Professional Documents
Culture Documents
W04 Practice Exam: By: Mariah Miller
W04 Practice Exam: By: Mariah Miller
Uploaded by
Romo Anthony0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 views22 pagesThis document contains a practice exam with multiple choice questions about anatomy and cell transport mechanisms. It asks about identifying parts of the cell like the mitochondrion and nucleus, naming body cavities, defining transport processes such as diffusion and osmosis, and matching key terms to their descriptions. The questions cover topics relating to cell structure, human anatomy, and cellular transport systems.
Original Description:
Original Title
Wo4 Practice Exam
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document contains a practice exam with multiple choice questions about anatomy and cell transport mechanisms. It asks about identifying parts of the cell like the mitochondrion and nucleus, naming body cavities, defining transport processes such as diffusion and osmosis, and matching key terms to their descriptions. The questions cover topics relating to cell structure, human anatomy, and cellular transport systems.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 views22 pagesW04 Practice Exam: By: Mariah Miller
W04 Practice Exam: By: Mariah Miller
Uploaded by
Romo AnthonyThis document contains a practice exam with multiple choice questions about anatomy and cell transport mechanisms. It asks about identifying parts of the cell like the mitochondrion and nucleus, naming body cavities, defining transport processes such as diffusion and osmosis, and matching key terms to their descriptions. The questions cover topics relating to cell structure, human anatomy, and cellular transport systems.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 22
W04 Practice Exam
By: Mariah Miller
What section of the cell is this
What is this part of the cell
What is this part of the cell
What plane is this
What plane is this?
What plane is this?
What body cavity is number one.
What body cavity is number 3
What body cavity is number 2?
What body cavity is number 4
Anatomy descriptions
This function in the body is the state of dynamic equilibrium
The closest point to the origin.
Located at the back of the body. Contains the cranial and spinal cavity
Located at the front of the body; consists of the thoracic and
abdominopelvic cavities
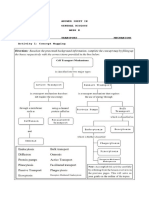
A passive transport mechanism that involves the movement of particles from an area of
higher to lower concentration
A passive transport mechanism involving the diffusion of water from an area of
greater concentration of water (and a lesser concentration of solutes) to an area
of lesser concentration of water (and a greater concentration of solutes)
Form of vesicular transport that releases substances outside the cell
Process in which fluid and dissolved particles are trapped in the plasma
membrane and brought into the cell
Process in which large particles are trapped in the plasma membrane and
brought into the cell
Transport process involving the diffusion of a substance through a channel
protein
KEY
1. Mitochondrion 1. Homeostasis
2. Nucleus 2. Proximal
3. Dorsal cavity
3. Centrioles 4. Ventral cavity
4. Transverse plane 5. Diffusion
6. Osmosis
5. Sagittal plane 7. Exocytosis
6. Frontal plane 8. Pinocytosis
9. Phagocytosis
7. Cranial cavity 10. Facilitated diffusion
8. Abdominal cavity
9. Thoracic cavity
10. Pelvic cavity
You might also like
- AS Biology, Cell Membranes and Transport 1Document49 pagesAS Biology, Cell Membranes and Transport 1sachinNo ratings yet
- Cell Membrane TransportDocument48 pagesCell Membrane TransportIndra3SHSNo ratings yet
- Biology - Module 4Document6 pagesBiology - Module 4ASHLEY MONICA PLATANo ratings yet
- Cellular Transport ConceptDocument7 pagesCellular Transport ConceptRuhul Qudus NaimNo ratings yet
- Membrane Transport, PHR121, Human Physiology 01Document7 pagesMembrane Transport, PHR121, Human Physiology 01Aanikul IslamNo ratings yet
- Cell Membrane: Function and Structure Grade 11 BiologyDocument51 pagesCell Membrane: Function and Structure Grade 11 BiologyChester WengerNo ratings yet
- Larutan Isotonik, Hipotonik, Hipertonik 1Document32 pagesLarutan Isotonik, Hipotonik, Hipertonik 1riskaczhrNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - Movement of Substances Across The Cell Membrane: Learning ObjectivesDocument16 pagesChapter 4 - Movement of Substances Across The Cell Membrane: Learning Objectivesthanks btNo ratings yet
- Active and Passive Transport LatestDocument51 pagesActive and Passive Transport Latestxianlagajenoseamg5No ratings yet
- Biology Test 2Document2 pagesBiology Test 2Rosa MendozaNo ratings yet
- Cell Membrane TransportDocument49 pagesCell Membrane TransportAlex VoicuNo ratings yet
- General Biology 1 Q1 Week 7Document14 pagesGeneral Biology 1 Q1 Week 7JewelNo ratings yet
- 1.3 Review-Cells-M1-L3Document1 page1.3 Review-Cells-M1-L3naomi burnsNo ratings yet
- Act2 Bio SciDocument4 pagesAct2 Bio SciPamaran, Kristel DenishNo ratings yet
- The Big Picture: Diffusion: Movement of Particles From A Region of Higher Concentration To A Region of LowDocument5 pagesThe Big Picture: Diffusion: Movement of Particles From A Region of Higher Concentration To A Region of LowNicolas Gomez CombellasNo ratings yet
- Lect 2 Membrane TransportDocument29 pagesLect 2 Membrane Transportramadan100% (1)
- BIO2 Diffusion OsmosisDocument11 pagesBIO2 Diffusion Osmosisarangosoangelo8No ratings yet
- A-Level Biology Transport NotesDocument82 pagesA-Level Biology Transport NotesbirizimanabNo ratings yet
- Cell Membrane Transport NotesDocument24 pagesCell Membrane Transport NotesJason RobinsonNo ratings yet
- Transport MechanismDocument28 pagesTransport MechanismRenz Marian LazanasNo ratings yet
- The Cell Division Is The Division of A Cell Into Two Daughter Cells With The Same Genetic MaterialDocument3 pagesThe Cell Division Is The Division of A Cell Into Two Daughter Cells With The Same Genetic MaterialSock SackNo ratings yet
- LESSON - 11 - Gen Biology 1Document4 pagesLESSON - 11 - Gen Biology 1Jhay Luiz Cajigal ArquinesNo ratings yet
- Cell Membrane TransportDocument5 pagesCell Membrane Transportronsta86No ratings yet
- Answer Sheet in General Biology Week 8 Cell Transport Mechanisms Activity 1: Concept MappingDocument8 pagesAnswer Sheet in General Biology Week 8 Cell Transport Mechanisms Activity 1: Concept MappingMark Joedel MendezNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Transport of SubstancesDocument25 pages1.1 Transport of SubstancesRayonesh RayanaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 5Document18 pagesLesson 5Mariz GenandaNo ratings yet
- السيد قشطةDocument138 pagesالسيد قشطةAhmed FrahatNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 Cellular TransportDocument22 pagesLesson 3 Cellular Transportjansameh16No ratings yet
- Movement of Substances Across The Plasma MembraneDocument33 pagesMovement of Substances Across The Plasma MembraneFauziah Abu BakarNo ratings yet
- 4 Movement of Substances Across The Cell MembraneDocument5 pages4 Movement of Substances Across The Cell MembraneVenice LoNo ratings yet
- Letran de Davao, IncDocument3 pagesLetran de Davao, IncPatricia DianeNo ratings yet
- Senior High School: Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics (Stem) Specialized SubjectDocument53 pagesSenior High School: Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics (Stem) Specialized Subjectpotato macchiatoNo ratings yet
- BiologyDocument2 pagesBiologyChaca LurpheChachos XiaraNo ratings yet
- Cell Membrane Membrane: How Substances Get Across The MembraneDocument15 pagesCell Membrane Membrane: How Substances Get Across The MembraneMariane CarandangNo ratings yet
- Cell Physiology: Membrane Transport: Prepared By: Mr. Charlie C. Falguera, RN, MANDocument15 pagesCell Physiology: Membrane Transport: Prepared By: Mr. Charlie C. Falguera, RN, MANchfalgueraNo ratings yet
- II. Perjalanan Obat Dalam TubuhDocument45 pagesII. Perjalanan Obat Dalam TubuhNyiet 'nya Garry NiyyNo ratings yet
- Chapter Two ThreeDocument50 pagesChapter Two Threerue pattinsonNo ratings yet
- Histology: Cytology, The Study of The Structure and Function of CellsDocument48 pagesHistology: Cytology, The Study of The Structure and Function of CellsZmeu CristinaNo ratings yet
- Transport MechanismDocument31 pagesTransport MechanismCecillia Evan100% (1)
- Obero, Jecamiah E. - LAB # 6Document5 pagesObero, Jecamiah E. - LAB # 6JECAMIAH OBERONo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Vanders Human Physiology 15th Edition by Eric WidmaierDocument37 pagesTest Bank For Vanders Human Physiology 15th Edition by Eric Widmaieramandapughspriybdxnz100% (18)
- General Biology 1Document15 pagesGeneral Biology 1Beejae ApalisNo ratings yet
- Cell TransportDocument37 pagesCell TransportxspiirONo ratings yet
- 1 Movement of Substances Across The Plasma MembranDocument34 pages1 Movement of Substances Across The Plasma MembranMohammed RidzuwanNo ratings yet
- SAQ EmbryologyDocument9 pagesSAQ EmbryologyShilpa DuttaNo ratings yet
- Membrane Structure and Homesostasis 2007Document59 pagesMembrane Structure and Homesostasis 2007kathryn_bruyèreNo ratings yet
- ICSE Board Class X Biology Board Paper 2015 (Solution)Document7 pagesICSE Board Class X Biology Board Paper 2015 (Solution)DAMAYANTI MITRANo ratings yet
- ANPH-M1-CU2. The Cell & Cellular Metabolism and Reproduction (Mitosis and Meiosis)Document25 pagesANPH-M1-CU2. The Cell & Cellular Metabolism and Reproduction (Mitosis and Meiosis)Angelo SoteroNo ratings yet
- Session 1,2 - Human Organism Cell Structures and Their FunctionsDocument92 pagesSession 1,2 - Human Organism Cell Structures and Their FunctionsalamisjealdenNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Ch. 3 NotesDocument8 pagesUnit 1 Ch. 3 Notesanthony.brown2No ratings yet
- 1-4 Fertilization & Fetal DevelopmentDocument9 pages1-4 Fertilization & Fetal DevelopmentElla DionedaNo ratings yet
- Transport Across The Cell MembraneDocument16 pagesTransport Across The Cell MembraneJagruti MaratheNo ratings yet
- MODULE 1.3 Cell Membrane TransportDocument11 pagesMODULE 1.3 Cell Membrane TransportBrandon James SevillaNo ratings yet
- Science 2.1 ReviewDocument6 pagesScience 2.1 ReviewInes GarciaNo ratings yet
- Physiological Practical 1Document4 pagesPhysiological Practical 1Khezia ChalweNo ratings yet
- Fertilization and Fetal DevelopmentDocument50 pagesFertilization and Fetal DevelopmentMark Ludwig Labastida100% (1)
- Anaphy Lesson IDocument3 pagesAnaphy Lesson IPerpolNo ratings yet
- Cell Maintain A BalanceDocument26 pagesCell Maintain A BalanceAchRudiNNo ratings yet
- General Biology 1 Self-Learning Packet Preliminaries Module # 4-Cell TransportDocument9 pagesGeneral Biology 1 Self-Learning Packet Preliminaries Module # 4-Cell TransportGi GiNo ratings yet
- The Shape of Life: Genes, Development, and the Evolution of Animal FormFrom EverandThe Shape of Life: Genes, Development, and the Evolution of Animal FormNo ratings yet
- Week 4 Practice ExamDocument24 pagesWeek 4 Practice ExamRomo AnthonyNo ratings yet
- W04 Directed Study AccessibleAnthony Romo OptionDocument2 pagesW04 Directed Study AccessibleAnthony Romo OptionRomo AnthonyNo ratings yet
- BIO 230 Exam 1 ReviewDocument31 pagesBIO 230 Exam 1 ReviewRomo AnthonyNo ratings yet
- Anthony Romo Rel200 - Document - Plptemplate FITNESS XDCMXDDocument5 pagesAnthony Romo Rel200 - Document - Plptemplate FITNESS XDCMXDRomo AnthonyNo ratings yet
- Anthony Romo Rel200 - Document - Plptemplate FITNESS XDDocument4 pagesAnthony Romo Rel200 - Document - Plptemplate FITNESS XDRomo AnthonyNo ratings yet
- Hs420 Document InterventionsTableDocument2 pagesHs420 Document InterventionsTableRomo AnthonyNo ratings yet
- Gulbrandsen Master PDFDocument100 pagesGulbrandsen Master PDFRomo AnthonyNo ratings yet