Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Maintenance Engineering (CH: 2,0) : Instructors: Dr. M. Zeeshan Zahir Engr. Adnan Rasheed
Maintenance Engineering (CH: 2,0) : Instructors: Dr. M. Zeeshan Zahir Engr. Adnan Rasheed
Uploaded by
Altamash MunirCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Lesson 6 Designing and Managing ServiceDocument15 pagesLesson 6 Designing and Managing ServiceKryssel AsleyNo ratings yet
- RA15 Application Form For Repaying Funds To Restored Companies (Cb4)Document2 pagesRA15 Application Form For Repaying Funds To Restored Companies (Cb4)Vikas OberoiNo ratings yet
- Adams 2013 Training 740 WorkbookDocument458 pagesAdams 2013 Training 740 WorkbookAnonymous ZC1ld1CLm100% (1)
- Level 3 - Advanced Bookkeeping - Question BankDocument368 pagesLevel 3 - Advanced Bookkeeping - Question BanktrueNo ratings yet
- Maintenance and Operational Reliability: 24 Essential Building BlocksFrom EverandMaintenance and Operational Reliability: 24 Essential Building BlocksNo ratings yet
- Maintenance and Its Types PDFDocument35 pagesMaintenance and Its Types PDFSamwel MmariNo ratings yet
- Lecture No 12 MaintainabilityDocument25 pagesLecture No 12 MaintainabilityAltamash MunirNo ratings yet
- Maintenance Engineering (CH: 2,0) : Instructors: Dr. M. Zeeshan Zahir Engr. Adnan RasheedDocument13 pagesMaintenance Engineering (CH: 2,0) : Instructors: Dr. M. Zeeshan Zahir Engr. Adnan RasheedMinhaj UllahNo ratings yet
- 0 MaintenanceDocument35 pages0 MaintenanceMohamed Al-OdatNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Maintenance: Environment Maintenance and Safety 6 Semester Spring 2020Document50 pagesIntroduction To Maintenance: Environment Maintenance and Safety 6 Semester Spring 2020Jawad Ahmad Bin KhanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - Preventive and Predictive MaintenanceDocument61 pagesChapter 4 - Preventive and Predictive Maintenance000No ratings yet
- Maintenance DefinitionDocument50 pagesMaintenance DefinitionVinitSinhaNo ratings yet
- Maintenance DefinitionDocument36 pagesMaintenance DefinitionakanawNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - Preventive and Predictive MaintenanceDocument61 pagesChapter 4 - Preventive and Predictive MaintenanceAzimZakwanNo ratings yet
- LEC1 Maintenance DefinitionDocument35 pagesLEC1 Maintenance DefinitionabdulNo ratings yet
- Maintenance of Machinery Course Code: Mceng 5142 Instructor: Mesfin S. (PH.D.)Document30 pagesMaintenance of Machinery Course Code: Mceng 5142 Instructor: Mesfin S. (PH.D.)Mikias Tefera100% (1)
- Maintenance: Condition Monitoring and Maintenance (MT-362)Document21 pagesMaintenance: Condition Monitoring and Maintenance (MT-362)Engr.shamiNo ratings yet
- Chap. OneDocument26 pagesChap. OnesitoawNo ratings yet
- 1maintenance M Introduction WK1Document70 pages1maintenance M Introduction WK1aimanfznnnNo ratings yet
- Engineering Maintenance AND ManagementDocument18 pagesEngineering Maintenance AND ManagementM Soban FurqanNo ratings yet
- Maintenance of Medical EquipmentDocument33 pagesMaintenance of Medical EquipmentAbe CyberCrewPlusDotmy100% (1)
- Training On Maintenance SystemDocument32 pagesTraining On Maintenance SystemmubashirNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document51 pagesChapter 1arayaNo ratings yet
- Maintenance: Condition Monitoring and Maintenance (MT-362)Document41 pagesMaintenance: Condition Monitoring and Maintenance (MT-362)Engr.shamiNo ratings yet
- Topic 1 - DJJ50203 Maintenance and TroubleshootingDocument37 pagesTopic 1 - DJJ50203 Maintenance and TroubleshootingNazuan NazriNo ratings yet
- 1 - DJJ6153 Topic 1 - 12 July 19Document34 pages1 - DJJ6153 Topic 1 - 12 July 19Annur FatihahNo ratings yet
- Chapter Five - TEED 2106 - Maintenance Engineering NotesDocument23 pagesChapter Five - TEED 2106 - Maintenance Engineering Notesodeke aronNo ratings yet
- CH 01 IntrouctionDocument49 pagesCH 01 Introuctionlayike alemayehuNo ratings yet
- CH 01, Introduction To MaintenanceDocument50 pagesCH 01, Introduction To MaintenanceSurafel AlemuNo ratings yet
- Chap 1 (Introduction)Document26 pagesChap 1 (Introduction)Samuel WozabNo ratings yet
- Maintenance DefinitionDocument35 pagesMaintenance DefinitionVaraGoudNo ratings yet
- Part One (1&2) Introduction & Damages-1Document93 pagesPart One (1&2) Introduction & Damages-1leakebelaysmNo ratings yet
- 1&2 - Chapter 1 Introduction Maintenance and Chapter 2 Theories of DamagesDocument39 pages1&2 - Chapter 1 Introduction Maintenance and Chapter 2 Theories of Damageskeno teshomeNo ratings yet
- Advanced Maintenance Management: Jose K Puthur RCBSDocument178 pagesAdvanced Maintenance Management: Jose K Puthur RCBSSharath PanickerNo ratings yet
- Maintenance Engineering (Che-405) : DR Sikander Rafiq Assoc. ProfessorDocument37 pagesMaintenance Engineering (Che-405) : DR Sikander Rafiq Assoc. ProfessorHajra AamirNo ratings yet
- Maintenance of Machinery and Installation (Meng5311) : Adama Science and Technology UniversityDocument16 pagesMaintenance of Machinery and Installation (Meng5311) : Adama Science and Technology UniversityAbel MeketaNo ratings yet
- Enhancing Productivity Through Maintenance Management IJERTV2IS111134Document3 pagesEnhancing Productivity Through Maintenance Management IJERTV2IS111134Hen OkNo ratings yet
- Preventive Maintenance Part IDocument21 pagesPreventive Maintenance Part IKABADDI RISINGNo ratings yet
- Past Year Questions SMSDocument6 pagesPast Year Questions SMShanina1176No ratings yet
- Medical Equipment Maintenance: Dr. Mahmoud Al-RumaimaDocument28 pagesMedical Equipment Maintenance: Dr. Mahmoud Al-Rumaimaمحمد الاشولNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Maintenance of MachineryDocument41 pagesIntroduction To Maintenance of MachineryWA ADNo ratings yet
- Preventive Maintenance Part IDocument20 pagesPreventive Maintenance Part Ismodi20No ratings yet
- Easychair Preprint: Ratendra Kumar and Virender NarulaDocument8 pagesEasychair Preprint: Ratendra Kumar and Virender NarulaMohammad NajibullahNo ratings yet
- Chapter (2) 2.0 Maintenance Management System: November 2017Document28 pagesChapter (2) 2.0 Maintenance Management System: November 2017Eslam MansourNo ratings yet
- Chap1 BASIC NOTION AND CONCEPT OF MAINTENANC1Document3 pagesChap1 BASIC NOTION AND CONCEPT OF MAINTENANC1Kasi FilsNo ratings yet
- Maintenance of Machinery and Installation (Meng5311) : Adama Science and Technology UniversityDocument49 pagesMaintenance of Machinery and Installation (Meng5311) : Adama Science and Technology UniversityAbel MeketaNo ratings yet
- Class 02 - Types of Maintenance updated 1 لDocument38 pagesClass 02 - Types of Maintenance updated 1 لAbdulrahman MahmoudNo ratings yet
- CH 01 Introduction To MaintenanceDocument77 pagesCH 01 Introduction To Maintenanceyohanes AsefaNo ratings yet
- Chapter-1 IntroductionDocument21 pagesChapter-1 Introductiondawit solomonNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Djj50203Document29 pagesChapter 1 Djj50203Ulul AzmiNo ratings yet
- LEC1-Maintenance DefinitionDocument35 pagesLEC1-Maintenance DefinitionMilin SutharNo ratings yet
- Maintenance Strategies: DR David Baglee School of Computing and TechnologyDocument23 pagesMaintenance Strategies: DR David Baglee School of Computing and TechnologyThaierNo ratings yet
- Maintenance Planning and SchedulingDocument257 pagesMaintenance Planning and Schedulinglobitodelperu100% (5)
- CHP 5 FRSI 2043 Type of MaintenanceDocument41 pagesCHP 5 FRSI 2043 Type of MaintenanceFusi MokoenaNo ratings yet
- TQM - TPMDocument11 pagesTQM - TPMPandi ANo ratings yet
- Lecture 3A MaintenanceDocument43 pagesLecture 3A Maintenancemoyo josephNo ratings yet
- TX427 01 PDFDocument8 pagesTX427 01 PDFEdivaldo VisqueNo ratings yet
- Maintenance 19meDocument104 pagesMaintenance 19meawaiszulfiqar050No ratings yet
- Lect-4-Maintenance TypesDocument20 pagesLect-4-Maintenance TypesRNo ratings yet
- Guide for Asset Integrity Managers: A Comprehensive Guide to Strategies, Practices and BenchmarkingFrom EverandGuide for Asset Integrity Managers: A Comprehensive Guide to Strategies, Practices and BenchmarkingNo ratings yet
- Practical, Made Easy Guide To Building, Office And Home Automation Systems - Part OneFrom EverandPractical, Made Easy Guide To Building, Office And Home Automation Systems - Part OneNo ratings yet
- Process Control for Sheet-Metal Stamping: Process Modeling, Controller Design and Shop-Floor ImplementationFrom EverandProcess Control for Sheet-Metal Stamping: Process Modeling, Controller Design and Shop-Floor ImplementationNo ratings yet
- Maintenance Excellence: Principles, Practices, and Future TrendsFrom EverandMaintenance Excellence: Principles, Practices, and Future TrendsNo ratings yet
- University of Engineering & Technology Peshawar: Management of Kia MotorsDocument5 pagesUniversity of Engineering & Technology Peshawar: Management of Kia MotorsAltamash MunirNo ratings yet
- Project Crashing ProblemDocument9 pagesProject Crashing ProblemAltamash MunirNo ratings yet
- Experiment No. 2 Pressure Measuring Instruments: ObjectivesDocument3 pagesExperiment No. 2 Pressure Measuring Instruments: ObjectivesAltamash MunirNo ratings yet
- Experiment No. 1 Basic Terminologies in Instrumentation and ControlDocument4 pagesExperiment No. 1 Basic Terminologies in Instrumentation and ControlAltamash MunirNo ratings yet
- Experiment No. 4 Temperature Measuring Instruments: ObjectivesDocument5 pagesExperiment No. 4 Temperature Measuring Instruments: ObjectivesAltamash MunirNo ratings yet
- ME 403 Maintenance Engineering (CH: 2,0) : Instructors: Dr. M. Zeeshan Zahir Engr. Adnan RasheedDocument17 pagesME 403 Maintenance Engineering (CH: 2,0) : Instructors: Dr. M. Zeeshan Zahir Engr. Adnan RasheedAltamash MunirNo ratings yet
- Lectures 4 Maitntenance Knowledge and Engineer Job ResponsibilitiesDocument12 pagesLectures 4 Maitntenance Knowledge and Engineer Job ResponsibilitiesAltamash MunirNo ratings yet
- Lecture No 11 Reliability Centered MaintenanceDocument33 pagesLecture No 11 Reliability Centered MaintenanceAltamash Munir100% (1)
- Mid Term Exam Q PaperDocument2 pagesMid Term Exam Q PaperAltamash MunirNo ratings yet
- Attempt All Parts. Answers Should Be Concise and To The Point. - All Questions Carry 5 Marks EachDocument1 pageAttempt All Parts. Answers Should Be Concise and To The Point. - All Questions Carry 5 Marks EachAltamash MunirNo ratings yet
- ME 403 Maintenance Engineering (CH: 2,0) : Instructors: Dr. M. Zeeshan Zahir Engr. Adnan RasheedDocument18 pagesME 403 Maintenance Engineering (CH: 2,0) : Instructors: Dr. M. Zeeshan Zahir Engr. Adnan RasheedAltamash MunirNo ratings yet
- Industrial ManagementDocument10 pagesIndustrial ManagementAltamash MunirNo ratings yet
- Instructors: Dr. M. Zeeshan Zahir Engr. Adnan Rasheed: Maintenance Engineering (CH: 2,0)Document13 pagesInstructors: Dr. M. Zeeshan Zahir Engr. Adnan Rasheed: Maintenance Engineering (CH: 2,0)Altamash MunirNo ratings yet
- Experimental Investigation of The Effect of BaffleDocument5 pagesExperimental Investigation of The Effect of BaffleAltamash MunirNo ratings yet
- Physics Chapter 6 Energy Tranformations and Energy TransfersDocument27 pagesPhysics Chapter 6 Energy Tranformations and Energy Transfers0pthanatos flameNo ratings yet
- Hospitals Air DistributionDocument51 pagesHospitals Air DistributionluisNo ratings yet
- Proceso Quiros and Leonarda Villegas v. Marcelo Arjona, Teresita Balarbar, Josephine Arjona, and Conchita ArjonaDocument2 pagesProceso Quiros and Leonarda Villegas v. Marcelo Arjona, Teresita Balarbar, Josephine Arjona, and Conchita Arjonacassandra leeNo ratings yet
- Wartsila Brochure - Marine Solutions 2016Document228 pagesWartsila Brochure - Marine Solutions 2016OnceoffpleaseNo ratings yet
- ProductUploadTutorial RenderosityDocument4 pagesProductUploadTutorial RenderositySilvia SaavedraNo ratings yet
- Vadodara Stock Exchange Ltd.Document97 pagesVadodara Stock Exchange Ltd.Ashwin KevatNo ratings yet
- Individual Daily Log and Accomplishment Report: Enclosure No. 3 To Deped Order No. 011, S. 2020Document2 pagesIndividual Daily Log and Accomplishment Report: Enclosure No. 3 To Deped Order No. 011, S. 2020cristina maquintoNo ratings yet
- LM Comandi Marzo 2022Document11 pagesLM Comandi Marzo 2022grazianonetNo ratings yet
- Isoquinoline Alkenylboron ACIE 2023Document9 pagesIsoquinoline Alkenylboron ACIE 2023Mutiva YyNo ratings yet
- Vedic Multiplier DesignDocument39 pagesVedic Multiplier DesignVeena Sridhar100% (1)
- ATOM V-808: Cleaning InstructionsDocument10 pagesATOM V-808: Cleaning Instructionsjerson_rojas19899571No ratings yet
- Lion Air Eticket Itinerary / ReceiptDocument2 pagesLion Air Eticket Itinerary / ReceiptKokoh RayNo ratings yet
- Historical Development of Human RightsDocument3 pagesHistorical Development of Human RightsHazel UsanaNo ratings yet
- PSBRC Module 3 - Media Relations PowerpointDocument58 pagesPSBRC Module 3 - Media Relations PowerpointGlen LunaNo ratings yet
- Znotes-Org-Caie-IgDocument12 pagesZnotes-Org-Caie-IgMaheen EshalNo ratings yet
- M-Cic: Standard TechnologyDocument2 pagesM-Cic: Standard TechnologyAdna GezoNo ratings yet
- Astm f2164 PDFDocument5 pagesAstm f2164 PDFLuis J Villa Roel Bullon100% (1)
- Onkar Rohit ResearchDocument7 pagesOnkar Rohit ResearchBhumika IngleNo ratings yet
- Download: Setting Goals and ObjectivesDocument4 pagesDownload: Setting Goals and ObjectivesJacques VisserNo ratings yet
- RF Test Report 1851136 PDFDocument30 pagesRF Test Report 1851136 PDFlucas barriosNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Recruitement Process in JCB IndiaDocument62 pagesAnalysis of Recruitement Process in JCB IndiaAmar Rajput33% (3)
- Highway Engineering Questions and AnswersDocument221 pagesHighway Engineering Questions and Answersshafiullah100% (7)
- Technical Data Sheet NORMET Variomec MF 050 MDocument7 pagesTechnical Data Sheet NORMET Variomec MF 050 MmariaandreagfNo ratings yet
- Thefirstdayofschoolharrywong PDFDocument339 pagesThefirstdayofschoolharrywong PDFsauldez100% (1)
- Mechatronics EngineeringDocument128 pagesMechatronics EngineeringAkarsh ManojNo ratings yet
- Operational and Expenditure Plan of Result Area 2 of Strive Spiu AssamDocument2 pagesOperational and Expenditure Plan of Result Area 2 of Strive Spiu AssamKaushik DasNo ratings yet
Maintenance Engineering (CH: 2,0) : Instructors: Dr. M. Zeeshan Zahir Engr. Adnan Rasheed
Maintenance Engineering (CH: 2,0) : Instructors: Dr. M. Zeeshan Zahir Engr. Adnan Rasheed
Uploaded by
Altamash MunirOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Maintenance Engineering (CH: 2,0) : Instructors: Dr. M. Zeeshan Zahir Engr. Adnan Rasheed
Maintenance Engineering (CH: 2,0) : Instructors: Dr. M. Zeeshan Zahir Engr. Adnan Rasheed
Uploaded by
Altamash MunirCopyright:
Available Formats
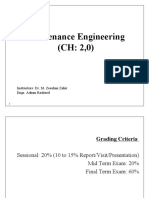
Maintenance Engineering
(CH: 2,0)
Instructors: Dr. M. Zeeshan Zahir
Engr. Adnan Rasheed
Grading Criteria
Sessional: 20% (10 to 15% Report/Visit/Presentation)
Mid Term Exam: 20%
Final Term Exam: 60%
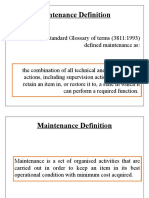
Maintenance Definition
British Standard Glossary of terms (3811:1993)
defined maintenance as:
the combination of all technical and administrative
actions, including supervision actions, intended to
retain an item in, or restore it to, a state in which it
can perform a required function.
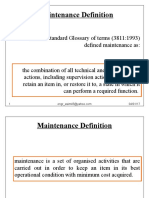
Maintenance Definition
maintenance is a set of organised activities that are
carried out in order to keep an item in its best
operational condition with minimum cost acquired.
Maintenance Activities
Activities of maintenance function could be either
repair or replacement activities, which are necessary
for an item to reach its acceptable productivity
condition and these activities, should be carried out
with a minimum possible cost.
Maintenance History
1. In the period of pre-World War II, people thought
of maintenance as an added cost to the plant which
did not increase the value of finished product.
Therefore, the maintenance at that era was
restricted to fixing the unit when it breaks because
it was the cheapest alternative
Maintenance History
2. During and after World War II at the time when the
advances of engineering and scientific technology
developed, people developed other types of
maintenance, which were much cheaper such as
preventive maintenance.
In addition, people in this era classified
maintenance as a function of the production system.
Maintenance History
Term terotechnology-
.introduced
-Recognition of need to
Development of Maintenance
present equipment
failures.
-Models for preventive
maintenance developed.
-Increased awareness of:
-Environment
-Safety
-Quality
Fix the equipment when -Need for reliable equipment.
it breaks -Reduction in costs.
Time
Pre-World War II Post-World War II Onwards 1980
Figure 2.2 Maintenance History
(Adapted From Shenoy, Bhadury
1998)
Maintenance History
3. Nowadays, increased awareness of such issues as
environment safety, quality of product and services
makes maintenance one of the most important
functions that contribute to the success of the
industry.
World-class companies are in
continuous need of a very well organised
maintenance programme to compete world-wide.
Maintenance Objectives
Maintenance objectives should be consistent with and
subordinate to production goals.
The relation between maintenance objectives and
production goals is reflected in the action of keeping
production machines and facilities in the best possible
condition.
Maintenance Objectives
• Maximising production or increasing facilities
availability at the lowest cost and at the highest
quality and safety standards.
• Reducing breakdowns and emergency shutdowns.
• Optimising resources utilisation.
• Reducing downtime.
• Improving spares stock control.
Maintenance Objectives
• Improving equipment efficiency and reducing scrap
rate.
• Minimising energy usage.
• Optimising the useful life of equipment.
• Providing reliable cost and budgetary control.
• Identifying and implementing cost reductions.
Maintenance Objectives
PLANT
Maximising Production Reduce Breakdowns
M
A
Minimising Energy I Reduce Downtime
Usage N
T
Optimising Useful Life of Improving Equipment
E
Equipment Efficiency
N
Providing Budgetary A Improving Inventory
Control N Control
C
Optimising Resources E Implementing Cost
Utilisation Reduction
Figure 2.3 Maintenance
Objectives
You might also like
- Lesson 6 Designing and Managing ServiceDocument15 pagesLesson 6 Designing and Managing ServiceKryssel AsleyNo ratings yet
- RA15 Application Form For Repaying Funds To Restored Companies (Cb4)Document2 pagesRA15 Application Form For Repaying Funds To Restored Companies (Cb4)Vikas OberoiNo ratings yet
- Adams 2013 Training 740 WorkbookDocument458 pagesAdams 2013 Training 740 WorkbookAnonymous ZC1ld1CLm100% (1)
- Level 3 - Advanced Bookkeeping - Question BankDocument368 pagesLevel 3 - Advanced Bookkeeping - Question BanktrueNo ratings yet
- Maintenance and Operational Reliability: 24 Essential Building BlocksFrom EverandMaintenance and Operational Reliability: 24 Essential Building BlocksNo ratings yet
- Maintenance and Its Types PDFDocument35 pagesMaintenance and Its Types PDFSamwel MmariNo ratings yet
- Lecture No 12 MaintainabilityDocument25 pagesLecture No 12 MaintainabilityAltamash MunirNo ratings yet
- Maintenance Engineering (CH: 2,0) : Instructors: Dr. M. Zeeshan Zahir Engr. Adnan RasheedDocument13 pagesMaintenance Engineering (CH: 2,0) : Instructors: Dr. M. Zeeshan Zahir Engr. Adnan RasheedMinhaj UllahNo ratings yet
- 0 MaintenanceDocument35 pages0 MaintenanceMohamed Al-OdatNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Maintenance: Environment Maintenance and Safety 6 Semester Spring 2020Document50 pagesIntroduction To Maintenance: Environment Maintenance and Safety 6 Semester Spring 2020Jawad Ahmad Bin KhanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - Preventive and Predictive MaintenanceDocument61 pagesChapter 4 - Preventive and Predictive Maintenance000No ratings yet
- Maintenance DefinitionDocument50 pagesMaintenance DefinitionVinitSinhaNo ratings yet
- Maintenance DefinitionDocument36 pagesMaintenance DefinitionakanawNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - Preventive and Predictive MaintenanceDocument61 pagesChapter 4 - Preventive and Predictive MaintenanceAzimZakwanNo ratings yet
- LEC1 Maintenance DefinitionDocument35 pagesLEC1 Maintenance DefinitionabdulNo ratings yet
- Maintenance of Machinery Course Code: Mceng 5142 Instructor: Mesfin S. (PH.D.)Document30 pagesMaintenance of Machinery Course Code: Mceng 5142 Instructor: Mesfin S. (PH.D.)Mikias Tefera100% (1)
- Maintenance: Condition Monitoring and Maintenance (MT-362)Document21 pagesMaintenance: Condition Monitoring and Maintenance (MT-362)Engr.shamiNo ratings yet
- Chap. OneDocument26 pagesChap. OnesitoawNo ratings yet
- 1maintenance M Introduction WK1Document70 pages1maintenance M Introduction WK1aimanfznnnNo ratings yet
- Engineering Maintenance AND ManagementDocument18 pagesEngineering Maintenance AND ManagementM Soban FurqanNo ratings yet
- Maintenance of Medical EquipmentDocument33 pagesMaintenance of Medical EquipmentAbe CyberCrewPlusDotmy100% (1)
- Training On Maintenance SystemDocument32 pagesTraining On Maintenance SystemmubashirNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document51 pagesChapter 1arayaNo ratings yet
- Maintenance: Condition Monitoring and Maintenance (MT-362)Document41 pagesMaintenance: Condition Monitoring and Maintenance (MT-362)Engr.shamiNo ratings yet
- Topic 1 - DJJ50203 Maintenance and TroubleshootingDocument37 pagesTopic 1 - DJJ50203 Maintenance and TroubleshootingNazuan NazriNo ratings yet
- 1 - DJJ6153 Topic 1 - 12 July 19Document34 pages1 - DJJ6153 Topic 1 - 12 July 19Annur FatihahNo ratings yet
- Chapter Five - TEED 2106 - Maintenance Engineering NotesDocument23 pagesChapter Five - TEED 2106 - Maintenance Engineering Notesodeke aronNo ratings yet
- CH 01 IntrouctionDocument49 pagesCH 01 Introuctionlayike alemayehuNo ratings yet
- CH 01, Introduction To MaintenanceDocument50 pagesCH 01, Introduction To MaintenanceSurafel AlemuNo ratings yet
- Chap 1 (Introduction)Document26 pagesChap 1 (Introduction)Samuel WozabNo ratings yet
- Maintenance DefinitionDocument35 pagesMaintenance DefinitionVaraGoudNo ratings yet
- Part One (1&2) Introduction & Damages-1Document93 pagesPart One (1&2) Introduction & Damages-1leakebelaysmNo ratings yet
- 1&2 - Chapter 1 Introduction Maintenance and Chapter 2 Theories of DamagesDocument39 pages1&2 - Chapter 1 Introduction Maintenance and Chapter 2 Theories of Damageskeno teshomeNo ratings yet
- Advanced Maintenance Management: Jose K Puthur RCBSDocument178 pagesAdvanced Maintenance Management: Jose K Puthur RCBSSharath PanickerNo ratings yet
- Maintenance Engineering (Che-405) : DR Sikander Rafiq Assoc. ProfessorDocument37 pagesMaintenance Engineering (Che-405) : DR Sikander Rafiq Assoc. ProfessorHajra AamirNo ratings yet
- Maintenance of Machinery and Installation (Meng5311) : Adama Science and Technology UniversityDocument16 pagesMaintenance of Machinery and Installation (Meng5311) : Adama Science and Technology UniversityAbel MeketaNo ratings yet
- Enhancing Productivity Through Maintenance Management IJERTV2IS111134Document3 pagesEnhancing Productivity Through Maintenance Management IJERTV2IS111134Hen OkNo ratings yet
- Preventive Maintenance Part IDocument21 pagesPreventive Maintenance Part IKABADDI RISINGNo ratings yet
- Past Year Questions SMSDocument6 pagesPast Year Questions SMShanina1176No ratings yet
- Medical Equipment Maintenance: Dr. Mahmoud Al-RumaimaDocument28 pagesMedical Equipment Maintenance: Dr. Mahmoud Al-Rumaimaمحمد الاشولNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Maintenance of MachineryDocument41 pagesIntroduction To Maintenance of MachineryWA ADNo ratings yet
- Preventive Maintenance Part IDocument20 pagesPreventive Maintenance Part Ismodi20No ratings yet
- Easychair Preprint: Ratendra Kumar and Virender NarulaDocument8 pagesEasychair Preprint: Ratendra Kumar and Virender NarulaMohammad NajibullahNo ratings yet
- Chapter (2) 2.0 Maintenance Management System: November 2017Document28 pagesChapter (2) 2.0 Maintenance Management System: November 2017Eslam MansourNo ratings yet
- Chap1 BASIC NOTION AND CONCEPT OF MAINTENANC1Document3 pagesChap1 BASIC NOTION AND CONCEPT OF MAINTENANC1Kasi FilsNo ratings yet
- Maintenance of Machinery and Installation (Meng5311) : Adama Science and Technology UniversityDocument49 pagesMaintenance of Machinery and Installation (Meng5311) : Adama Science and Technology UniversityAbel MeketaNo ratings yet
- Class 02 - Types of Maintenance updated 1 لDocument38 pagesClass 02 - Types of Maintenance updated 1 لAbdulrahman MahmoudNo ratings yet
- CH 01 Introduction To MaintenanceDocument77 pagesCH 01 Introduction To Maintenanceyohanes AsefaNo ratings yet
- Chapter-1 IntroductionDocument21 pagesChapter-1 Introductiondawit solomonNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Djj50203Document29 pagesChapter 1 Djj50203Ulul AzmiNo ratings yet
- LEC1-Maintenance DefinitionDocument35 pagesLEC1-Maintenance DefinitionMilin SutharNo ratings yet
- Maintenance Strategies: DR David Baglee School of Computing and TechnologyDocument23 pagesMaintenance Strategies: DR David Baglee School of Computing and TechnologyThaierNo ratings yet
- Maintenance Planning and SchedulingDocument257 pagesMaintenance Planning and Schedulinglobitodelperu100% (5)
- CHP 5 FRSI 2043 Type of MaintenanceDocument41 pagesCHP 5 FRSI 2043 Type of MaintenanceFusi MokoenaNo ratings yet
- TQM - TPMDocument11 pagesTQM - TPMPandi ANo ratings yet
- Lecture 3A MaintenanceDocument43 pagesLecture 3A Maintenancemoyo josephNo ratings yet
- TX427 01 PDFDocument8 pagesTX427 01 PDFEdivaldo VisqueNo ratings yet
- Maintenance 19meDocument104 pagesMaintenance 19meawaiszulfiqar050No ratings yet
- Lect-4-Maintenance TypesDocument20 pagesLect-4-Maintenance TypesRNo ratings yet
- Guide for Asset Integrity Managers: A Comprehensive Guide to Strategies, Practices and BenchmarkingFrom EverandGuide for Asset Integrity Managers: A Comprehensive Guide to Strategies, Practices and BenchmarkingNo ratings yet
- Practical, Made Easy Guide To Building, Office And Home Automation Systems - Part OneFrom EverandPractical, Made Easy Guide To Building, Office And Home Automation Systems - Part OneNo ratings yet
- Process Control for Sheet-Metal Stamping: Process Modeling, Controller Design and Shop-Floor ImplementationFrom EverandProcess Control for Sheet-Metal Stamping: Process Modeling, Controller Design and Shop-Floor ImplementationNo ratings yet
- Maintenance Excellence: Principles, Practices, and Future TrendsFrom EverandMaintenance Excellence: Principles, Practices, and Future TrendsNo ratings yet
- University of Engineering & Technology Peshawar: Management of Kia MotorsDocument5 pagesUniversity of Engineering & Technology Peshawar: Management of Kia MotorsAltamash MunirNo ratings yet
- Project Crashing ProblemDocument9 pagesProject Crashing ProblemAltamash MunirNo ratings yet
- Experiment No. 2 Pressure Measuring Instruments: ObjectivesDocument3 pagesExperiment No. 2 Pressure Measuring Instruments: ObjectivesAltamash MunirNo ratings yet
- Experiment No. 1 Basic Terminologies in Instrumentation and ControlDocument4 pagesExperiment No. 1 Basic Terminologies in Instrumentation and ControlAltamash MunirNo ratings yet
- Experiment No. 4 Temperature Measuring Instruments: ObjectivesDocument5 pagesExperiment No. 4 Temperature Measuring Instruments: ObjectivesAltamash MunirNo ratings yet
- ME 403 Maintenance Engineering (CH: 2,0) : Instructors: Dr. M. Zeeshan Zahir Engr. Adnan RasheedDocument17 pagesME 403 Maintenance Engineering (CH: 2,0) : Instructors: Dr. M. Zeeshan Zahir Engr. Adnan RasheedAltamash MunirNo ratings yet
- Lectures 4 Maitntenance Knowledge and Engineer Job ResponsibilitiesDocument12 pagesLectures 4 Maitntenance Knowledge and Engineer Job ResponsibilitiesAltamash MunirNo ratings yet
- Lecture No 11 Reliability Centered MaintenanceDocument33 pagesLecture No 11 Reliability Centered MaintenanceAltamash Munir100% (1)
- Mid Term Exam Q PaperDocument2 pagesMid Term Exam Q PaperAltamash MunirNo ratings yet
- Attempt All Parts. Answers Should Be Concise and To The Point. - All Questions Carry 5 Marks EachDocument1 pageAttempt All Parts. Answers Should Be Concise and To The Point. - All Questions Carry 5 Marks EachAltamash MunirNo ratings yet
- ME 403 Maintenance Engineering (CH: 2,0) : Instructors: Dr. M. Zeeshan Zahir Engr. Adnan RasheedDocument18 pagesME 403 Maintenance Engineering (CH: 2,0) : Instructors: Dr. M. Zeeshan Zahir Engr. Adnan RasheedAltamash MunirNo ratings yet
- Industrial ManagementDocument10 pagesIndustrial ManagementAltamash MunirNo ratings yet
- Instructors: Dr. M. Zeeshan Zahir Engr. Adnan Rasheed: Maintenance Engineering (CH: 2,0)Document13 pagesInstructors: Dr. M. Zeeshan Zahir Engr. Adnan Rasheed: Maintenance Engineering (CH: 2,0)Altamash MunirNo ratings yet
- Experimental Investigation of The Effect of BaffleDocument5 pagesExperimental Investigation of The Effect of BaffleAltamash MunirNo ratings yet
- Physics Chapter 6 Energy Tranformations and Energy TransfersDocument27 pagesPhysics Chapter 6 Energy Tranformations and Energy Transfers0pthanatos flameNo ratings yet
- Hospitals Air DistributionDocument51 pagesHospitals Air DistributionluisNo ratings yet
- Proceso Quiros and Leonarda Villegas v. Marcelo Arjona, Teresita Balarbar, Josephine Arjona, and Conchita ArjonaDocument2 pagesProceso Quiros and Leonarda Villegas v. Marcelo Arjona, Teresita Balarbar, Josephine Arjona, and Conchita Arjonacassandra leeNo ratings yet
- Wartsila Brochure - Marine Solutions 2016Document228 pagesWartsila Brochure - Marine Solutions 2016OnceoffpleaseNo ratings yet
- ProductUploadTutorial RenderosityDocument4 pagesProductUploadTutorial RenderositySilvia SaavedraNo ratings yet
- Vadodara Stock Exchange Ltd.Document97 pagesVadodara Stock Exchange Ltd.Ashwin KevatNo ratings yet
- Individual Daily Log and Accomplishment Report: Enclosure No. 3 To Deped Order No. 011, S. 2020Document2 pagesIndividual Daily Log and Accomplishment Report: Enclosure No. 3 To Deped Order No. 011, S. 2020cristina maquintoNo ratings yet
- LM Comandi Marzo 2022Document11 pagesLM Comandi Marzo 2022grazianonetNo ratings yet
- Isoquinoline Alkenylboron ACIE 2023Document9 pagesIsoquinoline Alkenylboron ACIE 2023Mutiva YyNo ratings yet
- Vedic Multiplier DesignDocument39 pagesVedic Multiplier DesignVeena Sridhar100% (1)
- ATOM V-808: Cleaning InstructionsDocument10 pagesATOM V-808: Cleaning Instructionsjerson_rojas19899571No ratings yet
- Lion Air Eticket Itinerary / ReceiptDocument2 pagesLion Air Eticket Itinerary / ReceiptKokoh RayNo ratings yet
- Historical Development of Human RightsDocument3 pagesHistorical Development of Human RightsHazel UsanaNo ratings yet
- PSBRC Module 3 - Media Relations PowerpointDocument58 pagesPSBRC Module 3 - Media Relations PowerpointGlen LunaNo ratings yet
- Znotes-Org-Caie-IgDocument12 pagesZnotes-Org-Caie-IgMaheen EshalNo ratings yet
- M-Cic: Standard TechnologyDocument2 pagesM-Cic: Standard TechnologyAdna GezoNo ratings yet
- Astm f2164 PDFDocument5 pagesAstm f2164 PDFLuis J Villa Roel Bullon100% (1)
- Onkar Rohit ResearchDocument7 pagesOnkar Rohit ResearchBhumika IngleNo ratings yet
- Download: Setting Goals and ObjectivesDocument4 pagesDownload: Setting Goals and ObjectivesJacques VisserNo ratings yet
- RF Test Report 1851136 PDFDocument30 pagesRF Test Report 1851136 PDFlucas barriosNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Recruitement Process in JCB IndiaDocument62 pagesAnalysis of Recruitement Process in JCB IndiaAmar Rajput33% (3)
- Highway Engineering Questions and AnswersDocument221 pagesHighway Engineering Questions and Answersshafiullah100% (7)
- Technical Data Sheet NORMET Variomec MF 050 MDocument7 pagesTechnical Data Sheet NORMET Variomec MF 050 MmariaandreagfNo ratings yet
- Thefirstdayofschoolharrywong PDFDocument339 pagesThefirstdayofschoolharrywong PDFsauldez100% (1)
- Mechatronics EngineeringDocument128 pagesMechatronics EngineeringAkarsh ManojNo ratings yet
- Operational and Expenditure Plan of Result Area 2 of Strive Spiu AssamDocument2 pagesOperational and Expenditure Plan of Result Area 2 of Strive Spiu AssamKaushik DasNo ratings yet