Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Authoritarian States: Cuba and Fidel Castro. The Beginning of Revolution
Authoritarian States: Cuba and Fidel Castro. The Beginning of Revolution
Uploaded by
Enrique0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1 views17 pagesOriginal Title
Authoritarian_States_Cuba_I (2).pptx
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1 views17 pagesAuthoritarian States: Cuba and Fidel Castro. The Beginning of Revolution
Authoritarian States: Cuba and Fidel Castro. The Beginning of Revolution
Uploaded by
EnriqueCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 17
Authoritarian States
Cuba and Fidel Castro. The beginning of Revolution
Overview
● 1902: Cuba got its independence from Spain with the help of USA
● However, the US Platt Amendment of 1901, which the 1902 Cuban
constitution had to include, gave the USA powers of supervision and
intervention.
● Cuban politics was corrupt (obbey the US will) and, in the 1920s, students
and others launched radical protest movements.
● From 1927, Cuba was ruled by the dictator Gerardo Machado, but protests
and a general strike in 1933 forced him to flee. The hopes of the 1933
radicals ended in 1934, when power increasingly passed to Fulgencio
Batista.From 1934 to 1959, Batista ruled directly or through a series of puppet
presidents.
Overview
● In 1953, Fidel Castro launched an unsuccessful attack on the army barracks
at Moncada. In Mexico, his 26 July Movement planned Batista’s overthrow.
● In 1956, Castro landed in Cuba with a small group of revolutionaries. The
group included Che Guevara. By 1959, their guerrilla war had forced Batista
to free Cuba
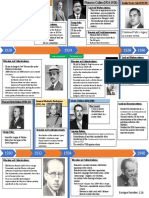
The Cuban Revolution Fulgencio
Batista
● The Cuban Revolution was a conflict
between supporters of the government of
Cuba & anti-government rebels – Gov.
leader = Fulgencio Batista – Rebel leader =
Fidel Castro
● The war would draw on Cold War ideas &
involve both superpowers Fidel
Castro
Who was Batista
● Batista was a former military officer who
rose to power with the help of the US.-
- A big anti-Communist supporter
- Allowed US companies in Cuba
● Batista used secret police & terror to
control the country – Ruled from 1933 till
Batista and
1959 the US
● He made himself dictator: Many people president
Eisenhower
were discontent (poor education, poverty,
healthcare was limited)
● Poverty was mostly because the the
Economy of Cuba was based only in
sugarcane exports to the US.
Who is Fidel Castro?
● Fidel Castro is a former lawyer turned
revolutionary – A believer that reform is
needed in Cuba without US help
● astro attempted to overthrow Batista’s
government for seven years.
● He lost many battles, and even he got
arrested by Batista in Mexico until 1955
when he wa released. Immediately put
together a new group of rebel fighters
● Leads a group of rebels known as the “26th
of July Movement” – Gifted speaker &
organizer
The issues of Castro and his follower against Batista
● Castro & the “26th of July Movement” wished to
see democratic reforms brought to Cuba – Open
elections – More civil rights – Economic /
education reforms
● Castro & his supporters also wanted to remove
the US’ dominance of Cuba's economy
How did Fidel wage his war against Batista?
● Fidel & his followers waged a guerilla war
against Batista’ s government – Attacked
from Sierra Maestra Mountains
● Used hit-and-run tactics against Batista’s
troops – Popular among the poor people
of Cuba
How did Castro eventually defeat Batista & gain
control of Cuba’s government?
● Two (2) things: – Batista looses the
support of the people – The US
withdraws its support
● Without American backing, Batista is
forced to flee – Castro takes control of
the government
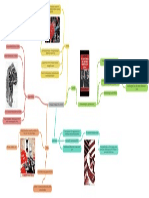
CUBA VS USA
● Castro's government and the US
government did not get along.
● US didn’t like having a communist
country so close.
● Americans who owned land/businesses
in Cuba lost their property.
● Castro forced American civilian to leave
Cuba.
Washington Kennedy He sent to During his period The terrorist attacks
suspended the installed the total Congress the still in terrorist attacks against Cuban’s
purchase of blockade against force Cuban against Cuba embassies abroad
sugar from Cuba Cuba, during his Adjustment Law, increased, like increased. In 1976
and closed its term was the this legislation the fisherman's there was a terrorist
embassy in attack in the Bay grants special kidnappings. attack planned by
Havana after the of Pigs and the benefits to Cubans the CIA against a
approval of the Missile Crisis arriving in the Cuban airplane
Agrarian Reform. broke out. United States, even which left 76
if it is illegally. deaths.
Cuba: Bay of pigs (1961)
● The purpose was to overthrow Castro
● Us government (John F. Kennedy) planned
to arm Cuban exiles living in Florida: Once
the exiles arrived Cuba, unhappy Cubans
would join them at the Bay of Pigs and
overthrow Castro.
● The invasion was a disaster: Castro’s
forces intercepted the plan and captures
the invaders. the US government didn’t
into account that Castro had a lot of
followers in the rural area and those areas
were reinforced with guerrilla military
experts.
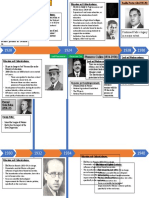
Castro’s ideology
● Before 1959, Castro’s ideology was a radical mix,
influenced by Cuban radical nationalists such as José
Martí and the leaders of resistance in the 1920s and
1930s.
● The main aims of his ideology were for fairness, social
welfare, modernisation and independence from US
interference
● In 1960, Cuba made several trade agreements with
the Soviet Union, East European states, and China. As Ernesto “che”
Guevara. With Catro’s
a result of increasing US economic restrictions, Castro
brothers led the
nationalised US companies operating in Cuba. revolution. He also
● In April 1961, Castro made the first announcement of traveled many latin
American countries to
Cuba’s move to socialism. This was reinforced by the spread the revolution.
URSS connection
● Castro didn’t want another events like those
in the Pigs bay. So he consider to get in touch
with the URSS, which it was the world rival of
the USA.
● How he do it? Castro make public the
ideological attached with the communism and
the URSS. Of course at the beginning Castro
and Guevara doctrine had more in common Fidel and soviet leader Nikita Kruschev
May 1, 1963
with the communist China than the URSS, but
the last one was more powerful and could
protect Cuba from the neighbor invader.
● Also Castro admired the industrialization and
modernization of the URSS from Stalin and
he wanted to replicate that on Cuba
Missile Crisis (1962)
After the Bay of Pigs incident, Castro feared that
the USA would attempt another invasion and, in
November 1961, Kennedy did in fact authorise one.
For protection, Castro asked the Soviet Union for
more weapons; from May 1962, the Soviet Union
delivered tanks and military aircraft, and increased
its troops on Cuba to 42,000.
Given the USA’s big lead in nuclear weapons, Nikita
Khrushchev, the Soviet premier, thought that
placing nuclear missiles in Cuba would balance the
threat from the US missiles in Turkey – this move
Missile Crisis (1962). WWIII?
For the next 13 days, the world seemed close to a
nuclear war. On 22 October, Kennedy imposed –
against international law – a naval blockade of Cuba.
Although the Soviet Union said it would not comply, on
24 October, Khrushchev ordered Soviet ships heading
for Cuba to turn back. The USA then said it would
invade Cuba if the missiles were not removed.
Khrushchev – without consulting Castro – sent letters to
Kennedy on 26 and 27 October, promising to remove
the missiles if the USA promised not to invade Cuba
and remove US missiles from Turkey. Kennedy agreed,
but insisted that the US side of the deal should be kept
secret: the threat of a nuclear Third World War ended.
End of the Missile Crisis
● In those agreements Castro wasn’t consulted.
In fact, Castro never wanted nuclear weapons -
just regular military weapons under a military
agreement between URSS and Cuba.
● He didn’t want Cuba to be considered a URSS
military base. Only military partners (equals).
● So Castro was upset with Kruschev and the
URSS. Khrushchev -in the other side- wanted
to arrange the problems with Cuba and invited
Castro to the URSS to sign some economic
agreements with Cuban sugarcane.
You might also like
- Cockney MonologuesDocument2 pagesCockney MonologuesLaReceHawkins86% (7)
- 100 Q&A of GCE O'Level Economics 2281Document32 pages100 Q&A of GCE O'Level Economics 2281Hassan Asghar100% (4)
- THINK L4 Unit 6 Grammar BasicDocument2 pagesTHINK L4 Unit 6 Grammar Basicniyazi polatNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Criminology (Review Materials For 2013 Criminology Board Examination)Document43 pagesIntroduction To Criminology (Review Materials For 2013 Criminology Board Examination)Clarito Lopez88% (33)
- Cuban Missile Crisis - UpdatedDocument27 pagesCuban Missile Crisis - UpdatedabbyhendrataNo ratings yet
- Fidel Castro: Early YearsDocument5 pagesFidel Castro: Early Yearsalexcharles433No ratings yet
- Document 3Document11 pagesDocument 3ShrinwantiNo ratings yet
- Fidel Castro - (B. 1927) : Leader of Cuba (1959-Present)Document5 pagesFidel Castro - (B. 1927) : Leader of Cuba (1959-Present)Tiana RimtonNo ratings yet
- The First Phase of My Research Into The CastroDocument2 pagesThe First Phase of My Research Into The Castrodarionomari15No ratings yet
- Cuba-Why It Is Important: Spanish-American War Spain United StatesDocument2 pagesCuba-Why It Is Important: Spanish-American War Spain United StatesKAULIK MITRANo ratings yet
- Castro Ib Topic Author. States NotesDocument12 pagesCastro Ib Topic Author. States NotestobymydogiscoolNo ratings yet
- A Brief History of The Cuban RevolutionDocument4 pagesA Brief History of The Cuban RevolutionYohan Alberto Manco DurangoNo ratings yet
- Theme 7 - The USA in The Caribbean 1776 - 1985Document9 pagesTheme 7 - The USA in The Caribbean 1776 - 1985majesty.555.1111No ratings yet
- La Toya Joseph: Soviet Union Relations With The USSRDocument4 pagesLa Toya Joseph: Soviet Union Relations With The USSRserrajNo ratings yet
- Policies of Cuba United States in The CaribbeanDocument4 pagesPolicies of Cuba United States in The Caribbeanceddia taylorNo ratings yet
- Cuba 1Document9 pagesCuba 1kgotsoprincekebaetseNo ratings yet
- Cuban RevolutionDocument2 pagesCuban Revolutionapi-395314479No ratings yet
- CubaDocument3 pagesCubaJavan GentlesNo ratings yet
- Fidel Castro and His Communist Marxist Government - Biography 5th Grade | Children's Biography BooksFrom EverandFidel Castro and His Communist Marxist Government - Biography 5th Grade | Children's Biography BooksNo ratings yet
- Cuban Revolution 1953 - 1959Document19 pagesCuban Revolution 1953 - 1959Usra RasoolNo ratings yet
- Bay of Pigs InvasionDocument24 pagesBay of Pigs InvasionasodhfnNo ratings yet
- J.F. Kennedy and The Bay of PigsDocument7 pagesJ.F. Kennedy and The Bay of PigsShifa GoyalNo ratings yet
- WH Unit 6 Readings For Decolonization SketchnotesDocument12 pagesWH Unit 6 Readings For Decolonization SketchnotesChristian SmartNo ratings yet
- History G11 Exam Preparation - CubaDocument13 pagesHistory G11 Exam Preparation - Cuba2024.mayte.flores.mendozaNo ratings yet
- Origins and Development of Authoritarian and Single-Party States - Michael Lynch - Hodder 2013-209-246Document38 pagesOrigins and Development of Authoritarian and Single-Party States - Michael Lynch - Hodder 2013-209-246Sara ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- The Cuban Revolution: Matvey KuznetsovDocument8 pagesThe Cuban Revolution: Matvey KuznetsovабобаNo ratings yet
- Cuban Revolution PDFDocument11 pagesCuban Revolution PDFDeroy Garry100% (3)
- Cuba and The Cold WarDocument10 pagesCuba and The Cold WarKashish SharmaNo ratings yet
- Fidel Castro PaperDocument5 pagesFidel Castro PapermacneilccNo ratings yet
- Cuban Revolution and Its Affects On The Three PowersDocument9 pagesCuban Revolution and Its Affects On The Three PowersmacneilccNo ratings yet
- Fidel Castro BiographyDocument12 pagesFidel Castro BiographyKiskedvenc OkosNo ratings yet
- ACFrOgDP MyeYhaaPui8W8 Up 4gK0yOYUSvkblV-ACdTTFufbVJw-ltnpXgkOsdRe3SIPZbdCQDqLqVMwIY4Hia2oGUWJO-W4nAFHbVDhCOZTy4iuyBH7kLZbL0yFmo pW6CyWRoM9DCd7b9kar PDFDocument3 pagesACFrOgDP MyeYhaaPui8W8 Up 4gK0yOYUSvkblV-ACdTTFufbVJw-ltnpXgkOsdRe3SIPZbdCQDqLqVMwIY4Hia2oGUWJO-W4nAFHbVDhCOZTy4iuyBH7kLZbL0yFmo pW6CyWRoM9DCd7b9kar PDFShantejah MitchellNo ratings yet
- The Rise of Castro and The Outbreak of RevolutionDocument5 pagesThe Rise of Castro and The Outbreak of Revolutiondarionomari15No ratings yet
- Notes Castro in PowerDocument9 pagesNotes Castro in PowerJennifer TsangNo ratings yet
- Latin American Cold WarDocument1 pageLatin American Cold War5A05 Mahid ZamanNo ratings yet
- Fidel Castro and CubaDocument2 pagesFidel Castro and Cuba2023cherryberryNo ratings yet
- Korean Crisis: Cold War Warm War America Russia Communist China World War TwoDocument9 pagesKorean Crisis: Cold War Warm War America Russia Communist China World War TwoHumera FatimaNo ratings yet
- Fidel Alejandro Castro RuzDocument1 pageFidel Alejandro Castro RuzMihai MelenciucNo ratings yet
- Castro Notes NathanDocument13 pagesCastro Notes Nathan6rkkrcgbrcNo ratings yet
- WAR & PEACE: Two Nations DividedDocument2 pagesWAR & PEACE: Two Nations Dividedapi-293389854No ratings yet
- Fidel Alejandro Castro Ruiz: Los Misiles (1962) Aseguró La Pervivencia de La Revolución, Socavó También SuDocument8 pagesFidel Alejandro Castro Ruiz: Los Misiles (1962) Aseguró La Pervivencia de La Revolución, Socavó También SuJenny Ra HuNo ratings yet
- The Cuban RevolutionDocument44 pagesThe Cuban RevolutionAbbiha PurserNo ratings yet
- Cuba and U SDocument20 pagesCuba and U Sapi-316953628No ratings yet
- History NotesDocument36 pagesHistory NotesmNo ratings yet
- The Cuban Missile CrisisDocument8 pagesThe Cuban Missile Crisissweetie2blueNo ratings yet
- YR11 MH Cuba NotesDocument17 pagesYR11 MH Cuba Notestetece8105No ratings yet
- Cuban Revolution - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument13 pagesCuban Revolution - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaCNo ratings yet
- Cuba 2Document14 pagesCuba 2ciucaoctavian386No ratings yet
- My History Assignment: Name: Uhraine Miller Grade: 9BHC2 Date: 25/5/2019 Topic: Cuban RevolutionDocument14 pagesMy History Assignment: Name: Uhraine Miller Grade: 9BHC2 Date: 25/5/2019 Topic: Cuban Revolutionuhraine millerNo ratings yet
- CH 33 Sec 4 - The Cold War Divides The World PDFDocument6 pagesCH 33 Sec 4 - The Cold War Divides The World PDFMrEHsiehNo ratings yet
- Running Head: How Class Politics Shaped Fidel Castro'S Life 1Document9 pagesRunning Head: How Class Politics Shaped Fidel Castro'S Life 1Steve JonesNo ratings yet
- Fidel Castro Ruz: Brief BiographyDocument3 pagesFidel Castro Ruz: Brief Biographywaterfall-city8975No ratings yet
- The Administration of John F. KennedyDocument16 pagesThe Administration of John F. KennedyMoiraAcuñaNo ratings yet
- Detente SummaryDocument15 pagesDetente SummaryIsmail M HassaniNo ratings yet
- The Cold War Stations ActivityDocument6 pagesThe Cold War Stations ActivityMegamanNo ratings yet
- Castro and Cuba Rise-Rule-PoliciesDocument100 pagesCastro and Cuba Rise-Rule-PoliciesGiuliana ProctorNo ratings yet
- Castro, Cuban Ruler Who Defied 10 U.S. PresidentsDocument13 pagesCastro, Cuban Ruler Who Defied 10 U.S. Presidentsxylas_zeusNo ratings yet
- Cuba A Country StudyDocument12 pagesCuba A Country StudyJan Zalewski100% (1)
- Cuban RevolutionDocument32 pagesCuban RevolutionDaniel WalshNo ratings yet
- History Authoritarian States Online ResourcesDocument7 pagesHistory Authoritarian States Online ResourcesSusi MeierNo ratings yet
- Cuban Revolution 1953 - 1959Document19 pagesCuban Revolution 1953 - 1959MEOW41100% (1)
- Essays About the Revolution In Nicaragua and a Psychological Profile of Ernesto Che GuevaraFrom EverandEssays About the Revolution In Nicaragua and a Psychological Profile of Ernesto Che GuevaraNo ratings yet
- Response to Revolution: The United States and the Cuban Revolution, 1959-1961From EverandResponse to Revolution: The United States and the Cuban Revolution, 1959-1961No ratings yet
- The Missile Crisis: Context, Roles and PerspectivesDocument12 pagesThe Missile Crisis: Context, Roles and PerspectivesEnriqueNo ratings yet
- Latin America Confronts The Great Depression: Brazil and ArgentinaDocument24 pagesLatin America Confronts The Great Depression: Brazil and ArgentinaEnriqueNo ratings yet
- Source Analysis Origins of NazismDocument2 pagesSource Analysis Origins of NazismEnriqueNo ratings yet
- Continued Calle S Legacy in A Major Extent.: December 1st Until NovemberDocument2 pagesContinued Calle S Legacy in A Major Extent.: December 1st Until NovemberEnriqueNo ratings yet
- Authoritarian States: Cuba III: Social Impact of The RevolutionDocument10 pagesAuthoritarian States: Cuba III: Social Impact of The RevolutionEnriqueNo ratings yet
- Impact of Fascism On Italian Foreign Policy (1870-1933)Document20 pagesImpact of Fascism On Italian Foreign Policy (1870-1933)EnriqueNo ratings yet
- International Response To The 2nd SJWDocument1 pageInternational Response To The 2nd SJWEnriqueNo ratings yet
- Paper 1: Move To Global War Japanese Expansion in East AsiaDocument48 pagesPaper 1: Move To Global War Japanese Expansion in East AsiaEnriqueNo ratings yet
- Authoritarian States: Cuba: Castro and The Consolidation of His PowerDocument17 pagesAuthoritarian States: Cuba: Castro and The Consolidation of His PowerEnriqueNo ratings yet
- Japanese Expansionism East Asia Until 1931Document1 pageJapanese Expansionism East Asia Until 1931EnriqueNo ratings yet
- The Mexican Revolution (II) : Develop, Leaders and EffectsDocument18 pagesThe Mexican Revolution (II) : Develop, Leaders and EffectsEnriqueNo ratings yet
- Section 1.2: Japanese Expansion in South-East Asia, 1931-41Document49 pagesSection 1.2: Japanese Expansion in South-East Asia, 1931-41Enrique100% (2)
- The Mexican Revolution (I) : Origins and CausesDocument11 pagesThe Mexican Revolution (I) : Origins and CausesEnriqueNo ratings yet
- What Was The International Response To The Invasion of Manchuria?Document32 pagesWhat Was The International Response To The Invasion of Manchuria?EnriqueNo ratings yet
- The Cultural Impact of The Mexican RevolutionDocument19 pagesThe Cultural Impact of The Mexican RevolutionEnriqueNo ratings yet
- The Mexican Revolution: The Construction of The Post Revolutinoary State (1920-1940)Document27 pagesThe Mexican Revolution: The Construction of The Post Revolutinoary State (1920-1940)EnriqueNo ratings yet
- Plutarco Calles (1924-1928) : Continued Calle S Legacy in A Major ExtentDocument2 pagesPlutarco Calles (1924-1928) : Continued Calle S Legacy in A Major ExtentEnriqueNo ratings yet
- Neuromusic IIIDocument3 pagesNeuromusic IIIJudit VallejoNo ratings yet
- Routing CodesDocument4 pagesRouting CodesScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- Grade 7 Module Answer SheetsDocument12 pagesGrade 7 Module Answer SheetsArian May MarcosNo ratings yet
- Principles of Growth and DevelopmentDocument2 pagesPrinciples of Growth and DevelopmentMerlin AlfaneNo ratings yet
- MAN0019215 - TaqPathCOVID-19 - CE-IVD - RT-PCR Kit - IFUDocument27 pagesMAN0019215 - TaqPathCOVID-19 - CE-IVD - RT-PCR Kit - IFUFe LipeNo ratings yet
- Green AlgaeDocument3 pagesGreen AlgaeGladys CardonaNo ratings yet
- Punsalan, Jr. vs. Vda. de LacsamanaDocument11 pagesPunsalan, Jr. vs. Vda. de LacsamanaLoubert BartolomeNo ratings yet
- Barker CH Naish D - Where On Earth Dinosaurs and Other Prehistoric Life The Amazing History of Earth 39 S Most Incredible ADocument162 pagesBarker CH Naish D - Where On Earth Dinosaurs and Other Prehistoric Life The Amazing History of Earth 39 S Most Incredible ARumen Deshkov100% (3)
- Esoteric Christianity 06 Being Born AgainDocument15 pagesEsoteric Christianity 06 Being Born AgainTortura ChinaNo ratings yet
- ProsidingDocument13 pagesProsidingAlfi Amalia S.E.I, M.E.INo ratings yet
- Lê Thị Thu Thuỷ - Luận vănDocument97 pagesLê Thị Thu Thuỷ - Luận vănĐào Nguyễn Duy TùngNo ratings yet
- Renesas Application Note AN1340Document6 pagesRenesas Application Note AN1340Rip_BarNo ratings yet
- People Vs Vicente MenilDocument2 pagesPeople Vs Vicente MenilMarco Arpon100% (1)
- Architecture in EthDocument4 pagesArchitecture in Ethmelakumikias2No ratings yet
- 1 Cyber Law PDFDocument2 pages1 Cyber Law PDFKRISHNA VIDHUSHANo ratings yet
- LSM MockDocument5 pagesLSM MockKazi Rafsan NoorNo ratings yet
- Lucies Farm Data Protection ComplaintDocument186 pagesLucies Farm Data Protection ComplaintcraigwalshNo ratings yet
- AC S08 Week 08Document3 pagesAC S08 Week 08ERICK BORJA DELGADONo ratings yet
- Design and Construction of Oil Expeller Press With Structural Analysis of Screw With AnsysDocument6 pagesDesign and Construction of Oil Expeller Press With Structural Analysis of Screw With AnsysShahzad AbbasNo ratings yet
- 1999 Aversion Therapy-BEDocument6 pages1999 Aversion Therapy-BEprabhaNo ratings yet
- Ruq Abdominal PainDocument55 pagesRuq Abdominal PainriphqaNo ratings yet
- Lab 5 Virtual Local Area Network (VLAN)Document16 pagesLab 5 Virtual Local Area Network (VLAN)Programming CodingNo ratings yet
- HP Scanjet Pro 2500 F1 Flatbed Scanner: DatasheetDocument2 pagesHP Scanjet Pro 2500 F1 Flatbed Scanner: DatasheetKarkittykatNo ratings yet
- DLL WK 10 LC 171819Document14 pagesDLL WK 10 LC 171819Regiel Guiang ArnibalNo ratings yet
- Preliminary PagesDocument9 pagesPreliminary PagesdorothyNo ratings yet
- (Lovebook care - Anh) Đề thi thử THPTQG trường THPT Chuyên Cao Bằng lần 1Document16 pages(Lovebook care - Anh) Đề thi thử THPTQG trường THPT Chuyên Cao Bằng lần 1Dương Viết ĐạtNo ratings yet