Professional Documents
Culture Documents
HRM 212B: Culinary Arts and Science: Our Lady of Fatima University
HRM 212B: Culinary Arts and Science: Our Lady of Fatima University
Uploaded by
Bharat Nailwal0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
39 views20 pagesThis document discusses the classification, composition, and preparation of fruits and vegetables. It describes how fruits and vegetables can be classified according to the plant part used, chemical composition, and nutritive value. Common examples are provided for each classification. The document also covers the composition of fruits and vegetables, which are generally low in calories, fat, and sodium but high in water, carbohydrates, vitamins, and minerals. Principles for preparing and cooking fruits and vegetables to maximize nutritional retention are outlined.
Original Description:
Original Title
Culinary_17_Fruits_and_Vegetables.pptx
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document discusses the classification, composition, and preparation of fruits and vegetables. It describes how fruits and vegetables can be classified according to the plant part used, chemical composition, and nutritive value. Common examples are provided for each classification. The document also covers the composition of fruits and vegetables, which are generally low in calories, fat, and sodium but high in water, carbohydrates, vitamins, and minerals. Principles for preparing and cooking fruits and vegetables to maximize nutritional retention are outlined.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
39 views20 pagesHRM 212B: Culinary Arts and Science: Our Lady of Fatima University
HRM 212B: Culinary Arts and Science: Our Lady of Fatima University
Uploaded by
Bharat NailwalThis document discusses the classification, composition, and preparation of fruits and vegetables. It describes how fruits and vegetables can be classified according to the plant part used, chemical composition, and nutritive value. Common examples are provided for each classification. The document also covers the composition of fruits and vegetables, which are generally low in calories, fat, and sodium but high in water, carbohydrates, vitamins, and minerals. Principles for preparing and cooking fruits and vegetables to maximize nutritional retention are outlined.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 20
OUR LADY OF FATIMA UNIVERSITY
HRM 212B:
CULINARY ARTS AND SCIENCE
Week 16 – Eggs
COLLEGE OF HOSPITALITY AND INSTITUTIONAL MANAGEMENT
OUR LADY OF FATIMA UNIVERSITY
FOOD AND CULINARY
COLLEGE OF HOSPITALITY AND INSTITUTIONAL MANAGEMENT
OUR LADY OF FATIMA UNIVERSITY
FRUITS – are the fleshy, juicy products of plants and when
ripe, they are edible without cooking. Fruits can also be
defined as a ripened ovary or ovaries of plants. They are
usually eaten at the end of the meal.
COLLEGE OF HOSPITALITY AND INSTITUTIONAL MANAGEMENT
OUR LADY OF FATIMA UNIVERSITY
VEGETABLES – these are plants or parts of plants such
as roots, tubers, bulbs, shoots, stems, leaves, fruits and
flowers that are used either raw or cooked
COLLEGE OF HOSPITALITY AND INSTITUTIONAL MANAGEMENT
OUR LADY OF FATIMA UNIVERSITY
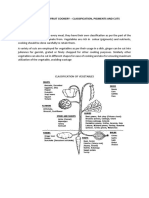
Classification of Vegetables are according to
1. Parts of plant used
2. Plant chemical composition
3. Nutritive value
COLLEGE OF HOSPITALITY AND INSTITUTIONAL MANAGEMENT
OUR LADY OF FATIMA UNIVERSITY
According to Parts of Plant Used:
1. Roots are underground parts of plant. It is high in
carbohydrates and low in water. Examples: kamote or sweet
potato, kamoteng kahoy or cassava, labanos or radish,
singkamas or yam bean, tugi or spiny yam, ubi or purple yam.
2. Tubers are short thickened, fleshy parts of an underground
stem such as potatoes and Jerusalem artichokes.
COLLEGE OF HOSPITALITY AND INSTITUTIONAL MANAGEMENT
OUR LADY OF FATIMA UNIVERSITY
3. Bulbs are underground buds that send down roots and are
made up of a very short stem covered with layers.
Examples are shallots, onions, garlic, leeks and chives.
4. Seeds are parts from which a new plant will grow.
Examples: munggo or mung beans, garabansos or chick-
peas, patani or lima beans.
5. Stem and shoots are stalks supporting leaves, flowers or
fruits. Examples are asparagus, celery.
COLLEGE OF HOSPITALITY AND INSTITUTIONAL MANAGEMENT
OUR LADY OF FATIMA UNIVERSITY
6. Leaves includes alugbati or Malabar night shade,
kangkong or swamp cabbage.
7. Fruits include ampalaya or bitter melon, upo or
bottle gourd, patola or sponge gourd, siling labuyo
or cayenne pepper, avocado, cucumber, eggplant,
okra, squash and tomato.
COLLEGE OF HOSPITALITY AND INSTITUTIONAL MANAGEMENT
OUR LADY OF FATIMA UNIVERSITY
8. Flowers include artichoke, broccoli, cauliflower
COLLEGE OF HOSPITALITY AND INSTITUTIONAL MANAGEMENT
OUR LADY OF FATIMA UNIVERSITY
Classification of Vegetables according to Chemical composition
1. Carbohydrates – such as seeds, roots, and tubers
2. Protein-rich – include seeds such as legumes and pulses
3. Fat-rich such as nuts, olives, and avocado
4. High moisture content such as mushrooms, tomatoes, celery,
cauliflower and cabbage
COLLEGE OF HOSPITALITY AND INSTITUTIONAL MANAGEMENT
OUR LADY OF FATIMA UNIVERSITY
Classification of Vegetables according to Nutritive
1. Sources of Vitamin A – green leafy vegetables and yellow fruits
2. Sources of Vitamin C – guavas, tomatoes, and other succulent
fruits
3. Sources of Vitamin B Complex – beans and leafy greens
COLLEGE OF HOSPITALITY AND INSTITUTIONAL MANAGEMENT
Broiling seems to be contacti
OUR LADY OF FATIMA UNIVERSITY
Composition of Vegetables
• Low in calories, cholesterol, sodium and fat
• Good sources of carbohydrates (especially fiber), certain
vitamins/minerals
COLLEGE OF HOSPITALITY AND INSTITUTIONAL MANAGEMENT
OUR LADY OF FATIMA UNIVERSITY
Classification of Fruits
1. Simple fruits – develop from one flower. They include:
• Drupes: fruit with seeds encased in a pit such as
apricot, cherries, peaches, and plums
• Pomes: fruits with seeds contained in a center core,
such as apples, and pears
• Citrus: oranges, grapefruits, lemons, limes and
mandarins
COLLEGE OF HOSPITALITY AND INSTITUTIONAL MANAGEMENT
OUR LADY OF FATIMA UNIVERSITY
2. Aggregate fruits – develop from several ovaries in one flower,
they include blackberries, raspberries and strawberries
3. Multiple fruits – develop from a cluster of several flowers. They
include pineapples and figs
COLLEGE OF HOSPITALITY AND INSTITUTIONAL MANAGEMENT
OUR LADY OF FATIMA UNIVERSITY
Composition of Fruits
• Low I calories, fat and protein
• High in water and carbohydrates
• Excellent sources of vitamin C, beta-carotene, iron or potassium
COLLEGE OF HOSPITALITY AND INSTITUTIONAL MANAGEMENT
Preparation of Fruits
Most fruits can be kept beyond the growing season by combining
it with sugar in the following forms of fruit spreads:
1. Preserves – made from whole fruit, halves or chunks
2. Jams – ground or mashed whole cooked fruit
3. Conserves – made from a mixture of fruits (usually including
citrus) to which nuts and raisins are added but no sugar are
added
4. Jellies – made from the juice of cooked fruit, with added sugar
and pectin
5. Marmalades – juice combined with thin slices of fruit and rind,
especially citrus fruits
6. Butters – thick and smooth made fro sieved, long-cooked fruit,
usually less sweet than jams and jellies and more perishable
than other fruit spreads
PRINCIPLES INVOLVED IN FRUITS AND VEGETABLES
COOKERY
PRINCIPLES REASON BEHIND
Fruits & veggies should be washed before To prevent vitamin loss especially water
peeling or eating soluble vitamins as well as to remove dirt
Choose veggies that are crisp and bright in Proper selection of veggies results to a
color with o sign of spoilage tasty and appetizing dishes
Always use a sharp knife in preparing fruits A dull knife causes a fruit and veggies to
& veggies become wrinkled and lose its vit. C content
Cont. Principles Involved….
PRINCIPLES REASON BEHIND
Fruits & veggies like bananas, apple, Easily discolor after peeling due to
potato, eggplant require special treatment enzymatic browning. To prevent this, soak
during the preparation in acid water, soak in water, blanch to
destroy the enzyme
Salad greens should be thoroughly washed These are eaten raw
and drained
Chill salad greens in the refrigerator first for To make them more crispy and fresh
at least 2 hrs
Cont. Principles Involved…
PRINCIPLES REASON BEHIND
It is better to break salad greens by the To lessen browning and discoloration as
hand than by knife well as the loss of vit. C
Salt and sugar should not be kept adding in It toughens and shrivels the corn kernel
cooking corn
Veggies should be cooked quickly To shorten cooking time and eaten more
with quality
You might also like
- Komatsu Hydraulic Excavator Pc210lc 11 Hydraulic Electric Circuit DiagramsDocument22 pagesKomatsu Hydraulic Excavator Pc210lc 11 Hydraulic Electric Circuit Diagramsbrianwong090198pni100% (12)
- The Ass Goblins of Auschwitz by Cameron PierceDocument104 pagesThe Ass Goblins of Auschwitz by Cameron PierceIntron Retrotransposon33% (3)
- Fruits & VegetablesDocument24 pagesFruits & VegetablesSai CampbellNo ratings yet
- Prepare Vegetable and Seafood DishesDocument120 pagesPrepare Vegetable and Seafood DishesJoeven Pantaleon67% (3)
- Snickers BrandDocument2 pagesSnickers Brandopaze45No ratings yet
- SITHKOP002 Plan and Cost Basic MenuDocument26 pagesSITHKOP002 Plan and Cost Basic Menurajgill1808100% (2)
- Candy Manufacturing Technology and Candy Manufacturing Techniques Are FascinatingDocument7 pagesCandy Manufacturing Technology and Candy Manufacturing Techniques Are FascinatingJorge Meza100% (2)
- Module 7 Prepare Vegetable DishesDocument9 pagesModule 7 Prepare Vegetable DishesGilbert LoredoNo ratings yet
- Module 9Document27 pagesModule 9Camille MalvecinoNo ratings yet
- Fruits and VegetablesDocument35 pagesFruits and VegetablesAvegael PedregosaNo ratings yet
- Tlefop Note Fruitandvegetables Group4 1Document8 pagesTlefop Note Fruitandvegetables Group4 1Tayapad, Irene C.No ratings yet
- Unit IDocument36 pagesUnit IJithin JasinNo ratings yet
- Q2 2preparing Raw Materials Sugar ConcentrationDocument18 pagesQ2 2preparing Raw Materials Sugar ConcentrationRozenn Joi TabucolNo ratings yet
- Unit 6 Vegetable and Fruit CookeryDocument8 pagesUnit 6 Vegetable and Fruit CookeryKMCTCOLLEGEOFHOTELMANAGEMENT ANDCATERINGTECHNOLOGYNo ratings yet
- VegetablesDocument21 pagesVegetablesDaisy HelenNo ratings yet
- L15 Fruits and Vegetables LectureDocument16 pagesL15 Fruits and Vegetables LecturecyanNo ratings yet
- Module 6Document124 pagesModule 6Janel Buhat GrimaldoNo ratings yet
- Reprt in TVLDocument29 pagesReprt in TVLriejinesaldivar250No ratings yet
- He ReviewerDocument14 pagesHe Reviewerxls.cineNo ratings yet
- Fruits and VegetablesDocument13 pagesFruits and VegetablesiwayanwidartaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document20 pagesChapter 5bane largoNo ratings yet
- Fruits and VegetablesDocument16 pagesFruits and Vegetablescarlo jay evardoneNo ratings yet
- 6th Unit VegetableDocument3 pages6th Unit VegetableLohitesh JenaNo ratings yet
- Culinary Part3Document37 pagesCulinary Part3Madel ErandioNo ratings yet
- Classification of Vegetables:: 1. TubersDocument4 pagesClassification of Vegetables:: 1. TubersmichelleNo ratings yet
- Preparation and Cooking of FoodsDocument41 pagesPreparation and Cooking of FoodsGladys BaliwagNo ratings yet
- Fruits (Aballe)Document19 pagesFruits (Aballe)CHRISTINE ABALLENo ratings yet
- Tle 1Document6 pagesTle 1Soleil RiegoNo ratings yet
- Advance NutritionDocument5 pagesAdvance NutritionJenna Mae AgripaNo ratings yet
- COOKERY 10 Quarter 2 LAS No. 1Document9 pagesCOOKERY 10 Quarter 2 LAS No. 1Chema PacionesNo ratings yet
- TLE Cookery 10 2nd Grading ReviewersDocument5 pagesTLE Cookery 10 2nd Grading ReviewersWilma AmliwNo ratings yet
- Tle 10 Mise en PlaceDocument38 pagesTle 10 Mise en PlaceEdmark RosalesNo ratings yet
- Fruit and Vegetable Process Tecnology Chapter 3Document89 pagesFruit and Vegetable Process Tecnology Chapter 3robel kassawNo ratings yet
- MODULE 1 CookeryDocument18 pagesMODULE 1 CookeryMaribel B GarciaNo ratings yet
- What Is A Fruit: Suggestion: Access 'Vegetables" Select 'Tomato' Click 'Go'Document5 pagesWhat Is A Fruit: Suggestion: Access 'Vegetables" Select 'Tomato' Click 'Go'Al-juffrey Luis AmilhamjaNo ratings yet
- I.s7 Fruits VegetablesDocument11 pagesI.s7 Fruits VegetablesSophia MatorreNo ratings yet
- l2 Quarter 2 Week 1 - Prepare Mise en PlaceDocument38 pagesl2 Quarter 2 Week 1 - Prepare Mise en PlaceGwyneth VicenteNo ratings yet
- Informationsheet Cookery10.ADocument5 pagesInformationsheet Cookery10.Amarilyn bristolNo ratings yet
- Informationsheet Cookery10.ADocument5 pagesInformationsheet Cookery10.Amarilyn bristolNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Prepare Vegetable Dishes Tlte10Document5 pagesLesson 1 Prepare Vegetable Dishes Tlte10Kimby VentuzoNo ratings yet
- Cookery 10 Quarter 2 m1Document37 pagesCookery 10 Quarter 2 m1Jennifer CarpioNo ratings yet
- Prepare Vegetable and Seafood DishesDocument60 pagesPrepare Vegetable and Seafood DishesAlodie Dela Raiz Asuncion89% (9)
- Fruits and VegetablesDocument65 pagesFruits and VegetablesjanlorainelumogdangNo ratings yet
- PLANT UTILITY - 20240317 - 214052 - 0000 (1) - CompressedDocument18 pagesPLANT UTILITY - 20240317 - 214052 - 0000 (1) - CompressedAyisha PSNo ratings yet
- Q2 L1 - Perform Mise'en PlaceDocument10 pagesQ2 L1 - Perform Mise'en PlacePaolo Olivas100% (1)
- 3.prepare Vegetable DishesDocument38 pages3.prepare Vegetable DishesaileenNo ratings yet
- WHLP Cookery 10 q2w1Document6 pagesWHLP Cookery 10 q2w1Sean Thomas Kurt RoblesNo ratings yet
- TLE ReviewerDocument8 pagesTLE ReviewerAndrea JimenezNo ratings yet
- Fruits Group 3Document12 pagesFruits Group 3Jean EquizNo ratings yet
- Volume FiveDocument241 pagesVolume Fiveshbhgy9dm7No ratings yet
- 10 Cookery ReviewerDocument18 pages10 Cookery Reviewerferlynmae.bautista528No ratings yet
- Republic of The Philippines Iloilo Science and Technology UniversityDocument6 pagesRepublic of The Philippines Iloilo Science and Technology UniversityKate Ashley MuedaNo ratings yet
- Cookery 9 LAS-Q2-W2Document9 pagesCookery 9 LAS-Q2-W2ChelleyOllitroNo ratings yet
- Q2 Guide 1Document4 pagesQ2 Guide 1Gerald EscobalNo ratings yet
- Unit - 2 (Food Production)Document5 pagesUnit - 2 (Food Production)Santosh ThapaNo ratings yet
- Dess LAS1 COPY FinalDocument9 pagesDess LAS1 COPY Finaldelacruzderickmiguel0303No ratings yet
- LESSON V FruitsDocument4 pagesLESSON V FruitsRaquel Saquing FernalenNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Prepare Vegetable DishesDocument108 pagesLesson 1 Prepare Vegetable DishesRonald Serrano100% (3)
- LAS 10 m1Document7 pagesLAS 10 m1Song Joong WeiNo ratings yet
- TLE-031-Module 6Document10 pagesTLE-031-Module 6Jing KhaiNo ratings yet
- Vegetable CookeryDocument47 pagesVegetable CookeryKayla PyneNo ratings yet
- Factors To Consider in Choosing Good Quality VegetablesDocument17 pagesFactors To Consider in Choosing Good Quality VegetablesMeldin May Perez100% (8)
- FS 103 - VegetablesDocument27 pagesFS 103 - VegetablesMa. Isabel C. ChicoNo ratings yet
- Quarter II Prepare Salad and Dressing Learning Outcome 1 Perform Mise' en PlaceDocument7 pagesQuarter II Prepare Salad and Dressing Learning Outcome 1 Perform Mise' en Placemarilyn bristolNo ratings yet
- SABADocument7 pagesSABABharat NailwalNo ratings yet
- Classification of FishDocument16 pagesClassification of FishBharat NailwalNo ratings yet
- Forcemeats: Food Production V SemesterDocument11 pagesForcemeats: Food Production V SemesterBharat Nailwal100% (1)
- Food ProductionDocument12 pagesFood ProductionBharat Nailwal100% (1)
- Aspic & Gelee: Presented by - Jayanti, Karan, Kartikeya and KavyaDocument14 pagesAspic & Gelee: Presented by - Jayanti, Karan, Kartikeya and KavyaBharat NailwalNo ratings yet
- Module For Food HandlersDocument33 pagesModule For Food HandlersBharat NailwalNo ratings yet
- Forcemeats and MousseDocument11 pagesForcemeats and MousseBharat NailwalNo ratings yet
- Firangi Zaika: List of Menu Items With CostingDocument2 pagesFirangi Zaika: List of Menu Items With CostingBharat NailwalNo ratings yet
- Buffet Counter: Restaurant Sitting Plan For Stone Laying CeremonyDocument1 pageBuffet Counter: Restaurant Sitting Plan For Stone Laying CeremonyBharat NailwalNo ratings yet
- Online Classes-New Normal (To Be Designed)Document8 pagesOnline Classes-New Normal (To Be Designed)Bharat NailwalNo ratings yet
- Breadman Op Manual TR900sDocument100 pagesBreadman Op Manual TR900sLutfbhangarNo ratings yet
- Beef StroganoffDocument2 pagesBeef StroganoffduhgeorgeNo ratings yet
- A Project Plan For Cooking Pancit BihonDocument4 pagesA Project Plan For Cooking Pancit BihonCarmel Raine Canoy73% (15)
- The Art of FlavorDocument12 pagesThe Art of FlavordonNo ratings yet
- Abcd QZDocument8 pagesAbcd QZLifted AndrianNo ratings yet
- Boko Boko Harees Wheat Paste FoodDocument1 pageBoko Boko Harees Wheat Paste Foodanandkavi10No ratings yet
- All Day Breakfast: .Served With Cappuccino or Espresso or Lime Juice or TeaDocument7 pagesAll Day Breakfast: .Served With Cappuccino or Espresso or Lime Juice or TeaBryan KuoKyNo ratings yet
- Muhammad Azhar 14801 Thesis ReportDocument59 pagesMuhammad Azhar 14801 Thesis ReportBismah Saleem SiddiquiNo ratings yet
- 7 Days of Healthy Meals On A BudgetDocument7 pages7 Days of Healthy Meals On A BudgetMay Ann GorresNo ratings yet
- Breadth and Depth of Brand - Amul TheDocument31 pagesBreadth and Depth of Brand - Amul Thepayal0212No ratings yet
- List Produk BCMDocument38 pagesList Produk BCMChristian AriNo ratings yet
- Top Delicious Keto Recipes To Lose WeightDocument12 pagesTop Delicious Keto Recipes To Lose WeightAntonioNo ratings yet
- Kitchen Equipment, Tools & SuppliesDocument11 pagesKitchen Equipment, Tools & SuppliesRonald BañaresNo ratings yet
- Dairy ProductDocument12 pagesDairy ProductMeha RajNo ratings yet
- Modern and Ayurvedic Aspects of Guda With Special Reference To JaggeryDocument7 pagesModern and Ayurvedic Aspects of Guda With Special Reference To Jaggerydr d b moteNo ratings yet
- (2g Net Carb!) Gluten Free & Keto Tortillas - Gnom-GnomDocument2 pages(2g Net Carb!) Gluten Free & Keto Tortillas - Gnom-GnomCiupi TikNo ratings yet
- Gout Diet Patient Handout in Creole PDFDocument3 pagesGout Diet Patient Handout in Creole PDFMicheleNo ratings yet
- Filipino DelicaciesDocument6 pagesFilipino DelicaciesMega BytesNo ratings yet
- REady To EatDocument2 pagesREady To EatDnyaneshwar Dattatraya PhadatareNo ratings yet
- Holiday InvitationDocument1 pageHoliday InvitationGerrie SchipskeNo ratings yet
- Nestle Pakistan Internship ReportDocument31 pagesNestle Pakistan Internship ReportAHMAD ALINo ratings yet
- Evidence Plan: Competency Standard Unit of CompetencyDocument2 pagesEvidence Plan: Competency Standard Unit of CompetencyJEMYRAH100% (1)
- WRITING UNIT 6 Health-Giving-AdviceDocument7 pagesWRITING UNIT 6 Health-Giving-AdviceAxlDhNo ratings yet
- Answer All Questions in Both SectionsDocument8 pagesAnswer All Questions in Both SectionsAlfred MwayutaNo ratings yet
- Types of Orchard: What I Need To KnowDocument8 pagesTypes of Orchard: What I Need To KnowMayaman Usman50% (2)