Professional Documents
Culture Documents
3 Sequential Circuit Design 1
3 Sequential Circuit Design 1
Uploaded by
مهيمن الابراهيمي0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
18 views13 pagesSynchronous counters use a common clock pulse to synchronize all flip-flops. A 2-bit synchronous binary counter is described which uses the output of the first flip-flop as input to the second. Counters can be connected in cascade to achieve higher-modulus counting. Digital counters have applications such as digital clocks, automatic parking control systems, and parallel to serial data conversion.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentSynchronous counters use a common clock pulse to synchronize all flip-flops. A 2-bit synchronous binary counter is described which uses the output of the first flip-flop as input to the second. Counters can be connected in cascade to achieve higher-modulus counting. Digital counters have applications such as digital clocks, automatic parking control systems, and parallel to serial data conversion.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
18 views13 pages3 Sequential Circuit Design 1
3 Sequential Circuit Design 1
Uploaded by
مهيمن الابراهيميSynchronous counters use a common clock pulse to synchronize all flip-flops. A 2-bit synchronous binary counter is described which uses the output of the first flip-flop as input to the second. Counters can be connected in cascade to achieve higher-modulus counting. Digital counters have applications such as digital clocks, automatic parking control systems, and parallel to serial data conversion.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 13
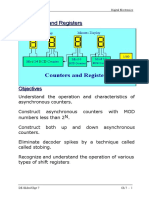
Synchronous Counters
The term synchronous refers to events that have a fixed time
relationship with each other. A
synchronous counter is one in which all flip-flops are clocked
at the same time by a common
.clock pulse
A two-bit synchronous binary counter
Figure shows a 2-bit synchronous binary counter. Notice that
the J1, K1 inputs of the second
flip-flop FF1 are taken from the Q output of the first flip-flop
FF0. The timing diagram is shown
.in figure 7b
Three-bit synchronous binary counter
Q//Design of synchronous counters
Transition table of a J-K flip-flop
Example: Draw the implementation of
decoding of binary state 2, and binary
state 6 of a 3- bit synchronous binary
counter. Show the entire timing
diagram and the output waveforms of
the decoding gates.
Cascaded Counters
Counters can be connected in cascade to achieve higher-modulus operation. The
output of the last stage of the counter is used as an input to the next counter.
Counter applications
Digital counters are used in many useful applications such as digital clock, automatic
parking control system, parallel to serial data converters and many others. (Read in Floyd
for more details)
• Digital clock digital clock implementation
using decade count.
• Automobile Parking Control.
• Parallel to Serial data converter.
Auto park control
Shift Registers
• A shift register consists of a number of D-type flip
flops with two basic functions; data storage and
data movement
Types of shift registers •
:Basically, there are four types of shift registers •
Serial in/Serial out (SISO) -1 •
Parallel in/Serial out (PISO) -2 •
Serial in/Parallel out (SIPO) -3 •
Parallel in/ Parallel out (PIPO) -4 •
You might also like
- Universal Shift Register1Document25 pagesUniversal Shift Register1sandeep_03671% (7)
- Shift RegisterDocument25 pagesShift RegisterdianseptyaNo ratings yet
- Shift Register Teknik DigitalDocument25 pagesShift Register Teknik DigitalMIlhamMaulana100% (1)
- Counter - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument6 pagesCounter - Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopediadeepakk_alpineNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6-Shift RegisterDocument18 pagesChapter 6-Shift RegisterAnonymous On47lKiNo ratings yet
- Counter and RegisterDocument56 pagesCounter and RegisterCapt. NuhaminNo ratings yet
- End Term Pratical: Diwesh Kumar Chaudhary REG No:12002572 Project TitleDocument7 pagesEnd Term Pratical: Diwesh Kumar Chaudhary REG No:12002572 Project TitleSagar singhNo ratings yet
- Counters and Shift Registers: - Sipo - PisoDocument52 pagesCounters and Shift Registers: - Sipo - PisoSathish KumarNo ratings yet
- Ring JohnsonDocument31 pagesRing JohnsonBharadwaja PisupatiNo ratings yet
- Counters & Shifters: by Dr. Alok Kumar Rastogi Professor of Physics Department of Physics & Electronics IEHE, BhopalDocument45 pagesCounters & Shifters: by Dr. Alok Kumar Rastogi Professor of Physics Department of Physics & Electronics IEHE, BhopalKritiiNo ratings yet
- In Electronics: Digital Logic Computing Event Process Clock SignalDocument7 pagesIn Electronics: Digital Logic Computing Event Process Clock SignalROhan GoelNo ratings yet
- Shift Register and Its TypesDocument22 pagesShift Register and Its TypeschoprahridyeshNo ratings yet
- What Is Counter?: Flip-FlopDocument8 pagesWhat Is Counter?: Flip-FlopArunNo ratings yet
- Study of Shift Register (SISO, SIPO, PISO, PISO) : To Study Various Shift Registers and It's ApplicationsDocument13 pagesStudy of Shift Register (SISO, SIPO, PISO, PISO) : To Study Various Shift Registers and It's ApplicationsNilesh MungaseNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4Document30 pagesLecture 4زياد عبدالله عبدالحميدNo ratings yet
- CSE 307: Digital TechniqueDocument33 pagesCSE 307: Digital TechniquemmlabjpNo ratings yet
- DLLec8c NotesDocument8 pagesDLLec8c NotesChintan MandalNo ratings yet
- Lecture3030 12284 Register 1Document30 pagesLecture3030 12284 Register 1shivali.vannarathNo ratings yet
- Coeng3059:: Digital Logic DesignDocument72 pagesCoeng3059:: Digital Logic DesignALEMU DEMIRACHEWNo ratings yet
- In Electronics: Digital Logic Computing Event Process Clock SignalDocument12 pagesIn Electronics: Digital Logic Computing Event Process Clock SignalabhiloveNo ratings yet
- Sift RegisterDocument16 pagesSift RegisterSinta Ariyanti50% (2)
- Counter VHDLDocument12 pagesCounter VHDLbparthageneNo ratings yet
- CountersDocument2 pagesCounterskhushiyadav88400No ratings yet
- Unit 3Document42 pagesUnit 3MaheshBlNo ratings yet
- Ram & RomDocument29 pagesRam & RomDr A Pradeep Kumar asst.Prof(ECE)No ratings yet
- Registers & Counters: Mantıksal Tasarım - BBM231 M. Önder Efe Onderefe@cs - Hacettepe.edu - TRDocument42 pagesRegisters & Counters: Mantıksal Tasarım - BBM231 M. Önder Efe Onderefe@cs - Hacettepe.edu - TRjagruthimsNo ratings yet
- LD6-Mano Registers and CountersDocument32 pagesLD6-Mano Registers and CountersAmr HefnyNo ratings yet
- Shift RegisterDocument21 pagesShift RegisterPurva ChaudhariNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 RegistersDocument17 pagesUnit 5 RegistersmaruthinmdcNo ratings yet
- Digital Electronics Synchronous Circuits:: Up-Down CounterDocument7 pagesDigital Electronics Synchronous Circuits:: Up-Down CounterRahul GuptaNo ratings yet
- Applications of Flip FlopDocument85 pagesApplications of Flip FlopJohaira Maute100% (1)
- Registers and CountersDocument6 pagesRegisters and CountersgeethajeganNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Digital DesignDocument15 pagesIntroduction To Digital DesignOzioma Teddy UkwuomaNo ratings yet
- CH 7Document23 pagesCH 7Anonymous 7WsOWImuNo ratings yet
- Digital CountersDocument16 pagesDigital CountersTapiwanashe MugoniwaNo ratings yet
- Mini Project DigitDocument7 pagesMini Project DigitMUHAMMAD IZZAT BIN ZULKIFLI STUDENTNo ratings yet
- CountersDocument5 pagesCountersHemant SaraswatNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 Sequential Logic DesignDocument74 pagesUnit 5 Sequential Logic DesignsharvarictamaneNo ratings yet
- Programming Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCS)Document47 pagesProgramming Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCS)eyob feshaNo ratings yet
- Digital Systems Laboratory: Experiment 3 Shifters and CountersDocument10 pagesDigital Systems Laboratory: Experiment 3 Shifters and CountersBillie Chuz ArmstrongNo ratings yet
- RegistersDocument2 pagesRegistersCelio GalenzogaNo ratings yet
- Mini Project DigitDocument7 pagesMini Project DigitMUHAMMAD IZZAT BIN ZULKIFLI STUDENTNo ratings yet
- 7 Counters PDFDocument23 pages7 Counters PDFIhuhwa Marta TauNo ratings yet
- CounterDocument3 pagesCounterMuhammad SulemanNo ratings yet
- Frequency Division Using Flip-FlopsDocument4 pagesFrequency Division Using Flip-FlopsBapanapalli Tejeshwar100% (1)
- DS2020 Lab4Document8 pagesDS2020 Lab4hoi.banhphu2710No ratings yet
- DIGI260 Registers1Document27 pagesDIGI260 Registers1Ilaiyaveni IyanduraiNo ratings yet
- Session - 16 17 - Asyn Sync CountersDocument18 pagesSession - 16 17 - Asyn Sync CountersMaruthi RompicherlaNo ratings yet
- Digital ApplicationsDocument14 pagesDigital Applications22e132No ratings yet
- Chapter #7: Sequential Logic Case StudiesDocument48 pagesChapter #7: Sequential Logic Case StudiesShivani AggarwalNo ratings yet
- Design of CountersDocument52 pagesDesign of CountersSrimay RayNo ratings yet
- Gray Code CountersDocument5 pagesGray Code CountersMehmet ZirekNo ratings yet
- Asynchronous Counters: Asynchronous 4-Bit UP CounterDocument13 pagesAsynchronous Counters: Asynchronous 4-Bit UP CounterAbhiNo ratings yet
- RegistersDocument3 pagesRegistersPaw PaladanNo ratings yet
- Numaratoare PDFDocument17 pagesNumaratoare PDFAndrei OlaruNo ratings yet
- Application of Shift Registers: Guided By: Jeyapandi PrathapDocument9 pagesApplication of Shift Registers: Guided By: Jeyapandi PrathapCC PrintsNo ratings yet
- UNIT3Document41 pagesUNIT3Azliana Mohd TaibNo ratings yet
- 8shift Registers PDFDocument48 pages8shift Registers PDFHasmizi Che DeramanNo ratings yet
- Digital Electronics 2: Sequential and Arithmetic Logic CircuitsFrom EverandDigital Electronics 2: Sequential and Arithmetic Logic CircuitsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Linear Programming and The Simplex Method by Ali Dhaher Hussein Supervisor by DR - Ekhlas Mhawi (2019-2020)Document11 pagesLinear Programming and The Simplex Method by Ali Dhaher Hussein Supervisor by DR - Ekhlas Mhawi (2019-2020)مهيمن الابراهيميNo ratings yet
- Design and Implementation of A Smart GreenhouseDocument5 pagesDesign and Implementation of A Smart Greenhouseمهيمن الابراهيميNo ratings yet
- Noise-Induced Hearing Loss: Indian Journal of Otology December 2014Document4 pagesNoise-Induced Hearing Loss: Indian Journal of Otology December 2014مهيمن الابراهيميNo ratings yet
- Ali DhaherDocument10 pagesAli Dhaherمهيمن الابراهيميNo ratings yet
- 1-fainle exam third 2019-2020- 1 نموذجDocument3 pages1-fainle exam third 2019-2020- 1 نموذجمهيمن الابراهيميNo ratings yet
- بنين عباس حسين تجربةDocument5 pagesبنين عباس حسين تجربةمهيمن الابراهيميNo ratings yet
- High WayDocument11 pagesHigh Wayمهيمن الابراهيميNo ratings yet
- Intendedartificial Intelligence in MedicineDocument11 pagesIntendedartificial Intelligence in Medicineمهيمن الابراهيميNo ratings yet
- 8086 Instruction Set String Instruction: Assist. Prof. Dr. Hadeel Nasrat AbdullahDocument13 pages8086 Instruction Set String Instruction: Assist. Prof. Dr. Hadeel Nasrat Abdullahمهيمن الابراهيميNo ratings yet
- Answer Five (5) Questions OnlyDocument2 pagesAnswer Five (5) Questions Onlyمهيمن الابراهيميNo ratings yet
- 4th Lecture Semester 2Document4 pages4th Lecture Semester 2مهيمن الابراهيميNo ratings yet
- Republic of Iraq Minstrey of Higher Education and Scientific Research University of BabylonDocument18 pagesRepublic of Iraq Minstrey of Higher Education and Scientific Research University of Babylonمهيمن الابراهيميNo ratings yet
- Artificial Intelligence in Medical Application: Electrical and Electronic Engineering DepartmentDocument18 pagesArtificial Intelligence in Medical Application: Electrical and Electronic Engineering Departmentمهيمن الابراهيميNo ratings yet
- Subject: Instrumentation& Measurement Class: Second Divisions: Electrical&Electronic (1) Time: 3 Hours Examiner: Lecturer Faten Fakhry Date: 2016Document2 pagesSubject: Instrumentation& Measurement Class: Second Divisions: Electrical&Electronic (1) Time: 3 Hours Examiner: Lecturer Faten Fakhry Date: 2016مهيمن الابراهيميNo ratings yet
- Microcontroller Lab: Baqir Haider FadelDocument10 pagesMicrocontroller Lab: Baqir Haider Fadelمهيمن الابراهيميNo ratings yet
- Final Exam (2) 2016-2017Document2 pagesFinal Exam (2) 2016-2017مهيمن الابراهيميNo ratings yet
- هوم ورك معالجDocument11 pagesهوم ورك معالجمهيمن الابراهيميNo ratings yet
- 2-Satellite - Systems 2 - Orbits IIIDocument42 pages2-Satellite - Systems 2 - Orbits IIIمهيمن الابراهيميNo ratings yet
- Sheet 10Document5 pagesSheet 10مهيمن الابراهيميNo ratings yet
- Three Phase CircuitsDocument15 pagesThree Phase Circuitsمهيمن الابراهيميNo ratings yet
- Assessment of Water Quality Along Euphrates River in Iraq UsingDocument33 pagesAssessment of Water Quality Along Euphrates River in Iraq Usingمهيمن الابراهيميNo ratings yet
- 2 Sequential Circuit Design 1Document9 pages2 Sequential Circuit Design 1مهيمن الابراهيميNo ratings yet
- Review of Error Detection of Data Link Layer in Computer NetworkDocument6 pagesReview of Error Detection of Data Link Layer in Computer Networkمهيمن الابراهيميNo ratings yet
- Satellite Communication MCQ Bank: June 2013Document68 pagesSatellite Communication MCQ Bank: June 2013مهيمن الابراهيميNo ratings yet
- Audio Amplifier Frequency Response: Bode 100 - Application NoteDocument21 pagesAudio Amplifier Frequency Response: Bode 100 - Application Noteمهيمن الابراهيميNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 OSI Data Link LayerDocument7 pagesChapter 7 OSI Data Link Layerمهيمن الابراهيميNo ratings yet
- 1 Sequential Circuit Design 1Document8 pages1 Sequential Circuit Design 1مهيمن الابراهيميNo ratings yet
- Binary Frequency-Shift Keying (BFSK) : ManualDocument7 pagesBinary Frequency-Shift Keying (BFSK) : Manualمهيمن الابراهيميNo ratings yet