Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Cell Types, Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic
Cell Types, Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic
Uploaded by
Jefrey Paglinawan0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
33 views33 pagesCells are the basic unit of life and come in two main types: prokaryotic and eukaryotic. Prokaryotic cells lack a nucleus and other organelles, while eukaryotic cells have a nucleus that contains their DNA as well as other organelles. Organisms made of one cell are unicellular, like bacteria, while multicellular organisms like humans contain trillions of cells performing different functions. Prokaryotes were the first life on Earth and are single-celled, while eukaryotes later evolved and can be single or multicellular.
Original Description:
Original Title
cell types, prokaryotic and eukaryotic
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCells are the basic unit of life and come in two main types: prokaryotic and eukaryotic. Prokaryotic cells lack a nucleus and other organelles, while eukaryotic cells have a nucleus that contains their DNA as well as other organelles. Organisms made of one cell are unicellular, like bacteria, while multicellular organisms like humans contain trillions of cells performing different functions. Prokaryotes were the first life on Earth and are single-celled, while eukaryotes later evolved and can be single or multicellular.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
33 views33 pagesCell Types, Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic
Cell Types, Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic
Uploaded by
Jefrey PaglinawanCells are the basic unit of life and come in two main types: prokaryotic and eukaryotic. Prokaryotic cells lack a nucleus and other organelles, while eukaryotic cells have a nucleus that contains their DNA as well as other organelles. Organisms made of one cell are unicellular, like bacteria, while multicellular organisms like humans contain trillions of cells performing different functions. Prokaryotes were the first life on Earth and are single-celled, while eukaryotes later evolved and can be single or multicellular.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 33
Cells are the basic unit
of life, the same way
that atoms are the basic
units of matter. All
living organisms are
made up of one or more
cells.
Organisms made up
of just one cell are
unicellular –
bacteria are
unicellular.
Organisms
made up of
many cells are
multicellular.
You yourself have
more than 10 trillion
cells in your body and
the diversity of things
they do is amazing.
Right now, muscle cells are
moving your eyeballs as you
follow the text on this slide,
sensory cells in your eyes are
taking the shapes of the
letters, cells in your ears are
absorbing nearby sounds.
Some extremely
impressive cells – the
neurons in your brain –
are producing your
thoughts about how
amazing cells are.
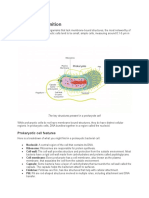
There are two types
of cells found in
different living
organisms today.
They are distinguished
primarily by the
presence or absence of
a nucleus, a distinct
structure within the cell
that contains the cell’s
DNA.
Prokaryotic cells do
not have a nucleus
(pro means “before”
and karyote refers to
“nut” or “nucleus”)
Eukaryotic cells
(“true nucleus”) have
a nucleus as well as
other structures not
present in prokaryotic
cells.
Organisms with
prokaryotic cells are
called prokaryotes, and
organisms with
eukaryotic cells are
called eukaryotes.
Prokaryotes have existed
on Earth far longer than
eukaryotes. Prokaryotes
first evolved 3.5 billion to
4 billion years ago, when
the first eukaryotes
appeared.
Prokaryotes are single
celled organisms and very
small, ranging from 0.1 to
10 micrometers in
diameter. Their structure
is simpler than that of
eukaryotes.
The DNA of
prokaryotes is found
in a single circular
structure and is not
contained within the
nucleus.
Most prokaryotes
have an outer cell
wall that helps
protect the cell.
Bacteria
Eukaryotes can be
single celled, like
prokaryotes, or they
can be composed of
many cells.
The fungus known as
baker’s yeast,
commonly used in
baking and brewing, is
a single celled
eukaryote.
Humans are
multicellular
eukaryotes. Eukaryotes
include all animals,
plants, fungi and
protists.
Eukaryotic cells have
their DNA inside a
distinct nucleus, a
feature that
distinguishes them
from prokaryotes.
In addition, the DNA
of eukaryotic cells is
found in linear, rather
than circular,
chromosomes.
Eukaryotic cells also
have numerous
organelles, structures
that perform specific
functions for the cell.
Finally eukaryotic cells are
larger than prokaryotic cells –
whereas prokaryotic cells
measures 0.1 to 10
micrometers, eukaryotic cells
usually measure 10 to 100
micrometers.
You might also like
- DTDC ReportDocument30 pagesDTDC ReportSujit_tdNo ratings yet
- Ar SKK Migas 2019 EnglishDocument194 pagesAr SKK Migas 2019 EnglishthuanNo ratings yet
- Mumbai CxoDocument9 pagesMumbai CxopoonamNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotic & Eukaryotic CellsDocument20 pagesProkaryotic & Eukaryotic CellsZay SalazarNo ratings yet
- Eukaryotic Cell Structure and FunctionDocument1 pageEukaryotic Cell Structure and FunctionJu LanNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Prokaryotes and EukaryotesDocument2 pagesIntroduction To Prokaryotes and EukaryotesRahul PalsNo ratings yet
- Prokaryote Vs EukaryoteDocument19 pagesProkaryote Vs Eukaryoteapi-296074239No ratings yet
- Prokaryote Vs EukaryoteDocument19 pagesProkaryote Vs Eukaryoteapi-302494239No ratings yet
- Unit 4 CELL BIO - 2014 FinalDocument17 pagesUnit 4 CELL BIO - 2014 FinalTizita EmanaNo ratings yet
- Lecturer 3Document22 pagesLecturer 3Rao ChandNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells: Endoplasmic ReticulumDocument10 pagesProkaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells: Endoplasmic ReticulumChristopher PhilipNo ratings yet
- Interactive Textbook1 1Document9 pagesInteractive Textbook1 1api-240094705No ratings yet
- Cell - The Building Blocks of LifeDocument4 pagesCell - The Building Blocks of LifeUzair SoomroNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes. Two Types of Cells Are Recognized in Living Things: Prokaryotes andDocument2 pagesProkaryotes and Eukaryotes. Two Types of Cells Are Recognized in Living Things: Prokaryotes andprachi guptaNo ratings yet
- Cells AssignmentDocument18 pagesCells AssignmentMuqadasNo ratings yet
- Biology: Classification of CellsDocument28 pagesBiology: Classification of CellskerbieNo ratings yet
- Prokaryote Vs Eukaryote WorksheeetDocument3 pagesProkaryote Vs Eukaryote Worksheeetsomeone swagNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 The Cell: Prepared By: Asley Raven MacatiagDocument29 pagesLesson 2 The Cell: Prepared By: Asley Raven MacatiagescribdeeNo ratings yet
- Levels of OrganizationDocument4 pagesLevels of OrganizationSwayangdipta TalapatraNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotic Eukaryotic CellsDocument11 pagesProkaryotic Eukaryotic CellsKriezhel Kim TadleNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 CELL BIO - 2023 - 230215 - 182618Document15 pagesUnit 4 CELL BIO - 2023 - 230215 - 182618SB silentNo ratings yet
- Endosymbiotic Theory - Ask A BiologistDocument3 pagesEndosymbiotic Theory - Ask A BiologistMnNo ratings yet
- Two Types of Cells:: Prokaryote Cells and Eukaryote CellsDocument18 pagesTwo Types of Cells:: Prokaryote Cells and Eukaryote CellsShahrat Farsim ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- Parts of The CellDocument5 pagesParts of The CellJane TolentinoNo ratings yet
- Karen Nares Essay About The Differences and Similarities of Animal and Plant CellsDocument1 pageKaren Nares Essay About The Differences and Similarities of Animal and Plant CellsKaren NaresNo ratings yet
- The Cell/ All About CellsDocument35 pagesThe Cell/ All About CellsJandrew Gomez DimapasocNo ratings yet
- Prokaryote Vs EukaryoteDocument18 pagesProkaryote Vs Eukaryotecj bariasNo ratings yet
- Prokaryote Vs EukaryoteDocument19 pagesProkaryote Vs EukaryotehamnaNo ratings yet
- Cell Biology:: Mycoplasmas Are The Smallest Known Bacteria. They Are Cell Wall DeficientDocument8 pagesCell Biology:: Mycoplasmas Are The Smallest Known Bacteria. They Are Cell Wall DeficientMark Dave Benito TolentinoNo ratings yet
- Cells Structure and Function Part One PowerpointDocument21 pagesCells Structure and Function Part One Powerpointnancie8No ratings yet
- Prokaryoticandeukaryotic Cells Close ReadingDocument4 pagesProkaryoticandeukaryotic Cells Close Readingapi-165869000No ratings yet
- Cellular: Cellular Component Refers To The Unique, Highly Organized Substances of WhichDocument1 pageCellular: Cellular Component Refers To The Unique, Highly Organized Substances of WhichksrbalachandranNo ratings yet
- ملزمة بايولوجي محاضرة 1Document16 pagesملزمة بايولوجي محاضرة 1The ConsigliereNo ratings yet
- Lecturer 1 Cells StructureDocument24 pagesLecturer 1 Cells StructureShivangi VermaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1-Introduction To The CellDocument18 pagesLecture 1-Introduction To The CellThuto SmithNo ratings yet
- Eukaryots and ProkaryotsDocument8 pagesEukaryots and ProkaryotsNida AhmadNo ratings yet
- Cell Presentation NXPowerLiteDocument13 pagesCell Presentation NXPowerLiteLavinia DonaldNo ratings yet
- Prokar and Eukar - 11104Document17 pagesProkar and Eukar - 11104Jerra MaeNo ratings yet
- How MuchDocument16 pagesHow MuchSathyabala BalamuruganNo ratings yet
- Biology Bacterium Yeast: Cell, inDocument11 pagesBiology Bacterium Yeast: Cell, inAlelli Bianca Daniel AlipioNo ratings yet
- MelaiDocument2 pagesMelaiDonna Patria Fe GumabonNo ratings yet
- EED 5 Unit 3Document23 pagesEED 5 Unit 3Lara Mariz FragataNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotes Vs EukaryotesDocument17 pagesProkaryotes Vs EukaryotesJermaine Barnett-WeeksNo ratings yet
- BIOLOGYDocument103 pagesBIOLOGYKamesh RamamoorthyNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotic Cells and Eukaryotic Cells: There Are Two Types of CellsDocument15 pagesProkaryotic Cells and Eukaryotic Cells: There Are Two Types of CellsgAARaNo ratings yet
- Cell TheoryDocument5 pagesCell TheoryAdit KumarNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2.3 General BiologyDocument15 pagesLesson 2.3 General BiologyMeiko DesantoresNo ratings yet
- Gen Bio w1 SummaryDocument5 pagesGen Bio w1 Summaryyxcz.rzNo ratings yet
- Prokaryote Definition: Prokaryotic Cell FeaturesDocument5 pagesProkaryote Definition: Prokaryotic Cell FeaturesAli ShanNo ratings yet
- The Cell and Division Biology for Kids | Children's Biology BooksFrom EverandThe Cell and Division Biology for Kids | Children's Biology BooksNo ratings yet
- The Animal Cell and Division Biology for Kids | Children's Biology BooksFrom EverandThe Animal Cell and Division Biology for Kids | Children's Biology BooksNo ratings yet
- Gen Bio ReviewerDocument19 pagesGen Bio ReviewerAliah Bianca SolisNo ratings yet
- 1-Medical Biology PDFDocument5 pages1-Medical Biology PDFAbbas TalibNo ratings yet
- CellDocument4 pagesCellKintina MorataNo ratings yet
- Building Blocks of LifeDocument5 pagesBuilding Blocks of LifeJesse James Olac PigonNo ratings yet
- The Cell TheoryDocument8 pagesThe Cell Theorymuhamadxalid961No ratings yet
- Cell - The Basic Unit of LifeDocument3 pagesCell - The Basic Unit of Lifepoonam_goyal26No ratings yet
- (07Q2W2) What Makes Us LivingDocument46 pages(07Q2W2) What Makes Us LivingAldwinC EspirituNo ratings yet
- Cell InformationDocument2 pagesCell InformationpkokateNo ratings yet
- Nitin Evolution of Cells-1Document25 pagesNitin Evolution of Cells-1Siddharth BirlaNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 8 Science Chapter 8 Cell Structure and Functions Revision NotesDocument17 pagesCBSE Class 8 Science Chapter 8 Cell Structure and Functions Revision Notesyashgodse kendriyavidyalayakoliwada.inNo ratings yet
- Asian Ideologies On The Creation of The EmpireDocument52 pagesAsian Ideologies On The Creation of The EmpireJefrey PaglinawanNo ratings yet
- Cultural Evolution in AsiaDocument30 pagesCultural Evolution in AsiaJefrey PaglinawanNo ratings yet
- Ancient Civilizations in AsiaDocument62 pagesAncient Civilizations in AsiaJefrey PaglinawanNo ratings yet
- East Asia (Confucianism, Taoism, Legalism, Shinto)Document29 pagesEast Asia (Confucianism, Taoism, Legalism, Shinto)Jefrey PaglinawanNo ratings yet
- Second Periodical Test in Math 9Document3 pagesSecond Periodical Test in Math 9Jefrey PaglinawanNo ratings yet
- Magnitude and IntensityDocument45 pagesMagnitude and IntensityJefrey PaglinawanNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Hospitality Fifth Edition John R. Walker: Chapter 3: The Hotel BusinessDocument24 pagesIntroduction To Hospitality Fifth Edition John R. Walker: Chapter 3: The Hotel BusinessScotch PelosoNo ratings yet
- E-Vehicle Article FinalDocument22 pagesE-Vehicle Article Finalvishnu varthanNo ratings yet
- City Motion To Dissmiss Anjanette Young LawsuitDocument39 pagesCity Motion To Dissmiss Anjanette Young LawsuitJohn DodgeNo ratings yet
- A Histeria - Teoria e Clínica PsicanalíticaDocument653 pagesA Histeria - Teoria e Clínica PsicanalíticaDaniel BraunaNo ratings yet
- Lesson Exemplar School Grade Level Teacher Learning Area Practical Research 2 Teaching Date Quarter Teaching Time No. of DaysDocument9 pagesLesson Exemplar School Grade Level Teacher Learning Area Practical Research 2 Teaching Date Quarter Teaching Time No. of DaysJovie Bitas DaeloNo ratings yet
- Duane Shinn Piano Course CatalogDocument13 pagesDuane Shinn Piano Course Catalog4scribble0375% (4)
- DaburDocument20 pagesDaburMANDHAPALLY MANISHANo ratings yet
- Aztec MagicDocument2 pagesAztec MagicBob MarinoNo ratings yet
- 25 Nonfiction Passages With Vocab Build'g CrosswordsDocument65 pages25 Nonfiction Passages With Vocab Build'g Crosswordsvsroilgas78% (9)
- Research in Organizational Behavior: Sabine SonnentagDocument17 pagesResearch in Organizational Behavior: Sabine SonnentagBobby DNo ratings yet
- NBTS PlannerDocument1 pageNBTS Planneradriyanmohammed786No ratings yet
- Anatomia de Un Plan de Negocio - Linda Pinson PDFDocument282 pagesAnatomia de Un Plan de Negocio - Linda Pinson PDFCarolina RuizNo ratings yet
- Messianic Theology and Christian Faith - G. A. RigganDocument206 pagesMessianic Theology and Christian Faith - G. A. RigganLucianaNo ratings yet
- Effect of IBA and NAA With or Without GA Treatment On Rooting Attributes of Hard Wood Stem Cuttings of Pomegranate (Punica Granatum L.)Document5 pagesEffect of IBA and NAA With or Without GA Treatment On Rooting Attributes of Hard Wood Stem Cuttings of Pomegranate (Punica Granatum L.)warlord_ckNo ratings yet
- Below Mentioned Is The List of Mumbai Management CollegesDocument3 pagesBelow Mentioned Is The List of Mumbai Management CollegesManish SainiNo ratings yet
- The Role of Majority and Minority Language Input in The Early Development of A Bilingual VocabularyDocument15 pagesThe Role of Majority and Minority Language Input in The Early Development of A Bilingual VocabularyPoly45No ratings yet
- Ileus ObstructionDocument22 pagesIleus ObstructionfitrahNo ratings yet
- E FilingDocument259 pagesE FilingtestingNo ratings yet
- Edmentum TrainingDocument20 pagesEdmentum Trainingapi-557217750No ratings yet
- Fashion Construction SyllabusDocument7 pagesFashion Construction Syllabusapi-293881613No ratings yet
- Green Banking - Green Financial Products With Special Emphasis On Retail Banking ProductsDocument8 pagesGreen Banking - Green Financial Products With Special Emphasis On Retail Banking ProductsMudrikaNo ratings yet
- Arts 8Document34 pagesArts 8Joanna joannaNo ratings yet
- Glutamine USPDocument3 pagesGlutamine USPJai MurugeshNo ratings yet
- SSB Tanitim CatalogDocument201 pagesSSB Tanitim CatalogAmir Cahyadi100% (1)
- Cambridge Ordinary LevelDocument20 pagesCambridge Ordinary Levelrania moomalNo ratings yet
- 1359 - 1368. TingkahanDocument5 pages1359 - 1368. TingkahanRizal Daujr Tingkahan IIINo ratings yet
- Essentials of Comparative Politics 4th Edition Oneil Test BankDocument8 pagesEssentials of Comparative Politics 4th Edition Oneil Test Bankrobertjarvismdqarpsxdjnc100% (16)