Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
26 viewsCommon-Base Configuration
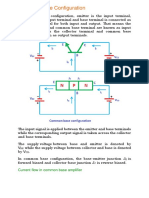
Common-Base Configuration
Uploaded by
Rakin Mohammad SifullahIn common base configuration:
- The base terminal is connected as a common terminal for both input and output of the transistor. The emitter and base terminals form the input, and the collector and base terminals form the output.
- A signal is applied between the emitter and base terminals as input, and the corresponding output signal is taken from the collector and base terminals.
- The base-emitter junction is forward biased, allowing electrons to flow from the emitter to the base. The collector-base junction is reverse biased. This current flow through the transistor constitutes the common base amplification.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Sigma Elevator Manual PDFDocument3 pagesSigma Elevator Manual PDFNadeem KhanNo ratings yet
- Experiment: 5: AIM: Study of CB & CE Characteristics of Transistor TheoryDocument5 pagesExperiment: 5: AIM: Study of CB & CE Characteristics of Transistor TheorysanjuNo ratings yet
- 10 - (NPN BJT Common Base)Document7 pages10 - (NPN BJT Common Base)Merry Kristina PanjaitanNo ratings yet
- Transistor ConfigurationDocument33 pagesTransistor ConfigurationAkanchha Mayank RusiaNo ratings yet
- CB Ce CC ConfigurationsDocument51 pagesCB Ce CC ConfigurationschanduNo ratings yet
- Lesson 5 - BJTDocument17 pagesLesson 5 - BJTPavan G MNo ratings yet
- Common Base ConfigurationDocument4 pagesCommon Base ConfigurationGiri PrasadNo ratings yet
- EDC Unit-3Document25 pagesEDC Unit-3laxmanabcdNo ratings yet
- 50 EC 301-Electron Devices and Circuits: Unit-I TransistorsDocument47 pages50 EC 301-Electron Devices and Circuits: Unit-I TransistorsTAMILSELVI S S TAMILSELVI S SNo ratings yet
- Best Unit-Ii: Civil Engineering (Vi Sem)Document54 pagesBest Unit-Ii: Civil Engineering (Vi Sem)KumarNo ratings yet
- Experiment 11 BJT As Common Base Amplifier ObjectivesDocument5 pagesExperiment 11 BJT As Common Base Amplifier ObjectiveswajahatNo ratings yet
- BJT MODULE1 PPTDocument23 pagesBJT MODULE1 PPTPurva JageNo ratings yet
- Transistor. s2r PDFDocument60 pagesTransistor. s2r PDFdiya shajiNo ratings yet
- 1.5 Bipolar Junction TransistorDocument65 pages1.5 Bipolar Junction Transistor727723euee070No ratings yet
- BJTDocument22 pagesBJTAliyan TahirNo ratings yet
- Physics TransistorDocument11 pagesPhysics TransistorMajid KhanNo ratings yet
- BE Unit-II PDFDocument21 pagesBE Unit-II PDFJagadeesh KaruturiNo ratings yet
- Transistor PPT ElecttronicsDocument77 pagesTransistor PPT ElecttronicsAnjali KumbharNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics Lec4.Document13 pagesPower Electronics Lec4.Fahmeed Ali MeoNo ratings yet
- PHY PROJ - SynopsisDocument13 pagesPHY PROJ - SynopsisPiyush HarlalkaNo ratings yet
- BJT 12122023Document38 pagesBJT 12122023Saravanan SNo ratings yet
- Unit-2 (BJTand FET) - NewDocument32 pagesUnit-2 (BJTand FET) - NewdevanshhubNo ratings yet
- 8 - Bipolar Junction TransistorDocument38 pages8 - Bipolar Junction TransistorShahnail MemonNo ratings yet
- Bipolar Junction TransistorDocument38 pagesBipolar Junction TransistorKanak KhandelwalNo ratings yet
- BJT Written Report Group 8Document11 pagesBJT Written Report Group 8Jayvee GusenalemNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 - Bipolar Junction TransistorDocument38 pagesUnit 4 - Bipolar Junction TransistorCel LuviaNo ratings yet
- Bipolar Junction TransistorsDocument41 pagesBipolar Junction Transistorshabibur rahman khanNo ratings yet
- Bi-Polar Junction TransistorDocument28 pagesBi-Polar Junction TransistorMasanam MunishNo ratings yet
- Bipolar Junction Transistor PPT - RemovedDocument12 pagesBipolar Junction Transistor PPT - RemovedsatyashopperNo ratings yet
- Ppt-Chapter 2-BJTappli and Feedback AmpliDocument81 pagesPpt-Chapter 2-BJTappli and Feedback Ampliramya hegdeNo ratings yet
- Configuration of Bipolar Junction TransistorDocument6 pagesConfiguration of Bipolar Junction TransistorhilloNo ratings yet
- Uni Junction Transistor: Working Principle of UJTDocument6 pagesUni Junction Transistor: Working Principle of UJTSanyam jainNo ratings yet
- TransistorDocument19 pagesTransistorKetaki SNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Part1Document61 pagesUnit 2 Part1thamizhan4341No ratings yet
- Ade All UnitsDocument764 pagesAde All UnitsVEDANTNo ratings yet
- AaryaDocument36 pagesAaryaKumari RaginiNo ratings yet
- BJT PresentationDocument42 pagesBJT PresentationVinodhini SNo ratings yet
- AE Unit - 2Document13 pagesAE Unit - 2aamirnasirNo ratings yet
- Bipolar TransistorDocument8 pagesBipolar TransistorHarsh VardhanNo ratings yet
- Task 2 DhiviyanshDocument15 pagesTask 2 DhiviyanshDhiviyansh Punamiya OT3 - 433No ratings yet
- 6088dbipolar Transistor ConfigurationsDocument5 pages6088dbipolar Transistor ConfigurationsSheibbanPervezNo ratings yet
- Transistor in Common Base (Continuation) and Common Emitter ConfigurationDocument14 pagesTransistor in Common Base (Continuation) and Common Emitter ConfigurationBangla TweaksNo ratings yet
- Bipolar TransistorDocument8 pagesBipolar TransistorfcmandiNo ratings yet
- UNIT-3 Bipolar Junction Transistor (BJT)Document68 pagesUNIT-3 Bipolar Junction Transistor (BJT)laxmanNo ratings yet
- 3Document80 pages3robelassefa708No ratings yet
- E-Note 12138 Content Document 20231030103638AMDocument23 pagesE-Note 12138 Content Document 20231030103638AMArun ANo ratings yet
- Lesson 7 BJTTransistorsDocument15 pagesLesson 7 BJTTransistorsBlueprint MihNo ratings yet
- Bipolar TransisDocument21 pagesBipolar TransisYashobhit SharmaNo ratings yet
- Module IvDocument10 pagesModule IvAby KhanNo ratings yet
- Lecture 6 (Ee201)Document34 pagesLecture 6 (Ee201)raphaNo ratings yet
- BJT - FET - Basic ElexDocument39 pagesBJT - FET - Basic ElexRafael Bustamante VargasNo ratings yet
- Sylhet International UniversityDocument20 pagesSylhet International UniversitySourav DipNo ratings yet
- Bipolar Junction TransistorsDocument37 pagesBipolar Junction Transistorsakshatvishwakarma06No ratings yet
- Welcome To My PresentationDocument45 pagesWelcome To My PresentationLaxman BabuNo ratings yet
- Unit 6. Introduction To Bi-Polar Junction Transistor (BJT)Document9 pagesUnit 6. Introduction To Bi-Polar Junction Transistor (BJT)Gunjan GuptaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 BJT2Document32 pagesLecture 3 BJT2MegaHertz_92No ratings yet
- Unit 5 Transistor NotesDocument12 pagesUnit 5 Transistor NotesShreyash SargarNo ratings yet
- Bipolar Junction TransistorDocument6 pagesBipolar Junction TransistorPadirikuppam PavithraNo ratings yet
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Rating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (3)
- Sorting AlgorithmsDocument9 pagesSorting AlgorithmsRakin Mohammad SifullahNo ratings yet
- Routing Information ProtocolDocument11 pagesRouting Information ProtocolRakin Mohammad SifullahNo ratings yet
- A - (A-Star) SearchingDocument2 pagesA - (A-Star) SearchingRakin Mohammad SifullahNo ratings yet
- Searching AlgorithmsDocument5 pagesSearching AlgorithmsRakin Mohammad SifullahNo ratings yet
- Traffic Light Control SystemDocument6 pagesTraffic Light Control SystemRakin Mohammad SifullahNo ratings yet
- Predicates and QuantifiersDocument31 pagesPredicates and QuantifiersRakin Mohammad SifullahNo ratings yet
- Discrete Math 3Document36 pagesDiscrete Math 3Rakin Mohammad SifullahNo ratings yet
- Propositions: Is A Declarative Sentence (That Is, A Sentence ThatDocument28 pagesPropositions: Is A Declarative Sentence (That Is, A Sentence ThatRakin Mohammad SifullahNo ratings yet
- Project IdeasDocument22 pagesProject IdeasRakin Mohammad SifullahNo ratings yet
- Python Project ProposalDocument29 pagesPython Project ProposalRakin Mohammad SifullahNo ratings yet
- Online Pharmacy Store SystemDocument3 pagesOnline Pharmacy Store SystemRakin Mohammad SifullahNo ratings yet
- SPD04N80C3 Cool MOS™ Power Transistor: FeatureDocument11 pagesSPD04N80C3 Cool MOS™ Power Transistor: FeatureOliveira OliveiraNo ratings yet
- CAO PPT Unit 1Document16 pagesCAO PPT Unit 1mdmomin7517No ratings yet
- Mobile Application Testing ChecklistDocument6 pagesMobile Application Testing ChecklistUtsav Patel0% (1)
- File PDF 3MB PDFDocument77 pagesFile PDF 3MB PDFErwin HidayatullahNo ratings yet
- October 2014Document24 pagesOctober 2014arthifexNo ratings yet
- Cummins Speed Controleer DatasheetDocument7 pagesCummins Speed Controleer DatasheetArgee PadauanNo ratings yet
- Css Slem Format s2q1 Week 1Document11 pagesCss Slem Format s2q1 Week 1John David Martizano FetalsanaNo ratings yet
- H3U - Flyer Spreads Web - EN - v3.8Document3 pagesH3U - Flyer Spreads Web - EN - v3.8saravananNo ratings yet
- Fabrication and Characterization of A PH SensorDocument4 pagesFabrication and Characterization of A PH SensorNathalia Jaquelin Gonzalez DiazNo ratings yet
- Lec 2 Introduction of It ConceptDocument11 pagesLec 2 Introduction of It ConceptWaseem QasimNo ratings yet
- KHS 700 ManualDocument27 pagesKHS 700 ManualWalterNo ratings yet
- Bcs-ICT-Question BankDocument145 pagesBcs-ICT-Question BankAzwad Abeer100% (2)
- Control Wave RTUDocument22 pagesControl Wave RTUAnonymous awwd0cnNo ratings yet
- SGM6502 8-Input, 6-Output Video Switch Matrix With Output Drivers, Input Clamp, and Bias CircuitryDocument14 pagesSGM6502 8-Input, 6-Output Video Switch Matrix With Output Drivers, Input Clamp, and Bias CircuitryblackhaWKfelNo ratings yet
- Analog and Digital Communication (ELE-323) Lecture # 6: Course Instructor: Dr. Uzma NawazDocument21 pagesAnalog and Digital Communication (ELE-323) Lecture # 6: Course Instructor: Dr. Uzma NawazZulfiqar AliNo ratings yet
- TCD ListDocument14 pagesTCD ListtechnicalofficerNo ratings yet
- ITC Assignment 02 PDFDocument7 pagesITC Assignment 02 PDFMark IlyasNo ratings yet
- Advanced Operating System CSN-502Document4 pagesAdvanced Operating System CSN-502jaibran mohd kundjee 23911004No ratings yet
- Sesi II 2021 Topicd Lect3Document29 pagesSesi II 2021 Topicd Lect3mbagavan 0712No ratings yet
- Basic - Digital - Circuits v7Document64 pagesBasic - Digital - Circuits v7Marco LopezNo ratings yet
- Determine Best Fit TopologyDocument48 pagesDetermine Best Fit TopologyLily Eudaimonia Solomon100% (2)
- ENG 571 - Lecture - Notes - Week - 7 - Part - 1Document8 pagesENG 571 - Lecture - Notes - Week - 7 - Part - 1Vinod KumarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 20 - Current Mirrors: - Input SideDocument7 pagesChapter 20 - Current Mirrors: - Input SideJesus SalvadorNo ratings yet
- Thinvent All in One PC T215 DatasheetDocument2 pagesThinvent All in One PC T215 Datasheetlax4saxNo ratings yet
- A GSM-Based Remote Temperature and Humidity MonitoDocument5 pagesA GSM-Based Remote Temperature and Humidity Monitoabdulrazaq bibinuNo ratings yet
- 10 - Chapter 2Document96 pages10 - Chapter 2Sheila JoyNo ratings yet
- Simatic Loadable Driver For CP 341 Modbus ASCII Master With 32-Bit ExtensionsDocument77 pagesSimatic Loadable Driver For CP 341 Modbus ASCII Master With 32-Bit ExtensionsSukrija RazicNo ratings yet
- Power System Protection: Dr. Lionel R. Orama Exclusa, PE Week 4Document12 pagesPower System Protection: Dr. Lionel R. Orama Exclusa, PE Week 4anuragpugaliaNo ratings yet
- K4N35 - K4N36 - K4N37: PhotocouplerDocument3 pagesK4N35 - K4N36 - K4N37: PhotocouplerrobinrofeNo ratings yet
Common-Base Configuration
Common-Base Configuration
Uploaded by
Rakin Mohammad Sifullah0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
26 views10 pagesIn common base configuration:
- The base terminal is connected as a common terminal for both input and output of the transistor. The emitter and base terminals form the input, and the collector and base terminals form the output.
- A signal is applied between the emitter and base terminals as input, and the corresponding output signal is taken from the collector and base terminals.
- The base-emitter junction is forward biased, allowing electrons to flow from the emitter to the base. The collector-base junction is reverse biased. This current flow through the transistor constitutes the common base amplification.
Original Description:
Original Title
common-base configuration
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentIn common base configuration:
- The base terminal is connected as a common terminal for both input and output of the transistor. The emitter and base terminals form the input, and the collector and base terminals form the output.
- A signal is applied between the emitter and base terminals as input, and the corresponding output signal is taken from the collector and base terminals.
- The base-emitter junction is forward biased, allowing electrons to flow from the emitter to the base. The collector-base junction is reverse biased. This current flow through the transistor constitutes the common base amplification.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
26 views10 pagesCommon-Base Configuration
Common-Base Configuration
Uploaded by
Rakin Mohammad SifullahIn common base configuration:
- The base terminal is connected as a common terminal for both input and output of the transistor. The emitter and base terminals form the input, and the collector and base terminals form the output.
- A signal is applied between the emitter and base terminals as input, and the corresponding output signal is taken from the collector and base terminals.
- The base-emitter junction is forward biased, allowing electrons to flow from the emitter to the base. The collector-base junction is reverse biased. This current flow through the transistor constitutes the common base amplification.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 10
WELCOME EVERYONE
What is Common Base Configuration ?
* In common base configuration, emitter is the input terminal, collector is
the output terminal and base terminal is connected as a common terminal for
both input and output. That means the emitter terminal and common base
terminal are known as input terminals whereas the collector terminal and
common base terminal are known as output terminals.
The input signal is applied between the emitter and base terminals while the
corresponding output signal is taken across the collector and base terminals.
Thus the base terminal of a transistor is common for both input and output
terminals and hence it is named as common base configuration.
• In common base configuration, the base terminal is grounded
so the common base configuration is also known as grounded
base configuration. Sometimes common base configuration is
referred to as common base amplifier, CB amplifier, or CB
configuration.
* The supply voltage between base and
emitter is denoted by VBE while the supply
voltage between collector and base is
denoted by VCB.
* In every configuration, the base-emitter
junction JE is always forward biased and
collector-base junction JC is always reverse
biased. Therefore, in common base
configuration, the base-emitter junction JE is
forward biased and collector-base junction
JC is reverse biased.
CURRENT FLOW IN COMMON BASE AMPLIFIER
For the sake of understanding, let us consider NPN transistor in
common base configuration.
Due to the forward bias voltage VBE, the free electrons (majority
carriers) in the emitter region experience a repulsive force from the
negative terminal of the battery similarly holes (majority carriers) in
the base region experience a repulsive force from the positive terminal
of the battery.
As a result, free electrons start
flowing from emitter to base
similarly holes start flowing from
base to emitter. Thus free
electrons which are flowing from
emitter to base and holes which
are flowing from base to emitter
conducts electric current. The
actual current is carried by free
electrons which are flowing from
emitter to base
INPUT CHARACTERISTICS
• The input characteristics describe the relationship between input
current (IE) and the input voltage (VBE).
OUTPUT CHARACTERISTICS
• The output characteristics describe the relationship between
output current (IC) and the output voltage (VCB).
THANK YOU
You might also like
- Sigma Elevator Manual PDFDocument3 pagesSigma Elevator Manual PDFNadeem KhanNo ratings yet
- Experiment: 5: AIM: Study of CB & CE Characteristics of Transistor TheoryDocument5 pagesExperiment: 5: AIM: Study of CB & CE Characteristics of Transistor TheorysanjuNo ratings yet
- 10 - (NPN BJT Common Base)Document7 pages10 - (NPN BJT Common Base)Merry Kristina PanjaitanNo ratings yet
- Transistor ConfigurationDocument33 pagesTransistor ConfigurationAkanchha Mayank RusiaNo ratings yet
- CB Ce CC ConfigurationsDocument51 pagesCB Ce CC ConfigurationschanduNo ratings yet
- Lesson 5 - BJTDocument17 pagesLesson 5 - BJTPavan G MNo ratings yet
- Common Base ConfigurationDocument4 pagesCommon Base ConfigurationGiri PrasadNo ratings yet
- EDC Unit-3Document25 pagesEDC Unit-3laxmanabcdNo ratings yet
- 50 EC 301-Electron Devices and Circuits: Unit-I TransistorsDocument47 pages50 EC 301-Electron Devices and Circuits: Unit-I TransistorsTAMILSELVI S S TAMILSELVI S SNo ratings yet
- Best Unit-Ii: Civil Engineering (Vi Sem)Document54 pagesBest Unit-Ii: Civil Engineering (Vi Sem)KumarNo ratings yet
- Experiment 11 BJT As Common Base Amplifier ObjectivesDocument5 pagesExperiment 11 BJT As Common Base Amplifier ObjectiveswajahatNo ratings yet
- BJT MODULE1 PPTDocument23 pagesBJT MODULE1 PPTPurva JageNo ratings yet
- Transistor. s2r PDFDocument60 pagesTransistor. s2r PDFdiya shajiNo ratings yet
- 1.5 Bipolar Junction TransistorDocument65 pages1.5 Bipolar Junction Transistor727723euee070No ratings yet
- BJTDocument22 pagesBJTAliyan TahirNo ratings yet
- Physics TransistorDocument11 pagesPhysics TransistorMajid KhanNo ratings yet
- BE Unit-II PDFDocument21 pagesBE Unit-II PDFJagadeesh KaruturiNo ratings yet
- Transistor PPT ElecttronicsDocument77 pagesTransistor PPT ElecttronicsAnjali KumbharNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics Lec4.Document13 pagesPower Electronics Lec4.Fahmeed Ali MeoNo ratings yet
- PHY PROJ - SynopsisDocument13 pagesPHY PROJ - SynopsisPiyush HarlalkaNo ratings yet
- BJT 12122023Document38 pagesBJT 12122023Saravanan SNo ratings yet
- Unit-2 (BJTand FET) - NewDocument32 pagesUnit-2 (BJTand FET) - NewdevanshhubNo ratings yet
- 8 - Bipolar Junction TransistorDocument38 pages8 - Bipolar Junction TransistorShahnail MemonNo ratings yet
- Bipolar Junction TransistorDocument38 pagesBipolar Junction TransistorKanak KhandelwalNo ratings yet
- BJT Written Report Group 8Document11 pagesBJT Written Report Group 8Jayvee GusenalemNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 - Bipolar Junction TransistorDocument38 pagesUnit 4 - Bipolar Junction TransistorCel LuviaNo ratings yet
- Bipolar Junction TransistorsDocument41 pagesBipolar Junction Transistorshabibur rahman khanNo ratings yet
- Bi-Polar Junction TransistorDocument28 pagesBi-Polar Junction TransistorMasanam MunishNo ratings yet
- Bipolar Junction Transistor PPT - RemovedDocument12 pagesBipolar Junction Transistor PPT - RemovedsatyashopperNo ratings yet
- Ppt-Chapter 2-BJTappli and Feedback AmpliDocument81 pagesPpt-Chapter 2-BJTappli and Feedback Ampliramya hegdeNo ratings yet
- Configuration of Bipolar Junction TransistorDocument6 pagesConfiguration of Bipolar Junction TransistorhilloNo ratings yet
- Uni Junction Transistor: Working Principle of UJTDocument6 pagesUni Junction Transistor: Working Principle of UJTSanyam jainNo ratings yet
- TransistorDocument19 pagesTransistorKetaki SNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Part1Document61 pagesUnit 2 Part1thamizhan4341No ratings yet
- Ade All UnitsDocument764 pagesAde All UnitsVEDANTNo ratings yet
- AaryaDocument36 pagesAaryaKumari RaginiNo ratings yet
- BJT PresentationDocument42 pagesBJT PresentationVinodhini SNo ratings yet
- AE Unit - 2Document13 pagesAE Unit - 2aamirnasirNo ratings yet
- Bipolar TransistorDocument8 pagesBipolar TransistorHarsh VardhanNo ratings yet
- Task 2 DhiviyanshDocument15 pagesTask 2 DhiviyanshDhiviyansh Punamiya OT3 - 433No ratings yet
- 6088dbipolar Transistor ConfigurationsDocument5 pages6088dbipolar Transistor ConfigurationsSheibbanPervezNo ratings yet
- Transistor in Common Base (Continuation) and Common Emitter ConfigurationDocument14 pagesTransistor in Common Base (Continuation) and Common Emitter ConfigurationBangla TweaksNo ratings yet
- Bipolar TransistorDocument8 pagesBipolar TransistorfcmandiNo ratings yet
- UNIT-3 Bipolar Junction Transistor (BJT)Document68 pagesUNIT-3 Bipolar Junction Transistor (BJT)laxmanNo ratings yet
- 3Document80 pages3robelassefa708No ratings yet
- E-Note 12138 Content Document 20231030103638AMDocument23 pagesE-Note 12138 Content Document 20231030103638AMArun ANo ratings yet
- Lesson 7 BJTTransistorsDocument15 pagesLesson 7 BJTTransistorsBlueprint MihNo ratings yet
- Bipolar TransisDocument21 pagesBipolar TransisYashobhit SharmaNo ratings yet
- Module IvDocument10 pagesModule IvAby KhanNo ratings yet
- Lecture 6 (Ee201)Document34 pagesLecture 6 (Ee201)raphaNo ratings yet
- BJT - FET - Basic ElexDocument39 pagesBJT - FET - Basic ElexRafael Bustamante VargasNo ratings yet
- Sylhet International UniversityDocument20 pagesSylhet International UniversitySourav DipNo ratings yet
- Bipolar Junction TransistorsDocument37 pagesBipolar Junction Transistorsakshatvishwakarma06No ratings yet
- Welcome To My PresentationDocument45 pagesWelcome To My PresentationLaxman BabuNo ratings yet
- Unit 6. Introduction To Bi-Polar Junction Transistor (BJT)Document9 pagesUnit 6. Introduction To Bi-Polar Junction Transistor (BJT)Gunjan GuptaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 BJT2Document32 pagesLecture 3 BJT2MegaHertz_92No ratings yet
- Unit 5 Transistor NotesDocument12 pagesUnit 5 Transistor NotesShreyash SargarNo ratings yet
- Bipolar Junction TransistorDocument6 pagesBipolar Junction TransistorPadirikuppam PavithraNo ratings yet
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Rating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (3)
- Sorting AlgorithmsDocument9 pagesSorting AlgorithmsRakin Mohammad SifullahNo ratings yet
- Routing Information ProtocolDocument11 pagesRouting Information ProtocolRakin Mohammad SifullahNo ratings yet
- A - (A-Star) SearchingDocument2 pagesA - (A-Star) SearchingRakin Mohammad SifullahNo ratings yet
- Searching AlgorithmsDocument5 pagesSearching AlgorithmsRakin Mohammad SifullahNo ratings yet
- Traffic Light Control SystemDocument6 pagesTraffic Light Control SystemRakin Mohammad SifullahNo ratings yet
- Predicates and QuantifiersDocument31 pagesPredicates and QuantifiersRakin Mohammad SifullahNo ratings yet
- Discrete Math 3Document36 pagesDiscrete Math 3Rakin Mohammad SifullahNo ratings yet
- Propositions: Is A Declarative Sentence (That Is, A Sentence ThatDocument28 pagesPropositions: Is A Declarative Sentence (That Is, A Sentence ThatRakin Mohammad SifullahNo ratings yet
- Project IdeasDocument22 pagesProject IdeasRakin Mohammad SifullahNo ratings yet
- Python Project ProposalDocument29 pagesPython Project ProposalRakin Mohammad SifullahNo ratings yet
- Online Pharmacy Store SystemDocument3 pagesOnline Pharmacy Store SystemRakin Mohammad SifullahNo ratings yet
- SPD04N80C3 Cool MOS™ Power Transistor: FeatureDocument11 pagesSPD04N80C3 Cool MOS™ Power Transistor: FeatureOliveira OliveiraNo ratings yet
- CAO PPT Unit 1Document16 pagesCAO PPT Unit 1mdmomin7517No ratings yet
- Mobile Application Testing ChecklistDocument6 pagesMobile Application Testing ChecklistUtsav Patel0% (1)
- File PDF 3MB PDFDocument77 pagesFile PDF 3MB PDFErwin HidayatullahNo ratings yet
- October 2014Document24 pagesOctober 2014arthifexNo ratings yet
- Cummins Speed Controleer DatasheetDocument7 pagesCummins Speed Controleer DatasheetArgee PadauanNo ratings yet
- Css Slem Format s2q1 Week 1Document11 pagesCss Slem Format s2q1 Week 1John David Martizano FetalsanaNo ratings yet
- H3U - Flyer Spreads Web - EN - v3.8Document3 pagesH3U - Flyer Spreads Web - EN - v3.8saravananNo ratings yet
- Fabrication and Characterization of A PH SensorDocument4 pagesFabrication and Characterization of A PH SensorNathalia Jaquelin Gonzalez DiazNo ratings yet
- Lec 2 Introduction of It ConceptDocument11 pagesLec 2 Introduction of It ConceptWaseem QasimNo ratings yet
- KHS 700 ManualDocument27 pagesKHS 700 ManualWalterNo ratings yet
- Bcs-ICT-Question BankDocument145 pagesBcs-ICT-Question BankAzwad Abeer100% (2)
- Control Wave RTUDocument22 pagesControl Wave RTUAnonymous awwd0cnNo ratings yet
- SGM6502 8-Input, 6-Output Video Switch Matrix With Output Drivers, Input Clamp, and Bias CircuitryDocument14 pagesSGM6502 8-Input, 6-Output Video Switch Matrix With Output Drivers, Input Clamp, and Bias CircuitryblackhaWKfelNo ratings yet
- Analog and Digital Communication (ELE-323) Lecture # 6: Course Instructor: Dr. Uzma NawazDocument21 pagesAnalog and Digital Communication (ELE-323) Lecture # 6: Course Instructor: Dr. Uzma NawazZulfiqar AliNo ratings yet
- TCD ListDocument14 pagesTCD ListtechnicalofficerNo ratings yet
- ITC Assignment 02 PDFDocument7 pagesITC Assignment 02 PDFMark IlyasNo ratings yet
- Advanced Operating System CSN-502Document4 pagesAdvanced Operating System CSN-502jaibran mohd kundjee 23911004No ratings yet
- Sesi II 2021 Topicd Lect3Document29 pagesSesi II 2021 Topicd Lect3mbagavan 0712No ratings yet
- Basic - Digital - Circuits v7Document64 pagesBasic - Digital - Circuits v7Marco LopezNo ratings yet
- Determine Best Fit TopologyDocument48 pagesDetermine Best Fit TopologyLily Eudaimonia Solomon100% (2)
- ENG 571 - Lecture - Notes - Week - 7 - Part - 1Document8 pagesENG 571 - Lecture - Notes - Week - 7 - Part - 1Vinod KumarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 20 - Current Mirrors: - Input SideDocument7 pagesChapter 20 - Current Mirrors: - Input SideJesus SalvadorNo ratings yet
- Thinvent All in One PC T215 DatasheetDocument2 pagesThinvent All in One PC T215 Datasheetlax4saxNo ratings yet
- A GSM-Based Remote Temperature and Humidity MonitoDocument5 pagesA GSM-Based Remote Temperature and Humidity Monitoabdulrazaq bibinuNo ratings yet
- 10 - Chapter 2Document96 pages10 - Chapter 2Sheila JoyNo ratings yet
- Simatic Loadable Driver For CP 341 Modbus ASCII Master With 32-Bit ExtensionsDocument77 pagesSimatic Loadable Driver For CP 341 Modbus ASCII Master With 32-Bit ExtensionsSukrija RazicNo ratings yet
- Power System Protection: Dr. Lionel R. Orama Exclusa, PE Week 4Document12 pagesPower System Protection: Dr. Lionel R. Orama Exclusa, PE Week 4anuragpugaliaNo ratings yet
- K4N35 - K4N36 - K4N37: PhotocouplerDocument3 pagesK4N35 - K4N36 - K4N37: PhotocouplerrobinrofeNo ratings yet