Professional Documents
Culture Documents
ENTREPRENEURIAL MOTIVATION Assignment
ENTREPRENEURIAL MOTIVATION Assignment
Uploaded by
xakil0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
180 views26 pagesThe document discusses several theories of entrepreneurial motivation:
1. McClelland's Achievement Motivation Theory proposes that a strong need for achievement is important for entrepreneurial success and can be developed through training.
2. Schumpeter viewed entrepreneurs as innovators who create "new combinations" like new products or processes.
3. Hagen's theory of social change argues that societies transition from authoritarian personalities resistant to change to more innovative personalities open to entrepreneurial activity.
4. Maslow, Herzberg, and McGregor's motivation theories are compared, with Maslow focusing on a hierarchy of needs and Herzberg distinguishing between motivators and hygiene factors.
Original Description:
Original Title
ENTREPRENEURIAL MOTIVATION assignment
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses several theories of entrepreneurial motivation:
1. McClelland's Achievement Motivation Theory proposes that a strong need for achievement is important for entrepreneurial success and can be developed through training.
2. Schumpeter viewed entrepreneurs as innovators who create "new combinations" like new products or processes.
3. Hagen's theory of social change argues that societies transition from authoritarian personalities resistant to change to more innovative personalities open to entrepreneurial activity.
4. Maslow, Herzberg, and McGregor's motivation theories are compared, with Maslow focusing on a hierarchy of needs and Herzberg distinguishing between motivators and hygiene factors.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
180 views26 pagesENTREPRENEURIAL MOTIVATION Assignment
ENTREPRENEURIAL MOTIVATION Assignment
Uploaded by
xakilThe document discusses several theories of entrepreneurial motivation:
1. McClelland's Achievement Motivation Theory proposes that a strong need for achievement is important for entrepreneurial success and can be developed through training.
2. Schumpeter viewed entrepreneurs as innovators who create "new combinations" like new products or processes.
3. Hagen's theory of social change argues that societies transition from authoritarian personalities resistant to change to more innovative personalities open to entrepreneurial activity.
4. Maslow, Herzberg, and McGregor's motivation theories are compared, with Maslow focusing on a hierarchy of needs and Herzberg distinguishing between motivators and hygiene factors.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 26
ENTREPRENEURIAL MOTIVATION
Razia Sultana Sumi
Associate Professor
• Motivation is the set of forces that causes people to
engage in one behavior rather than some alternative
behavior .
• The term, "Motivation" has come from the Latin word
‘movere’ the meaning of the same is “to move”. That
means to move from present situation to better
situation.
• Motivation is the willingness to do something, and is
conditioned by this action’s ability to satisfy some need
for the individual. The common man thinks that people
go for business to earn money, but it is not always true.
• Scott has defined motivation as "Motivation means a
process of stimulating people to action to accomplish
desired goals''
The characteristics of motivation are as under :
(1) It has two parts
• (a) to motivate self
• (b) to motivate others.
(2) The concept of motivation is based on
assumption that a behavior of a person is goal
oriented and it is directed to complete the task.
(3) The behavior varies from man to man.
(4) It is an internal condition
(5) It is an inspiring process to do work.
(6) It is goal oriented process
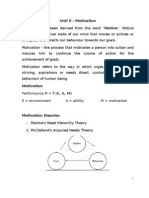
Motivation Theories
• McClelland’s Achievement Motivation Theory:
From the preliminary studies made by David
McClelland for the entrepreneurship
development it is noticed that for the growth of
entrepreneurship, achievement motivation is
very important factor which can be developed by
training and experience. He has also stated that
to get achievement some people have strong
drive while others have low drive. Those who
have strong drive are considered as high achiever.
Dominant Motivator Characteristics of This Person
• Achievement Has a strong need to set and accomplish challenging
goals.
Takes calculated risks to accomplish their goals.
Likes to receive regular feedback on their progress and achievements.
Often likes to work alone.
• Affiliation Wants to belong to the group.
Wants to be liked, and will often go along with whatever the rest of the
group wants to do
Favors collaboration over competition.
Doesn't like high risk or uncertainty.
• Power Wants to control and influence others.
Likes to win arguments.
Enjoys competition and winning.
Enjoys status and recognition.
• David McClelland has introduced short form ‘n-
Ach’ that means need for achievement. He has
defined ‘n-Ach’ as “behavior towards completion
with a standard of excellence”
• There is a direct relationship between the high
need for achievement and the successful
administration with high standard of results
oriented skill. For successful administration or
successful entrepreneurship high need for
achievement ‘n-Ach’ is very important factor. This
factor (need for achievement) can be measured
and developed by suitable training.
• Achievement
• People motivated by achievement need challenging,
but not impossible, projects. They thrive on
overcoming difficult problems or situations, so make
sure you keep them engaged this way. People
motivated by achievement work very effectively
either alone or with other high achievers.
• When providing feedback, give achievers a fair and
balanced appraisal. They want to know what they're
doing right – and wrong – so that they can improve
• Affiliation
• People motivated by affiliation work best in a group environment, so
try to integrate them with a team (versus working alone) whenever
possible. They also don't like uncertainty and risk. Therefore, when
assigning projects or tasks, save the risky ones for other people.
• When providing feedback to these people, be personal. It's still
important to give balanced feedback, but if you start your appraisal
by emphasizing their good working relationship and your trust in
them, they'll likely be more open to what you say. Remember that
these people often don't want to stand out, so it might be best to
praise them in private rather than in front of others.
• Power
• Those with a high need for power work best when
they're in charge. Because they enjoy competition,
they do well with goal-oriented projects or tasks. They
may also be very effective in negotiations or in
situations in which another party must be convinced
of an idea or goal.
• When providing feedback, be direct with these team
members. And keep them motivated by helping them
further their career goals.
CHARACTERISTICS OF THE PERSON WHO POSSESSES ACHIEVEMENT
MOTIVATION
1. High achievers search for areas of greater
personal responsibility and they readily accept it.
2. They take calculated risk.
3. They set challenging yet achievable goals.
4. They make detailed and comprehensive planning
to achieve the goals and get ready for the future.
5. They are ready to accept measurable feedback.
6. They reach for profitable industrial opportunities.
7. They show an attitude of sticking to the work
even in unfavorable conditions.
8. They tends to do something new.
9. They show certain inter personal competence.
10. High achievers have an attitude of bearing
uncertainties.
11. They are ready to migrate and start business
at any place.
12. They are adventurous.
High achievers can be developed by providing proper
atmosphere. They are generally attracted by the
following proposals.
1. When personal responsibility be assigned for goal
achievement.
2. Total freedom be given to them to set their goals.
3. For the results of the efforts, proper and without any
prejudice, information feedback be provided to
them.
4. Work should be assigned to do in a moderate risk
conditions.
5. 5. Proper recognition and appropriate returns be
given according to the work done successfully
Entrepreneurial Motivation
Part-II
Razia Sultana Sumi
Associate Professor
Schumpeter’s view on Entrepreneurship
Joseph Alois Schumpeter is regarded as one of the
greatest economists of the first half of the twentieth
century. The concepts of innovation and
entrepreneurship are probably Schumpeter’s most
distinctive contributions to economics. One of the most
common themes in Schumpeter’s writings was the role
of innovation (“new combinations”) and
entrepreneurship in economic growth.
He refers that entrepreneurs innovate the ideas & the
modes of translating those into reality. He perceives the
people who get pleasure in solving problems that others
cannot easily solve are with entrepreneurial trait.
Entrepreneurs get ego satisfaction by innovating
normally the ways as under:
• Form new product/ service ideas,
• Develop new cost-effective method without losing
quality postulate
• Create new customers
• Find new source of inputs & skills needed for quality
to withstand competition
• Develop new organizational set-up-monopoly or
other type
• Train employees get pleasure in doing the process
with economy
• Creates markets area for such products/ services
Schumpeter’s innovation theory
Although since the late 1880s there have been
reports of the use of the term “innovation” to
mean something unusual, none of first precursors
of innovation have been as influential as the
Schumpeter. According to him, consumer
preferences are already given and do not undergo
spontaneously. It means that they cannot be
cause of the economic change. The concept
covers the following five cases:
The concept covers the following five cases:
1. launch of a new product or a new species of
already known product;
2. application of new methods of production or sales
of a product (not yet proven in the industry);
3. opening of a new market (the market for which a
branch of the industry was not yet represented);
4. acquiring of new sources of supply of raw material
or semi-finished goods;
5. new industry structure such as the creation or
destruction of a monopoly position.
Theory of Social Change: Everett E. Hagen
• According to Hagen, all human personalities in all human
societies are either authoritarian or innovational. All members
of traditional and/or peasant societies have authoritarian
characters, are caught in an unresolved oedipal conflict with
their authoritarian fathers, and are resistant to change.
• Economic development is seen almost exclusively as a process
of technological change which is brought about the
technological creativity of individuals in the society. Hagen
postulates the sequence of changes separating the typical
authoritarian personality of a stable traditional society from
the emergence of creative entrepreneurial activity.
Everett Hagen’s view on the theory of Social change
Comparative study of Maslow, Hergberg and McGregor’ Motivation theories
Discussion on theories
• Maslow (1954) developed a new concept of motivation and
proposed a hierarchical order in the structure of human
needs.
• In the Maslowian paradigm five needs identified were:
Psychological, safety/security, social, self-esteem and self
actualization.
• This theory is based on assumption of internal-motivation--
the needs, wants and desires which exist within an individual
and influence the person by determining his thoughts, which
in turn lead to his/her behavior in a particular situation. For
example, a student who desires good grades in a course will
consider how he can fulfill the requirements for the grade.
• Herzberg (1959) sought a different answer to motivation and
propounded a bi-model theory of motivators and hygienes. The
motivators reflected the internal dynamics residing within the
individual and hygienes reflect the power of contextual factors like
money, work conditions, etc. which shape the motivation of the
individual.
• Herzberg's motivations described human beings relationship to what
he does, that is the content of the job. The hygienes on the other
hand reflect the situation in which he does the job, i.e. the context of
the job.
• If the hygiene factors, for example salary, working conditions, work
environment, safety and security are unsuitable (low level) at the
workplace, this can make individuals unhappy, dissatisfied with their
job.
• Motivating factors, on the other hand, can increase job satisfaction,
and motivation is based on an individual's need for personal growth.
• Quite contrary to the assumption of Maslow and Herzberg,
McGregor (1967) worked entirely on different hypothesis and
sought an answer to motivation in the nature of man.
• Theory X and Y reflect McGregor's efforts in understanding
human motivation vis-a-vis the nature of the person. `Theory X'
and `Theory Y' are quite different, almost poles apart and have
different sets of assumptions. Theory X assumes the human being
as lazy, idle and indolent. Such a person is averse to any effort
and would like to avoid any kind of responsibility. They prefer
being directed and avoid being independent decision maker. They
only work under direct control and threat of punishment.
• The theory ‘Y’ is in contradiction with theory `X'. Theory `Y'
projects the human being as a creative, open-minded and
energetic person for whom the work is as pleasant and natural as
play. Responsibility is a welcome concept and such people seek
self-regulatory behavior.
A proposed model of Entrepreneurial Motivation
• An implementation to outcome relationship describing various factors
the start up decision with issues of strategy formulation, implementation
and sustained entrepreneurial behavior.
• Perceptual interpretations made by the entrepreneur play a key role in
motivational process
• Strength of the relationship between the entrepreneur’s managerial
strategies and firm outcomes. The stronger the relationship is perceived
to be, the stronger will be the motivation to behave entrepreneurially
•Feedback on succeeding strategies, strategy implementation and
management of the firm. Entrepreneurs will be motivated to behave
entrepreneurially as long as they view that behavior being effective.
Firms performance may influence an entrepreneur but its only a part of
the picture.
Goal achievement and not performance: An entrepreneurial tendency can
be sustained as long there is a belief that there is no other viable option.
Thank you all
You might also like
- Bank Statement TemplateDocument2 pagesBank Statement TemplatexakilNo ratings yet
- Organizational Behavior Human Behavior at Work 14th Edition Newstrom Solutions Manual 1Document27 pagesOrganizational Behavior Human Behavior at Work 14th Edition Newstrom Solutions Manual 1george100% (52)
- Management For Rbi Sebi EtcDocument8 pagesManagement For Rbi Sebi EtcShubham Gupta100% (1)
- Approaches To EntrepreneurshipDocument40 pagesApproaches To Entrepreneurshipm umair zahirNo ratings yet
- Robert Dilts - Visionary Leadership SkillsDocument144 pagesRobert Dilts - Visionary Leadership SkillsJuliano Ferreira Do Nascimento100% (3)
- UNIT 1 (PM&Entr)Document13 pagesUNIT 1 (PM&Entr)Minal SinghNo ratings yet
- 3.unit 3 - Motivation LeadershipDocument33 pages3.unit 3 - Motivation LeadershipNivedita Suresh KumarNo ratings yet
- Theories of EntrepreneurshipDocument19 pagesTheories of EntrepreneurshipGauhar NeyazNo ratings yet
- Entrepreneurial MotivationDocument8 pagesEntrepreneurial MotivationkujaNo ratings yet
- Motivation 2Document22 pagesMotivation 2SankalpaNo ratings yet
- I170515 Obprojectpart2 PDFDocument13 pagesI170515 Obprojectpart2 PDFZarak Khan MahsudNo ratings yet
- Hbo Group 4Document7 pagesHbo Group 4valderamaangel92No ratings yet
- Entreprenuer Unit-2Document53 pagesEntreprenuer Unit-2Batchu SaaketNo ratings yet
- PPM Lesson 12Document14 pagesPPM Lesson 12annstine makenaNo ratings yet
- Question Bank For EndDocument23 pagesQuestion Bank For EndShruti ShrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Entrepreneuria L Development PresentationDocument21 pagesEntrepreneuria L Development PresentationMelodyo ZoneNo ratings yet
- Theories of EntrepreneurshipDocument22 pagesTheories of EntrepreneurshipBlue Stone100% (2)
- 4) UNIT - II Motivation (OK)Document15 pages4) UNIT - II Motivation (OK)Disha KediaNo ratings yet
- Motivation of Project EmployeesDocument16 pagesMotivation of Project Employeessoujee60No ratings yet
- MotivationDocument28 pagesMotivation19UME117 Praveen KumarNo ratings yet
- Aproaches To Entrepreneurship 1. Psychological Aproach I) David C Mcclelland'S Motivational Needs TheoryDocument8 pagesAproaches To Entrepreneurship 1. Psychological Aproach I) David C Mcclelland'S Motivational Needs TheoryGraceNo ratings yet
- Unit 2Document75 pagesUnit 2Dhamotharan SNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4 - Leading and DirectingDocument62 pagesLesson 4 - Leading and DirectingXzk MallaboNo ratings yet
- POM - Unit 4 - Directing - NotesDocument10 pagesPOM - Unit 4 - Directing - NotesmaNo ratings yet
- Modified Needs Hierarchy ModelDocument14 pagesModified Needs Hierarchy Modelkhalida khanNo ratings yet
- Motivation and Theories of Motivation: Dr. P.DeivasigamaniDocument24 pagesMotivation and Theories of Motivation: Dr. P.DeivasigamaniBally VidsNo ratings yet
- Unit 4Document45 pagesUnit 4Mahesh muthusamyNo ratings yet
- Ecu 302 Lecture Three NotesDocument7 pagesEcu 302 Lecture Three NotesKimani JohnNo ratings yet
- Unit II - Motivation: Performance P F (E, A, M) E Environment A Ability M MotivationDocument23 pagesUnit II - Motivation: Performance P F (E, A, M) E Environment A Ability M MotivationVairam MuthuNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1-Concept of EntreprenurshipDocument10 pagesChapter 1-Concept of EntreprenurshipjtpmlNo ratings yet
- Module 8 Motivation in Industry 1Document13 pagesModule 8 Motivation in Industry 1punzalanalvin526No ratings yet
- MTTM 03 2021Document14 pagesMTTM 03 2021Rajni KumariNo ratings yet
- Ed Unit 3 NotesDocument18 pagesEd Unit 3 Notess18424110No ratings yet
- Mbe Assign - MotivationDocument4 pagesMbe Assign - MotivationKiruthika ParamasivamNo ratings yet
- MDM B002 3T 202021 Notes On Influencing People - LunesDocument10 pagesMDM B002 3T 202021 Notes On Influencing People - LunesEevee CatNo ratings yet
- Theories of MotivationDocument5 pagesTheories of MotivationjithuNo ratings yet
- Entrepreneurship Ch.1Document39 pagesEntrepreneurship Ch.1Joseph Kinfe100% (1)
- Unit II MotivationDocument64 pagesUnit II MotivationKaushik SNo ratings yet
- Confronting The Challenges of Shifting To A Better Customer Relations CultureDocument14 pagesConfronting The Challenges of Shifting To A Better Customer Relations CultureAogo OlajideNo ratings yet
- Entrepreneur MotivationDocument19 pagesEntrepreneur MotivationGolam MostofaNo ratings yet
- Entrepreneurial BehaviourDocument43 pagesEntrepreneurial Behaviourutkarsha mishraNo ratings yet
- Organizational Behavior Human Behavior at Work 14Th Edition Newstrom Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFDocument36 pagesOrganizational Behavior Human Behavior at Work 14Th Edition Newstrom Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFmelissa.pauls349100% (11)
- Mind Map Chapter 14Document5 pagesMind Map Chapter 14Iglasses La PazNo ratings yet
- Unit 2.4 Motivation and Demotivation TheoriesDocument29 pagesUnit 2.4 Motivation and Demotivation TheoriesMarina Peña BenitaNo ratings yet
- اسئلة المقالي للمراجعةDocument12 pagesاسئلة المقالي للمراجعةOsamh AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Directin G: Group 7: Kristine Eria Anne Liezel Tambulasa Rachel Ann Bagio Alexis Mesina Ramon Golondrina Levi Moises RazoDocument48 pagesDirectin G: Group 7: Kristine Eria Anne Liezel Tambulasa Rachel Ann Bagio Alexis Mesina Ramon Golondrina Levi Moises RazoRazo Levi MoisesNo ratings yet
- Motivation ThoeriesDocument43 pagesMotivation ThoeriesRhen DacugNo ratings yet
- MBA Entrepreneurship ManagementDocument9 pagesMBA Entrepreneurship ManagementThatPeachNo ratings yet
- ABM601 Unit 2 Lesson 1Document6 pagesABM601 Unit 2 Lesson 1kaurharneet316No ratings yet
- Assignment 7 Group MembersDocument4 pagesAssignment 7 Group MembersRana UsmanNo ratings yet
- Theories of Entrepreneurship ASSIGNMENTDocument13 pagesTheories of Entrepreneurship ASSIGNMENTRashid De RadianceNo ratings yet
- Entrepreneurship Ch.1Document40 pagesEntrepreneurship Ch.1Amanuel AlemayehuNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Management Chapter Six 6. The Leading/Directing Function Chapter ObjectivesDocument15 pagesIntroduction To Management Chapter Six 6. The Leading/Directing Function Chapter ObjectivesfitsumNo ratings yet
- Theories of MotivationDocument17 pagesTheories of MotivationRohitNo ratings yet
- Goal Setting and Achievement ThinkingDocument15 pagesGoal Setting and Achievement ThinkingMeenakshi AnilNo ratings yet
- Kotter's ModelDocument19 pagesKotter's ModelIla Mehrotra AnandNo ratings yet
- World Wide Study of IndividualDocument7 pagesWorld Wide Study of IndividualshehabaldinNo ratings yet
- MotivationDocument49 pagesMotivationJosvin JoshyNo ratings yet
- Human Behavior in OrganizationDocument113 pagesHuman Behavior in OrganizationReynald AntasoNo ratings yet
- Motivation - PPT + + +Document53 pagesMotivation - PPT + + +Donnaleen Alim100% (2)
- Entrepreneurial Motivation and BarriersDocument23 pagesEntrepreneurial Motivation and Barriersvinaypandeychand100% (2)
- Module IIDocument68 pagesModule IISambhav BhansaliNo ratings yet
- Understanding Human Behaviour in The WorkplaceFrom EverandUnderstanding Human Behaviour in The WorkplaceRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- Who Ban Covid 19Document3 pagesWho Ban Covid 19xakilNo ratings yet
- Covid 19 Impact in BDDocument29 pagesCovid 19 Impact in BDxakilNo ratings yet
- Make Necessary Changes in Only Orange Colored Fields.: Proceed To Calculation Will Be Initially "No"Document36 pagesMake Necessary Changes in Only Orange Colored Fields.: Proceed To Calculation Will Be Initially "No"xakilNo ratings yet
- HR-Garment IndustryDocument6 pagesHR-Garment IndustrykattaaaaNo ratings yet
- Study of Employee RetentionDocument6 pagesStudy of Employee RetentionDrAmit DuttaNo ratings yet
- What Is Maslow's Hierarchy of NeedsDocument3 pagesWhat Is Maslow's Hierarchy of NeedsAizel Nova Fermilan ArañezNo ratings yet
- Two Factor Theory Motivation-Hygiene Theory: Dual-Factor Theory/ Theory of Work Behavior byDocument16 pagesTwo Factor Theory Motivation-Hygiene Theory: Dual-Factor Theory/ Theory of Work Behavior byAngha0% (1)
- Amity School of Business: Semester IvDocument41 pagesAmity School of Business: Semester IvDheeraj SinghalNo ratings yet
- A Study On Existing Talent Management Practice and PDFDocument14 pagesA Study On Existing Talent Management Practice and PDFS- AjmeriNo ratings yet
- Adiele & Abraham 2013Document5 pagesAdiele & Abraham 2013סשה איילהNo ratings yet
- 12 - Chapter 6Document4 pages12 - Chapter 6Chintu PandaNo ratings yet
- Full Download Test Bank For Canadian Organizational Behaviour 10th Edition Steven Mcshane Kevin Tasa PDF Full ChapterDocument36 pagesFull Download Test Bank For Canadian Organizational Behaviour 10th Edition Steven Mcshane Kevin Tasa PDF Full Chaptermockbird.romeward2jjg100% (20)
- PermitFlow AssignmentDocument3 pagesPermitFlow Assignmentأبورؤس عبدالكاشفNo ratings yet
- THC011 Activity 8 Case Study: Multicultural Diversity in The Workplace For The Tourism ProfessionalDocument4 pagesTHC011 Activity 8 Case Study: Multicultural Diversity in The Workplace For The Tourism ProfessionalMichael CruzcabreraNo ratings yet
- Retention and Separation PlanDocument10 pagesRetention and Separation Planjuma hassanNo ratings yet
- OB Week 10 LAQDocument3 pagesOB Week 10 LAQsyednovacNo ratings yet
- BA4102-Management Concepts and Organizational BehaviourDocument134 pagesBA4102-Management Concepts and Organizational BehaviourarunoasysitNo ratings yet
- State of Employee Engagement 2023 WorkBuzzDocument12 pagesState of Employee Engagement 2023 WorkBuzzerfan.hematzade77No ratings yet
- Part 3 CORE BEHAVIORAL COMPETENCIESDocument1 pagePart 3 CORE BEHAVIORAL COMPETENCIESmalay.bationNo ratings yet
- Organizational Culture and Ethics: 2 Types of Information Before Entering The OrganizationDocument10 pagesOrganizational Culture and Ethics: 2 Types of Information Before Entering The OrganizationMychie Lynne MayugaNo ratings yet
- Critical ReflectionDocument1 pageCritical ReflectionPatrina SamuelNo ratings yet
- Succession Planning and ManagementDocument16 pagesSuccession Planning and ManagementPrince Satish ReddyNo ratings yet
- 2ND Quarter Org and ManagementDocument4 pages2ND Quarter Org and ManagementalexNo ratings yet
- MBA-III-HRM-I Unit-IDocument15 pagesMBA-III-HRM-I Unit-Iachal sahareNo ratings yet
- Week 13 - How To Start Changing An Unhealthy Work EnvironmentDocument2 pagesWeek 13 - How To Start Changing An Unhealthy Work EnvironmentJell BesasNo ratings yet
- Human Resource Management Policy Framework & Manual For Ghana Public ServicesDocument154 pagesHuman Resource Management Policy Framework & Manual For Ghana Public ServicesPrɔf C. Joe-AdjeiNo ratings yet
- Case Studies On Leadership and ChangeDocument11 pagesCase Studies On Leadership and ChangeAnandRaj0% (1)
- CLC Onboarding ChecklistDocument3 pagesCLC Onboarding ChecklistMonica StanciuNo ratings yet
- Self Determination TheoryDocument11 pagesSelf Determination TheoryChetan Dasgupta100% (1)
- Administrative Management TheoryDocument4 pagesAdministrative Management TheorygulshanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Fundementals of OBDocument33 pagesChapter 1 Fundementals of OBbeka negewo100% (2)