Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Epidemiology of Endemic Fluorosis
Epidemiology of Endemic Fluorosis
Uploaded by
Ali HaDi Mohamed0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
117 views15 pagesFluorosis is caused by deposition of fluoride in tissues from drinking fluoride-rich water. It manifests as dental and skeletal fluorosis. Dental fluorosis causes tooth discoloration and pitting in children. Skeletal fluorosis causes pain and stiffness in the spine and joints in adults. Preventive measures include reducing fluoride intake through defluoridation of drinking water and increasing calcium and vitamin C consumption.
Original Description:
Original Title
Endemic Fluorosis
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentFluorosis is caused by deposition of fluoride in tissues from drinking fluoride-rich water. It manifests as dental and skeletal fluorosis. Dental fluorosis causes tooth discoloration and pitting in children. Skeletal fluorosis causes pain and stiffness in the spine and joints in adults. Preventive measures include reducing fluoride intake through defluoridation of drinking water and increasing calcium and vitamin C consumption.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as ppt, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
117 views15 pagesEpidemiology of Endemic Fluorosis
Epidemiology of Endemic Fluorosis
Uploaded by
Ali HaDi MohamedFluorosis is caused by deposition of fluoride in tissues from drinking fluoride-rich water. It manifests as dental and skeletal fluorosis. Dental fluorosis causes tooth discoloration and pitting in children. Skeletal fluorosis causes pain and stiffness in the spine and joints in adults. Preventive measures include reducing fluoride intake through defluoridation of drinking water and increasing calcium and vitamin C consumption.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as ppt, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 15
Epidemiology of Endemic Fluorosis
• Fluorosis is a public health problem in
many parts of the world. Onset of
fluorosis is not determined simply by
fluoride but a large number of agent,host
and environmental factors determine its
occurrence. Although fluorosis once
established is irreversible but it can be
prevented through simple interventions.
What is Fluorosis
• Fluorosis is a disease caused by deposition
of fluorides in the hard and soft tissues of
the body. It is not merely caused by excess
intake of fluoride but there are many other
attributes and variables which determine
the onset of fluorosis in human population.
It is usually characterised by discoloration
of teeth and crippling disorders.
• Worldwide in distribution
• Endemic in 22 countries
• Asia and in Asia,India and China are
worst affected
• Mexico and Argentina in Latin America
• East and North Africa are also endemic
AGENT FACTORS
• Primarily it is Fluoride which is present in drinking water
• when F in water is more than 1.5 mg per litre,it is toxic to
health
• pH in terms of alkalinity of water promotes the absorption
of F
• calcium in the diet reduces the absorption of F
• Hard water rich in Calcium reduces the F toxicity
• Fresh Fruits and Vit.C reduces the effect of F
• Trace elements like Molubdenum enhances the effect of F
Host Factors
• In School going children seen as dental
fluorosis.
• In third and fourth decade of life seen as
Skeletal Fluorosis.
• Males suffer more than females.
• Illitrates suffer more frequently in the fluorotic
belts.
• Where aluminium ores are mined,it is seen as
occupational health hazard.
Environmental Factors
• High Annual Mean Temperature
• Low Rainfall
• Low humidity
• F rich Natural subsoil rocks
• Vegetables from high F belts
• Fluoridated tooth paste particularly when used by
children
• Tropical climate
• Developing Countries
Clinical Picture of Endemic Fluorosis
• Dental Fluorosis in Children
• Skeletal Fluorosis in Adults
• Non Skeletal Fluorosis
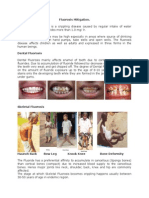
Dental Fluorosis
• Children living in high fluoride zone are bound to get
dental discoloration which may be seen even in deciduous
teeth.
• Initially glistening white teeth become dull and yellow-
white spots appear on the surface of teeth.
• Gradually these spots turn brown and presents itself in
brown streaks which are closer to the tip of the teeth.
• In late stages the whole teeth become black. Teeth may
be pitted or perforated and may even get chipped off.
• In endemic zones people lose their teeth at an early age
and may become edentate.
Skeletal Fluorosis
• It affects young as well as old. The symptoms
include severe pain and stiffness in the
backbone,joints and/or rigidity in hip bones.
• X-ray examinations of the bones reveals
thickening and high density of bones.
• Constriction of vertebral canal and
intervertebral foramen - pressure on nerves
leads to paralysis.
Tests for Skeletal Fluorosis
• Affection of the joints can be ascertained through simple tests
which can be carried out at the bed-head side and in the field:
• COIN TEST: The subject is asked to lift a coin from the floor
without bending the knee. A fluorotic subject would not be able
to lift the coin without flexing the large joints of lower extremity.
• CHIN TEST: The subject is asked to touch the anterior wall of
the chest with the chin. If there is pain or stiffness in the neck,it
indicates the presence of fluorosis.
• STRETCH TEST: The individual is made to stretch the arm
sideways,fold at elbow and touch the back of the head. When
there is pain and stiffness, it would not be possible to reach to
the occiput indicating presence of Fluorosis.
Detection of Endemicity
When more than one-fifth ( 20 % )
of the persons surveyed in a
known high fluoride area ahows
positivity of the clinical tests just
enumerated, it indicates the
endemicity.
Optimal Fluoride Intake
W.H.O. recommonds the
permissible limit of 1.5
mg/litre
Prevention of Fluorosis
• Since the major source of fluoride is
drinking water, de-fluoridation is the
best preventive measure which can be
carried out at domestic as well as
community level.
• Nutritional interventions like high intake
of vitamin C and Calcium also helps
reduce the problem.
De-fluorideation
• Precipitation methods are commonly used for de-
fluoridation.
• Lime treatment,routinely used for hardness
removal can remove F.
• Alum is used at domestic level in high doses to
remove the F.
• Resins and other filter beds are also available
filtering through which reduces the amount of F in
water.
You might also like
- Guidelines For Adverse PossessionDocument3 pagesGuidelines For Adverse Possessionlaptopdr100% (1)
- SSISDocument19 pagesSSISNag DhallNo ratings yet
- Legal Research On Rape in The PhilippinesDocument28 pagesLegal Research On Rape in The PhilippinesRbee C. Ablan100% (8)
- Epidemiology of Endemic FluorosisDocument18 pagesEpidemiology of Endemic Fluorosisfoysal100% (1)
- 1.1 BackgroundDocument43 pages1.1 Backgroundகாளையின் காதலன்No ratings yet
- National Programme For Prevention and Control of FluorosisDocument49 pagesNational Programme For Prevention and Control of FluorosisveereshNo ratings yet
- FluorosisDocument37 pagesFluorosisAreeba Babar100% (1)
- FluoriosisDocument73 pagesFluoriosisnathanielge19No ratings yet
- Dental Fluorosis and Its PreventionDocument53 pagesDental Fluorosis and Its Preventiontaramaher7No ratings yet
- 10 Fluoride 2Document70 pages10 Fluoride 2KK AgarwallNo ratings yet
- Fluoride: Nature's Cavity FighterDocument11 pagesFluoride: Nature's Cavity FighterAya OsamaNo ratings yet
- Fight For FluorideDocument21 pagesFight For Fluorideapi-462192740No ratings yet
- Should Fluoride Be Added To Drinking Water in The UK?: Chris Neurath, Fan, WhoDocument8 pagesShould Fluoride Be Added To Drinking Water in The UK?: Chris Neurath, Fan, WhoClaire LeightonNo ratings yet
- Prevention of Dental Caries - 3Document49 pagesPrevention of Dental Caries - 3j6r4qvkrkzNo ratings yet
- Dental Clinic PowerPoint TemplatesDocument14 pagesDental Clinic PowerPoint TemplatesnancyNo ratings yet
- Fluoride I Moodle 2011Document11 pagesFluoride I Moodle 2011noorNo ratings yet
- Lec 9 PDFDocument7 pagesLec 9 PDFFlorida ManNo ratings yet
- Fluoride ToxicityDocument14 pagesFluoride ToxicityLilly Paul0% (1)
- AppendicesDocument8 pagesAppendicesريام الموسويNo ratings yet
- Water Fluoridation PresentationDocument26 pagesWater Fluoridation Presentationtiara diah yepitalokaNo ratings yet
- Fluorides: Studentica: Dora Maršanić Kolegij: Engleski Jezik Voditelj Kolegija: Doc. Dr. Sc. Arijana Krišković, ProfDocument27 pagesFluorides: Studentica: Dora Maršanić Kolegij: Engleski Jezik Voditelj Kolegija: Doc. Dr. Sc. Arijana Krišković, ProfBokiNo ratings yet
- Tooth Discoloration Hypomineralization and HypoplasiaDocument5 pagesTooth Discoloration Hypomineralization and HypoplasiamirfanulhaqNo ratings yet
- Flourides and FluoridationDocument38 pagesFlourides and FluoridationmisdduaaNo ratings yet
- Fluorideindentistry 210630220303Document30 pagesFluorideindentistry 210630220303Fahad AliNo ratings yet
- Age Related Changes in Oral MucousDocument13 pagesAge Related Changes in Oral MucousJoyce Blancaflor LoganNo ratings yet
- New FluoridesDocument88 pagesNew FluoridesluckyNo ratings yet
- Fluoride ApplicationDocument14 pagesFluoride ApplicationsmhhjjyNo ratings yet
- Enamel Fluorosis in Primary Teeth, Pedodontics, by MeDocument4 pagesEnamel Fluorosis in Primary Teeth, Pedodontics, by MeRim FathallaNo ratings yet
- Fluorides in Caries Prevention: Vian Al-JafDocument54 pagesFluorides in Caries Prevention: Vian Al-JafShanaz ShaxawanNo ratings yet
- Dental FluorosisDocument8 pagesDental Fluorosiskuantumonline100% (1)
- Dental CariesDocument45 pagesDental CariesStephen AngelNo ratings yet
- TOXICITY of FLOURIDESDocument45 pagesTOXICITY of FLOURIDESNavneet KaurNo ratings yet
- Dental FluorosisDocument5 pagesDental FluorosisAbdullah EhsanNo ratings yet
- Dental Fluorosis and Its PreventionDocument4 pagesDental Fluorosis and Its PreventionSachinSharmaNo ratings yet
- Gastroenterology 09 01 2011 PDFDocument55 pagesGastroenterology 09 01 2011 PDFRita RikoNo ratings yet
- FluoridesDocument54 pagesFluoridesNAUMAN SHAHNo ratings yet
- Flouride in Dentistry by Ammar MohammedDocument10 pagesFlouride in Dentistry by Ammar Mohammedعمار محمد عباسNo ratings yet
- Consumer Health Articles - Fluoride, The Silent KillerDocument4 pagesConsumer Health Articles - Fluoride, The Silent KillershakeymacNo ratings yet
- Dental Public Health MSA BDocument83 pagesDental Public Health MSA BMustafa SaßerNo ratings yet
- Cleft Lip and Cleft Palate and Other CraniofacialDocument33 pagesCleft Lip and Cleft Palate and Other CraniofacialMurtadaNo ratings yet
- Dr. Ali Fahad Al-Fatlawi Community Dentistry LEC: 6Document3 pagesDr. Ali Fahad Al-Fatlawi Community Dentistry LEC: 6مؤمل رياض سعد كاظمNo ratings yet
- Wisconsin Department of Health Services Division of Public Health Oral Health Program P. O. Box 2659 Madison, WI 53701-2659Document2 pagesWisconsin Department of Health Services Division of Public Health Oral Health Program P. O. Box 2659 Madison, WI 53701-2659Foysal SirazeeNo ratings yet
- Fluoride Water in New ZealandDocument7 pagesFluoride Water in New ZealandMisbah Sajid ChaudhryNo ratings yet
- Diet and Dental CariesDocument10 pagesDiet and Dental Cariessh1minhNo ratings yet
- Cleft Lip PalateDocument54 pagesCleft Lip PalateGladys AilingNo ratings yet
- Tooth Wear Indices: DR Kassim AbdulazeezDocument73 pagesTooth Wear Indices: DR Kassim AbdulazeezKassim OboghenaNo ratings yet
- A Review On Effect of Fluoride Concentration in Drinking Water.Document4 pagesA Review On Effect of Fluoride Concentration in Drinking Water.Anonymous HXZigeNo ratings yet
- Presentation On Mitigation of FluorosisDocument67 pagesPresentation On Mitigation of FluorosisViswa NathanNo ratings yet
- Fluorosis Mitigation. FLUOROSIS: Fluorosis Is A Crippling Disease Caused by Regular Intake of WaterDocument2 pagesFluorosis Mitigation. FLUOROSIS: Fluorosis Is A Crippling Disease Caused by Regular Intake of Waterpanbu63No ratings yet
- Dental FluorosisDocument70 pagesDental Fluorosiskaran89No ratings yet
- 7 Oral Health of Geriatric People Modified Copy or ReferenceDocument15 pages7 Oral Health of Geriatric People Modified Copy or ReferenceNitya KrishnaNo ratings yet
- FluoridesDocument83 pagesFluoridesdr parveen bathlaNo ratings yet
- Dental Caries Booklet PDFDocument10 pagesDental Caries Booklet PDFIon BondariNo ratings yet
- Lesson 16Document20 pagesLesson 16Twinamasiko DanielNo ratings yet
- 03 Ibtw Lecture 10 PDFDocument9 pages03 Ibtw Lecture 10 PDFgreen1458No ratings yet
- Fluorosis Phosphorous Nitrate Toxicity in AnimalsDocument55 pagesFluorosis Phosphorous Nitrate Toxicity in AnimalsSunilNo ratings yet
- Ani Omfs JRNLDocument25 pagesAni Omfs JRNLAnirutha AnnaduraiNo ratings yet
- PS 2 2 1 FluorideUse - FCDocument6 pagesPS 2 2 1 FluorideUse - FCKaran AroraNo ratings yet
- Etiology of MalocclusionDocument46 pagesEtiology of MalocclusionMSA universityNo ratings yet
- A Simple Guide to Bad Breath and Mouth DiseasesFrom EverandA Simple Guide to Bad Breath and Mouth DiseasesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- Epidemiology of Endemic FluorosisDocument15 pagesEpidemiology of Endemic FluorosisAli HaDi MohamedNo ratings yet
- Epidemiology of Endemic FluorosisDocument15 pagesEpidemiology of Endemic FluorosisAli HaDi MohamedNo ratings yet
- Seminars - Next Wed. - Next TermDocument22 pagesSeminars - Next Wed. - Next TermAli HaDi MohamedNo ratings yet
- GraphsDocument20 pagesGraphsAli HaDi MohamedNo ratings yet
- Dental IndexDocument19 pagesDental IndexAli HaDi MohamedNo ratings yet
- CPS MotorolaDocument92 pagesCPS MotorolaAbdelilah CharboubNo ratings yet
- Postgraduate Research Supervision Logbook For SupervisorDocument4 pagesPostgraduate Research Supervision Logbook For SupervisorMuhammad Hilmi bin Abd Rashid Fakulti Pendidikan & Sains Sosial (FPSS)No ratings yet
- Learner Analysis QuestionsDocument1 pageLearner Analysis Questionsapi-323641842No ratings yet
- Module 5: Data Presentation: Learning Outcome: Create Appropriate Tabular and Graphical Displays Using RDocument24 pagesModule 5: Data Presentation: Learning Outcome: Create Appropriate Tabular and Graphical Displays Using RABAGAEL CACHONo ratings yet
- HW 5Document15 pagesHW 5ottoporNo ratings yet
- Klintoe PDFDocument31 pagesKlintoe PDFVelmurugan KNo ratings yet
- Safety ExercisessDocument1 pageSafety ExercisessAvralinetine EpinNo ratings yet
- Coping With Chronic Illness FinalDocument24 pagesCoping With Chronic Illness FinalNadiaNo ratings yet
- Ekman 1992Document33 pagesEkman 1992Zaima Sartaj TaheriNo ratings yet
- Games & Gambling - KitesDocument51 pagesGames & Gambling - KitesThe 18th Century Material Culture Resource Center100% (4)
- Biology ProjectDocument19 pagesBiology ProjectJaya mohanNo ratings yet
- Chapter Quiz 1. MCNDocument4 pagesChapter Quiz 1. MCNAngie SaquingNo ratings yet
- People Vs Rizal (1981)Document21 pagesPeople Vs Rizal (1981)Abigail DeeNo ratings yet
- Financing Foreign Trade PDFDocument16 pagesFinancing Foreign Trade PDFHemanth Kumar89% (9)
- 5 2 ConceptualDocument4 pages5 2 ConceptualArfiNo ratings yet
- Rabagia - MatenTertiary Tectonic and Sedimentological Evolution of The South Carpathians Foredeep: Tectonic Versus Eustatic Controlco (1999)Document22 pagesRabagia - MatenTertiary Tectonic and Sedimentological Evolution of The South Carpathians Foredeep: Tectonic Versus Eustatic Controlco (1999)Lex AlexaNo ratings yet
- Bachelor Thesis Brenda Van VeldhuizenDocument61 pagesBachelor Thesis Brenda Van Veldhuizenadolphekamsa691No ratings yet
- 5564 Quantitative TechniquesDocument8 pages5564 Quantitative TechniquesTalat RaniNo ratings yet
- Yoga InvocationsDocument4 pagesYoga InvocationsJon DoughNo ratings yet
- OralComm Q2 W6 GLAKDocument20 pagesOralComm Q2 W6 GLAKCherryl GallegoNo ratings yet
- GRE Physics Test: Practice BookDocument91 pagesGRE Physics Test: Practice BookGalo CandelaNo ratings yet
- BS en 00408-2010 PDFDocument40 pagesBS en 00408-2010 PDFShan Sandaruwan Abeywardene100% (2)
- Jenga Blocks GameDocument2 pagesJenga Blocks GameAnonymous pcR3LbvNo ratings yet
- Augustine & Original SinDocument18 pagesAugustine & Original SinSeth Walters100% (1)
- Grade 9: Research Quiz: Citation FormatsDocument20 pagesGrade 9: Research Quiz: Citation Formatsvia macario100% (1)
- Sense of BelongingnessDocument25 pagesSense of BelongingnessSrirrangam MathewNo ratings yet
- Lateral ThinkingDocument6 pagesLateral ThinkingKrengy TwiggAlinaNo ratings yet