Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Antithyroid Medications
Antithyroid Medications
Uploaded by
mkct1110 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
16 views4 pagesThis document discusses different medications used to treat hyperthyroidism. It describes how antithyroid medications like propylthiouracil (PTU) and methimazole work by inhibiting the thyroid's production of thyroid hormones. It notes some of the potential side effects of these drugs and reasons for using PTU over methimazole. Inorganic iodide and lithium carbonate are also mentioned as having inhibitory effects on the thyroid gland. Propranolol is described as helping to minimize sympathetic overactivity in hyperthyroid patients.
Original Description:
Antithyroid meds (notes from Cummings)
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document discusses different medications used to treat hyperthyroidism. It describes how antithyroid medications like propylthiouracil (PTU) and methimazole work by inhibiting the thyroid's production of thyroid hormones. It notes some of the potential side effects of these drugs and reasons for using PTU over methimazole. Inorganic iodide and lithium carbonate are also mentioned as having inhibitory effects on the thyroid gland. Propranolol is described as helping to minimize sympathetic overactivity in hyperthyroid patients.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
16 views4 pagesAntithyroid Medications
Antithyroid Medications
Uploaded by
mkct111This document discusses different medications used to treat hyperthyroidism. It describes how antithyroid medications like propylthiouracil (PTU) and methimazole work by inhibiting the thyroid's production of thyroid hormones. It notes some of the potential side effects of these drugs and reasons for using PTU over methimazole. Inorganic iodide and lithium carbonate are also mentioned as having inhibitory effects on the thyroid gland. Propranolol is described as helping to minimize sympathetic overactivity in hyperthyroid patients.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 4
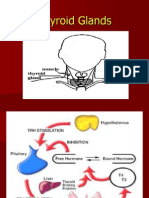
ANTITHYROID MEDICATIONS
INHIBITS
oxidation and coupling of
organification of iodine iodotyrosines
***PTU- inhibits the thyroidal and extrathyroidal conversion of T4 to T3
ANTITHYROID MEDICATIONS
AGRANULOCYTOSIS- most dangerous side effect; occurs in 0.2%
Methimazole: Chlolestatic hepatitis
PTU: hepatocellular hepatitis, lupuslike vasculitis
Instances when PTU is used as primary medication:
First trimester pregnancy
Thyroid storm
Patients who show sensitivity and intolerance to methimazole
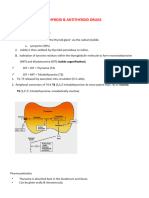
INORGANIC IODIDE
MOA:
Inhibits thyroglobulin proteolysis
Inhibits thyroidal iodine transport, oxidation, and organification
5 to 10 drops of a saturated solution of potassium iodide (Lugol solution)
several times daily
Given in preparation to thyroidectomy
Lithium carbonate-proved effective in doses of 300 mg three or four
times daily
PROPRANOLOL
Minimize many of the sympathetic overdrive
Can benefit patients with atrial fibrillation and heart failure
Reduce symptoms of thyrotoxicosis:
before and for several weeks after 131I therapy
before subtotal thyroidectomy
Thyroiditis
Thyroid storm
You might also like
- Osce - D&CDocument2 pagesOsce - D&Cmkct111No ratings yet
- Hema RecallDocument11 pagesHema Recallmkct111100% (1)
- Thyroid and Antithyroid Drugs-1Document24 pagesThyroid and Antithyroid Drugs-1fourtechmediadmeagentsNo ratings yet
- Treatment of ThyroidDocument2 pagesTreatment of ThyroidFirdaus Fariq AhmadNo ratings yet
- Antithyroid Drugs: Pharmacology and Therapy Faculty of Medicine Lampung UniversityDocument26 pagesAntithyroid Drugs: Pharmacology and Therapy Faculty of Medicine Lampung UniversityRiska PriyaniNo ratings yet
- Anti - Thyroid Drugs: Renju.S.RaviDocument27 pagesAnti - Thyroid Drugs: Renju.S.RavidrfatimarizNo ratings yet
- Antithyroid Drugs: Dr. Novita Carolia, M.Sc. Pharmacology and Therapy Faculty of Medicine Lampung UniversityDocument26 pagesAntithyroid Drugs: Dr. Novita Carolia, M.Sc. Pharmacology and Therapy Faculty of Medicine Lampung Universitynovita caroliaNo ratings yet
- Antithyroid Drugs: Dr. Novita Carolia, M.Sc. Pharmacology and Therapy Faculty of Medicine Lampung UniversityDocument26 pagesAntithyroid Drugs: Dr. Novita Carolia, M.Sc. Pharmacology and Therapy Faculty of Medicine Lampung UniversityDhita Dwi NandaNo ratings yet
- The First Line of Treatment For HypDocument1 pageThe First Line of Treatment For HypMuhammad Baihaqi SiddiqNo ratings yet
- Treatment of HyperthyroidismDocument9 pagesTreatment of HyperthyroidismAmit NayakNo ratings yet
- Anti-Thyroid and Thyroid DrugsDocument36 pagesAnti-Thyroid and Thyroid DrugsDylan MansillaNo ratings yet
- Thyroid DrugsDocument6 pagesThyroid DrugsThe Real UploaderNo ratings yet
- Thyroid Disorders - 2023Document82 pagesThyroid Disorders - 2023JEPHTHAH KWASI DANSONo ratings yet
- Anti Thyroid DrugsDocument16 pagesAnti Thyroid DrugsDeshmukh KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 6 Thyroid and Antithyroid DrugsDocument28 pagesLesson 6 Thyroid and Antithyroid DrugstheintrovNo ratings yet
- DG and Poison ResearchDocument5 pagesDG and Poison ResearchBishoy EmileNo ratings yet
- Tyroid Drug - ppt3Document15 pagesTyroid Drug - ppt3nurliah armandNo ratings yet
- Antithyroid DrugsDocument52 pagesAntithyroid DrugsYeyen MusainiNo ratings yet
- 2 Thyroid and Antithyroid DrugsDocument24 pages2 Thyroid and Antithyroid DrugsLiza Marie de Guzman100% (1)
- 14) Drugs For Thyroid DisordersDocument13 pages14) Drugs For Thyroid DisordersLatiNo ratings yet
- Thyroid & Antithyroid DrugsDocument27 pagesThyroid & Antithyroid DrugsjabirNo ratings yet
- Thyroid CrisisDocument34 pagesThyroid CrisisRidyah Ning TyasNo ratings yet
- Theme 2: Thyroid Diseases: Study GoalsDocument9 pagesTheme 2: Thyroid Diseases: Study GoalsOlesyaNo ratings yet
- 11 - Drugs For Thyroid Problems2Document51 pages11 - Drugs For Thyroid Problems2nica velanoNo ratings yet
- I. Answer The Following QuestionsDocument9 pagesI. Answer The Following QuestionsFaheem MusthafaNo ratings yet
- 05 Chapter Endrocrine SystemDocument40 pages05 Chapter Endrocrine SystemMSKCNo ratings yet
- Thyroid & Anti-Thyroid Drugs: Prof. Dr. Abdul RashidDocument36 pagesThyroid & Anti-Thyroid Drugs: Prof. Dr. Abdul RashidMomina TariqNo ratings yet
- Endocrine Drug: T4 Is Secreted in Excess To T3Document10 pagesEndocrine Drug: T4 Is Secreted in Excess To T3emmanuelNo ratings yet
- ThyroidDocument5 pagesThyroiddewisuryandariNo ratings yet
- Anti-Thyroid DrugsDocument17 pagesAnti-Thyroid DrugsVersatile UnitNo ratings yet
- Endocrine Pharmacology: Thyroid & AntithyroidDocument54 pagesEndocrine Pharmacology: Thyroid & AntithyroidRegina CiputraNo ratings yet
- Thyroid & Antithyroid Drugs - 2020Document7 pagesThyroid & Antithyroid Drugs - 2020ireneNo ratings yet
- Anti Thyroid DrugsDocument38 pagesAnti Thyroid Drugsone_nd_onlyuNo ratings yet
- Antithyroid Drugs and LiverDocument70 pagesAntithyroid Drugs and LiverInar shalhoobNo ratings yet
- Endocrine Pharmacology by DR - Mayur SaytaDocument27 pagesEndocrine Pharmacology by DR - Mayur Saytasahilthakker2012No ratings yet
- Management and Medications in Thyroid Strom and Myxoedema ComaDocument41 pagesManagement and Medications in Thyroid Strom and Myxoedema ComaBhavesh kunvarNo ratings yet
- The Thyroid Gland PRINT 2021Document9 pagesThe Thyroid Gland PRINT 2021abcde990075No ratings yet
- Thyroid DisordersDocument62 pagesThyroid Disorderslibentadesse57No ratings yet
- Outpatient Management of Thyroid Disorders PDFDocument8 pagesOutpatient Management of Thyroid Disorders PDFمحمد سلام محمدNo ratings yet
- Endo PDFDocument16 pagesEndo PDFDanekka TanNo ratings yet
- Methotrexte PIDocument27 pagesMethotrexte PIMichael FreudigerNo ratings yet
- Jabrocka Hybel2015Document21 pagesJabrocka Hybel2015Ana CortezNo ratings yet
- Anti ThyroidDocument19 pagesAnti ThyroidRia MicuaNo ratings yet
- Propylthiouracil 2Document14 pagesPropylthiouracil 2Magdy Ali ELsherbenyNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology of ThyroidDocument32 pagesPharmacology of Thyroidbrigita charvioNo ratings yet
- Thyroid and Antithyroid DrugsDocument38 pagesThyroid and Antithyroid DrugsbrkbsnNo ratings yet
- REVISED Thyroid and Antithyroid AgentsDocument27 pagesREVISED Thyroid and Antithyroid AgentsDUEÑAS, MARIELNo ratings yet
- Thyroid DisorderDocument10 pagesThyroid DisorderDr-Mohammed ElsawyNo ratings yet
- Thyroid Hormones & DrugsDocument51 pagesThyroid Hormones & DrugsSUTHANNo ratings yet
- Trachea: Thyroid Agents Thyroid Gland Is Located in The Middle of The Neck and SurroundsDocument10 pagesTrachea: Thyroid Agents Thyroid Gland Is Located in The Middle of The Neck and SurroundsMIR SARTAJNo ratings yet
- Anti-Thyroid Drugs and Thyroid HormoneDocument7 pagesAnti-Thyroid Drugs and Thyroid Hormonemicheal1960100% (1)
- Antithyroid DrugsDocument46 pagesAntithyroid Drugsalhsnym820No ratings yet
- Pharmacological Properties of PTUDocument21 pagesPharmacological Properties of PTUHanif JundanaNo ratings yet
- Lecture3-Thyroid DrugsDocument20 pagesLecture3-Thyroid DrugsPeter MaithyaNo ratings yet
- Thyroid Disorders: Tapan A. Patel Cuong Nguyen Mona JamaldinianDocument41 pagesThyroid Disorders: Tapan A. Patel Cuong Nguyen Mona Jamaldiniansheila_kohNo ratings yet
- Radioactive Iodine Therapy (Rai) : GoalsDocument6 pagesRadioactive Iodine Therapy (Rai) : GoalsFirras SalsabilaNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology of Thyroid HormonesDocument56 pagesPharmacology of Thyroid HormonesDr.U.P.Rathnakar.MD.DIH.PGDHMNo ratings yet
- 15 2020 Thyroid - Antithyroid Drugs - SlidesDocument26 pages15 2020 Thyroid - Antithyroid Drugs - Slidesالبيان البيانNo ratings yet
- Obat AntitiroidDocument2 pagesObat AntitiroidIWayanSuparthanayaNo ratings yet
- Pharmacotherapy - Thyroid Disorder PDFDocument63 pagesPharmacotherapy - Thyroid Disorder PDFnadiah100% (3)
- Thyroid, Obesity and Metabolism: Exploring Links Between Thyroid Function, Obesity, Metabolism and LifestyleFrom EverandThyroid, Obesity and Metabolism: Exploring Links Between Thyroid Function, Obesity, Metabolism and LifestyleNo ratings yet
- Iodine Deficiency, A Simple Guide to the Condition, Treatment and Related DiseasesFrom EverandIodine Deficiency, A Simple Guide to the Condition, Treatment and Related DiseasesRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- CPG On Allergic Rhinitis 2Document8 pagesCPG On Allergic Rhinitis 2mkct111No ratings yet
- Physiology of The Auditory SystemDocument47 pagesPhysiology of The Auditory Systemmkct111No ratings yet
- Pediatric Neurology - Pediatric Epilepsy SyndromeDocument6 pagesPediatric Neurology - Pediatric Epilepsy Syndromemkct111100% (1)
- Preventive Pediatrics Part 2Document5 pagesPreventive Pediatrics Part 2mkct111No ratings yet
- Eponymous Signs in EntDocument10 pagesEponymous Signs in Entmkct111No ratings yet
- Benign Lesions of The Ovary NotesDocument5 pagesBenign Lesions of The Ovary Notesmkct111No ratings yet
- Emailing CPG-E PDFDocument206 pagesEmailing CPG-E PDFCarlos H. AcuñaNo ratings yet
- Preventive Pediatrics Part 1Document6 pagesPreventive Pediatrics Part 1mkct111No ratings yet
- Preventive Pediatrics Part 3Document5 pagesPreventive Pediatrics Part 3mkct111No ratings yet
- Emergencies Flashcards CompleteDocument109 pagesEmergencies Flashcards Completemkct111No ratings yet
- Biochemist Ry Immunology Microbiolo Gy Pathology: Rapid ReviewDocument1 pageBiochemist Ry Immunology Microbiolo Gy Pathology: Rapid Reviewmkct111No ratings yet
- Sanctity and ScarcityDocument27 pagesSanctity and Scarcitymkct111No ratings yet
- Pediatric Surgery: Review Questions: Self-Assessment in General SurgeryDocument3 pagesPediatric Surgery: Review Questions: Self-Assessment in General Surgerymkct111No ratings yet
- OSCE - ColposDocument1 pageOSCE - Colposmkct111No ratings yet
- Pedia StickersDocument8 pagesPedia Stickersmkct111100% (1)
- Herpes SimpexDocument1 pageHerpes Simpexmkct111No ratings yet
- Psych ReviewerDocument28 pagesPsych Reviewermkct111No ratings yet