 timer
Dr. Ammar Hasan SEECS, NUST
Timing Devices
• 555 timer
• Freq:
• Duty cycle:
Dr. Ammar Hasan SEECS, NUST
Timing Devices
555 timer One shot pulse
from microseconds to minutes
Dr. Ammar Hasan SEECS, NUST
You might also like
- Alex Michaelides - Pacienta Tacuta CDocument358 pagesAlex Michaelides - Pacienta Tacuta Cslawth100% (3)
- Servo Amplifier - Troubleshooting GuideDocument5 pagesServo Amplifier - Troubleshooting GuideOmar Leon0% (1)
- EE428 Industrial Process Control: Dr. Ammar HasanDocument33 pagesEE428 Industrial Process Control: Dr. Ammar HasanUmer ImranNo ratings yet
- Instrumentation AmplifierDocument6 pagesInstrumentation Amplifiersarpanch100% (2)
- Automatic Capacitance & Tan Delta Test Sets: Acts-12K PlusDocument4 pagesAutomatic Capacitance & Tan Delta Test Sets: Acts-12K PlusPRBNo ratings yet
- Data Sheet ANTARES Troop 2014-21-05-18Document2 pagesData Sheet ANTARES Troop 2014-21-05-18Osiris LimonNo ratings yet
- Single Phase Automatic Voltage Regulator DesignDocument9 pagesSingle Phase Automatic Voltage Regulator DesignPeter JordanNo ratings yet
- Automation and Integration Solutions For Electric Power SystemsDocument16 pagesAutomation and Integration Solutions For Electric Power SystemsMadhusudhan SrinivasanNo ratings yet
- ON Semiconductor Is Now: To Learn More About Onsemi™, Please Visit Our Website atDocument44 pagesON Semiconductor Is Now: To Learn More About Onsemi™, Please Visit Our Website atMDG ElectronicaNo ratings yet
- Notes 3Document5 pagesNotes 3Joshika sri Ram prabhuNo ratings yet
- Haefely 2796 Ds 1612 SG SpecDocument6 pagesHaefely 2796 Ds 1612 SG Specpeppeto373137No ratings yet
- Meter Test Procedures For Today and The Future: 1.1 Why An Electronic Power Supply Unit?Document8 pagesMeter Test Procedures For Today and The Future: 1.1 Why An Electronic Power Supply Unit?Lana KetlynNo ratings yet
- Elspec BrochureDocument44 pagesElspec BrochuregidoNo ratings yet
- Franeo 800 Brochure EnuDocument12 pagesFraneo 800 Brochure Enu159753No ratings yet
- Chapter Six - 240621145628Document22 pagesChapter Six - 240621145628Yohannes GetinetNo ratings yet
- CT Afq enDocument12 pagesCT Afq enthulasiNo ratings yet
- Grup 2007 VAR Ang A3 01Document6 pagesGrup 2007 VAR Ang A3 01flywheel2006No ratings yet
- 1500wlprot6002-000 PDFDocument2 pages1500wlprot6002-000 PDFsy_binh97No ratings yet
- Npower CatalogoDocument16 pagesNpower CatalogoEmanuel DuarteNo ratings yet
- Rudolf - Digital Power AnalyzerDocument8 pagesRudolf - Digital Power Analyzerlaurence malanumNo ratings yet
- 315ASX DatasheetDocument4 pages315ASX DatasheetThong Hoang TrungNo ratings yet
- Basics of Excitation Systems PDFDocument35 pagesBasics of Excitation Systems PDFDinesh Lakmal Silva100% (2)
- 10 1 1 654 7756 PDFDocument6 pages10 1 1 654 7756 PDFankur rathiNo ratings yet
- OMICRON Product OverviewDocument2 pagesOMICRON Product OverviewMan TahoNo ratings yet
- 7BT60 Series: Vacuum Interrupter Test SetDocument2 pages7BT60 Series: Vacuum Interrupter Test SetenticoNo ratings yet
- Product Data: 220 VA Power Amplifier - Type 2707Document6 pagesProduct Data: 220 VA Power Amplifier - Type 2707jhon vargasNo ratings yet
- CapMedPlus Copley 281plus Gradient AmpDocument8 pagesCapMedPlus Copley 281plus Gradient AmpGiovanni100% (1)
- Onan S 1409 - PCC2100 PDFDocument9 pagesOnan S 1409 - PCC2100 PDFryan23No ratings yet
- Installation and Maintenance: Oe Uf V S UfDocument16 pagesInstallation and Maintenance: Oe Uf V S Uf3efooNo ratings yet
- Excitation System-4th July 2020Document68 pagesExcitation System-4th July 2020Srikanth Purushothaman0% (1)
- Actividad 8. Traduccion Datasheet. EquipoDocument6 pagesActividad 8. Traduccion Datasheet. EquipoAngel David Olivas ContrerasNo ratings yet
- 9001E Instruction Manual PDFDocument2 pages9001E Instruction Manual PDFReagan WisNo ratings yet
- Lecture-18: Signal Conditioning Circuits and Continuous ControllersDocument31 pagesLecture-18: Signal Conditioning Circuits and Continuous Controllersujjwal kumarNo ratings yet
- Op-Amp Based Static Over Current RelayDocument6 pagesOp-Amp Based Static Over Current RelayS Bharadwaj ReddyNo ratings yet
- 700 Series AC Dielectric Test SetsDocument7 pages700 Series AC Dielectric Test SetsKhoilnNo ratings yet
- Module 5Document71 pagesModule 5Jayasree ManoharanNo ratings yet
- Shunt-Based, 200-A Peak Current Measurement Reference Design Using Reinforced Isolation AmplifierDocument27 pagesShunt-Based, 200-A Peak Current Measurement Reference Design Using Reinforced Isolation AmplifiergofererNo ratings yet
- 2929 Ijecs Ijens PDFDocument6 pages2929 Ijecs Ijens PDFbahmanNo ratings yet
- Rohde Schwarz Power Electronics Fly en - 3608 5893 32 - v0100Document7 pagesRohde Schwarz Power Electronics Fly en - 3608 5893 32 - v0100lepinay OlivierNo ratings yet
- 852 Fa40Document10 pages852 Fa40M. T.No ratings yet
- Haefely - V Type Impulse GeneratorDocument11 pagesHaefely - V Type Impulse GeneratorAno035No ratings yet
- Block Appnotes TransformersDocument29 pagesBlock Appnotes TransformersTri KusworoNo ratings yet
- Electronics Tutorial About Operational AmplifiersDocument5 pagesElectronics Tutorial About Operational AmplifiersvikasbbNo ratings yet
- Multi-Functional Current Relay For AC CurrentsDocument4 pagesMulti-Functional Current Relay For AC CurrentsmuaadhNo ratings yet
- Brochure Keystone Epi 2 Quarter Turn Electric Actuators en 7736668Document8 pagesBrochure Keystone Epi 2 Quarter Turn Electric Actuators en 7736668Abhijeet RedekarNo ratings yet
- Spectrum Power enDocument2 pagesSpectrum Power enReza GhasemiNo ratings yet
- 2020 SEO Operational Amplifiers r1.0Document6 pages2020 SEO Operational Amplifiers r1.0Okiring JonahNo ratings yet
- Sigma 1 - Axis Servo Motor and Cables - Troubleshooting GuideDocument3 pagesSigma 1 - Axis Servo Motor and Cables - Troubleshooting GuideOmar LeonNo ratings yet
- FRAX150 DS enDocument8 pagesFRAX150 DS enYan Lin AungNo ratings yet
- Click Icon To Add PictureDocument22 pagesClick Icon To Add PictureAbdul wahedNo ratings yet
- Panamax MAX 5300 Owner's Manual (INS5300D)Document14 pagesPanamax MAX 5300 Owner's Manual (INS5300D)Bruno da CostaNo ratings yet
- Discontinued Product: Chopper-Stabilized Omnipolar Hall-Effect SwitchesDocument13 pagesDiscontinued Product: Chopper-Stabilized Omnipolar Hall-Effect SwitchesCristian BandilaNo ratings yet
- 3 Signal Conditioning AnalogDocument36 pages3 Signal Conditioning AnalogMorshedul IslamNo ratings yet
- 3 Signal Conditioning AnalogDocument36 pages3 Signal Conditioning AnalogMorshedul IslamNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Component Interconnection and Signal Conditioning - Part2Document35 pagesChapter 2 - Component Interconnection and Signal Conditioning - Part2cvkcuongNo ratings yet
- Pplications of Operational AmplifierDocument20 pagesPplications of Operational AmplifierJEEVITHESH BNo ratings yet
- Op Set: Approved Resp Dept Title Rev. Prepared Date Sheet Document No ContDocument8 pagesOp Set: Approved Resp Dept Title Rev. Prepared Date Sheet Document No Contykh92167No ratings yet
- Specifications: HI/ICMI UVR-1 Universal Voltage Regulator ControlDocument6 pagesSpecifications: HI/ICMI UVR-1 Universal Voltage Regulator ControlJunior Ramirez ReyesNo ratings yet
- HP Catalog 1943 FirstDocument26 pagesHP Catalog 1943 FirstMuhammad ShaffanNo ratings yet
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2No ratings yet
- EE428 Industrial Process Control: Dr. Ammar HasanDocument23 pagesEE428 Industrial Process Control: Dr. Ammar HasanUmer ImranNo ratings yet
- EE428 Industrial Process Control: Dr. Ammar HasanDocument110 pagesEE428 Industrial Process Control: Dr. Ammar HasanUmer ImranNo ratings yet
- Ch3 - Lecture 5Document49 pagesCh3 - Lecture 5Umer ImranNo ratings yet
- Ch1 - Lecture 2Document54 pagesCh1 - Lecture 2Umer ImranNo ratings yet
- EE428 Industrial Process Control: Dr. Ammar HasanDocument33 pagesEE428 Industrial Process Control: Dr. Ammar HasanUmer ImranNo ratings yet
- EE428 Industrial Process Control: Dr. Ammar HasanDocument27 pagesEE428 Industrial Process Control: Dr. Ammar HasanUmer ImranNo ratings yet
- Ch2 - Lecture 4Document22 pagesCh2 - Lecture 4Umer ImranNo ratings yet
- L02 PDFDocument17 pagesL02 PDFUmer ImranNo ratings yet
- L03 PDFDocument21 pagesL03 PDFUmer ImranNo ratings yet
- L01 PDFDocument19 pagesL01 PDFUmer ImranNo ratings yet
- L04 PDFDocument16 pagesL04 PDFUmer ImranNo ratings yet
- B224-125-16-51-VDR-7207 Vendor Data Requirements For InstrumentationDocument4 pagesB224-125-16-51-VDR-7207 Vendor Data Requirements For InstrumentationmanuneedhiNo ratings yet
- ROSES Flow Diagram For Systematic MapsDocument1 pageROSES Flow Diagram For Systematic MapsJoanne WongNo ratings yet
- 2020 Nissan Leaf Owner ManualDocument596 pages2020 Nissan Leaf Owner Manualhemaldis4144No ratings yet
- PMG Admin GuideDocument153 pagesPMG Admin GuideGustavo Javier Castañón SelemNo ratings yet
- Showvault PDFDocument118 pagesShowvault PDFCinema Cine MococaNo ratings yet
- Gross Heat in Petroleum Coke: Instrument: AC600Document2 pagesGross Heat in Petroleum Coke: Instrument: AC600Alfredo MarcanoNo ratings yet
- Spicy Presentations - Interactive PowerPoint Memory GameDocument3 pagesSpicy Presentations - Interactive PowerPoint Memory Gamesukasuki paNo ratings yet
- Turtle Cheat SheetDocument1 pageTurtle Cheat SheetNeo JabinNo ratings yet
- Video Editing - NotesDocument15 pagesVideo Editing - NotesLavanya AggarwalNo ratings yet
- Essay HisDocument3 pagesEssay HisGeeyan Marlchest B NavarroNo ratings yet
- Simple Atm FlowchartDocument1 pageSimple Atm FlowchartHai AwakNo ratings yet
- Load Bank Connetion Scheme Phase 1&2Document4 pagesLoad Bank Connetion Scheme Phase 1&2zainal anwarNo ratings yet
- Kulam Sahib Thambi Thottam, Kayalpattinam MunicipalityDocument5 pagesKulam Sahib Thambi Thottam, Kayalpattinam MunicipalitykayalonthewebNo ratings yet
- Padeye Calculator (Shackle Compatibility & Design Capacity) : ApplicationsDocument8 pagesPadeye Calculator (Shackle Compatibility & Design Capacity) : ApplicationsBayari ArNo ratings yet
- Sma Data Manager M With Sunny Portal Powered by Ennexos: Operating ManualDocument56 pagesSma Data Manager M With Sunny Portal Powered by Ennexos: Operating ManualMohamed MourtagaNo ratings yet
- Doing Agile Right Transformation Without Chaos - (PG 129 - 129)Document1 pageDoing Agile Right Transformation Without Chaos - (PG 129 - 129)malekloukaNo ratings yet
- MCS 211 DalalTechnologiesDocument22 pagesMCS 211 DalalTechnologiesdvedi2000No ratings yet
- Experiment: 01 Batch Size: 60 VocabularyDocument9 pagesExperiment: 01 Batch Size: 60 Vocabularygayathri yerukondaNo ratings yet
- Dhea Silvia - Argumentative EssayDocument5 pagesDhea Silvia - Argumentative EssayDheaaNo ratings yet
- Hp-Eva Xcs-11300000 Firmware RNDocument10 pagesHp-Eva Xcs-11300000 Firmware RNDavid BourdinNo ratings yet
- SummaryDocument2 pagesSummaryLucian MogosNo ratings yet
- Electrical Safety FOR Ev/EvseDocument16 pagesElectrical Safety FOR Ev/Evseilayaraja2k20No ratings yet
- NXL Fan Motor User's Manual EnglishDocument92 pagesNXL Fan Motor User's Manual EnglishDeased to ExistNo ratings yet
- Read 9780323392907 Self Assessment in Otolaryngology PaperbackDocument2 pagesRead 9780323392907 Self Assessment in Otolaryngology PaperbackAyman RagabNo ratings yet
- 2019 RWD Safety Shower and Eye Wash E-CatalogueDocument26 pages2019 RWD Safety Shower and Eye Wash E-Cataloguenguyenphuong.cap.ssgNo ratings yet
- Erp AssignmentDocument15 pagesErp AssignmentAfrah Abdul AzeezNo ratings yet
- Central Office: Republic of The PhilippinesDocument10 pagesCentral Office: Republic of The Philippinesbrian paulNo ratings yet
- IMPRINT Brochure FinalDocument28 pagesIMPRINT Brochure Finalnitish kumarNo ratings yet
- 3BSE038018-600 - en System 800xa 6.0 System Guide Functional DescriptionDocument588 pages3BSE038018-600 - en System 800xa 6.0 System Guide Functional DescriptionSabzgostar Avande ParsNo ratings yet