Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Basic Optical Laws and Definition
Basic Optical Laws and Definition
Uploaded by
Perumal Namasivayam0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
252 views13 pagesThis document discusses basic optical laws and definitions, including refractive index, reflection, refraction, and Snell's law. It then describes the typical structure of optical fibers, classifying them as step index or graded index fibers. Step index fibers have an abrupt change in refractive index at the core-cladding boundary, while graded index fibers have a refractive index that varies gradually from the core center to the cladding. The document provides examples of refractive index profiles for different fiber types and explains how light rays are transmitted within multimode graded index optical fibers.
Original Description:
OPTICS
Original Title
Basic_optical_laws_and_definition
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document discusses basic optical laws and definitions, including refractive index, reflection, refraction, and Snell's law. It then describes the typical structure of optical fibers, classifying them as step index or graded index fibers. Step index fibers have an abrupt change in refractive index at the core-cladding boundary, while graded index fibers have a refractive index that varies gradually from the core center to the cladding. The document provides examples of refractive index profiles for different fiber types and explains how light rays are transmitted within multimode graded index optical fibers.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
252 views13 pagesBasic Optical Laws and Definition
Basic Optical Laws and Definition
Uploaded by
Perumal NamasivayamThis document discusses basic optical laws and definitions, including refractive index, reflection, refraction, and Snell's law. It then describes the typical structure of optical fibers, classifying them as step index or graded index fibers. Step index fibers have an abrupt change in refractive index at the core-cladding boundary, while graded index fibers have a refractive index that varies gradually from the core center to the cladding. The document provides examples of refractive index profiles for different fiber types and explains how light rays are transmitted within multimode graded index optical fibers.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 13
Basic optical laws and definition
• Refractive index : n=c/v
c=speed of light wave in free space(3x108m/s).
v=velocity of light in non conducting medium.
n=1.00 for air , n=1.33 for water,1.45 for silica
glass,2.45 for diamond.
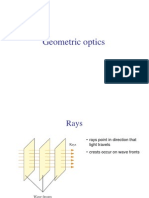
Reflection and Refraction
• When a light ray
encounters a boundary
separating two
different media , part
of ray is reflected back
in to first medium and
the remainder is bent
(refracted) as it enters
the second material.
• At interface by Snell’s law
n1 sinφ1 =n2 sinφ2
φ1=angle between the incident ray and the normal to
the surface is known as angle of incidence.
φ2=angle between the refracted ray and the normal
to the surface is known as angle of refraction.
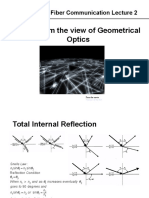
• As the angle of incidence becomes larger ,refracted
angle φ2 approaches π/2. beyond this point no
refraction is possible and the light rays become
totally internally reflected.
• Critical angle φc –light ray in air is parallel to the
surface .
When the light ray in air is parallel to glass surface,
then φ2=90 o so that sin φ2= 1
critical angle is sin φc = n2/n1
Typical structure of optical fiber
classification
• Step index:-refractive index of core is
uniform and undergoes an abrupt change
at the cladding boundary.
• Graded index:-core refractive index varies
as a function of radial distance from the
center of the fiber.
• Step and graded index again divided in to
single mode and multimode.
Step index
• Decreasing core index n(r) with radial distance
from a maximum value of n1 at the axis to a
constant value n2 beyond the core radius a in
the cladding.
• Index variation
n1 (1-2∆(r/a)α )1/2 r < a (core)
n(r) =
n1 (1-2∆)1/2 = n2 r≥ a(cladding)
• ∆ is the relative refractive index difference.
• α is the profile parameter which gives
characteristic refractive index profile of the
fiber core.
• When α = ∞ step index profile
α = 2 parabolic profile
α = 1 triangular profile
Refractive index profile and ray transmission
in multimode graded index fibers
Advantages
• Less intermodal dispersion when compared to
multimode step intermodal dispersion.
You might also like
- Basic Optical Laws and DefinitionDocument13 pagesBasic Optical Laws and Definitionmuhzinamoideen67% (3)
- Lec 2 - Features of Fibre OpticDocument21 pagesLec 2 - Features of Fibre OpticMtende MosesNo ratings yet
- Optic FibreDocument48 pagesOptic FibreSGSNo ratings yet
- Optical Fiber WaveGuiding PDFDocument51 pagesOptical Fiber WaveGuiding PDFHimanshu AgrawalNo ratings yet
- OC - Lect - 02 Aziz AlhaidariDocument21 pagesOC - Lect - 02 Aziz Alhaidariabdulaziz saif ali mansoorNo ratings yet
- Unit III - Fiber Optics and Photonics - PH101Document16 pagesUnit III - Fiber Optics and Photonics - PH101Kripanshu KumarNo ratings yet
- Ray Theory of TransmissionDocument44 pagesRay Theory of TransmissionAkhil Arora100% (1)
- Optical Fibers Wave GuidingDocument50 pagesOptical Fibers Wave GuidingAfsaribegum MohammadNo ratings yet
- Topics: 1) Basic Optical Laws and Definitions 2) Optical Modes and Congigurations Presented by Mrs. N.Beaula, Asst. Prof. / ECE, AcewDocument27 pagesTopics: 1) Basic Optical Laws and Definitions 2) Optical Modes and Congigurations Presented by Mrs. N.Beaula, Asst. Prof. / ECE, AcewbeaulajenishNo ratings yet
- Optical Fiber 2022Document12 pagesOptical Fiber 2022Nidhi R VassNo ratings yet
- As 23b OpticsDocument57 pagesAs 23b OpticsHany ElGezawyNo ratings yet
- Chapter Three Light As Wave MotionDocument11 pagesChapter Three Light As Wave MotionSabrina NevilleLongbottom RitterNo ratings yet
- Fiber Optic Network Troubleshooting MainDocument20 pagesFiber Optic Network Troubleshooting MainBheki TshimedziNo ratings yet
- Serat OptikDocument100 pagesSerat OptikNur Moh. Alif Al-wahidNo ratings yet
- Optical Fibers: Structures: Unit-2Document15 pagesOptical Fibers: Structures: Unit-2Mithun KumarNo ratings yet
- FibresDocument48 pagesFibresPrakash SheNo ratings yet
- Optical Fibers: Fiber Is TIR (Total Internal Reflection)Document12 pagesOptical Fibers: Fiber Is TIR (Total Internal Reflection)Ńovitatis ĎineshNo ratings yet
- Geometrical OpticsDocument30 pagesGeometrical Opticsdildar123No ratings yet
- Fibers From The View of Geometrical Optics: EE 230: Optical Fiber Communication Lecture 2Document21 pagesFibers From The View of Geometrical Optics: EE 230: Optical Fiber Communication Lecture 2mofiwNo ratings yet
- Day 3Document43 pagesDay 3Abhiram SwarnaNo ratings yet
- Ray Theory Transmission: Total Internal Reflection (Tir) Acceptance Angle (ϴa) Numerical Aperture (Na)Document9 pagesRay Theory Transmission: Total Internal Reflection (Tir) Acceptance Angle (ϴa) Numerical Aperture (Na)jeevanandhamrvsNo ratings yet
- OCN Unit - 1Document105 pagesOCN Unit - 1BinoStephenNo ratings yet
- FALLSEM2020-21 PHY1701 ETH VL2020210105688 Reference Material I 13-Oct-2020 Module-6 PDFDocument71 pagesFALLSEM2020-21 PHY1701 ETH VL2020210105688 Reference Material I 13-Oct-2020 Module-6 PDFSahil KalingNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Optical FibersDocument60 pagesChapter 2 - Optical Fiberseyohamehari235No ratings yet
- Optical Fibers WaveGuidingDocument52 pagesOptical Fibers WaveGuidingMd ShadabNo ratings yet
- 3 Light Propagation in Optical FibersDocument24 pages3 Light Propagation in Optical FibersbrooksNo ratings yet
- Lecture (Optics and Laser)Document40 pagesLecture (Optics and Laser)Salama NaumanNo ratings yet
- Numerical Problems On Optical Fibers and TheoryDocument72 pagesNumerical Problems On Optical Fibers and TheoryPavamana Giribhattanavar100% (1)
- Light Propagation in Optical FibresDocument31 pagesLight Propagation in Optical FibresWail HamedNo ratings yet
- FIBRE OPTICS Final 26.02.2021Document43 pagesFIBRE OPTICS Final 26.02.2021Mahir MittalNo ratings yet
- Fiber OpticsDocument25 pagesFiber OpticsAditya [Sem 1&2]No ratings yet
- Unit-V: Basics of Fiber OpticsDocument35 pagesUnit-V: Basics of Fiber OpticsthorasgardNo ratings yet
- Optical Communication (Eec-701) Unit - 1: By: Shubhanshi GuptaDocument9 pagesOptical Communication (Eec-701) Unit - 1: By: Shubhanshi GuptavivekNo ratings yet
- Ray Theory Transmission: Refractive IndexDocument7 pagesRay Theory Transmission: Refractive IndexranjithNo ratings yet
- Lasers Definition and TypesDocument5 pagesLasers Definition and TypesTony starkNo ratings yet
- Optical Fiber CommunicationDocument48 pagesOptical Fiber CommunicationPrateekMittalNo ratings yet
- LED ClassDocument10 pagesLED Classshubham saurabhNo ratings yet
- Chapter 25 - Instruments For Optical SpecDocument12 pagesChapter 25 - Instruments For Optical SpecS. MartinezNo ratings yet
- Numerical With AnswerDocument19 pagesNumerical With AnswerRahul KumarNo ratings yet
- Unit-4 Mwoc 5-12-22Document82 pagesUnit-4 Mwoc 5-12-22Tharun kondaNo ratings yet
- Day 4Document41 pagesDay 4Abhiram SwarnaNo ratings yet
- Physics Lab ManualDocument62 pagesPhysics Lab ManualKrishna MahajanNo ratings yet
- RefractionDocument42 pagesRefractionjanaNo ratings yet
- Reflection RefractionDocument20 pagesReflection RefractionCarl Daniel FandiñoNo ratings yet
- Ec8751-Optical Communication-534191069-Ec8751 Optical Communication Question BankDocument60 pagesEc8751-Optical Communication-534191069-Ec8751 Optical Communication Question Bankaajdufkf0% (1)
- Chapter 22.1 4Document34 pagesChapter 22.1 4Richard Renz VillafuerteNo ratings yet
- Ece Dept: Sri Mittapalli College of EngineeringDocument44 pagesEce Dept: Sri Mittapalli College of EngineeringbrsreddyNo ratings yet
- 2 Oed - M2Document27 pages2 Oed - M2Christy PollyNo ratings yet
- OCN Unit 1,2Document23 pagesOCN Unit 1,2M Madhu MaliniNo ratings yet
- OC PartDocument19 pagesOC PartEmad MasoodNo ratings yet
- Ray Theory Transmission in Optical FibersDocument27 pagesRay Theory Transmission in Optical FibersvardhanNo ratings yet
- Lecture #1 Optical FibersDocument59 pagesLecture #1 Optical Fibersjeddo2005No ratings yet
- FAL (2021-22) PHY1010 ETH AP2021222000083 Reference Material I 18-Aug-2021 Wave Optics-InterferenceDocument53 pagesFAL (2021-22) PHY1010 ETH AP2021222000083 Reference Material I 18-Aug-2021 Wave Optics-Interferencetejas paiNo ratings yet
- Fibre Optics StudentsDocument25 pagesFibre Optics StudentsmyselfnoobcoderNo ratings yet
- OpticsDocument51 pagesOpticsUday Kiran ChNo ratings yet
- Optical Full Units NOTESDocument98 pagesOptical Full Units NOTESkohilavaniapNo ratings yet
- 7 Optical CommunicationDocument30 pages7 Optical CommunicationSanjay DahalNo ratings yet
- OPTICAL FIBER COMMUNICATION Basic and CharactersticsDocument36 pagesOPTICAL FIBER COMMUNICATION Basic and CharactersticsabidNo ratings yet
- Optical CommunicationDocument16 pagesOptical CommunicationElma RaymondNo ratings yet
- Innovate or Perish: FPGA Physical Design: Taraneh Taghavi, Soheil Ghiasi Abhishek Ranjan, Salil Raje Majid SarrafzadehDocument8 pagesInnovate or Perish: FPGA Physical Design: Taraneh Taghavi, Soheil Ghiasi Abhishek Ranjan, Salil Raje Majid SarrafzadehPerumal NamasivayamNo ratings yet
- Nterconnect Odeling: M.Arvind 2 M.E MicroelectronicsDocument26 pagesNterconnect Odeling: M.Arvind 2 M.E MicroelectronicsPerumal NamasivayamNo ratings yet
- ChatLog ANITS - ECE Online Workshop 2020 - 05 - 29 11 - 26Document3 pagesChatLog ANITS - ECE Online Workshop 2020 - 05 - 29 11 - 26Perumal NamasivayamNo ratings yet
- Interconnect Delay ModelsDocument16 pagesInterconnect Delay ModelsPerumal NamasivayamNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 Design and Synthesis of Datapath Controllers: Department of Communication Engineering, NCTUDocument25 pagesUnit 4 Design and Synthesis of Datapath Controllers: Department of Communication Engineering, NCTUPerumal NamasivayamNo ratings yet
- Experiment 12:: SCR CharacteristicsDocument3 pagesExperiment 12:: SCR CharacteristicsPerumal NamasivayamNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Asic DesignDocument53 pagesIntroduction To Asic DesignPerumal NamasivayamNo ratings yet
- Fiber Optic SensorsDocument10 pagesFiber Optic SensorsPerumal NamasivayamNo ratings yet
- Post Harvest Technology of Maize (Maize Processing) : Dr. U. D. ChavanDocument32 pagesPost Harvest Technology of Maize (Maize Processing) : Dr. U. D. ChavanPerumal NamasivayamNo ratings yet
- Piezoelectric Transducer: E.Karolinekersin Assistant ProfessorDocument28 pagesPiezoelectric Transducer: E.Karolinekersin Assistant ProfessorPerumal NamasivayamNo ratings yet
- ChatLog ANITS - ECE Online Workshop 2020 - 05 - 29 12 - 48Document4 pagesChatLog ANITS - ECE Online Workshop 2020 - 05 - 29 12 - 48Perumal NamasivayamNo ratings yet
- ChatLog ANITS ECE WORKSHOP DAY 2 2020 - 05 - 30 10 - 54Document3 pagesChatLog ANITS ECE WORKSHOP DAY 2 2020 - 05 - 30 10 - 54Perumal NamasivayamNo ratings yet
- ChatLog Dassault 2020 - 07 - 10 12 - 20Document1 pageChatLog Dassault 2020 - 07 - 10 12 - 20Perumal NamasivayamNo ratings yet
- Electronics & Communicatio N Engineering: Annual Report 2016 - 17Document21 pagesElectronics & Communicatio N Engineering: Annual Report 2016 - 17Perumal NamasivayamNo ratings yet
- Digitized Pictures: by K. Karpoora Sundari ECE Department, K. Ramakrishnan College of Technology, SamayapuramDocument31 pagesDigitized Pictures: by K. Karpoora Sundari ECE Department, K. Ramakrishnan College of Technology, SamayapuramPerumal NamasivayamNo ratings yet
- Electronics & Communicatio N Engineering: Annual Report 2017 - 18Document18 pagesElectronics & Communicatio N Engineering: Annual Report 2017 - 18Perumal NamasivayamNo ratings yet
- NITPY Application FORMDocument8 pagesNITPY Application FORMPerumal NamasivayamNo ratings yet
- Design and Comparative Analysis of CMOS PDFDocument9 pagesDesign and Comparative Analysis of CMOS PDFPerumal NamasivayamNo ratings yet
- Test - Basic Hand Tools - Carpentry - QuizletDocument19 pagesTest - Basic Hand Tools - Carpentry - QuizletPerumal NamasivayamNo ratings yet
- GladeDocument1 pageGladePerumal NamasivayamNo ratings yet