Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Antibodies: Dr. Dalia Wehedi
Antibodies: Dr. Dalia Wehedi
Uploaded by
Fatima Adel0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views13 pagesAntibodies, also known as immunoglobulins, are Y-shaped proteins produced by plasma cells that bind to specific antigens to help fight pathogens. They have two heavy chains and two light chains that give them their distinctive shape. The variable regions at the amino terminal end of the chains allow antibodies to recognize different antigens. The constant regions mediate important immune functions like activating complement proteins. There are five classes of immunoglobulins - IgG, IgM, IgA, IgE, and IgD - that serve different roles in immunity.
Original Description:
Original Title
Antibodies 1 - Copy (1).pptx
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentAntibodies, also known as immunoglobulins, are Y-shaped proteins produced by plasma cells that bind to specific antigens to help fight pathogens. They have two heavy chains and two light chains that give them their distinctive shape. The variable regions at the amino terminal end of the chains allow antibodies to recognize different antigens. The constant regions mediate important immune functions like activating complement proteins. There are five classes of immunoglobulins - IgG, IgM, IgA, IgE, and IgD - that serve different roles in immunity.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views13 pagesAntibodies: Dr. Dalia Wehedi
Antibodies: Dr. Dalia Wehedi
Uploaded by
Fatima AdelAntibodies, also known as immunoglobulins, are Y-shaped proteins produced by plasma cells that bind to specific antigens to help fight pathogens. They have two heavy chains and two light chains that give them their distinctive shape. The variable regions at the amino terminal end of the chains allow antibodies to recognize different antigens. The constant regions mediate important immune functions like activating complement proteins. There are five classes of immunoglobulins - IgG, IgM, IgA, IgE, and IgD - that serve different roles in immunity.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 13
Antibodies
Dr. Dalia Wehedi
Introduction
• Antibodies are globulin proteins (immunoglobulins) that are synthesized in serum and tissue fluids,
which react specifically with the antigen that stimulated their production.
• Three types of globulins are present in the blood: alpha, beta, and gamma.
• The antibodies are the gamma globulins.
• Antibodies are one of the major plasma proteins, and against infection often referred to as “first
line of defense”.
• The most important function of antibodies is to confer protection against microbial pathogens.
Introduction
Antibodies confer protection in the following ways:
1. They prevent attachment of microbes to mucosal surfaces of the host.
2. They reduce virulence of microbes by neutralizing toxins and viruses.
3. They facilitate phagocytosis by opsonization of microbes.
4. They activate complement, leading to complement-mediated activities against microbes.
Immunoglobulins
• There are five classes of immunoglobulins:
(i) Immunoglobulin G (IgG)
(ii) Immunoglobulin M (IgM)
(iii)Immunoglobulin A (IgA)
(iv) Immunoglobulin E (IgE)
(v) Immunoglobulin D (IgD)
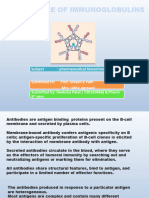
Structure of immunoglobulins
Immunoglobulins show the following properties:
■ They are glycoproteins.
■ They are a complex structure of four polypeptide chains:
two identical heavy (typically 55 kDa each) chains and two identical light chains (25 kDa each). This
gives immunoglobulin an overall ‘Y’ or ‘T’ shape, which is the most widely recognized feature of
immunoglobulin structure.
● The terms “heavy” and “light” refer to the molecular weights of the chains. The heavy chains have a
molecular weight of 50,000–70,000 Da, while light chains have a molecular weight of 25,000 Da. The
heavy chains are longer, and light chains are shorter.
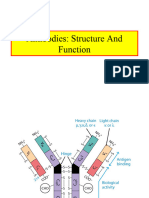
Structure of immunoglobulins
Heavy chains:
• An immunoglobulin molecule has two heavy chains.
• Each heavy chain is made up of 420–440 amino acids.
• The two heavy chains are held together by one to five disulfide (S—S) bonds.
• Each heavy chain is bound to a light chain by a disulfide bond and by noncovalent bonds, such as
salt linkages, hydrogen bonds, and hydrophobic bonds to form a heterodimer (H–L).
Structure of immunoglobulin
Structure of immunoglobulins
Light chains
• An immunoglobulin molecule has two light chains.
• Each light chain is made up of 220–240 amino acids.
• Light chain is attached to the heavy chain by a disulfide bond.
• The light chains are structurally and chemically similar in all classes of immunoglobulins.
• They are of two types: kappa () and lambda ().
• These two types differ in their amino acids present in constant regions.
• Each immunoglobulin has either two or two chains but never both.
• The kappa and lambda chains are present in human serum in a ratio of 2:1
Structure of immunoglobulins
Variable and constant chains:
• Each polypeptide chain of an immunoglobulin molecule contains an amino terminal part and a carboxy terminal part.
• The amino terminal part is called the variable region (V region) and the carboxy terminal part is called the constant
region (C region).
Both heavy and light chains contain variable and constant regions.
• These regions are composed of three-dimensional folded structures with repeating segments, which are called domains.
• Each heavy chain consists of one variable (VH) and three constant (CH) domains.
• IgG and IgA have three CH domains (CH1, CH2, and CH3), whereas IgM and IgE have four domains (CH1, CH2, CH3,
and CH4).
• Each light chain consists of one variable (VL) and one constant domain (CL).
Structure of immunoglobulins
Variable region:
• The amino-terminal half of the light or heavy chain, consisting of 100–110
amino acids
• V region is different for each class of immunoglobulin.
• The variable regions of both light and heavy chains consist of three highly
variable regions known as hypervariable regions.
• The antigen combining sites Fab of the antibody molecule that consists of
only 5–10 amino acids each are present in the hypervariable region of both the
light and heavy chains.
• The high specificity of antibodies is primarily due to the presence of these
hypervariable regions
Structure of immunoglobulins
Constant region:
• The carboxyl-terminal half of the molecule is called the constant (C) region.
• The constant region of the heavy chain has many biological functions.
• It is responsible for activation of the complement, binding to cell surface receptors, placental transfer, and many
other biological activities.
• The constant region of the light chain has no biological function.
• A single antibody molecule has two identical heavy chains and two identical light chains, H2L2, or a multiple (H2L2)n
of this basic four-chain structure.
• Sub isotypes exist for and chains, and this leads to the existence of subclasses of the respective immunoglobulins.
You might also like
- Edu Jacob Atmchem Problems Jan 2021Document77 pagesEdu Jacob Atmchem Problems Jan 2021Elle WoodsNo ratings yet
- Astm D5229Document18 pagesAstm D5229aletapia100% (1)
- Lect.7 BCH 606)Document13 pagesLect.7 BCH 606)Farah AftabNo ratings yet
- Interferons ImmunoglobilinsDocument20 pagesInterferons Immunoglobilinswritters2023No ratings yet
- Antibodies: Shashi AnandDocument40 pagesAntibodies: Shashi AnandDil NavabNo ratings yet
- Antibody Structure FunctionDocument12 pagesAntibody Structure FunctionMelaine Grace Gemoranion GeopanoNo ratings yet
- Geb 403chapter 3 (L1) - ImmunoglobulinDocument22 pagesGeb 403chapter 3 (L1) - ImmunoglobulinC JNo ratings yet
- AntibodyDocument58 pagesAntibodySubhas KarnaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5-3Document45 pagesLecture 5-3Emmanuel Thon MadingNo ratings yet
- Antigen AntibodyDocument54 pagesAntigen AntibodyInjamam ul hossainNo ratings yet
- 1.5 Antibody Structure Function Chapter 5Document18 pages1.5 Antibody Structure Function Chapter 5Eliariz Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- 4-ch5. Immunology (Cellular) PDFDocument41 pages4-ch5. Immunology (Cellular) PDFMohammad GhannamNo ratings yet
- Clinical Immunology - Topic 6 - Antibody Structure PDFDocument24 pagesClinical Immunology - Topic 6 - Antibody Structure PDFAliza FayyazNo ratings yet
- ANTIBODYDocument52 pagesANTIBODYVysakhNo ratings yet
- Immunology Lecture 03 - Antibodies Part 1 - 2018Document36 pagesImmunology Lecture 03 - Antibodies Part 1 - 2018api-273068056No ratings yet
- ImmunoglobulinsDocument11 pagesImmunoglobulinsIram AnwarNo ratings yet
- Unit IV - Antibody PDFDocument32 pagesUnit IV - Antibody PDFShashank TiwariNo ratings yet
- AntibodiesDocument39 pagesAntibodiespilot abdi baariNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 AntibodyDocument86 pagesChapter 11 AntibodyPinaki ChatterjeeNo ratings yet
- Immunoglobulins - AntibodiesDocument10 pagesImmunoglobulins - AntibodiesJesuhovie Solomon OkpobrisiNo ratings yet
- Immunoglobulins - Structure and Function Definition: Immunoglobulins (Ig)Document9 pagesImmunoglobulins - Structure and Function Definition: Immunoglobulins (Ig)Valdez Francis ZaccheauNo ratings yet
- Structure of AntibodyDocument3 pagesStructure of AntibodymaimoonaNo ratings yet
- 919 AntibodyDocument83 pages919 AntibodyShahil AlamNo ratings yet
- Immunoglobulins: Prof. DR: Sabah Abdel-HadyDocument22 pagesImmunoglobulins: Prof. DR: Sabah Abdel-HadylianazulakNo ratings yet
- Antibody Structure and Classes of ImmunoglobulinsDocument5 pagesAntibody Structure and Classes of Immunoglobulinssajjad100% (1)
- Immunoglobulins: Structure and Function Immunoglobulins (Ig) - Glycoprotein Molecules Which Are Produced by Plasma Cells inDocument14 pagesImmunoglobulins: Structure and Function Immunoglobulins (Ig) - Glycoprotein Molecules Which Are Produced by Plasma Cells inCristina GeorgianaNo ratings yet
- Reviewers AntibodyDocument3 pagesReviewers AntibodyLeanna DaneNo ratings yet
- Antibodies 2Document29 pagesAntibodies 2sulimansmart22No ratings yet
- Antigen Structure NotesDocument12 pagesAntigen Structure NotesViswadeep DasNo ratings yet
- 02 Antibody, Ag-Ab Interaction, Cytokines, ComplementDocument82 pages02 Antibody, Ag-Ab Interaction, Cytokines, ComplementDayledaniel SorvetoNo ratings yet
- Antibody Structure and Function PDFDocument8 pagesAntibody Structure and Function PDFJay JaswaniNo ratings yet
- Antibodies Structure and FunctionDocument16 pagesAntibodies Structure and Functionياسين احمد علي الشيخNo ratings yet
- ANTIBODIESDocument119 pagesANTIBODIESsaimNo ratings yet
- ABDocument22 pagesABpk 77No ratings yet
- Antibody-Structure, Classes and FunctionsDocument5 pagesAntibody-Structure, Classes and FunctionsNadia UmmahNo ratings yet
- ImmunoglobulinDocument23 pagesImmunoglobulinShovana DeyNo ratings yet
- Abo DescriptionDocument17 pagesAbo DescriptionMohamad IqbalNo ratings yet
- bms545 4Document28 pagesbms545 4nasrulursan15No ratings yet
- Chapter 8 Immunoglobulin Structure and FunctionDocument52 pagesChapter 8 Immunoglobulin Structure and FunctionTofikNo ratings yet
- Adaptive and Innate Immune SystemDocument26 pagesAdaptive and Innate Immune SystemArchana100% (1)
- Antibody Structure and Functions: ImmunologyDocument40 pagesAntibody Structure and Functions: ImmunologyMoody Maxi KhanNo ratings yet
- ImmunoglobulinDocument12 pagesImmunoglobulin19ph012 Jaya sangeethaNo ratings yet
- IMMUNOGLOBULINSDocument8 pagesIMMUNOGLOBULINSrednriNo ratings yet
- Y20150066 Structure of Immunoglobulins Deeksha Patel-1Document18 pagesY20150066 Structure of Immunoglobulins Deeksha Patel-1deekshapatel.7665No ratings yet
- Ag Ab AmerDocument24 pagesAg Ab AmerAmer WahanNo ratings yet
- Antibodies: Immunoglobulins - A Family of ProteinsDocument21 pagesAntibodies: Immunoglobulins - A Family of ProteinsMike zombieNo ratings yet
- 20 17-GlycoproteinsDocument3 pages20 17-GlycoproteinsCASTAÑEDA, Jameela AnneNo ratings yet
- Gamma Globulins: Include All Classes of Antibodies: 1 - CA Ete, DNPDocument8 pagesGamma Globulins: Include All Classes of Antibodies: 1 - CA Ete, DNPTrisha Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- 4. Antibodies Structure and Function تفريغDocument16 pages4. Antibodies Structure and Function تفريغayamalkawi204No ratings yet
- Antibodies 2-3Document29 pagesAntibodies 2-3Fatima AdelNo ratings yet
- Structures and Functions of ProteinDocument54 pagesStructures and Functions of ProteinRollyRiksantoNo ratings yet
- Antibodies CHPT 4Document38 pagesAntibodies CHPT 4ParulNo ratings yet
- AntibodiesDocument22 pagesAntibodieskrishnambnw100No ratings yet
- Antibodies Are The Globular Protein Belonging To Immunoglobulin #4Document4 pagesAntibodies Are The Globular Protein Belonging To Immunoglobulin #4Arsalan Abbas ZafarNo ratings yet
- Immunology - Chapter 3 - AntibodiesDocument56 pagesImmunology - Chapter 3 - AntibodiesMajed IaalyNo ratings yet
- Structure and Function of Different Class of Immunoglobulins Antigen Antibody InteractionDocument36 pagesStructure and Function of Different Class of Immunoglobulins Antigen Antibody InteractionNikita Singh RaghavNo ratings yet
- Plasma ChonDocument41 pagesPlasma ChonTwinkle SalongaNo ratings yet
- M - 4 Basic Structure and Functions of ImmunoglobulinDocument10 pagesM - 4 Basic Structure and Functions of ImmunoglobulinDr. Tapan Kr. DuttaNo ratings yet
- Immunoglobulins ClassDocument16 pagesImmunoglobulins ClassKoushali BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- Immunoglobulin: Wesam Mohammed EmharibDocument10 pagesImmunoglobulin: Wesam Mohammed Emharibنسيم حامدNo ratings yet
- A-level Biology Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandA-level Biology Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)
- A-level Sciences Revision Boxset: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandA-level Sciences Revision Boxset: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- Q2 Science 9 - Module 5Document22 pagesQ2 Science 9 - Module 5Eden Pearl LumaynoNo ratings yet
- LMR (Last Minute Revision) Chemistry 10TH - 2023 PDFDocument236 pagesLMR (Last Minute Revision) Chemistry 10TH - 2023 PDFSneh BhalodiaNo ratings yet
- Ammonium Chloride-Reaction EquilibriumDocument6 pagesAmmonium Chloride-Reaction Equilibriumfatemeh afariNo ratings yet
- GoudaDocument2 pagesGoudaKresna SuputraNo ratings yet
- Epoxy Floor Scope of Work and Specifications Bid - Fy170058Document9 pagesEpoxy Floor Scope of Work and Specifications Bid - Fy170058Bishop GilbertNo ratings yet
- Corrosion of High Temperature Alloys in Solar Salt at 400, 500, and 680°CDocument45 pagesCorrosion of High Temperature Alloys in Solar Salt at 400, 500, and 680°CXeeshan Ahmad ShaniNo ratings yet
- Diagonal Relationship: Li Be B C Na MG Al SiDocument4 pagesDiagonal Relationship: Li Be B C Na MG Al SiPAUL KOLERENo ratings yet
- Lime and Limestone: History. Limestone Was Probably Used in TheDocument32 pagesLime and Limestone: History. Limestone Was Probably Used in TheEbrahim BayoumiNo ratings yet
- Guttman N 1901Document22 pagesGuttman N 1901Abdullah FasihNo ratings yet
- Reaseach Paper For Powder CoatingDocument10 pagesReaseach Paper For Powder CoatingAkshay DhakanNo ratings yet
- Palm Oil Quotation RabDocument49 pagesPalm Oil Quotation RabEmel Mangkuraja WanitaNo ratings yet
- Cyclometalation Using D-Block Transition Metals Fundamental Aspects andDocument48 pagesCyclometalation Using D-Block Transition Metals Fundamental Aspects andNieves R. PicazoNo ratings yet
- Rubber Gloves Manufacturing Process Application Note B212055ENDocument3 pagesRubber Gloves Manufacturing Process Application Note B212055ENMuhammad ZikryNo ratings yet
- Exergy Analysis of The Process of Production of Dicalcium PhosphateDocument13 pagesExergy Analysis of The Process of Production of Dicalcium Phosphatedehkadeh7No ratings yet
- Mizoroki-Heck Intramolecular Usando AlcoholesDocument6 pagesMizoroki-Heck Intramolecular Usando AlcoholesDavid DelgadoNo ratings yet
- Gas-Phase Mass Transfer Coefficient of CO in Different Alkanolamine Solutions Within Packed-Bed Absorption ColumnDocument10 pagesGas-Phase Mass Transfer Coefficient of CO in Different Alkanolamine Solutions Within Packed-Bed Absorption ColumnHamza AliNo ratings yet
- 234M Parr Magnetic-Drive-Inst PDFDocument16 pages234M Parr Magnetic-Drive-Inst PDFNyu WertNo ratings yet
- Oh 2002Document6 pagesOh 2002tehtnicaNo ratings yet
- Mineral Preservatives in The Wood of Stradivari and GuarneriDocument9 pagesMineral Preservatives in The Wood of Stradivari and Guarneriponbohacop100% (1)
- Unit 6 Study Guide AnswersDocument3 pagesUnit 6 Study Guide Answersmisterbrowner100% (1)
- 3.1 Heat ExchangersDocument76 pages3.1 Heat Exchangersraghu_iictNo ratings yet
- D4.1 Refrigerants: Regulations: Properties of Industrial Heat Transfer MediaDocument94 pagesD4.1 Refrigerants: Regulations: Properties of Industrial Heat Transfer MediaANo ratings yet
- 2022 NCHE222 - Aanlyntoets 1 - Online Test 1 MemoDocument2 pages2022 NCHE222 - Aanlyntoets 1 - Online Test 1 MemoMartha FormalNo ratings yet
- Pocket Guide To College Success 2nd Edition Shushan Test BankDocument35 pagesPocket Guide To College Success 2nd Edition Shushan Test Bankconjectxanthinev76r100% (28)
- Chapter 3 Lab ReportDocument5 pagesChapter 3 Lab ReportJabin Sta. TeresaNo ratings yet
- Dimethyl Ether: A Review of Technologies and Production ChallengesDocument24 pagesDimethyl Ether: A Review of Technologies and Production ChallengesStephany PérezNo ratings yet
- WTP Chemical EquationDocument10 pagesWTP Chemical EquationSivakumar NagarathinamNo ratings yet
- Part Test - 3 (Senior) Question Paper 2011-P2 8-6-2020-FDocument14 pagesPart Test - 3 (Senior) Question Paper 2011-P2 8-6-2020-FJainNo ratings yet