Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 viewsDisease of The Biliary Tract: Abdifatah Osman Nur, MBBS, Mmed (General Surgery)
Disease of The Biliary Tract: Abdifatah Osman Nur, MBBS, Mmed (General Surgery)
Uploaded by
DrAisha QalbinurThis document discusses diseases of the biliary tract, including congenital abnormalities and diagnostic techniques. It covers the anatomy of the biliary tract and describes conditions like extrahepatic biliary atresia, Caroli's disease, and choledochal cysts. Treatment options are provided for various congenital abnormalities, including surgery and liver transplantation. Common imaging modalities for investigating the biliary tract are outlined, such as ultrasound, CT, ERCP, MRCP, PTC, and choledochoscopy.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Nightmaretaker GuideDocument12 pagesNightmaretaker Guidejese 08100% (3)
- Ford Transit 2006.5 04.2006 Workshop Manual ( (04.2006-) )Document834 pagesFord Transit 2006.5 04.2006 Workshop Manual ( (04.2006-) )slawek100% (2)
- Biliary Tract Disease - Emmet AndrewsDocument52 pagesBiliary Tract Disease - Emmet AndrewsBoneyJalgarNo ratings yet
- Powerpoint: Liver Surgical DiseasesDocument95 pagesPowerpoint: Liver Surgical Diseasesj.doe.hex_8792% (12)
- Fast Facts for Patients and Supporters: Cholangiocarcinoma: A cancer of the bile duct and liver Information + Taking Control = Best OutcomeFrom EverandFast Facts for Patients and Supporters: Cholangiocarcinoma: A cancer of the bile duct and liver Information + Taking Control = Best OutcomeNo ratings yet
- RulebookDocument296 pagesRulebookRogerio Lucena100% (2)
- 3.7 Types of Protein Exam QuestionDocument3 pages3.7 Types of Protein Exam QuestionjnfjngsdjNo ratings yet
- Biliary Surgery: Presenter: DR Muhuga JR Facilitator: DR MwashambwaDocument54 pagesBiliary Surgery: Presenter: DR Muhuga JR Facilitator: DR MwashambwaSamar AhmadNo ratings yet
- Surgical Anatomy of Extrahepatic Biliary ApparatusDocument33 pagesSurgical Anatomy of Extrahepatic Biliary ApparatussyedaNo ratings yet
- CholilithiasisDocument94 pagesCholilithiasisdr.hendraNo ratings yet
- Surgical JaundiceDocument35 pagesSurgical JaundiceIbsa ShumaNo ratings yet
- 1 Gallbladder Disease 2Document68 pages1 Gallbladder Disease 2salsabeelNo ratings yet
- Benign Hepatobiliary DisordersDocument29 pagesBenign Hepatobiliary DisordershafizahhoshniNo ratings yet
- SURG - Hepatobiliary, Pancreas, SpleenDocument230 pagesSURG - Hepatobiliary, Pancreas, SpleenJoan Timbol100% (1)
- Surgery of The Biliary System KFS 2022Document100 pagesSurgery of The Biliary System KFS 2022ahmedelkaranshawy123456789No ratings yet
- Obstructive JaundiceDocument34 pagesObstructive Jaundicemogesie1995No ratings yet
- The Gallbladder Diseases Bile Duct StoneDocument69 pagesThe Gallbladder Diseases Bile Duct Stoneحميد حيدرNo ratings yet
- (S-W5-Sun-Gen.S) (By Dr. Emad) Gall Bladder 1Document28 pages(S-W5-Sun-Gen.S) (By Dr. Emad) Gall Bladder 1Haider Nadhem AL-rubaiNo ratings yet
- Gall Bladder Stones: Surgical Treatment.: JournalDocument24 pagesGall Bladder Stones: Surgical Treatment.: JournalFika ResitaNo ratings yet
- Radiology of Hepatobiliary System Pancreas and Spleen: Nugzar LipartelianiDocument136 pagesRadiology of Hepatobiliary System Pancreas and Spleen: Nugzar LipartelianiShubham TanwarNo ratings yet
- Screenshot 2023-11-26 at 5.15.31 PMDocument39 pagesScreenshot 2023-11-26 at 5.15.31 PMgauravsingh708284No ratings yet
- 4.gall StoneDocument35 pages4.gall Stonejitendra magarNo ratings yet
- C 10 + 11 Gallbladder and Biliary TractDocument99 pagesC 10 + 11 Gallbladder and Biliary TractAdinaNo ratings yet
- Biliary SystemDocument83 pagesBiliary SystemeviltohuntNo ratings yet
- Cholesistitis (DR - Prema Hapsari, SPPD)Document28 pagesCholesistitis (DR - Prema Hapsari, SPPD)Niniek Iin F100% (1)
- 42 EsophagusDocument49 pages42 EsophagusShiva BhandariNo ratings yet
- Biliary Tract DiseaseDocument52 pagesBiliary Tract DiseaseAna Cotoman100% (1)
- CT Abdomen - Hosiana O W - 42180258Document18 pagesCT Abdomen - Hosiana O W - 42180258HOSIANAOWNo ratings yet
- Hepato-Biliary System 26.4.2016Document59 pagesHepato-Biliary System 26.4.2016S B SayedNo ratings yet
- Cholecystitis and Biliary Colic: Learning ObjectivesDocument37 pagesCholecystitis and Biliary Colic: Learning Objectivesapi-19641337No ratings yet
- Benign Colorectal Disease: Ahmed AlzahraniDocument47 pagesBenign Colorectal Disease: Ahmed Alzahraniahmad alzahraniNo ratings yet
- Acute AbdomenDocument73 pagesAcute AbdomenWahyu DustnamNo ratings yet
- Biliary Tract DiseaseDocument40 pagesBiliary Tract DiseaseIsaac MwangiNo ratings yet
- Advocate Aurora Health Institutional Repository Advocate Aurora Health Institutional RepositoryDocument33 pagesAdvocate Aurora Health Institutional Repository Advocate Aurora Health Institutional Repositoryvhy107No ratings yet
- Diverticular Disease: Maj Mohit Goyal Maj Rahul Goel Dept of SurgeryDocument67 pagesDiverticular Disease: Maj Mohit Goyal Maj Rahul Goel Dept of Surgeryunknownsince1986No ratings yet
- Common Bile Duct Stones StrictureDocument48 pagesCommon Bile Duct Stones StrictureSyarif MalawatNo ratings yet
- The Stomach and Duodenum: Dr. Elian EliasDocument48 pagesThe Stomach and Duodenum: Dr. Elian EliasmodarNo ratings yet
- Hepatic CirrhosisDocument20 pagesHepatic CirrhosisAnifowose samsonNo ratings yet
- Billiary SurgeriesDocument37 pagesBilliary Surgeriesgeorvin marcoNo ratings yet
- Overview of Gallstone Disease and ManagementDocument33 pagesOverview of Gallstone Disease and ManagementWONG LIONG SHING KPM-GuruNo ratings yet
- Small Intestine: Earle J. Niervo Medical ClerkDocument168 pagesSmall Intestine: Earle J. Niervo Medical ClerkEarle Jimenez Niervo RNNo ratings yet
- AscitesDocument63 pagesAscitesfeeo8266No ratings yet
- The PancreasDocument37 pagesThe PancreasFaiza AshrafNo ratings yet
- WelcomeDocument60 pagesWelcomepandem soniyaNo ratings yet
- Recent Management of Calculous Biliary DiseaseDocument35 pagesRecent Management of Calculous Biliary DiseaseAbhishek SarafNo ratings yet
- Colon: Malueth AbrahamDocument39 pagesColon: Malueth AbrahamMalueth AnguiNo ratings yet
- Colilithiasis 2Document53 pagesColilithiasis 2Worku KifleNo ratings yet
- Focal Lession of LiverDocument13 pagesFocal Lession of Liverdilekamunasinghe4No ratings yet
- Goo 2021Document72 pagesGoo 2021eviltohuntNo ratings yet
- Imaging Acute Abdomen DR - Rivani Kurniawan FixDocument86 pagesImaging Acute Abdomen DR - Rivani Kurniawan FixRivani KurniawanNo ratings yet
- Obstructive JaundiceDocument33 pagesObstructive JaundiceEvediciNo ratings yet
- URORADIOLOGYDocument34 pagesURORADIOLOGYMeg AmoonNo ratings yet
- Liver BiopsyDocument4 pagesLiver BiopsyLouis Fortunato100% (1)
- GallbladderDocument44 pagesGallbladderAli SafaaNo ratings yet
- Acute Calculous CholecystitisDocument25 pagesAcute Calculous CholecystitisShankar LamichhaneNo ratings yet
- Atresia BilierDocument41 pagesAtresia Bilierrizka hastari100% (1)
- Investigation and Treatment of Surgical JaundiceDocument38 pagesInvestigation and Treatment of Surgical JaundiceUjas PatelNo ratings yet
- 1100 Ultrasound of The Acute Abdomen 15 3Document84 pages1100 Ultrasound of The Acute Abdomen 15 3gp1promo2016No ratings yet
- Biliary Atresia: Dr. Boris Crossley NainggolanDocument41 pagesBiliary Atresia: Dr. Boris Crossley Nainggolanrizka hastariNo ratings yet
- Biliary Diseases: Dr. Wu Yang Dept. of Surgery The First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou UniversityDocument75 pagesBiliary Diseases: Dr. Wu Yang Dept. of Surgery The First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou Universityapi-19916399No ratings yet
- Carcinomagallbladder PDFDocument61 pagesCarcinomagallbladder PDFZaki DhiifNo ratings yet
- Investigation and Treatment of Surgical JaundiceDocument38 pagesInvestigation and Treatment of Surgical JaundiceUjas PatelNo ratings yet
- Liver CirrhosisDocument69 pagesLiver CirrhosisAhmed Alboun75% (4)
- Management of Abdominal Vascular Injury: DR Bashir Bin Yunus General Surgry Unit Akth 3/12/18Document62 pagesManagement of Abdominal Vascular Injury: DR Bashir Bin Yunus General Surgry Unit Akth 3/12/18Fendry KolondamNo ratings yet
- RB Cagmat Review Center: Central Mindanao University, CMU, Musuan, BukidnonDocument6 pagesRB Cagmat Review Center: Central Mindanao University, CMU, Musuan, BukidnonshakiraNo ratings yet
- DME Model QuesDocument3 pagesDME Model QuesSiva RamanNo ratings yet
- FuturaPC EngDocument36 pagesFuturaPC EngRashika SharmaNo ratings yet
- TrollsZine 9Document159 pagesTrollsZine 9Vaughn Everlast100% (1)
- DR Bach Flower Remedies 03-02-2017Document70 pagesDR Bach Flower Remedies 03-02-2017sadam ameerjohnNo ratings yet
- Observation Report: Analytical ChemistryDocument8 pagesObservation Report: Analytical ChemistryLindsay BulgerNo ratings yet
- GeneralMathematics11 q1 Mod5b LogarithmicfunctionDocument28 pagesGeneralMathematics11 q1 Mod5b LogarithmicfunctionBrendan Millard Cruda100% (1)
- HPhys Unit 02 BFPM Packet 2013Document16 pagesHPhys Unit 02 BFPM Packet 2013Kelly O'Shea100% (3)
- Control Valve CV - What It Means and How To Calculate It - Visaya PDFDocument8 pagesControl Valve CV - What It Means and How To Calculate It - Visaya PDFmurugan1984No ratings yet
- PQRST 08 Puzzle Competition Equate: PUZZLE 01 (10 Points Penalty For A Wrong Answer) 30 PointsDocument5 pagesPQRST 08 Puzzle Competition Equate: PUZZLE 01 (10 Points Penalty For A Wrong Answer) 30 PointsCernică AlexandruNo ratings yet
- Planetary UrbanisationDocument5 pagesPlanetary UrbanisationFaris DzulfikarNo ratings yet
- Appendix 19 U472 Community Facilitator Kolb Questionnaire FinalDocument8 pagesAppendix 19 U472 Community Facilitator Kolb Questionnaire FinalCarmen IoanaNo ratings yet
- Studio 8Document3 pagesStudio 8api-609099270No ratings yet
- Summer Training Report On: "Consumer Perception Towards Online Shopping"Document83 pagesSummer Training Report On: "Consumer Perception Towards Online Shopping"Swati TanwarNo ratings yet
- Gv300 ManualDocument22 pagesGv300 ManualCarmelo HoyosNo ratings yet
- Blockchain Merkle TreeDocument4 pagesBlockchain Merkle TreeResearch ParkNo ratings yet
- Volume III For Road Bridge Works PDFDocument355 pagesVolume III For Road Bridge Works PDFsanatan halder100% (1)
- Use of Computers For Environmental Epgineering Related To BuildingsDocument840 pagesUse of Computers For Environmental Epgineering Related To BuildingsJuan Jerez100% (1)
- Muet 1Document15 pagesMuet 1Sity Noor QiyahNo ratings yet
- Helicopter Chapter5Document34 pagesHelicopter Chapter5juanNo ratings yet
- 5 - Introduction To Psychology by James W. Kalat 5Document1 page5 - Introduction To Psychology by James W. Kalat 5Chester ChesterNo ratings yet
- HVAC Designing Drafting Estimation & InstallationDocument3 pagesHVAC Designing Drafting Estimation & Installationnoha azamali50% (2)
- VIBu Introduction Bio Counter 06 - 2012Document11 pagesVIBu Introduction Bio Counter 06 - 2012Asuka Q. QinNo ratings yet
- Make It Work Conventional Fire Alarms MobileDocument17 pagesMake It Work Conventional Fire Alarms MobileButt ManNo ratings yet
- Digital VocabDocument2 pagesDigital Vocabdesikudi9000No ratings yet
- Ground Floor Plan: Nitin SidhpuraDocument14 pagesGround Floor Plan: Nitin SidhpuraRam PatelNo ratings yet
Disease of The Biliary Tract: Abdifatah Osman Nur, MBBS, Mmed (General Surgery)
Disease of The Biliary Tract: Abdifatah Osman Nur, MBBS, Mmed (General Surgery)
Uploaded by
DrAisha Qalbinur0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 views33 pagesThis document discusses diseases of the biliary tract, including congenital abnormalities and diagnostic techniques. It covers the anatomy of the biliary tract and describes conditions like extrahepatic biliary atresia, Caroli's disease, and choledochal cysts. Treatment options are provided for various congenital abnormalities, including surgery and liver transplantation. Common imaging modalities for investigating the biliary tract are outlined, such as ultrasound, CT, ERCP, MRCP, PTC, and choledochoscopy.
Original Description:
Original Title
Biliary disease copy.pptx
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document discusses diseases of the biliary tract, including congenital abnormalities and diagnostic techniques. It covers the anatomy of the biliary tract and describes conditions like extrahepatic biliary atresia, Caroli's disease, and choledochal cysts. Treatment options are provided for various congenital abnormalities, including surgery and liver transplantation. Common imaging modalities for investigating the biliary tract are outlined, such as ultrasound, CT, ERCP, MRCP, PTC, and choledochoscopy.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 views33 pagesDisease of The Biliary Tract: Abdifatah Osman Nur, MBBS, Mmed (General Surgery)
Disease of The Biliary Tract: Abdifatah Osman Nur, MBBS, Mmed (General Surgery)
Uploaded by
DrAisha QalbinurThis document discusses diseases of the biliary tract, including congenital abnormalities and diagnostic techniques. It covers the anatomy of the biliary tract and describes conditions like extrahepatic biliary atresia, Caroli's disease, and choledochal cysts. Treatment options are provided for various congenital abnormalities, including surgery and liver transplantation. Common imaging modalities for investigating the biliary tract are outlined, such as ultrasound, CT, ERCP, MRCP, PTC, and choledochoscopy.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 33
Disease of The Biliary Tract
Abdifatah Osman Nur,MBBS,Mmed(General Surgery)
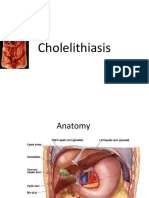
Anatomy Review
• Biliary tract
– Intra-hepatic bile duct
– Extra-hepatic bile duct
– Gallbladder
– Oddi sphincter
From bile canaliculi to the ampulla of Vater.
Intra-hepatic Bile Duct
• Bile canaliculi.
• Segmental bile duct
• Lobal bile duct
• Hepatic part of left and right hepatic duct
Extra-hepatic Bile Duct
• Left and right hepatic duct
• The common hepatic duct
-Diameter :0.4-0.6 cm ,
- length: less than 2cm
• Common bile duct(4 parts).
-Diameter:0.6-0.8cm
-length:2.5cm
• Gallbladder:
- Body, Fundus and Neck
• Cyst duct
Calot triangle:
• The triangle bounded by the common hepatic duct
medially, the cystic duct lateraly and the inferior
surface of the right liver superiorly is known as
Calot triangle.
• The fact that cystic artery ,right hepatic artery &
para-right hepatic duct run within the triangle
makes an important area of dissection during
cholecytectomy.
• The sphincter of Oddi:
• The distal bile and pancreatic ducts and the
common channel are surrounded by circular
and longitudinal smooth muscle, this muscle
complex is known as the sphincter of Oddi.
CONGENITAL Abnormalities
Extrahepatic biliary atresia
• Biliary atresia presents in 1 per 12 000 live
births.
• Affects both gender equally.
• Aetiology is unclear.
• Untreated, death from the consequences of
liver failure occurs before the age of 3 years.
• About 20% of cases there will be associated
anomalies.
Three main types
• Type I: Atresia restricted to the common bile duct;
• Type II: Atresia of the common hepatic duct;
• Type III: Atresia of the right and left hepatic ducts
Clinical features
• Obstructive jaundice features
• Biliary rickets.
• Clubbing and skin xanthomas(raised serum
cholesterol).
Treatment
• Surgery
-A direct Roux-en-Y hepaticojejunostomy(type1).
- Kasai procedure( type 2 and 3).
• Liver transplantation(liver failure or unsuccessful
of kasai procedure) .
Caroli’s disease
• Multiple irregular saccular dilatations of the
intrahepatic ducts, separated by segments of
normal or stenotic ducts, with a normal
extrahepatic biliary system.
• The majority of patients present before the age of
30.
• Sex distribution is equal.
• The biliary dilatation is associated with congenital
hepatic fibrosis.
• Hepatic resection is indicated in limited disease.
• liver transplantation for diffuse disease and
concomitant hepatic fibrosis.
• long-term surveillance is required.
Choledochal cyst
• Choledochal cysts are congenital dilations of the
intra and/or extrahepatic biliary system.
• Classification of cystic disease of the biliary tract
- Type I:Diffuse cystic.
- Type II: Diverticulum of common bile duct.
- Type III Diverticulum within pancreas.
- Type IV: extension into the liver.
• Type V: cystic dilatation only of the
intrahepatic ducts(caroli disease).
• Type I cysts are the most common and account for
approximately 75% of patients.
• jaundice, fever, abdominal pain and a right upper
quadrant mass on examination.
• U/S will confirm the presence of cyst.
• (MRI/MRCP) will reveal the anatomy, in particular
the relationship between the lower end of the bile
duct and the pancreatic duct.
• CT is also useful for delineating the extent of the
intra- or extrahepatic dilatation.
• Radical excision of the cyst is the treatment of
choice, with reconstruction of the biliary tract using
a Roux-en-Y loop of jejunum.
• Complete resection of the cyst is important
because of the association with the development of
cholangiocarcinoma.
• Resection and roux-en-Y reconstruction are also
associated with a reduced incidence of stricture
formation and recurrent cholangitis.
Special Investigation of
the biliary Tract
Ultrasound
• Non-invasive
• painless
• Easily performed
• First choice for biliary tract disease
• Bile duct stones
• Stones in gallbladder
- High echo which cast an acoustic shadow
and which move with changes in posture
• Jaundice differential diagnosis:
-Dilatation of the ducts
-CBD: diameter > 1.0cm
• Other disease: Cholecytitis, tumor ect.
• Computed tomography(CT)
• Endoscopic retrograde cholangio-
pancreatography(ERCP)
-Outline the biliary tree and pancreatic duct
-Inspect the ampulla of Vater
-Exam of the fluid of duodenum ,bile, pancreatic
fluid.
• Magnetic resonance cholangio-pancreatography
(MRCP)
Percutaneous transhepatic cholangiography
(PTC)
• T-tube Cholangiography during &
postoperation
• Choledochoscopy
– Operation
– Post operation
• Thank you.
You might also like
- Nightmaretaker GuideDocument12 pagesNightmaretaker Guidejese 08100% (3)
- Ford Transit 2006.5 04.2006 Workshop Manual ( (04.2006-) )Document834 pagesFord Transit 2006.5 04.2006 Workshop Manual ( (04.2006-) )slawek100% (2)
- Biliary Tract Disease - Emmet AndrewsDocument52 pagesBiliary Tract Disease - Emmet AndrewsBoneyJalgarNo ratings yet
- Powerpoint: Liver Surgical DiseasesDocument95 pagesPowerpoint: Liver Surgical Diseasesj.doe.hex_8792% (12)
- Fast Facts for Patients and Supporters: Cholangiocarcinoma: A cancer of the bile duct and liver Information + Taking Control = Best OutcomeFrom EverandFast Facts for Patients and Supporters: Cholangiocarcinoma: A cancer of the bile duct and liver Information + Taking Control = Best OutcomeNo ratings yet
- RulebookDocument296 pagesRulebookRogerio Lucena100% (2)
- 3.7 Types of Protein Exam QuestionDocument3 pages3.7 Types of Protein Exam QuestionjnfjngsdjNo ratings yet
- Biliary Surgery: Presenter: DR Muhuga JR Facilitator: DR MwashambwaDocument54 pagesBiliary Surgery: Presenter: DR Muhuga JR Facilitator: DR MwashambwaSamar AhmadNo ratings yet
- Surgical Anatomy of Extrahepatic Biliary ApparatusDocument33 pagesSurgical Anatomy of Extrahepatic Biliary ApparatussyedaNo ratings yet
- CholilithiasisDocument94 pagesCholilithiasisdr.hendraNo ratings yet
- Surgical JaundiceDocument35 pagesSurgical JaundiceIbsa ShumaNo ratings yet
- 1 Gallbladder Disease 2Document68 pages1 Gallbladder Disease 2salsabeelNo ratings yet
- Benign Hepatobiliary DisordersDocument29 pagesBenign Hepatobiliary DisordershafizahhoshniNo ratings yet
- SURG - Hepatobiliary, Pancreas, SpleenDocument230 pagesSURG - Hepatobiliary, Pancreas, SpleenJoan Timbol100% (1)
- Surgery of The Biliary System KFS 2022Document100 pagesSurgery of The Biliary System KFS 2022ahmedelkaranshawy123456789No ratings yet
- Obstructive JaundiceDocument34 pagesObstructive Jaundicemogesie1995No ratings yet
- The Gallbladder Diseases Bile Duct StoneDocument69 pagesThe Gallbladder Diseases Bile Duct Stoneحميد حيدرNo ratings yet
- (S-W5-Sun-Gen.S) (By Dr. Emad) Gall Bladder 1Document28 pages(S-W5-Sun-Gen.S) (By Dr. Emad) Gall Bladder 1Haider Nadhem AL-rubaiNo ratings yet
- Gall Bladder Stones: Surgical Treatment.: JournalDocument24 pagesGall Bladder Stones: Surgical Treatment.: JournalFika ResitaNo ratings yet
- Radiology of Hepatobiliary System Pancreas and Spleen: Nugzar LipartelianiDocument136 pagesRadiology of Hepatobiliary System Pancreas and Spleen: Nugzar LipartelianiShubham TanwarNo ratings yet
- Screenshot 2023-11-26 at 5.15.31 PMDocument39 pagesScreenshot 2023-11-26 at 5.15.31 PMgauravsingh708284No ratings yet
- 4.gall StoneDocument35 pages4.gall Stonejitendra magarNo ratings yet
- C 10 + 11 Gallbladder and Biliary TractDocument99 pagesC 10 + 11 Gallbladder and Biliary TractAdinaNo ratings yet
- Biliary SystemDocument83 pagesBiliary SystemeviltohuntNo ratings yet
- Cholesistitis (DR - Prema Hapsari, SPPD)Document28 pagesCholesistitis (DR - Prema Hapsari, SPPD)Niniek Iin F100% (1)
- 42 EsophagusDocument49 pages42 EsophagusShiva BhandariNo ratings yet
- Biliary Tract DiseaseDocument52 pagesBiliary Tract DiseaseAna Cotoman100% (1)
- CT Abdomen - Hosiana O W - 42180258Document18 pagesCT Abdomen - Hosiana O W - 42180258HOSIANAOWNo ratings yet
- Hepato-Biliary System 26.4.2016Document59 pagesHepato-Biliary System 26.4.2016S B SayedNo ratings yet
- Cholecystitis and Biliary Colic: Learning ObjectivesDocument37 pagesCholecystitis and Biliary Colic: Learning Objectivesapi-19641337No ratings yet
- Benign Colorectal Disease: Ahmed AlzahraniDocument47 pagesBenign Colorectal Disease: Ahmed Alzahraniahmad alzahraniNo ratings yet
- Acute AbdomenDocument73 pagesAcute AbdomenWahyu DustnamNo ratings yet
- Biliary Tract DiseaseDocument40 pagesBiliary Tract DiseaseIsaac MwangiNo ratings yet
- Advocate Aurora Health Institutional Repository Advocate Aurora Health Institutional RepositoryDocument33 pagesAdvocate Aurora Health Institutional Repository Advocate Aurora Health Institutional Repositoryvhy107No ratings yet
- Diverticular Disease: Maj Mohit Goyal Maj Rahul Goel Dept of SurgeryDocument67 pagesDiverticular Disease: Maj Mohit Goyal Maj Rahul Goel Dept of Surgeryunknownsince1986No ratings yet
- Common Bile Duct Stones StrictureDocument48 pagesCommon Bile Duct Stones StrictureSyarif MalawatNo ratings yet
- The Stomach and Duodenum: Dr. Elian EliasDocument48 pagesThe Stomach and Duodenum: Dr. Elian EliasmodarNo ratings yet
- Hepatic CirrhosisDocument20 pagesHepatic CirrhosisAnifowose samsonNo ratings yet
- Billiary SurgeriesDocument37 pagesBilliary Surgeriesgeorvin marcoNo ratings yet
- Overview of Gallstone Disease and ManagementDocument33 pagesOverview of Gallstone Disease and ManagementWONG LIONG SHING KPM-GuruNo ratings yet
- Small Intestine: Earle J. Niervo Medical ClerkDocument168 pagesSmall Intestine: Earle J. Niervo Medical ClerkEarle Jimenez Niervo RNNo ratings yet
- AscitesDocument63 pagesAscitesfeeo8266No ratings yet
- The PancreasDocument37 pagesThe PancreasFaiza AshrafNo ratings yet
- WelcomeDocument60 pagesWelcomepandem soniyaNo ratings yet
- Recent Management of Calculous Biliary DiseaseDocument35 pagesRecent Management of Calculous Biliary DiseaseAbhishek SarafNo ratings yet
- Colon: Malueth AbrahamDocument39 pagesColon: Malueth AbrahamMalueth AnguiNo ratings yet
- Colilithiasis 2Document53 pagesColilithiasis 2Worku KifleNo ratings yet
- Focal Lession of LiverDocument13 pagesFocal Lession of Liverdilekamunasinghe4No ratings yet
- Goo 2021Document72 pagesGoo 2021eviltohuntNo ratings yet
- Imaging Acute Abdomen DR - Rivani Kurniawan FixDocument86 pagesImaging Acute Abdomen DR - Rivani Kurniawan FixRivani KurniawanNo ratings yet
- Obstructive JaundiceDocument33 pagesObstructive JaundiceEvediciNo ratings yet
- URORADIOLOGYDocument34 pagesURORADIOLOGYMeg AmoonNo ratings yet
- Liver BiopsyDocument4 pagesLiver BiopsyLouis Fortunato100% (1)
- GallbladderDocument44 pagesGallbladderAli SafaaNo ratings yet
- Acute Calculous CholecystitisDocument25 pagesAcute Calculous CholecystitisShankar LamichhaneNo ratings yet
- Atresia BilierDocument41 pagesAtresia Bilierrizka hastari100% (1)
- Investigation and Treatment of Surgical JaundiceDocument38 pagesInvestigation and Treatment of Surgical JaundiceUjas PatelNo ratings yet
- 1100 Ultrasound of The Acute Abdomen 15 3Document84 pages1100 Ultrasound of The Acute Abdomen 15 3gp1promo2016No ratings yet
- Biliary Atresia: Dr. Boris Crossley NainggolanDocument41 pagesBiliary Atresia: Dr. Boris Crossley Nainggolanrizka hastariNo ratings yet
- Biliary Diseases: Dr. Wu Yang Dept. of Surgery The First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou UniversityDocument75 pagesBiliary Diseases: Dr. Wu Yang Dept. of Surgery The First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou Universityapi-19916399No ratings yet
- Carcinomagallbladder PDFDocument61 pagesCarcinomagallbladder PDFZaki DhiifNo ratings yet
- Investigation and Treatment of Surgical JaundiceDocument38 pagesInvestigation and Treatment of Surgical JaundiceUjas PatelNo ratings yet
- Liver CirrhosisDocument69 pagesLiver CirrhosisAhmed Alboun75% (4)
- Management of Abdominal Vascular Injury: DR Bashir Bin Yunus General Surgry Unit Akth 3/12/18Document62 pagesManagement of Abdominal Vascular Injury: DR Bashir Bin Yunus General Surgry Unit Akth 3/12/18Fendry KolondamNo ratings yet
- RB Cagmat Review Center: Central Mindanao University, CMU, Musuan, BukidnonDocument6 pagesRB Cagmat Review Center: Central Mindanao University, CMU, Musuan, BukidnonshakiraNo ratings yet
- DME Model QuesDocument3 pagesDME Model QuesSiva RamanNo ratings yet
- FuturaPC EngDocument36 pagesFuturaPC EngRashika SharmaNo ratings yet
- TrollsZine 9Document159 pagesTrollsZine 9Vaughn Everlast100% (1)
- DR Bach Flower Remedies 03-02-2017Document70 pagesDR Bach Flower Remedies 03-02-2017sadam ameerjohnNo ratings yet
- Observation Report: Analytical ChemistryDocument8 pagesObservation Report: Analytical ChemistryLindsay BulgerNo ratings yet
- GeneralMathematics11 q1 Mod5b LogarithmicfunctionDocument28 pagesGeneralMathematics11 q1 Mod5b LogarithmicfunctionBrendan Millard Cruda100% (1)
- HPhys Unit 02 BFPM Packet 2013Document16 pagesHPhys Unit 02 BFPM Packet 2013Kelly O'Shea100% (3)
- Control Valve CV - What It Means and How To Calculate It - Visaya PDFDocument8 pagesControl Valve CV - What It Means and How To Calculate It - Visaya PDFmurugan1984No ratings yet
- PQRST 08 Puzzle Competition Equate: PUZZLE 01 (10 Points Penalty For A Wrong Answer) 30 PointsDocument5 pagesPQRST 08 Puzzle Competition Equate: PUZZLE 01 (10 Points Penalty For A Wrong Answer) 30 PointsCernică AlexandruNo ratings yet
- Planetary UrbanisationDocument5 pagesPlanetary UrbanisationFaris DzulfikarNo ratings yet
- Appendix 19 U472 Community Facilitator Kolb Questionnaire FinalDocument8 pagesAppendix 19 U472 Community Facilitator Kolb Questionnaire FinalCarmen IoanaNo ratings yet
- Studio 8Document3 pagesStudio 8api-609099270No ratings yet
- Summer Training Report On: "Consumer Perception Towards Online Shopping"Document83 pagesSummer Training Report On: "Consumer Perception Towards Online Shopping"Swati TanwarNo ratings yet
- Gv300 ManualDocument22 pagesGv300 ManualCarmelo HoyosNo ratings yet
- Blockchain Merkle TreeDocument4 pagesBlockchain Merkle TreeResearch ParkNo ratings yet
- Volume III For Road Bridge Works PDFDocument355 pagesVolume III For Road Bridge Works PDFsanatan halder100% (1)
- Use of Computers For Environmental Epgineering Related To BuildingsDocument840 pagesUse of Computers For Environmental Epgineering Related To BuildingsJuan Jerez100% (1)
- Muet 1Document15 pagesMuet 1Sity Noor QiyahNo ratings yet
- Helicopter Chapter5Document34 pagesHelicopter Chapter5juanNo ratings yet
- 5 - Introduction To Psychology by James W. Kalat 5Document1 page5 - Introduction To Psychology by James W. Kalat 5Chester ChesterNo ratings yet
- HVAC Designing Drafting Estimation & InstallationDocument3 pagesHVAC Designing Drafting Estimation & Installationnoha azamali50% (2)
- VIBu Introduction Bio Counter 06 - 2012Document11 pagesVIBu Introduction Bio Counter 06 - 2012Asuka Q. QinNo ratings yet
- Make It Work Conventional Fire Alarms MobileDocument17 pagesMake It Work Conventional Fire Alarms MobileButt ManNo ratings yet
- Digital VocabDocument2 pagesDigital Vocabdesikudi9000No ratings yet
- Ground Floor Plan: Nitin SidhpuraDocument14 pagesGround Floor Plan: Nitin SidhpuraRam PatelNo ratings yet