Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Food Safety New
Food Safety New
Uploaded by
Norazura Mikey100%(1)100% found this document useful (1 vote)
86 views19 pages Wrong. Live animals should not be allowed in food preparation or service areas, with the exception of service animals, to prevent potential contamination of food.
Original Description:
Original Title
food safety new (1)
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Document Wrong. Live animals should not be allowed in food preparation or service areas, with the exception of service animals, to prevent potential contamination of food.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
100%(1)100% found this document useful (1 vote)
86 views19 pagesFood Safety New
Food Safety New
Uploaded by
Norazura Mikey Wrong. Live animals should not be allowed in food preparation or service areas, with the exception of service animals, to prevent potential contamination of food.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 19
FOOD HISTORY
Our existence has been Hunting and fishing to They moving from one
dependant on food gather food place to another
Human learn how to
cultivate crops and Nowdays , individuals
domesticate animal and families be able to Modern food system
and they started to make their own food
form small village
Malaysia’s Food Safety System
“The Malaysia food safety system is
characterized by its complexity and
diversity; with different authority
entrusted with the task of
ensuring food safety at
different stages
of the food chain”
FOOD SAFETY & QUALITY CONTROL
To Protect The Public Against Food
Related Hazards & Fraud As Well As
To Motivate And Promote The
Preparation, Handling, Distribution,
Sale And Consumption Of Safe And
Quality Food
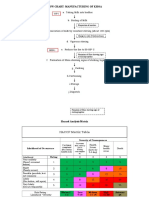
Hazard Analysis Critical Control Point
Food Safety Management System
It Identifies, Evaluate and Controls Hazards which
are Significant for Food Safe
DEFINITION
• HACCP is a systematic approach to
identify, evaluate and control food safety
hazards that are caused by biological,
chemical or physical agents.
• These agents can cause illness if not
controlled.
WHO RESPONBILITY
• All food handlers - proper implementation of food
safety standards
• Only archived by proper training and contant
demotration
• Commitment to food safety standards are required
OBJECTIVE
• To ensure that the food served to the guest is safe for human
consumption.
• Awareness to food handling techniques.
• Understanding the faults and taking corrective action.
• Better knowledge to food handlers for longer shelf life of
cooked and raw food.
• This methods also has other benefits of maintaining food
quality and managing food cost
The Beginning of HACCP
• A forerunner of HACCP was developed
during World War II
• Jointly developed by the Pilsbury Company,
and NASA to prevents astronauts from
getting food poisoning
• Their goal was produce 100% safe food
HAZARDS
• A biological, chemical or physical agent that is reasonably
likely to cause illness or injury in the absence of its control .
Example :
• Biological Hazards - Microorganisms & Parasitic worms
• Chemical Hazards – Harvesting, storage, preparation &
service
• Physical Hazards - Accidental conramination & poor food
handling pratices
FOOD HANDLERS
• Training of food handlers:
•To increase the awareness of food handlers on
food hygiene and sanitation in a more
structured and systematic manner, through
Accreditation Food Handlers Training
Institutions – 1996
• Training of Trainer’s - 1998
FOOD HYGIENE
• The conditions and measures necessary to
ensure the safety of food from production to
compumtion
• Because the less food hygiene the food will
be get a diseases
• Its because the consumer will get the
diseases and maybe will dead
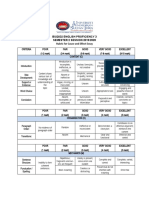
7 Steps To Wash Hands
Step 2 - Rub your
palms together.
Activity
Food Handler -- Right or
Wrong?
Food Handler -- Right or Wrong?
Food Handler -- Right or Wrong?
ANIMALS
Live animals cannot be on the premises except for:
*Edible/decorative fish in an aquarium
*Shellfish or crustacea on ice under refrigeration or in display tanks
*Patrol dogs or sentry dogs
*Service animals
*Live fish bait
You might also like
- RSPH Level 4 Award in Haccp Management For Food ManufacturingDocument19 pagesRSPH Level 4 Award in Haccp Management For Food ManufacturingHema HemaNo ratings yet
- ASSESSMENT 1 - Assignment - Case StudiesDocument7 pagesASSESSMENT 1 - Assignment - Case StudiesSameera100% (1)
- Fact Sheet - Food Poisoning - and - Food Poisoning BacteriaDocument2 pagesFact Sheet - Food Poisoning - and - Food Poisoning BacteriaAidil FitrianshahNo ratings yet
- Hazard Analysis Worksheet For Glass ContainersDocument6 pagesHazard Analysis Worksheet For Glass ContainersAdare Oluwafemi Thomas100% (1)
- Bedb Sme Guide Book (2012)Document58 pagesBedb Sme Guide Book (2012)Mohd Fadhilullah100% (1)
- Food Safety Sanitation and Personal Hygiene 1481758586Document75 pagesFood Safety Sanitation and Personal Hygiene 1481758586Mutiara SyafitriNo ratings yet
- Risk Management For CQEDocument25 pagesRisk Management For CQEAhmed M. HashimNo ratings yet
- Report VitagenDocument4 pagesReport Vitagencikgunita90No ratings yet
- Module 1 Trainer Manual PDFDocument26 pagesModule 1 Trainer Manual PDFSanath KamilaNo ratings yet
- Food Processing1Document19 pagesFood Processing1daabgchiNo ratings yet
- Bacterial Food IntoxicationDocument46 pagesBacterial Food IntoxicationAnonymous hTivgzixVNNo ratings yet
- A Guide To Food Hygiene Quiz Sheet 1Document1 pageA Guide To Food Hygiene Quiz Sheet 1José Figueiredo100% (1)
- Institutional Food ManagementDocument10 pagesInstitutional Food ManagementSurya NivruthaNo ratings yet
- Food Safety Q1Document4 pagesFood Safety Q1derossi95No ratings yet
- Lecture 1. Sources of Microorganisms in FoodDocument23 pagesLecture 1. Sources of Microorganisms in FoodAnégria GahimbareNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 HaccpDocument41 pagesChapter 4 HaccpSPMUSER9ANo ratings yet
- Lecture 1. Introduction To Fish Processing Plant Management PDFDocument35 pagesLecture 1. Introduction To Fish Processing Plant Management PDFLarraine Chaste Ponteres100% (1)
- Cas & Mas: Controlled Atmospheric Storage & Modified Atmospheric StorageDocument40 pagesCas & Mas: Controlled Atmospheric Storage & Modified Atmospheric StorageAbdul Wahid PNo ratings yet
- Chapter Four Food HygieneDocument23 pagesChapter Four Food HygieneHSC UNITEDNo ratings yet
- Food Safety Exam 4Document7 pagesFood Safety Exam 4Kari Kristine Hoskins Barrera100% (1)
- Introduction To Food QualityDocument40 pagesIntroduction To Food QualityAmor S. LazaroNo ratings yet
- Fruits, Vegetables and Agro-Processing IndustriesDocument15 pagesFruits, Vegetables and Agro-Processing IndustriesSALONI GOYALNo ratings yet
- 5 Pre Slaughter HandlingDocument35 pages5 Pre Slaughter HandlingZayyan Muafi100% (1)
- UntitledDocument6 pagesUntitledpokhralikanchha100% (1)
- Food Hygiene SanitationDocument2 pagesFood Hygiene Sanitationdrugdrug100% (1)
- Overview of Food Quality by M.SivarajanDocument27 pagesOverview of Food Quality by M.SivarajanervaishaliNo ratings yet
- Food Science and Technology Project Topics For StudentsDocument3 pagesFood Science and Technology Project Topics For Studentsandychukse100% (3)
- Food Processing Risk Assessment QuestionniareDocument2 pagesFood Processing Risk Assessment QuestionniarePaul Tese Ahire100% (2)
- Training Manual For Meat HandlersDocument56 pagesTraining Manual For Meat HandlersSoiab KhanNo ratings yet
- Postharvest Technology 1 1Document56 pagesPostharvest Technology 1 1Jr AquinoNo ratings yet
- FFA Meat QuizDocument11 pagesFFA Meat QuizInspire RajNo ratings yet
- Factors Causing Food SpoilageDocument6 pagesFactors Causing Food SpoilageAMIN BUHARI ABDUL KHADER100% (1)
- Milk ManualsDocument18 pagesMilk ManualsLAKSHYA VERMA0% (1)
- Food Safety Exam 5Document5 pagesFood Safety Exam 5Kari Kristine Hoskins BarreraNo ratings yet
- Assessment of Nutritional SituationDocument24 pagesAssessment of Nutritional SituationMawasumi Ayu Andini0% (1)
- HACCP in DairyDocument5 pagesHACCP in DairyPrashant TripathiNo ratings yet
- Food Safety in Bangladesh PDFDocument8 pagesFood Safety in Bangladesh PDFSaleh AhmedNo ratings yet
- Dietary Assessment Food RecordDocument9 pagesDietary Assessment Food RecordErfiFauziyaNo ratings yet
- Schedule-4 Part 2 & Part 5 MCQ Questions (English)Document7 pagesSchedule-4 Part 2 & Part 5 MCQ Questions (English)safefoodz.internNo ratings yet
- Shas Finals 2015Document7 pagesShas Finals 2015Gene Roy P. Hernandez100% (2)
- SyllabusDocument2 pagesSyllabus'Bernan Esguerra Bumatay100% (2)
- OSSC Food Safety Act and RulesDocument9 pagesOSSC Food Safety Act and RulesPadmanav SahooNo ratings yet
- Essential Requirements For Street-Vended Foods On SchoolsDocument20 pagesEssential Requirements For Street-Vended Foods On SchoolsJulieSanchezErsandoNo ratings yet
- FDADocument46 pagesFDAratridyahpNo ratings yet
- Food Laws and RegulationsDocument19 pagesFood Laws and RegulationsBhupendra ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Food Safety Management and GMP - DownloadDocument23 pagesIntroduction To Food Safety Management and GMP - DownloadShivakumara Arehalli100% (1)
- A5 Food Safety Booklets Food Safety Youre Part of It 12ppDocument12 pagesA5 Food Safety Booklets Food Safety Youre Part of It 12ppgiannis2No ratings yet
- Retort TechnologyDocument9 pagesRetort Technologysathwik sirigineediNo ratings yet
- Safe Food Handling QUIZ FINALDocument4 pagesSafe Food Handling QUIZ FINALmtlpcguys100% (1)
- WWW Dayjob Com Content Food Hygiene Quiz 829 HTMDocument12 pagesWWW Dayjob Com Content Food Hygiene Quiz 829 HTMJulay Cassandra DaioNo ratings yet
- CH # 10 Classification of FoodDocument3 pagesCH # 10 Classification of FoodUsman AhmadNo ratings yet
- Hygienic Milk ProductionDocument61 pagesHygienic Milk ProductionNisha Aravindan NairNo ratings yet
- Minimally Processed ProductsDocument3 pagesMinimally Processed ProductsOliver TalipNo ratings yet
- Syllabus Food - Analyst 1 PDFDocument3 pagesSyllabus Food - Analyst 1 PDFPadmanabhan DhanasekaranNo ratings yet
- Philippines Food Safety SystemDocument16 pagesPhilippines Food Safety SystemIka Putri MurwadiNo ratings yet
- Food ScienceDocument9 pagesFood ScienceTabasum BhatNo ratings yet
- Food Safety Word ScrambleDocument1 pageFood Safety Word ScrambleHomeFoodSafetyNo ratings yet
- Seven Principles of HACCPDocument3 pagesSeven Principles of HACCPEmperorr Tau MtetwaNo ratings yet
- Development of HACCP System For Assurance of Product Safety in A Gherkin Pickle IndustryDocument11 pagesDevelopment of HACCP System For Assurance of Product Safety in A Gherkin Pickle IndustryJournal of Nutritional Science and Healthy DietNo ratings yet
- Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points Lecture NotesDocument12 pagesHazard Analysis and Critical Control Points Lecture NotesDarlyn Denise PruebasNo ratings yet
- Foodtemp QuizDocument5 pagesFoodtemp QuizNorma Panares100% (1)
- Poultry Haccp PDFDocument17 pagesPoultry Haccp PDFPeter George100% (1)
- Food Selection and Preparation: A Laboratory ManualFrom EverandFood Selection and Preparation: A Laboratory ManualRating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (2)
- Food Adulteration and Its Detection: With photomicrographic plates and a bibliographical appendixFrom EverandFood Adulteration and Its Detection: With photomicrographic plates and a bibliographical appendixNo ratings yet
- Slide Pereka Sem 2,3 & 4Document29 pagesSlide Pereka Sem 2,3 & 4Norazura MikeyNo ratings yet
- List Nama Reka FesyenDocument3 pagesList Nama Reka FesyenNorazura MikeyNo ratings yet
- MyGuru AttandanceDocument1 pageMyGuru AttandanceNorazura MikeyNo ratings yet
- Scan With Mysejahtera App To Check-In: Warung Ayam Penyet Cut IntanDocument1 pageScan With Mysejahtera App To Check-In: Warung Ayam Penyet Cut IntanNorazura MikeyNo ratings yet
- K02256 - 20200626113602 - Assignment - Article Review BaratDocument2 pagesK02256 - 20200626113602 - Assignment - Article Review BaratNorazura MikeyNo ratings yet
- Biu2032 English Proficiency 3 SEMESTER 2 SESSION 2019/2020 Rubric For Cause and Effect EssayDocument3 pagesBiu2032 English Proficiency 3 SEMESTER 2 SESSION 2019/2020 Rubric For Cause and Effect EssayNorazura MikeyNo ratings yet
- Gourmet - Marketing PlanDocument39 pagesGourmet - Marketing PlanWaqas Shahzad67% (3)
- Topic 7: Preparation To Halal Foods/Products: Sharifah Anom BT OmarDocument19 pagesTopic 7: Preparation To Halal Foods/Products: Sharifah Anom BT OmarNur ShazieyahNo ratings yet
- Ovais - ResumeDocument3 pagesOvais - ResumeSyed Owais Ali NaqviNo ratings yet
- Hazard Analysis Critical Control Point (HACCP) Plan Submission Guidelines PDFDocument8 pagesHazard Analysis Critical Control Point (HACCP) Plan Submission Guidelines PDFThuyền TháiNo ratings yet
- BSCIC PresentationDocument60 pagesBSCIC PresentationVuppala SrinivasNo ratings yet
- SQE ManualDocument45 pagesSQE Manualjosecabrera25No ratings yet
- HACCP Methodology - KhoaDocument7 pagesHACCP Methodology - KhoaPawanNo ratings yet
- SFI-PUR-FO-001 Rev01 19aug2020 - Supplier Accreditation FormDocument4 pagesSFI-PUR-FO-001 Rev01 19aug2020 - Supplier Accreditation FormJona Marie FormelozaNo ratings yet
- Heat Chill IrelandDocument72 pagesHeat Chill IrelandAnggoro AntonoNo ratings yet
- Searching Keywords in IndiamartDocument11 pagesSearching Keywords in IndiamartRICL Sales ISONo ratings yet
- Food Safety System Design Using Hazard Analysis CRDocument6 pagesFood Safety System Design Using Hazard Analysis CRREMINGTON SALAYANo ratings yet
- SCM Final Assignment-2Document31 pagesSCM Final Assignment-2Sumon iqbalNo ratings yet
- The Design of Hazard Analysis Critical Control Point (HACCP) Plan For Biscuit PlantDocument7 pagesThe Design of Hazard Analysis Critical Control Point (HACCP) Plan For Biscuit Plantttk_maniNo ratings yet
- Profile Summary Core Competencies: Pravin Balasaheb ShindeDocument4 pagesProfile Summary Core Competencies: Pravin Balasaheb ShindePravin ShindeNo ratings yet
- Food Safety Management SystemsDocument87 pagesFood Safety Management SystemsAshish SahuNo ratings yet
- Job Description - Food & Safety ManagerDocument3 pagesJob Description - Food & Safety ManagerAyoubELBakiriNo ratings yet
- HaccpDocument14 pagesHaccpabdulshakoor100% (3)
- Food Service Management (FSM) CoursesDocument3 pagesFood Service Management (FSM) Coursesapi-537946671No ratings yet
- Creamery Juice HACCP Plan New - RtfwordDocument28 pagesCreamery Juice HACCP Plan New - RtfwordShenneth De CastroNo ratings yet
- Security in Logistic Systems: October 2014Document130 pagesSecurity in Logistic Systems: October 2014Tiberiu FalibogaNo ratings yet
- Haccp & Its Implementation in Food Industry: Dr. H. K. SharmaDocument58 pagesHaccp & Its Implementation in Food Industry: Dr. H. K. Sharmaankita pathaniaNo ratings yet
- Canadian Guidelines For Physical HazardsDocument4 pagesCanadian Guidelines For Physical HazardsGaganpreet KaurNo ratings yet
- Metro ProjectDocument36 pagesMetro ProjectHooriaKhanNo ratings yet
- Pre Assessment Questionnaire-FsmsDocument26 pagesPre Assessment Questionnaire-FsmsRamasubramanian SankaranarayananNo ratings yet
- FOOD PROCESS Week 6 Conduct Work in Accordance With Environmental Policies and ProceduresDocument27 pagesFOOD PROCESS Week 6 Conduct Work in Accordance With Environmental Policies and ProceduresLEO CRISOSTOMONo ratings yet