Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Development Economics: Prof. Dr. Hans H. Bass
Development Economics: Prof. Dr. Hans H. Bass
Uploaded by
SharaGailFuscablo0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views7 pagesThis document outlines the agenda for a development economics course. It discusses approaches in mainstream economics versus development economics. The course will cover the meaning and measurement of development. It poses questions about why poverty persists alongside affluence and whether traditional societies can transform into modern economies. The document then discusses the economic problem of scarcity and how mainstream economics has approached this issue from Adam Smith to modern assumptions of rational actors and perfect markets. For developing economies, the economic problem is how to efficiently allocate resources and promote rapid growth to improve conditions for the poor.
Original Description:
Original Title
1
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document outlines the agenda for a development economics course. It discusses approaches in mainstream economics versus development economics. The course will cover the meaning and measurement of development. It poses questions about why poverty persists alongside affluence and whether traditional societies can transform into modern economies. The document then discusses the economic problem of scarcity and how mainstream economics has approached this issue from Adam Smith to modern assumptions of rational actors and perfect markets. For developing economies, the economic problem is how to efficiently allocate resources and promote rapid growth to improve conditions for the poor.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as ppt, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views7 pagesDevelopment Economics: Prof. Dr. Hans H. Bass
Development Economics: Prof. Dr. Hans H. Bass
Uploaded by
SharaGailFuscabloThis document outlines the agenda for a development economics course. It discusses approaches in mainstream economics versus development economics. The course will cover the meaning and measurement of development. It poses questions about why poverty persists alongside affluence and whether traditional societies can transform into modern economies. The document then discusses the economic problem of scarcity and how mainstream economics has approached this issue from Adam Smith to modern assumptions of rational actors and perfect markets. For developing economies, the economic problem is how to efficiently allocate resources and promote rapid growth to improve conditions for the poor.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as ppt, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 7
Development Economics
Prof. Dr. Hans H. Bass
Jacobs University, Spring 2010
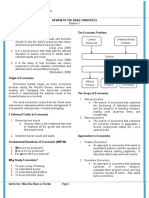
Development Economics Agenda Feb. 04
0. Introductory remarks, grading, topics for
presentation, and overview
1. Economics
1.1 Approaches in mainstream economics
1.2 Approaches in Development Economics
2. Development
2.1 Meaning
2.2 Measurement
Feb. 04, 2010 2
Development Economics Overview
Voices of the Poor ...
... and some questions for our course:
“Why does affluence coexist with dire poverty not only on
different continents but also within the same country?
Can traditional low-productivity, subsistence societies be
transformed into modern, high-productivity, high-income
nations?
To what extent are the development aspirations of poor nations
helped or hindered by the economic activities of rich
nations? ...”
(Todaro/Smith 2009, p. 7)
Feb. 04, 2010 3
1. Economics
1.1 Approaches in mainstream economics
1.2 Approaches in Development Economics The economic problem
2. Development
Material wants exceed productive capacity
scarcity!
Utility maximization under conditions of scarcity
Economics is about making choices
What is the most efficient way to allocate scarce
resources and allow optimal growth of these
resources?
Feb. 04, 2010 4
1. Economics
1.1 Approaches in mainstream economics From Adam Smith
1.2 Approaches in Development Economics
2. Development to modern times ...
Adam Smith, 1776 (founder of classical economics)
(„An Inquiry into the Nature and Cause of the Wealth of Nations“)
modern mainstream economics
(neo-classical and beyond)
Feb. 04, 2010 5
1. Economics
1.1 Approaches in mainstream economics Main neo-classical
1.2 Approaches in Development Economics
2. Development assumptions
homo economicus (fully informed, completely rational, utility
maximizing behavior)
decisions made on the basis of marginal, private-profit, and
utility calculations
consumer sovereignty, producer sovereignty
perfect markets
(perfect market information + no participant with market
power to set prices + no barrier to entry or exit + equal access
to production technology = perfect competition)
prices equate supply and demand, immediate price
adjustments
equilibrium outcomes in all product and factor markets
Feb. 04, 2010 6
1. Economics
1.1 Approaches in mainstream economics The new economic
1.2 Approaches in Development Economics
2. Development problem
What is the most efficient way to allocate scarce
resources and allow optimal growth of these
resources?
and: What are the economic, social, and political
mechanisms necessary to bring about rapid and
large-scale improvements for the world’s poor(est),
i.e. 150+ economies?
Feb. 04, 2010 7
You might also like
- Globalization - Reflection PaperDocument2 pagesGlobalization - Reflection PaperJaycel Bayron83% (6)
- Harvard Business Case Cadbury & SchweppesDocument24 pagesHarvard Business Case Cadbury & SchweppesPaul Morrison60% (10)
- VSA Bar Definitions V 2Document1 pageVSA Bar Definitions V 2No Name89% (9)
- Development Economics: Prof. Dr. Hans H. BassDocument30 pagesDevelopment Economics: Prof. Dr. Hans H. BassSharaGailFuscabloNo ratings yet
- Economic Development (Macroeconomics)Document9 pagesEconomic Development (Macroeconomics)Chriszel Mae PadalNo ratings yet
- Econ Dev Notes M1Document4 pagesEcon Dev Notes M1Cyra Paulin VistaNo ratings yet
- Development Economics III: Prof. Dr. Hans H. BassDocument14 pagesDevelopment Economics III: Prof. Dr. Hans H. BassbusybeefreedomNo ratings yet
- Economics of Development: Fall 2009Document57 pagesEconomics of Development: Fall 2009Wonseok ParkNo ratings yet
- BIOGRAPHY OF A SUBJECT - An Evolution of Development EconomicsDocument260 pagesBIOGRAPHY OF A SUBJECT - An Evolution of Development EconomicsIsabel Aristizábal MartínezNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan I. Objectives: A. Learning Area B. Topic C. ReferencesDocument4 pagesLesson Plan I. Objectives: A. Learning Area B. Topic C. ReferencesArjyl Tirao0% (1)
- EconomicsDocument14 pagesEconomicsGALO MARIEBELNo ratings yet
- Economic Development Full PowerpointDocument84 pagesEconomic Development Full PowerpointDamir Jovic100% (1)
- Teori Pembangunan KlasikDocument94 pagesTeori Pembangunan Klasikselvi slvNo ratings yet
- Managerial Economics Full NotesDocument116 pagesManagerial Economics Full NoteselevationonlineindNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Economics: Chapter OneDocument53 pagesIntroduction To Economics: Chapter OneetNo ratings yet
- Dualisme Ekonomi PembangunanDocument11 pagesDualisme Ekonomi PembangunanIsna HanifahNo ratings yet
- Slide Chap 2Document60 pagesSlide Chap 2k60.2112450022No ratings yet
- EconomicsDocument156 pagesEconomicsSandeep S YadavNo ratings yet
- KluyoiyoDocument313 pagesKluyoiyosonu alamNo ratings yet
- Theory DevelopmentDocument7 pagesTheory DevelopmentHerfin SopianNo ratings yet
- Basic Concept of Economics and Introduction To Micro Economics PDFDocument35 pagesBasic Concept of Economics and Introduction To Micro Economics PDFashish69250% (2)
- Econo - Intro Chapter 1Document54 pagesEcono - Intro Chapter 1numeerabdallaaNo ratings yet
- D-3. Theories of DVT & Their Evolution Chap 3-StudentsDocument169 pagesD-3. Theories of DVT & Their Evolution Chap 3-StudentsSamuel AsradeNo ratings yet
- Introduction To EconomicsDocument3 pagesIntroduction To Economicsqulb abbasNo ratings yet
- DBC011 Business Economics EMDocument338 pagesDBC011 Business Economics EMsandiNo ratings yet
- Welcome To Economics (MCR001) : A: Thursday 8.30amDocument48 pagesWelcome To Economics (MCR001) : A: Thursday 8.30amShivarni KumarNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes in EconomicsDocument5 pagesLecture Notes in EconomicsameenaNo ratings yet
- Economic Development Chapter 1-3Document6 pagesEconomic Development Chapter 1-3Assault ProNo ratings yet
- BasicsDocument22 pagesBasicsAshish RanjanNo ratings yet
- Introducing Economic Development: A Global PerspectiveDocument19 pagesIntroducing Economic Development: A Global PerspectiveABM 1212 Arevalo Kate AnnNo ratings yet
- Real Concept of DevelopmentDocument14 pagesReal Concept of DevelopmentHer Store100% (1)
- Economic Development: Econ 303Document10 pagesEconomic Development: Econ 303Mahmoud HassaanNo ratings yet
- Chapter One Inr EcoDocument53 pagesChapter One Inr EcoIbm FattyNo ratings yet
- Lesson I - Introduction of EconomicsDocument7 pagesLesson I - Introduction of EconomicsArven DulayNo ratings yet
- Modernisation - Theory ppt-1Document17 pagesModernisation - Theory ppt-1Ibrahim Mohamed Ibrahim100% (1)
- Development Economics PP Chapter OneDocument46 pagesDevelopment Economics PP Chapter OneFiraNo ratings yet
- Economic Development (Prelims)Document7 pagesEconomic Development (Prelims)JeanieNo ratings yet
- Econ 1 Module 1Document14 pagesEcon 1 Module 1solon_594bc100% (1)
- History of Economic Thought2018-19Document152 pagesHistory of Economic Thought2018-19LEWOYE BANTIENo ratings yet
- Economic and Development ReviewDocument16 pagesEconomic and Development ReviewMary Justine GallanoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - DDocument26 pagesChapter 1 - DSujani MaarasingheNo ratings yet
- Economic Analysis For Business UNIT1Document28 pagesEconomic Analysis For Business UNIT1rakeshparthasarathyNo ratings yet
- University of Waterloo Department of Economics: Econ 101 - Introduction To Micro EconomicsDocument48 pagesUniversity of Waterloo Department of Economics: Econ 101 - Introduction To Micro EconomicsnahlaNo ratings yet
- D-3. Theories of DVT & Their Evolution Chap 3-StudentsDocument169 pagesD-3. Theories of DVT & Their Evolution Chap 3-StudentsSamuel AsradeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document66 pagesChapter 1Haaromsaa Taayyee TolasaaNo ratings yet
- Goods and Services People: - Trade - Skills/Profession - Immegration/Culture/ - Labor - Money - InvestmentDocument13 pagesGoods and Services People: - Trade - Skills/Profession - Immegration/Culture/ - Labor - Money - InvestmentcassandraNo ratings yet
- Unit1 150428082524 Conversion Gate01Document85 pagesUnit1 150428082524 Conversion Gate01Joseph CabreraNo ratings yet
- University of Puthisastra: Economic DevelopmentDocument30 pagesUniversity of Puthisastra: Economic DevelopmentHeng HengNo ratings yet
- Economic Development LessonsDocument8 pagesEconomic Development LessonsAngelNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 and 2Document119 pagesUnit 1 and 2Piyush SinglaNo ratings yet
- Relevance of EconomcisDocument4 pagesRelevance of EconomcismezevNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document7 pagesChapter 1ayandasmtsNo ratings yet
- SSE 108 Module-1-Introduction-to-EconomicsDocument33 pagesSSE 108 Module-1-Introduction-to-EconomicssmileydaintyNo ratings yet
- Farzana Yeasmin, Lecture-1Document25 pagesFarzana Yeasmin, Lecture-1Nizhum FarzanaNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Lesson 1Document19 pagesUnit 1 Lesson 1Suan , Troy Justine , R.No ratings yet
- Information Sheet Pr-1.1.1 "The Nature of Development Economics"Document43 pagesInformation Sheet Pr-1.1.1 "The Nature of Development Economics"Marielle JalandoniNo ratings yet
- ExamDocument1 pageExamapi-3827598No ratings yet
- International Economics DevelopmentDocument31 pagesInternational Economics Developmentketty giiNo ratings yet
- I. Structural Adjustment ProgramsDocument6 pagesI. Structural Adjustment ProgramsMo AlamNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Economics: (A) What Economics Is All About ?Document16 pagesIntroduction To Economics: (A) What Economics Is All About ?Smriti JoshiNo ratings yet
- 01 Review of The Basic PrinciplesDocument1 page01 Review of The Basic Principlescatherine tucayNo ratings yet
- OioiDocument5 pagesOioiSharaGailFuscabloNo ratings yet
- Welcome To WPS OfficeDocument84 pagesWelcome To WPS OfficeSharaGailFuscabloNo ratings yet
- Mindanao State University: Request To Conduct "In-Campus" Activities And/Or To Use FacilitiesDocument2 pagesMindanao State University: Request To Conduct "In-Campus" Activities And/Or To Use FacilitiesSharaGailFuscabloNo ratings yet
- Ce Great Minds PrebDocument5 pagesCe Great Minds PrebSharaGailFuscabloNo ratings yet
- PHD Thesis JsmithDocument224 pagesPHD Thesis JsmithSharaGailFuscabloNo ratings yet
- Physical and Chemical Properties of Soil: The Regents of The University of CaliforniaDocument1 pagePhysical and Chemical Properties of Soil: The Regents of The University of CaliforniaSharaGailFuscabloNo ratings yet
- Religious Discrimination, Reasonable Accommodation For Religious Beliefs and Religious Practices in The WorkplaceDocument38 pagesReligious Discrimination, Reasonable Accommodation For Religious Beliefs and Religious Practices in The WorkplaceSharaGailFuscabloNo ratings yet
- BJ ' B S: (Exit. Only)Document2 pagesBJ ' B S: (Exit. Only)SharaGailFuscabloNo ratings yet
- Numericals Solved - Demand Theory - Unit - 3Document6 pagesNumericals Solved - Demand Theory - Unit - 3shankar0% (2)
- Business Studies NotesDocument55 pagesBusiness Studies NotesCyrus Ngugi100% (1)
- Assignment #1 - ECON 435 - 635 (W24)Document3 pagesAssignment #1 - ECON 435 - 635 (W24)georgeaamoakoNo ratings yet
- Spontaneous FundsDocument5 pagesSpontaneous FundsTobelaNcube100% (2)
- Ecs 1501Document26 pagesEcs 1501Anonymous jRavc6No ratings yet
- Strategic MGMT HULDocument10 pagesStrategic MGMT HULTasha RobinsonNo ratings yet
- Slide 08 UnemploymentDocument100 pagesSlide 08 Unemploymentcrazyboy94372No ratings yet
- Positive Accounting Theory Lecture NotesDocument7 pagesPositive Accounting Theory Lecture NotesKweku_Affir_Hayf_886100% (3)
- Economics Marathi VersionDocument271 pagesEconomics Marathi VersionHarsh SanganiNo ratings yet
- BA Hons Political ScienceDocument26 pagesBA Hons Political ScienceBhavna MuthyalaNo ratings yet
- Stupid Economy PDFDocument27 pagesStupid Economy PDFAndrea PérezNo ratings yet
- Fleurbaey - Optimal Taxation Theory and Principles of FairnessDocument56 pagesFleurbaey - Optimal Taxation Theory and Principles of Fairnessandri heryantoNo ratings yet
- Itc FMCGDocument21 pagesItc FMCGYogesh RawoolNo ratings yet
- Wcms 670542Document122 pagesWcms 670542bulchit buqsNo ratings yet
- Motives of Internationalization of FirmsDocument5 pagesMotives of Internationalization of FirmsNeeraj Jain100% (1)
- Seligram Case QuestionsDocument2 pagesSeligram Case QuestionsZain Bharwani100% (1)
- Global Prospects and Policies: Global Economy Climbing Out of The Depths, Prone To SetbacksDocument64 pagesGlobal Prospects and Policies: Global Economy Climbing Out of The Depths, Prone To SetbacksOrestis VelmachosNo ratings yet
- Understanding Vietnam - A Look Beyond The Facts and PDFDocument24 pagesUnderstanding Vietnam - A Look Beyond The Facts and PDFDawood GacayanNo ratings yet
- The Importance of Competition and Enterprise CompetitivenessDocument6 pagesThe Importance of Competition and Enterprise CompetitivenessNastea SelariNo ratings yet
- Cobb-Douglas Utility Function 2.5Document17 pagesCobb-Douglas Utility Function 2.5Adrian BrenesNo ratings yet
- Module 1meDocument3 pagesModule 1meSaeym SegoviaNo ratings yet
- 08me-Managerial Theories of The FirmDocument8 pages08me-Managerial Theories of The FirmRajiv KarNo ratings yet
- 2010-03-09 031501 AnswerDocument4 pages2010-03-09 031501 Answerahmetdursun03No ratings yet
- Managerial Economics and Financial Analysis: Unit-IDocument24 pagesManagerial Economics and Financial Analysis: Unit-IJanu JahnaviNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Household Behavior and Consumer ChoiceDocument43 pagesChapter 6 Household Behavior and Consumer ChoiceTori BankruptNo ratings yet
- Marketing Strategy ProcessDocument70 pagesMarketing Strategy ProcessDaman AroraNo ratings yet
- Entrep 1Document10 pagesEntrep 1ayra cyreneNo ratings yet