Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
38 viewsElectroconvulsive Therapy: by Shekhar Suntha M.SC Nursing
Electroconvulsive Therapy: by Shekhar Suntha M.SC Nursing
Uploaded by
Shekhar SunthaECT is a psychiatric treatment where seizures are electrically induced under anesthesia to have therapeutic effects. Electrodes are placed on the head to deliver a current and induce a grand mal seizure. ECT is effective for severe depression, bipolar disorder, schizophrenia, and other conditions when other treatments have failed. The treatment involves anesthesia, muscle relaxation, and inducing seizures for 30-60 seconds. Patients typically receive 6-12 treatments with precautions taken for safety and recovery monitoring.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- NP3Document12 pagesNP3Lyca Berin100% (1)
- Acuscope Myopulse M Treatment ProceeduresDocument4 pagesAcuscope Myopulse M Treatment ProceeduresshendaiNo ratings yet
- Somatic TherapiesDocument12 pagesSomatic TherapiesJasmin JacobNo ratings yet
- Life Span Development Notes-Chapter 2Document6 pagesLife Span Development Notes-Chapter 2Kayelita Wu100% (1)
- Electroconvulsive TherapyDocument11 pagesElectroconvulsive TherapyAnusha Verghese100% (1)
- Ocfs-Medical Statement of Child in ChildcareDocument2 pagesOcfs-Medical Statement of Child in ChildcareNikki NievesNo ratings yet
- Electroconvulsive Therapy: Presented By: Shweta Surwase F.Y. M.Sc. (Mental Health Nursing) MIMH, PuneDocument48 pagesElectroconvulsive Therapy: Presented By: Shweta Surwase F.Y. M.Sc. (Mental Health Nursing) MIMH, PuneShweta KateNo ratings yet
- ECTDocument8 pagesECTRoshita G PillaiNo ratings yet
- Electro Convulsive TherapyDocument5 pagesElectro Convulsive Therapysp2056251No ratings yet
- ECT PowerPoint PresentationDocument19 pagesECT PowerPoint PresentationRajesh kumar100% (1)
- Electro Convulsive Therapy: by Ms. Deepika.K, M.SC (N) - I Year, Dept of Psychiatric Nursing, KGNCDocument24 pagesElectro Convulsive Therapy: by Ms. Deepika.K, M.SC (N) - I Year, Dept of Psychiatric Nursing, KGNCNaveen RajaduraiNo ratings yet
- Ect Procedure.... 2023Document51 pagesEct Procedure.... 2023suhani.munjal27No ratings yet
- Electro Convulsive Therapy Ect by MR Kalyan Kumar MSC N CompressDocument22 pagesElectro Convulsive Therapy Ect by MR Kalyan Kumar MSC N Compresseightbal rawkNo ratings yet
- Electro Convulsive TherapyDocument15 pagesElectro Convulsive TherapyjyotichoithramNo ratings yet
- Subject: Mental Health Nursing - IDocument9 pagesSubject: Mental Health Nursing - Irupali kharabeNo ratings yet
- Electro Convulsive TherapyDocument7 pagesElectro Convulsive TherapySanjeevNo ratings yet
- EctDocument4 pagesEctRJ MarquezNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care in ECTDocument3 pagesNursing Care in ECTRawan KhateebNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care in ECTDocument3 pagesNursing Care in ECTRawan KhateebNo ratings yet
- Electroconvulsive Therapy: Aban, Katherine Maebelle G. Esguerra, Dianne Carmela RDocument46 pagesElectroconvulsive Therapy: Aban, Katherine Maebelle G. Esguerra, Dianne Carmela REdgar ManoodNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care in ECTDocument4 pagesNursing Care in ECTMarigold CortezNo ratings yet
- Electroconvulsive TherapyDocument2 pagesElectroconvulsive TherapyRiz BorbonNo ratings yet
- Electroconvulsive Therapy (ECT) : Dr. Altaf Qadir Khan Professor of Psychiatry PGMI/ LGH, LahoreDocument44 pagesElectroconvulsive Therapy (ECT) : Dr. Altaf Qadir Khan Professor of Psychiatry PGMI/ LGH, LahoreAalia RanaNo ratings yet
- Electroconvulsive TherapyDocument20 pagesElectroconvulsive TherapyHamze Abdullah Al-ShawaheenNo ratings yet
- Electroconvulsive TherapyDocument3 pagesElectroconvulsive TherapyPart movieNo ratings yet
- PSYCHIATRY Nursing SeminarDocument36 pagesPSYCHIATRY Nursing SeminarGulmoharNo ratings yet
- Electroconvulsive Therapy (ECT)Document5 pagesElectroconvulsive Therapy (ECT)Deepshikha AhlawatNo ratings yet
- ECT OrientationDocument23 pagesECT Orientationdivyaky100% (1)
- Electroconvulsive Therapy: SATHISH Rajamani M.SC (N) Lecturer Annai Meenakshi College of Nursing CoimbatoreDocument27 pagesElectroconvulsive Therapy: SATHISH Rajamani M.SC (N) Lecturer Annai Meenakshi College of Nursing CoimbatoreSathish Rajamani100% (2)
- Electroconvulsive Therapy Ect FormDocument5 pagesElectroconvulsive Therapy Ect FormRoshita G PillaiNo ratings yet
- 2 Electroconvulsive TherapyDocument3 pages2 Electroconvulsive TherapyEyad GoudaaNo ratings yet
- ECTDocument11 pagesECTmanu sethi75% (4)
- JP Electroconvulsive TherapyDocument3 pagesJP Electroconvulsive TherapyMarianne PradoNo ratings yet
- Information For Candidate: You Are ADocument9 pagesInformation For Candidate: You Are AnaungsanNo ratings yet
- Merge Merge Merge MergeDocument3 pagesMerge Merge Merge MergeJade CentinoNo ratings yet
- Electroconvulsive Therapy: Course Instructor - (Clinical) : Ms. Agnes MonicaDocument18 pagesElectroconvulsive Therapy: Course Instructor - (Clinical) : Ms. Agnes Monicaf7kx7s5ptxNo ratings yet
- Assignmment Electroconvulsive Therapy FFGDocument5 pagesAssignmment Electroconvulsive Therapy FFGRawan KhateebNo ratings yet
- Electroconvulsive TherapyDocument8 pagesElectroconvulsive TherapySimranjeet KaurNo ratings yet
- 07 - 203gangguan Psikiatrik Pada Pasien Penyakit Ginjal KronikDocument7 pages07 - 203gangguan Psikiatrik Pada Pasien Penyakit Ginjal KronikadityadefenserNo ratings yet
- Ect Protocol 2023-2024Document14 pagesEct Protocol 2023-2024Psiquiatria Clinica ProyectarteNo ratings yet
- Electroconvulsive TherapyDocument79 pagesElectroconvulsive TherapyMariam IftikharNo ratings yet
- End-Of-Electric Shock Therapy QuotationaryDocument155 pagesEnd-Of-Electric Shock Therapy QuotationaryPatrick BrodnikNo ratings yet
- Electroconvulsive TherapyDocument23 pagesElectroconvulsive TherapyRaymund Christopher Dela PeñaNo ratings yet
- Ect NotesDocument3 pagesEct NotesStudentNo ratings yet
- Amorsolo ECTDocument3 pagesAmorsolo ECTTherese ArambuloNo ratings yet
- Ect 1Document28 pagesEct 1غيداء الذويبيNo ratings yet
- ECT NDocument28 pagesECT Nammaramaryam6463No ratings yet
- ECT BrochureDocument12 pagesECT BrochureAyedh Talha100% (1)
- ECT CompDocument23 pagesECT CompPinak DeNo ratings yet
- Ect 2Document3 pagesEct 2Dinesh SharmaNo ratings yet
- Unit Ix. Somatic Therapies and Psychopharmacology Part I. Somatic Therapies A. Electroconvulsive TherapyDocument4 pagesUnit Ix. Somatic Therapies and Psychopharmacology Part I. Somatic Therapies A. Electroconvulsive TherapyKim GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Electro Convulsive Therapy (ECT)Document8 pagesElectro Convulsive Therapy (ECT)Lone SaithaNo ratings yet
- Electroconvulsive TherapyDocument11 pagesElectroconvulsive TherapySimran JosanNo ratings yet
- Electroconvulsive TherapyDocument9 pagesElectroconvulsive TherapyRoanne LaguaNo ratings yet
- 36rashmipal EtalDocument6 pages36rashmipal EtaleditorijmrhsNo ratings yet
- Electroconvulsive TherapyDocument22 pagesElectroconvulsive TherapyJasmin JacobNo ratings yet
- EPILEPSYDocument37 pagesEPILEPSYPauline AñesNo ratings yet
- Electroconvulsive Therapy: Two Types A. ModifiedDocument3 pagesElectroconvulsive Therapy: Two Types A. ModifiedXyza AlcorizaNo ratings yet
- E Stim PDFDocument6 pagesE Stim PDFAlvaro Toledo100% (2)
- EctDocument2 pagesEctJagdishVankarNo ratings yet
- Each Day I Like It Better: Autism, ECT, and the Treatment of Our Most Impaired ChildrenFrom EverandEach Day I Like It Better: Autism, ECT, and the Treatment of Our Most Impaired ChildrenRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- Each Day I Like It Better: Autism, ECT, and the Treatment of Our Most Impaired ChildrenFrom EverandEach Day I Like It Better: Autism, ECT, and the Treatment of Our Most Impaired ChildrenNo ratings yet
- Symptoms: Products & ServicesDocument4 pagesSymptoms: Products & ServicesShekhar Suntha100% (1)
- Hemant MethotologyDocument22 pagesHemant MethotologyShekhar SunthaNo ratings yet
- Lession PlanDocument14 pagesLession PlanShekhar SunthaNo ratings yet
- Preventing Mother-to-Child Transmission of HIV After Birth: Key PointsDocument7 pagesPreventing Mother-to-Child Transmission of HIV After Birth: Key PointsShekhar SunthaNo ratings yet
- Adoption and Change: Col Zulfiquer Ahmed Amin Armed Forces Medical Institute (AFMI)Document49 pagesAdoption and Change: Col Zulfiquer Ahmed Amin Armed Forces Medical Institute (AFMI)Shekhar SunthaNo ratings yet
- Concepts of ManagementDocument15 pagesConcepts of ManagementShekhar SunthaNo ratings yet
- Code of Ethics: by - Shekhar Suntha M.SC Nursing Mental Health NursingDocument56 pagesCode of Ethics: by - Shekhar Suntha M.SC Nursing Mental Health NursingShekhar SunthaNo ratings yet
- Conflict by Shekhar SunthaDocument30 pagesConflict by Shekhar SunthaShekhar SunthaNo ratings yet
- AsepsisDocument27 pagesAsepsisShekhar SunthaNo ratings yet
- Eye Care With Lesson PlanDocument12 pagesEye Care With Lesson PlanShekhar Suntha100% (1)
- Compiled Teanage PregnancyDocument101 pagesCompiled Teanage PregnancyShekhar SunthaNo ratings yet
- Effects of Heat Stress On Some Blood Parameters in BroilersDocument4 pagesEffects of Heat Stress On Some Blood Parameters in BroilersRobert PaulisNo ratings yet
- Ayushman Bharat Detailed ExplanationDocument3 pagesAyushman Bharat Detailed ExplanationnirmalNo ratings yet
- Spesifikasi - VYGON Emergency APO CPAP KitDocument2 pagesSpesifikasi - VYGON Emergency APO CPAP KitNanno LadowogoNo ratings yet
- Enhanced External Counterpulsation NewDocument11 pagesEnhanced External Counterpulsation NewRinda Putri AnggrainiNo ratings yet
- LithotripsyDocument3 pagesLithotripsyLoNo ratings yet
- Cap 6 Heart and Cardiovascular SystemDocument19 pagesCap 6 Heart and Cardiovascular Systemgorexz goreNo ratings yet
- Jurnal Sabhanga: Vol. 2 No. 2 Juli 2020: 1-8Document8 pagesJurnal Sabhanga: Vol. 2 No. 2 Juli 2020: 1-8Marsella MarsellaNo ratings yet
- Provider Building Address Street/Area P.O.Box Specialities Phone FAXDocument10 pagesProvider Building Address Street/Area P.O.Box Specialities Phone FAXnaishajNo ratings yet
- Generic Name: VORICONAZOLE Brand Name: Vfend Classification: Azole Antifungal Dosage/frequency and RouteDocument26 pagesGeneric Name: VORICONAZOLE Brand Name: Vfend Classification: Azole Antifungal Dosage/frequency and Routeanne marieNo ratings yet
- ASADocument3 pagesASAMelisa Malik50% (2)
- Procalcitonin: Uses in The Clinical Laboratory For The Diagnosis of SepsisDocument5 pagesProcalcitonin: Uses in The Clinical Laboratory For The Diagnosis of SepsismarselyagNo ratings yet
- Final Drug StudyDocument14 pagesFinal Drug StudyStephany Rae MamauagNo ratings yet
- Tatunay Reflective-Questions PDFDocument3 pagesTatunay Reflective-Questions PDFDexel Lorren ValdezNo ratings yet
- Antidyslipidemia and Antioxidant Activity of AndroDocument7 pagesAntidyslipidemia and Antioxidant Activity of AndroLorreine Elisa FaruqNo ratings yet
- IJRPR7440Document11 pagesIJRPR7440Nikhil BisuiNo ratings yet
- Nico East Ave NCP and Drug Study OBDocument3 pagesNico East Ave NCP and Drug Study OBManuel LavariasNo ratings yet
- CSP_22P31A05A5Document51 pagesCSP_22P31A05A5kavyanambariNo ratings yet
- Traumatic Brain InjuryDocument33 pagesTraumatic Brain InjuryBibaswan ChakrabartyNo ratings yet
- Hemostasis and Fibrinolysis: Adelina VladDocument82 pagesHemostasis and Fibrinolysis: Adelina VladLoly SinagaNo ratings yet
- Alcohol Withdrawal - Epidemiology, Clinical Manifestations, Course, Assessment, and Diagnosis - UpToDateDocument22 pagesAlcohol Withdrawal - Epidemiology, Clinical Manifestations, Course, Assessment, and Diagnosis - UpToDateSanti Herrera100% (1)
- GRIPHON AppendixDocument25 pagesGRIPHON AppendixYaya YayaNo ratings yet
- MPBR, Sop 3101, B 01, Version 04, Sep 42009Document78 pagesMPBR, Sop 3101, B 01, Version 04, Sep 42009SDENo ratings yet
- Presentation Thyroid ScanDocument20 pagesPresentation Thyroid ScanMuhammad Safwan Ahmad FadzilNo ratings yet
- Surgery - 2020 With CorrectionDocument74 pagesSurgery - 2020 With CorrectionUmar JameelNo ratings yet
- Indonesia) Berupa Buku Yang Diterbitkan Oleh PT EGC Pada Tahun 2009 Di JakartaDocument1 pageIndonesia) Berupa Buku Yang Diterbitkan Oleh PT EGC Pada Tahun 2009 Di JakartarivannyNo ratings yet
- Informed Consent - Laser Hair RemovalDocument4 pagesInformed Consent - Laser Hair RemovalAshraf AboNo ratings yet
- EP Lec 4 - Medical-Surgical Equipment in Acute Care SettingsDocument27 pagesEP Lec 4 - Medical-Surgical Equipment in Acute Care SettingsMichels Garments S.H Nawaz HosieryNo ratings yet
Electroconvulsive Therapy: by Shekhar Suntha M.SC Nursing
Electroconvulsive Therapy: by Shekhar Suntha M.SC Nursing
Uploaded by
Shekhar Suntha0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
38 views32 pagesECT is a psychiatric treatment where seizures are electrically induced under anesthesia to have therapeutic effects. Electrodes are placed on the head to deliver a current and induce a grand mal seizure. ECT is effective for severe depression, bipolar disorder, schizophrenia, and other conditions when other treatments have failed. The treatment involves anesthesia, muscle relaxation, and inducing seizures for 30-60 seconds. Patients typically receive 6-12 treatments with precautions taken for safety and recovery monitoring.
Original Description:
Original Title
electroconvulsivetheraphy
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentECT is a psychiatric treatment where seizures are electrically induced under anesthesia to have therapeutic effects. Electrodes are placed on the head to deliver a current and induce a grand mal seizure. ECT is effective for severe depression, bipolar disorder, schizophrenia, and other conditions when other treatments have failed. The treatment involves anesthesia, muscle relaxation, and inducing seizures for 30-60 seconds. Patients typically receive 6-12 treatments with precautions taken for safety and recovery monitoring.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
38 views32 pagesElectroconvulsive Therapy: by Shekhar Suntha M.SC Nursing
Electroconvulsive Therapy: by Shekhar Suntha M.SC Nursing
Uploaded by
Shekhar SunthaECT is a psychiatric treatment where seizures are electrically induced under anesthesia to have therapeutic effects. Electrodes are placed on the head to deliver a current and induce a grand mal seizure. ECT is effective for severe depression, bipolar disorder, schizophrenia, and other conditions when other treatments have failed. The treatment involves anesthesia, muscle relaxation, and inducing seizures for 30-60 seconds. Patients typically receive 6-12 treatments with precautions taken for safety and recovery monitoring.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 32
ELECTROCONVULSIVE
THERAPY
BY SHEKHAR SUNTHA M.SC NURSING
Electroconvulsive therapy (ECT), also known
as
is a well established, albeit
controversial psychiatric treatment in which
seizures are electrically induced in anesthetized
patients for therapeutic effects.
2. ECT is a physical/somatic therapy in which
the help of two electrodes, current is passed
through the temporal region in between the
two hemispheres of the brain, to produce a
grand mal type of seizure.
: 70-120
(The volts
usual amount of
passed in ECT is 200- current
1600mA)
: 0.7-1...5
sec
ECT relief very severe depressive illnesses when
other treatments have failed.
ECT has saved patient’s live because 15% of people
with severe depression will kill themselves.
ECT works faster than all antidepressants drugs.
Major Depression w/ or w/o psychotic features.
Bipolar disorder manic
- or depressed phase.
Acute or Catatonic Schizophrenia.
Some studies have shown efficacy in treating OCD,
Delirium, Chronic pain syndromes, and intractable
seizure disorders.
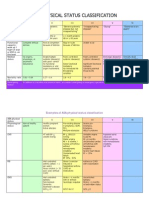
Absolute
Increased
ICP
Relative
1. Cardiovascular diseas HT Aneurysms,
problems e, N,
2. Cerebro vascular
Coronary artery
Arrhythmias
effects Spac occupyi lesion
Recent e ng s,
3. Severe
strokes,pulmonary
Aneurysms
disease
TB, Pneumonia,
The exact mechanism of action is not
known
One hypothesis
. states that ECT possibly
affects the catecholamine pathways between
diencephalon (from where seizure generalization
occurs) and limbic systems (which may be
responsible for mood disorders), also involving
the hypothalamus.
DIRECT ECT
In this, ECT is given in the absence
of anesthesia and muscular
relaxation.
This is not a commonlyused
method now.
Electrodes are placed on the side of a
patient’s head just above the temples.
The patient is given anesthetic injections and
a muscle relaxant to stop muscle contractions
that can lead to broken bones.
A small electric current is passed through the
brain.
Bilatera
l Most common, most effective
and most
cognitive dysfunction.
Each electrode placed 2.5 – 4
cm (1-1.5 inches) on the
midpoint on a line joining the
tragus of the ear and the lateral
canthus of the eye.
Unilateral
less cognitive
may be effect,
clinically
effective. less
Electrodes are
only on
placed side
one
head of
usually
dominant no
side. n
Treatmentof depression usually consists of 6-
12
treatments.
Psychosis and mania upto (or sometimes more than)
20 treatments.
Catatonia usually resolves in 3-5 treatments.
Inj. Atropine (0.6mg to 1mg)
Inj. Succinylecholine (1mg/kg/b.wt)
Inj. Sodium thiopendothal
(3-5mg/kg/b.wt)
A pretreatmentmedication such as
atropinesulfate, glycopyrolate is
administered IM 30 min before treatment,
(to decrease secretion and counteract the
effect of vagal stimulation induced by ECT).
A short acting anesthesia (the patient should
be unconscious when the ECT is given).
Muscle relaxant (to prevent muscle
contraction during the seizure reduction of
possibility of fracture or dislocated bone).
Pure oxygen before and after treatment
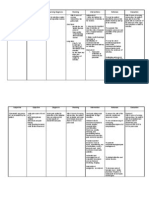
3 rooms
1. Waiting
room
2. ECT room
3. Recovery
room
Articles for
anesthesia Suction
apparatus Face
mask
Oxygen cylinder
Tongue depressor
Mouth gag
Resuscitation
apparatus
Full set of emergency drugs,
ECT drugs Defibrillator
Time 10-15mit (or more
time preparation and recovery)
Intravenous (IV) catheter
Oxygenmaskmay be
given
Electrodes are placed on the
head either unilateral or
bilateral
Anesthetic is injected into IV
Unconscious and unaware of
procedure Musclerelaxant is injected
BP cuff placed around forearm or ankle. To
Prevents muscle relaxant from paralyzing, so
doctor can confirm seizure with movement
of hand/foot.
Electric current is sent through electrodes to
brain.
Seizure lasts 30-60 seconds.
Few min later, anesthetic and muscle relaxant
wear off.
• Pre ECT care
• Intra procedure
care
• Post procedure
care
Informed consent
Fully explain the risks and
benefits of procedure and answer
questions from patients or relatives.
Information sheets.
Reduce patientsanxiety and help establish
good relationship(nurse-patient, doctor-
patient).
Administration of
drugs. Check patient
Cont…
Explain procedure.
Keep patient on NPO 6-8 hours before
ECT.
Discourage smoking just before
ECT.
Remove artificial dentures and
articles.
Vital signs.
Ensure emergency articles are
accessible. Emotional support.
Transfer patient to ECT room with
necessary records.
Checks patients identity.
Check patient is NPO and has emptied
their bowelsand bladder prior to
coming to treatment room.
Check patient is not have
jewellery/dentures wearing
been
restrictiveclothing
and
removed. ConsultECT record of treatments(including
previous anestheticproblems).
Ensure consent form is signed appropriately.
Check no medication that might or
increase seizure threshold has reduce
CheckECTbeenrecently
machine given.
is
functioning correctly.
Reassurance & support.
Place patient in supine
position. Necessary
drug administration.
Mouth gag.
Apply upward pressure
to mandible. Oxygen
administration.
Cleanthe scalp with normal
saline. Prevent fall, fracture,
dislocation
Remove the mouth gag after
Shift client post – procedure
room. Check vital signs
every 15 min.
Administerdrugs if patient is aggressive / violated
/ confused.
If respiratory
difficulty continueoxygen.
Provide side rails.
Be with the
patient.
Documentation.
You might also like
- NP3Document12 pagesNP3Lyca Berin100% (1)
- Acuscope Myopulse M Treatment ProceeduresDocument4 pagesAcuscope Myopulse M Treatment ProceeduresshendaiNo ratings yet
- Somatic TherapiesDocument12 pagesSomatic TherapiesJasmin JacobNo ratings yet
- Life Span Development Notes-Chapter 2Document6 pagesLife Span Development Notes-Chapter 2Kayelita Wu100% (1)
- Electroconvulsive TherapyDocument11 pagesElectroconvulsive TherapyAnusha Verghese100% (1)
- Ocfs-Medical Statement of Child in ChildcareDocument2 pagesOcfs-Medical Statement of Child in ChildcareNikki NievesNo ratings yet
- Electroconvulsive Therapy: Presented By: Shweta Surwase F.Y. M.Sc. (Mental Health Nursing) MIMH, PuneDocument48 pagesElectroconvulsive Therapy: Presented By: Shweta Surwase F.Y. M.Sc. (Mental Health Nursing) MIMH, PuneShweta KateNo ratings yet
- ECTDocument8 pagesECTRoshita G PillaiNo ratings yet
- Electro Convulsive TherapyDocument5 pagesElectro Convulsive Therapysp2056251No ratings yet
- ECT PowerPoint PresentationDocument19 pagesECT PowerPoint PresentationRajesh kumar100% (1)
- Electro Convulsive Therapy: by Ms. Deepika.K, M.SC (N) - I Year, Dept of Psychiatric Nursing, KGNCDocument24 pagesElectro Convulsive Therapy: by Ms. Deepika.K, M.SC (N) - I Year, Dept of Psychiatric Nursing, KGNCNaveen RajaduraiNo ratings yet
- Ect Procedure.... 2023Document51 pagesEct Procedure.... 2023suhani.munjal27No ratings yet
- Electro Convulsive Therapy Ect by MR Kalyan Kumar MSC N CompressDocument22 pagesElectro Convulsive Therapy Ect by MR Kalyan Kumar MSC N Compresseightbal rawkNo ratings yet
- Electro Convulsive TherapyDocument15 pagesElectro Convulsive TherapyjyotichoithramNo ratings yet
- Subject: Mental Health Nursing - IDocument9 pagesSubject: Mental Health Nursing - Irupali kharabeNo ratings yet
- Electro Convulsive TherapyDocument7 pagesElectro Convulsive TherapySanjeevNo ratings yet
- EctDocument4 pagesEctRJ MarquezNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care in ECTDocument3 pagesNursing Care in ECTRawan KhateebNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care in ECTDocument3 pagesNursing Care in ECTRawan KhateebNo ratings yet
- Electroconvulsive Therapy: Aban, Katherine Maebelle G. Esguerra, Dianne Carmela RDocument46 pagesElectroconvulsive Therapy: Aban, Katherine Maebelle G. Esguerra, Dianne Carmela REdgar ManoodNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care in ECTDocument4 pagesNursing Care in ECTMarigold CortezNo ratings yet
- Electroconvulsive TherapyDocument2 pagesElectroconvulsive TherapyRiz BorbonNo ratings yet
- Electroconvulsive Therapy (ECT) : Dr. Altaf Qadir Khan Professor of Psychiatry PGMI/ LGH, LahoreDocument44 pagesElectroconvulsive Therapy (ECT) : Dr. Altaf Qadir Khan Professor of Psychiatry PGMI/ LGH, LahoreAalia RanaNo ratings yet
- Electroconvulsive TherapyDocument20 pagesElectroconvulsive TherapyHamze Abdullah Al-ShawaheenNo ratings yet
- Electroconvulsive TherapyDocument3 pagesElectroconvulsive TherapyPart movieNo ratings yet
- PSYCHIATRY Nursing SeminarDocument36 pagesPSYCHIATRY Nursing SeminarGulmoharNo ratings yet
- Electroconvulsive Therapy (ECT)Document5 pagesElectroconvulsive Therapy (ECT)Deepshikha AhlawatNo ratings yet
- ECT OrientationDocument23 pagesECT Orientationdivyaky100% (1)
- Electroconvulsive Therapy: SATHISH Rajamani M.SC (N) Lecturer Annai Meenakshi College of Nursing CoimbatoreDocument27 pagesElectroconvulsive Therapy: SATHISH Rajamani M.SC (N) Lecturer Annai Meenakshi College of Nursing CoimbatoreSathish Rajamani100% (2)
- Electroconvulsive Therapy Ect FormDocument5 pagesElectroconvulsive Therapy Ect FormRoshita G PillaiNo ratings yet
- 2 Electroconvulsive TherapyDocument3 pages2 Electroconvulsive TherapyEyad GoudaaNo ratings yet
- ECTDocument11 pagesECTmanu sethi75% (4)
- JP Electroconvulsive TherapyDocument3 pagesJP Electroconvulsive TherapyMarianne PradoNo ratings yet
- Information For Candidate: You Are ADocument9 pagesInformation For Candidate: You Are AnaungsanNo ratings yet
- Merge Merge Merge MergeDocument3 pagesMerge Merge Merge MergeJade CentinoNo ratings yet
- Electroconvulsive Therapy: Course Instructor - (Clinical) : Ms. Agnes MonicaDocument18 pagesElectroconvulsive Therapy: Course Instructor - (Clinical) : Ms. Agnes Monicaf7kx7s5ptxNo ratings yet
- Assignmment Electroconvulsive Therapy FFGDocument5 pagesAssignmment Electroconvulsive Therapy FFGRawan KhateebNo ratings yet
- Electroconvulsive TherapyDocument8 pagesElectroconvulsive TherapySimranjeet KaurNo ratings yet
- 07 - 203gangguan Psikiatrik Pada Pasien Penyakit Ginjal KronikDocument7 pages07 - 203gangguan Psikiatrik Pada Pasien Penyakit Ginjal KronikadityadefenserNo ratings yet
- Ect Protocol 2023-2024Document14 pagesEct Protocol 2023-2024Psiquiatria Clinica ProyectarteNo ratings yet
- Electroconvulsive TherapyDocument79 pagesElectroconvulsive TherapyMariam IftikharNo ratings yet
- End-Of-Electric Shock Therapy QuotationaryDocument155 pagesEnd-Of-Electric Shock Therapy QuotationaryPatrick BrodnikNo ratings yet
- Electroconvulsive TherapyDocument23 pagesElectroconvulsive TherapyRaymund Christopher Dela PeñaNo ratings yet
- Ect NotesDocument3 pagesEct NotesStudentNo ratings yet
- Amorsolo ECTDocument3 pagesAmorsolo ECTTherese ArambuloNo ratings yet
- Ect 1Document28 pagesEct 1غيداء الذويبيNo ratings yet
- ECT NDocument28 pagesECT Nammaramaryam6463No ratings yet
- ECT BrochureDocument12 pagesECT BrochureAyedh Talha100% (1)
- ECT CompDocument23 pagesECT CompPinak DeNo ratings yet
- Ect 2Document3 pagesEct 2Dinesh SharmaNo ratings yet
- Unit Ix. Somatic Therapies and Psychopharmacology Part I. Somatic Therapies A. Electroconvulsive TherapyDocument4 pagesUnit Ix. Somatic Therapies and Psychopharmacology Part I. Somatic Therapies A. Electroconvulsive TherapyKim GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Electro Convulsive Therapy (ECT)Document8 pagesElectro Convulsive Therapy (ECT)Lone SaithaNo ratings yet
- Electroconvulsive TherapyDocument11 pagesElectroconvulsive TherapySimran JosanNo ratings yet
- Electroconvulsive TherapyDocument9 pagesElectroconvulsive TherapyRoanne LaguaNo ratings yet
- 36rashmipal EtalDocument6 pages36rashmipal EtaleditorijmrhsNo ratings yet
- Electroconvulsive TherapyDocument22 pagesElectroconvulsive TherapyJasmin JacobNo ratings yet
- EPILEPSYDocument37 pagesEPILEPSYPauline AñesNo ratings yet
- Electroconvulsive Therapy: Two Types A. ModifiedDocument3 pagesElectroconvulsive Therapy: Two Types A. ModifiedXyza AlcorizaNo ratings yet
- E Stim PDFDocument6 pagesE Stim PDFAlvaro Toledo100% (2)
- EctDocument2 pagesEctJagdishVankarNo ratings yet
- Each Day I Like It Better: Autism, ECT, and the Treatment of Our Most Impaired ChildrenFrom EverandEach Day I Like It Better: Autism, ECT, and the Treatment of Our Most Impaired ChildrenRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- Each Day I Like It Better: Autism, ECT, and the Treatment of Our Most Impaired ChildrenFrom EverandEach Day I Like It Better: Autism, ECT, and the Treatment of Our Most Impaired ChildrenNo ratings yet
- Symptoms: Products & ServicesDocument4 pagesSymptoms: Products & ServicesShekhar Suntha100% (1)
- Hemant MethotologyDocument22 pagesHemant MethotologyShekhar SunthaNo ratings yet
- Lession PlanDocument14 pagesLession PlanShekhar SunthaNo ratings yet
- Preventing Mother-to-Child Transmission of HIV After Birth: Key PointsDocument7 pagesPreventing Mother-to-Child Transmission of HIV After Birth: Key PointsShekhar SunthaNo ratings yet
- Adoption and Change: Col Zulfiquer Ahmed Amin Armed Forces Medical Institute (AFMI)Document49 pagesAdoption and Change: Col Zulfiquer Ahmed Amin Armed Forces Medical Institute (AFMI)Shekhar SunthaNo ratings yet
- Concepts of ManagementDocument15 pagesConcepts of ManagementShekhar SunthaNo ratings yet
- Code of Ethics: by - Shekhar Suntha M.SC Nursing Mental Health NursingDocument56 pagesCode of Ethics: by - Shekhar Suntha M.SC Nursing Mental Health NursingShekhar SunthaNo ratings yet
- Conflict by Shekhar SunthaDocument30 pagesConflict by Shekhar SunthaShekhar SunthaNo ratings yet
- AsepsisDocument27 pagesAsepsisShekhar SunthaNo ratings yet
- Eye Care With Lesson PlanDocument12 pagesEye Care With Lesson PlanShekhar Suntha100% (1)
- Compiled Teanage PregnancyDocument101 pagesCompiled Teanage PregnancyShekhar SunthaNo ratings yet
- Effects of Heat Stress On Some Blood Parameters in BroilersDocument4 pagesEffects of Heat Stress On Some Blood Parameters in BroilersRobert PaulisNo ratings yet
- Ayushman Bharat Detailed ExplanationDocument3 pagesAyushman Bharat Detailed ExplanationnirmalNo ratings yet
- Spesifikasi - VYGON Emergency APO CPAP KitDocument2 pagesSpesifikasi - VYGON Emergency APO CPAP KitNanno LadowogoNo ratings yet
- Enhanced External Counterpulsation NewDocument11 pagesEnhanced External Counterpulsation NewRinda Putri AnggrainiNo ratings yet
- LithotripsyDocument3 pagesLithotripsyLoNo ratings yet
- Cap 6 Heart and Cardiovascular SystemDocument19 pagesCap 6 Heart and Cardiovascular Systemgorexz goreNo ratings yet
- Jurnal Sabhanga: Vol. 2 No. 2 Juli 2020: 1-8Document8 pagesJurnal Sabhanga: Vol. 2 No. 2 Juli 2020: 1-8Marsella MarsellaNo ratings yet
- Provider Building Address Street/Area P.O.Box Specialities Phone FAXDocument10 pagesProvider Building Address Street/Area P.O.Box Specialities Phone FAXnaishajNo ratings yet
- Generic Name: VORICONAZOLE Brand Name: Vfend Classification: Azole Antifungal Dosage/frequency and RouteDocument26 pagesGeneric Name: VORICONAZOLE Brand Name: Vfend Classification: Azole Antifungal Dosage/frequency and Routeanne marieNo ratings yet
- ASADocument3 pagesASAMelisa Malik50% (2)
- Procalcitonin: Uses in The Clinical Laboratory For The Diagnosis of SepsisDocument5 pagesProcalcitonin: Uses in The Clinical Laboratory For The Diagnosis of SepsismarselyagNo ratings yet
- Final Drug StudyDocument14 pagesFinal Drug StudyStephany Rae MamauagNo ratings yet
- Tatunay Reflective-Questions PDFDocument3 pagesTatunay Reflective-Questions PDFDexel Lorren ValdezNo ratings yet
- Antidyslipidemia and Antioxidant Activity of AndroDocument7 pagesAntidyslipidemia and Antioxidant Activity of AndroLorreine Elisa FaruqNo ratings yet
- IJRPR7440Document11 pagesIJRPR7440Nikhil BisuiNo ratings yet
- Nico East Ave NCP and Drug Study OBDocument3 pagesNico East Ave NCP and Drug Study OBManuel LavariasNo ratings yet
- CSP_22P31A05A5Document51 pagesCSP_22P31A05A5kavyanambariNo ratings yet
- Traumatic Brain InjuryDocument33 pagesTraumatic Brain InjuryBibaswan ChakrabartyNo ratings yet
- Hemostasis and Fibrinolysis: Adelina VladDocument82 pagesHemostasis and Fibrinolysis: Adelina VladLoly SinagaNo ratings yet
- Alcohol Withdrawal - Epidemiology, Clinical Manifestations, Course, Assessment, and Diagnosis - UpToDateDocument22 pagesAlcohol Withdrawal - Epidemiology, Clinical Manifestations, Course, Assessment, and Diagnosis - UpToDateSanti Herrera100% (1)
- GRIPHON AppendixDocument25 pagesGRIPHON AppendixYaya YayaNo ratings yet
- MPBR, Sop 3101, B 01, Version 04, Sep 42009Document78 pagesMPBR, Sop 3101, B 01, Version 04, Sep 42009SDENo ratings yet
- Presentation Thyroid ScanDocument20 pagesPresentation Thyroid ScanMuhammad Safwan Ahmad FadzilNo ratings yet
- Surgery - 2020 With CorrectionDocument74 pagesSurgery - 2020 With CorrectionUmar JameelNo ratings yet
- Indonesia) Berupa Buku Yang Diterbitkan Oleh PT EGC Pada Tahun 2009 Di JakartaDocument1 pageIndonesia) Berupa Buku Yang Diterbitkan Oleh PT EGC Pada Tahun 2009 Di JakartarivannyNo ratings yet
- Informed Consent - Laser Hair RemovalDocument4 pagesInformed Consent - Laser Hair RemovalAshraf AboNo ratings yet
- EP Lec 4 - Medical-Surgical Equipment in Acute Care SettingsDocument27 pagesEP Lec 4 - Medical-Surgical Equipment in Acute Care SettingsMichels Garments S.H Nawaz HosieryNo ratings yet