Professional Documents
Culture Documents
1 of 20 1 of 36: © Boardworks LTD 2004 © Boardworks LTD 2005
1 of 20 1 of 36: © Boardworks LTD 2004 © Boardworks LTD 2005
Uploaded by
MindOfPrince0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views19 pagesOriginal Title
Spotting_Patterns__2_
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views19 pages1 of 20 1 of 36: © Boardworks LTD 2004 © Boardworks LTD 2005
1 of 20 1 of 36: © Boardworks LTD 2004 © Boardworks LTD 2005
Uploaded by
MindOfPrinceCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 19
1 of 36
20 © Boardworks Ltd 2005
2004
• L.O.: • H.W:
Spotting 1- To identify the physical and • 1-Name the least reactive
patterns the chemical properties. metal in group 1
2- Spotting patterns and • 2- How many outer shell
trends ascross periods and electrons in:
down groups. • Group 1
3- Electron arrangement in • Group 2
shells.
• Draw an atomic diagram
2- Keywords: for Mg.
• properties.
• shells
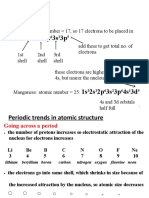
Periodic Law
The periodic recurrence of elements with similar
physical and chemical properties, when the
elements are listed in order of increasing atomic
number, results directly from the periodic
recurrence of similar electronic configurations in
the outer shells of respective atoms
Arrangement of electrons
• Valence electrons are the electrons
in the outermost electron shell of
an element. Sometimes, it is also
regarded as the basis of Modern
Periodic Table. In a period, the
number of valence electrons
Valence elect increases as we move from left to
rons right side. However, in a group this
periodic trend is constant, that is
the number of valence electrons
remains the same.
Predicting properties
• L.Os:
• To know that the physical and chemical • Keywords:
properties of elements can be
predicted from periodic table. • Predict
• To Be able to plot graphs showing the • chemical behaviour
relation between physical properties
and the arrangement of elements • physical behaviour
• To predict the formula of products from
the reaction of metals with halogens
• The greater the atomic number the
greater the mass number.
• There is a relation between the mass
of the atom and the physical properties
like boiling point.
The trend in
boiling point in
periods 2&3
elements
• A graph to show how atomic number affects the atomic mass- this data
will allow the chemist to predict the state of the element at room
temperature
• As you move from the top to the bottom of the periodic
table, you’ll find a rough correlation exists between the
atomic mass of elements and their boiling points. Lighter
elements such as hydrogen and helium tend to have very low
boiling points, and elements with greater atomic mass boil at
higher temperatures. The atomic mass affects the forces
between atoms, which in turn determine boiling points.
Reactions of halogens with metals p 65
• L.O:
• We can predict the formula of products for
metals and halogens if we know any of them.
• Sodium + chlorine sodium chloride
• The product is always a solid and the ending
changes into -ide.
• HW.
• 1- Which is more reactive Iodine or chlorine?
• 2- What would you call LiBr?
• 3- Predict the melting point and the boiling
point of group 7 element astatine.
You might also like
- 1 of 20 1 of 36: © Boardworks LTD 2004 © Boardworks LTD 2005Document24 pages1 of 20 1 of 36: © Boardworks LTD 2004 © Boardworks LTD 2005MindOfPrinceNo ratings yet
- Chemistry SS2 EditedDocument150 pagesChemistry SS2 EditedSamuel BiyamaNo ratings yet
- Periodic Table: Oakland Schools Chemistry Resource UnitDocument42 pagesPeriodic Table: Oakland Schools Chemistry Resource UnitAnum TauqirNo ratings yet
- Ib PPT 3 SL PDFDocument24 pagesIb PPT 3 SL PDFzarna nirmal rawalNo ratings yet
- Periodic TableDocument59 pagesPeriodic TableTrudy- Ann CaineNo ratings yet
- Notes - Periodic Classification of Elements - C-XDocument4 pagesNotes - Periodic Classification of Elements - C-Xpratishtha MishraNo ratings yet
- Periodic Trends: Elemental Properties and PatternsDocument35 pagesPeriodic Trends: Elemental Properties and PatternsJared MutindaNo ratings yet
- Periodic Properties Chemistry Class 11Document32 pagesPeriodic Properties Chemistry Class 11Ravinder singhNo ratings yet
- CH4701/4001 2019 Lecture 16 and 17 Trends in The Periodic TableDocument52 pagesCH4701/4001 2019 Lecture 16 and 17 Trends in The Periodic TableJason ZhangNo ratings yet
- Grade 11 Periodicity PPT (Autosaved)Document40 pagesGrade 11 Periodicity PPT (Autosaved)prateekshadharaniNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry Che 101: Prof. Moavin Islam PHD Ficorr Mim Ceng (Mvi)Document77 pagesGeneral Chemistry Che 101: Prof. Moavin Islam PHD Ficorr Mim Ceng (Mvi)Irfanul HoqueNo ratings yet
- AOS1: The Periodic Table: Atomic Theory RevisionDocument6 pagesAOS1: The Periodic Table: Atomic Theory RevisionNicola NguyenNo ratings yet
- Periodic Table NotesDocument34 pagesPeriodic Table NotesMiraNo ratings yet
- Bai GiangDocument104 pagesBai GiangminhyNo ratings yet
- 1s 2s 2p 3s 3p: ExamplesDocument104 pages1s 2s 2p 3s 3p: ExamplesminhyNo ratings yet
- Periodic Table Periodic Properties and Variations of PropertiesDocument4 pagesPeriodic Table Periodic Properties and Variations of PropertiesSANDEEP SINGHNo ratings yet
- Periodic Trends CompleteDocument51 pagesPeriodic Trends CompleteZal Fildan DuomaNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Concept Chemistry For Senior High School Grade 10Document23 pagesAnalysis of Concept Chemistry For Senior High School Grade 10insecundaNo ratings yet
- The Periodic Table: Home WorkDocument52 pagesThe Periodic Table: Home WorkSam LoveNo ratings yet
- Pertemuan 2 - Kimia - DosenDocument49 pagesPertemuan 2 - Kimia - Dosenraaflie caesarNo ratings yet
- 09 The Periodic Table SlidesDocument19 pages09 The Periodic Table Slidesjackoread28No ratings yet
- The Modern Periodic Table Chemistry PresentationDocument15 pagesThe Modern Periodic Table Chemistry PresentationShee YingNo ratings yet
- Topic 3 - Periodicity SL and HLDocument30 pagesTopic 3 - Periodicity SL and HLsharmag25No ratings yet
- The Periodic Trends Updated 2023Document58 pagesThe Periodic Trends Updated 2023stutireddy1912No ratings yet
- Mse Group 2Document100 pagesMse Group 2Nicko CortoNo ratings yet
- Atoms, Electrons & Energy Levels: Electrons Are The Bonds That Hold The World Together!Document41 pagesAtoms, Electrons & Energy Levels: Electrons Are The Bonds That Hold The World Together!cmillica1176100% (3)
- Chemistry Exam Notes Semester 2Document37 pagesChemistry Exam Notes Semester 2AnjaliNo ratings yet
- Unidad 1. Tabla PeriodicaDocument17 pagesUnidad 1. Tabla PeriodicaAlrisha6No ratings yet
- Elements and The PeriodicDocument45 pagesElements and The PeriodicRenata AlvesNo ratings yet
- Periodic Properties of The Elements: Theodore L. Brown H. Eugene Lemay, Jr. and Bruce E. BurstenDocument63 pagesPeriodic Properties of The Elements: Theodore L. Brown H. Eugene Lemay, Jr. and Bruce E. BurstenAbaring KathrynaNo ratings yet
- 1-Atoms and Molecules - 2022Document50 pages1-Atoms and Molecules - 2022riva rizkianaNo ratings yet
- 2 Atomic Structure & BondingDocument15 pages2 Atomic Structure & BondingAl K MicNo ratings yet
- Chem PDFDocument37 pagesChem PDFJhonsen BarengNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3+4: Periodic Properties Off The ElementsDocument34 pagesLecture 3+4: Periodic Properties Off The ElementsHIEP PHAM HOANGNo ratings yet
- 2023 H1 H2 Periodic Table - Notes and TutorialDocument37 pages2023 H1 H2 Periodic Table - Notes and TutorialElean NgNo ratings yet
- Trends in The Periodic TableDocument54 pagesTrends in The Periodic TableLaura DíazNo ratings yet
- Organic MoleculesDocument106 pagesOrganic MoleculesAnonymous GUExuPNo ratings yet
- Periodic Table of ElementsDocument27 pagesPeriodic Table of ElementsRiane Venice PamintuanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - Electronic Structure and PeriodicityDocument10 pagesChapter 4 - Electronic Structure and PeriodicityAbrienne CaprichoNo ratings yet
- Periodic Table-WPS OfficeDocument30 pagesPeriodic Table-WPS Officenabeel0% (1)
- Topic 3 - Periodicity SLDocument20 pagesTopic 3 - Periodicity SLnikes 1No ratings yet
- Electron Configuration and Periodic TableDocument18 pagesElectron Configuration and Periodic TableHannah AlicayaNo ratings yet
- Trends - Periodic TableDocument34 pagesTrends - Periodic Tableaaahluma.gxeesiNo ratings yet
- Topic 2 Periodic TableDocument47 pagesTopic 2 Periodic TableAidah HanidaNo ratings yet
- Lecture Note 13-02-2024Document5 pagesLecture Note 13-02-2024mvikosiphosethu2407No ratings yet
- Materials, Processes and Defects 1Document10 pagesMaterials, Processes and Defects 1mangsureshNo ratings yet
- Periodic Trends: Elemental Properties and PatternsDocument42 pagesPeriodic Trends: Elemental Properties and PatternsreedskyNo ratings yet
- Periodic Properties and The Periodic TableDocument6 pagesPeriodic Properties and The Periodic TableAurobinda MaharanaNo ratings yet
- Periodic Classification of Elements Xerox 2020Document7 pagesPeriodic Classification of Elements Xerox 2020irehan.saiyedNo ratings yet
- Unit 3.2 - Covalent BondingDocument11 pagesUnit 3.2 - Covalent BondingAylin KasaNo ratings yet
- History of The PeriodicTableDocument50 pagesHistory of The PeriodicTablePscf CarmonaNo ratings yet
- IMFA and Chemical BondingDocument137 pagesIMFA and Chemical BondingEnna SertNo ratings yet
- Ib PPT 4 SL PDFDocument103 pagesIb PPT 4 SL PDFzarna nirmal rawalNo ratings yet
- Lecture03-04 Bonding StructureDocument103 pagesLecture03-04 Bonding StructureLeslieLooNo ratings yet
- 3A The Periodic TableDocument7 pages3A The Periodic TableMohammed TarekNo ratings yet
- Solid State PhysicsDocument9 pagesSolid State Physicssjo05No ratings yet
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: The Periodic Table with AnswersFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: The Periodic Table with AnswersRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Reactivity SeriesDocument25 pagesReactivity SeriesMindOfPrinceNo ratings yet
- Metals and Non-Metals 1Document32 pagesMetals and Non-Metals 1MindOfPrinceNo ratings yet
- Food Digestion To PrintDocument44 pagesFood Digestion To PrintMindOfPrinceNo ratings yet
- Atom Element and Atomic StructrureDocument48 pagesAtom Element and Atomic StructrureMindOfPrinceNo ratings yet
- GDJP Q BabkkDocument6 pagesGDJP Q BabkkganeshkumarbemechNo ratings yet
- 04 - Crystallogaphy III Miller Indices-Faces-Forms-EditedDocument63 pages04 - Crystallogaphy III Miller Indices-Faces-Forms-EditedMaisha MujibNo ratings yet
- Suitability Criteria For Different CropsDocument4 pagesSuitability Criteria For Different CropsKani ManikandanNo ratings yet
- Organic SL With AnswersDocument38 pagesOrganic SL With Answerswakoaisha2No ratings yet
- TP-N01013 Determination of Gardner Color NumberDocument2 pagesTP-N01013 Determination of Gardner Color Numberm.cj1No ratings yet
- Capacity of PileDocument4 pagesCapacity of PileHanafiahHamzahNo ratings yet
- MMS Evaluation of High Integrity Pressure Protection SystemDocument137 pagesMMS Evaluation of High Integrity Pressure Protection SystemEyoma EtimNo ratings yet
- New Microsoft Office Word DocumentDocument4 pagesNew Microsoft Office Word DocumentahmadfarrizNo ratings yet
- Precision "Heavy Duty" Pressure Gauges: Trade Catalogue 2005Document38 pagesPrecision "Heavy Duty" Pressure Gauges: Trade Catalogue 2005marcosNo ratings yet
- Areading 11Document3 pagesAreading 11IVy ViOlet ThOrnNo ratings yet
- SUMITOMO Fiber Cleaver FC 6R Series Data SheetETK1324238BDocument1 pageSUMITOMO Fiber Cleaver FC 6R Series Data SheetETK1324238BAnte KerumNo ratings yet
- Repairs of Asphalt RoadsDocument16 pagesRepairs of Asphalt RoadsPradeepLokhandeNo ratings yet
- Article Acsomega 5 9055Document10 pagesArticle Acsomega 5 9055Nikanor NatanNo ratings yet
- 22-12-2023 - Sr.S60 - Elite, Target & LIIT-BTs - 1st Year Syllabus - Jee-Main-GTM-02 - KEY & Sol'sDocument14 pages22-12-2023 - Sr.S60 - Elite, Target & LIIT-BTs - 1st Year Syllabus - Jee-Main-GTM-02 - KEY & Sol'sKillerpkNo ratings yet
- Table of NeurotransmittersDocument10 pagesTable of NeurotransmittersAmanda Shabrina PutriNo ratings yet
- Exam Schedule PDFDocument24 pagesExam Schedule PDFKhagapati KandagoriNo ratings yet
- Flash Calculation: SeaderDocument24 pagesFlash Calculation: SeaderaaaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 14 Exergy Analysis of Integrated Trigeneration and Multigeneration Systems 2013 Exergy Second EditionDocument16 pagesChapter 14 Exergy Analysis of Integrated Trigeneration and Multigeneration Systems 2013 Exergy Second EditionAnonymous dUXvWL61No ratings yet
- Section I: (Multiple Choice Questions) : Physics (Part - A) )Document11 pagesSection I: (Multiple Choice Questions) : Physics (Part - A) )Aisha SinghNo ratings yet
- PRISM For Earthquake Engineering A Program For Seismic Response Analysis of SDOF SystemDocument13 pagesPRISM For Earthquake Engineering A Program For Seismic Response Analysis of SDOF SystemPrabhat KumarNo ratings yet
- Span Rev11Document170 pagesSpan Rev11fnanamNo ratings yet
- l4 PDFDocument48 pagesl4 PDFRahul SinghNo ratings yet
- Prima RCPA 2014 GuidlineDocument7 pagesPrima RCPA 2014 GuidlineRajendra KumarNo ratings yet
- Speaking Practice Questions Answers PDFDocument85 pagesSpeaking Practice Questions Answers PDFkomal naeemNo ratings yet
- Le Nouveau Taxi! 1Document32 pagesLe Nouveau Taxi! 1Jay Rắc RốiNo ratings yet
- Studies On N 2 Aurivillius Phases: Structure of The Series Bi La Tinbo (0.0 X 1.0)Document20 pagesStudies On N 2 Aurivillius Phases: Structure of The Series Bi La Tinbo (0.0 X 1.0)books0702No ratings yet
- Final Dead Load, Along Wind, Across Wind and Temparature Stresses Calculation of 80m Chimney Line Model 181019Document50 pagesFinal Dead Load, Along Wind, Across Wind and Temparature Stresses Calculation of 80m Chimney Line Model 181019Umang LapsiwalaNo ratings yet
- Development and Evaluation of Anti-Dandruff Hair Gel: IJRPC 2011, 1Document9 pagesDevelopment and Evaluation of Anti-Dandruff Hair Gel: IJRPC 2011, 1Hastuti RahmasariiNo ratings yet
- Ermeto FITTINGS Part 3Document36 pagesErmeto FITTINGS Part 3carmaNo ratings yet
- Formulation and Evaluation of Natural Lipstick From Coloured Pigments of Beta Vulgaris Taproot 65 71Document7 pagesFormulation and Evaluation of Natural Lipstick From Coloured Pigments of Beta Vulgaris Taproot 65 71Debora Debbie AgustineNo ratings yet