Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Let's Have A Review!: When Jim Studied in The Sweet Shop For His
Let's Have A Review!: When Jim Studied in The Sweet Shop For His
Uploaded by
Alita Leal Leguro-Delos Santos0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
31 views22 pagesThis document defines and provides examples of four types of conjunctions: coordinating conjunctions, correlative conjunctions, subordinating conjunctions, and conjunctive adverbs. It lists the seven coordinating conjunctions and provides examples of how they connect independent clauses. It also defines correlative conjunctions and provides examples of how they connect similar words or groups of words in pairs. Subordinating conjunctions introduce or signal adverbial clauses and connect unequal ideas. Finally, conjunctive adverbs function as connectors between independent clauses.
Original Description:
Original Title
CONJUNCTIONS
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document defines and provides examples of four types of conjunctions: coordinating conjunctions, correlative conjunctions, subordinating conjunctions, and conjunctive adverbs. It lists the seven coordinating conjunctions and provides examples of how they connect independent clauses. It also defines correlative conjunctions and provides examples of how they connect similar words or groups of words in pairs. Subordinating conjunctions introduce or signal adverbial clauses and connect unequal ideas. Finally, conjunctive adverbs function as connectors between independent clauses.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
31 views22 pagesLet's Have A Review!: When Jim Studied in The Sweet Shop For His
Let's Have A Review!: When Jim Studied in The Sweet Shop For His
Uploaded by
Alita Leal Leguro-Delos SantosThis document defines and provides examples of four types of conjunctions: coordinating conjunctions, correlative conjunctions, subordinating conjunctions, and conjunctive adverbs. It lists the seven coordinating conjunctions and provides examples of how they connect independent clauses. It also defines correlative conjunctions and provides examples of how they connect similar words or groups of words in pairs. Subordinating conjunctions introduce or signal adverbial clauses and connect unequal ideas. Finally, conjunctive adverbs function as connectors between independent clauses.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 22
●Clause -
a group of words that includes a subject and
a verb to form a simple sentence or only part of a
sentence.
❑ Independent Clause - An independent clause is a
Let’s group of words that contains a subject and verb and
expresses a complete thought.
have a ⮚Jim studied in the Sweet Shop for his chemistry quiz.
❑Dependent Clause - A dependent clause is a group of
review! words that contains a subject and verb but does not
express a complete thought. A dependent clause
cannot be a sentence.
⮚When Jim studied in the Sweet Shop for his
chemistry quiz.
CONJUNCTION
S
Are words used to connect
other words or group of
words.
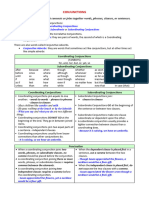
●Coordinating Conjunctions
FOUR TYPES OF ●Correlative Conjunctions
CONJUNCTION
S ●Subordinating Conjunctions
●Conjunctive Adverbs
Coordinating Conjunctions
Connect similar kinds of words or
similar groups of words.
They can join two verbs, two
nouns, two adjectives, two
phrases, or two independent
clauses.
For
And
7
Nor
Coordinating But
Conjunctions
Or
Yet
So
●Hunting songs are
considered special
purpose poems, for they
Examples: are closely connected
specifically with hunting.
●The dog barked but
wagged his tail.
The best way to remember the
seven coordinating conjunctions
is by using the
acronym FANBOYS.
Correlative Conjunctions
It also connects similar
words or group of
words. However, they
always appear in pairs.
both … and
either … or
Correlative
Conjunctions neither… nor
not only … but also
whether … or
●Work songs are not only sung
while a labourer works or
performs a task but they also
Examples: express the labourer’s
sentiments about his/her job
and working conditions.
●He lost both the necklace and
the ring.
Subordinate Conjunctions
-Connect two unequal ideas- a
dependent clause and independent
clause. This connection results to
construct a complex sentence.
-Introduce or signal adverbial
clause.
⮚They show or illustrate
the importance of the
Functions of independent clause.
Subordinate
Conjunctions
⮚They provide a
transition between two
ideas in the same
sentence.
SUBORDINATE CONJUCTIONS
After In order that Till Whether
Although Lest Unless While
As No matter Until Who
Because So that What Why
Before Since When Which
But that Supporting Whenever Wherever
Even though Than Where Though
How That Whereas If
●As the rain ended, a
rainbow appeared.
Examples: ●Hunters often celebrate
their victory after they
have made a successful
hunt.
Conjunctive Adverbs
- These are the adverbs that function as
conjunction and connectors.
- they hook up or link two independent
clauses.
- when it is being used to connect two main
ideas, a period (.) or a semi-colon( ;) is used.
A comma (,) usually follows after the
conjunctive adverb.
-it also introduces, interrupts, or concludes
an independent clause.
CONJUNCTIVE ADVERBS
Accordingly Consequentl Indeed Otherwise Still
y
Additionally Elsewhere Instead Therefore Then
Also Equally Likewise Thus Thereafter
Anyway Finally Meanwhile Next In
comparison
Besides Furthermore Moreover Now In contrast
Certainly Hence Nevertheless Similarly Namely
Comparativel In addition Rather Yet Nonetheless
y
●Hunting and military chants are
characterized by danger, pride
and glory. Moreover, both
chants convey the warriors’ and
Examples: hunters’ harsh struggle for
existence.
●Maureen would have come
with us; however she had a
project to finish.
You might also like
- Choice Words!: A Crash Course in Language ArtsFrom EverandChoice Words!: A Crash Course in Language ArtsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Conjunctions and It's Types-11Document7 pagesConjunctions and It's Types-11Mohammed AhamadNo ratings yet
- Grammar Mini-LessonDocument8 pagesGrammar Mini-Lessonapi-607962829No ratings yet
- Conjuction SDocument34 pagesConjuction SsandycamiNo ratings yet
- Q3 Module 5 ConjunctionsDocument61 pagesQ3 Module 5 ConjunctionsalvorjeanNo ratings yet
- Engl111 - Cm2-Cu6 Olfu ReviewerDocument2 pagesEngl111 - Cm2-Cu6 Olfu ReviewerelynpecsonNo ratings yet
- Conjunctions 1Document13 pagesConjunctions 1PICANHA foreverNo ratings yet
- CONJUNCTIONSDocument3 pagesCONJUNCTIONSMahmoud DaboulNo ratings yet
- PPT - Week 3 - Parts of Speech - Conj-Prep-IntjDocument27 pagesPPT - Week 3 - Parts of Speech - Conj-Prep-IntjNabil ImanNo ratings yet
- Types of SentencesDocument23 pagesTypes of SentencesAsma AslamNo ratings yet
- Teacher Notes For "Compound Sentences" About This LessonDocument9 pagesTeacher Notes For "Compound Sentences" About This Lessonapi-592289829No ratings yet
- 3.2 ConjunctionsDocument13 pages3.2 Conjunctionsmshamid AliNo ratings yet
- Compound Sentence: L/O/G/O By: Dwi Setiyadifandi Andikalussy Azizyahoby Robini 1 Sipil 2 PagiDocument7 pagesCompound Sentence: L/O/G/O By: Dwi Setiyadifandi Andikalussy Azizyahoby Robini 1 Sipil 2 Pagihaydarovj577No ratings yet
- Week 2 - Connecting Ideas Using Conjunctions in An Argumentative TextDocument31 pagesWeek 2 - Connecting Ideas Using Conjunctions in An Argumentative TextEicel PobleteNo ratings yet
- Conjuction SDocument14 pagesConjuction Smuhammadsaif shoukatNo ratings yet
- Syntax OutlinesDocument10 pagesSyntax OutlinesТаняNo ratings yet
- Conjunctive AdverbDocument5 pagesConjunctive Adverbapi-262484179No ratings yet
- Conjunctions and Transitions!Document9 pagesConjunctions and Transitions!Estefanía RamosNo ratings yet
- Conjuctions StudentsDocument13 pagesConjuctions StudentsJENITA BERLIAN NINDYASARINo ratings yet
- ConjunctionsDocument22 pagesConjunctionsFailan Mendez100% (1)
- Independant and Dependant ClausesDocument4 pagesIndependant and Dependant ClausesSage SultanNo ratings yet
- Independant and Dependant ClausesDocument4 pagesIndependant and Dependant ClausesSage SultanNo ratings yet
- Academic WritingDocument54 pagesAcademic WritingSantiago Suárez TovarNo ratings yet
- Conjunctions Prepositions InterjectionsDocument5 pagesConjunctions Prepositions InterjectionsAlmere AzurNo ratings yet
- Logical ConnectorsDocument23 pagesLogical ConnectorsGrace BullequeNo ratings yet
- Coordination PDFDocument3 pagesCoordination PDFTamer ObeidNo ratings yet
- English Lesson 4Document10 pagesEnglish Lesson 4Erwin OsorioNo ratings yet
- Writing CivuDocument29 pagesWriting CivumarcosherrerauwuNo ratings yet
- Clause 3Document4 pagesClause 3abdellaouikarima55No ratings yet
- GrammarDocument14 pagesGrammarLogi CheminotNo ratings yet
- Topic:5 Parts of SpeechDocument25 pagesTopic:5 Parts of SpeechVIMAL NAIR SURESHNo ratings yet
- Using Conjunctions: Hard Time With The Homework, Both and Are The Correlative Conjunctions.)Document2 pagesUsing Conjunctions: Hard Time With The Homework, Both and Are The Correlative Conjunctions.)Skruzdelyte MielaNo ratings yet
- Conjunctions: By: Hizra Marisa S.IP M.SiDocument14 pagesConjunctions: By: Hizra Marisa S.IP M.SitariNo ratings yet
- Intermediate WritingPDF PDFDocument106 pagesIntermediate WritingPDF PDFGiulio BattistonNo ratings yet
- Fragments and Run-On: Ms. Asmaa MahmoudDocument21 pagesFragments and Run-On: Ms. Asmaa MahmoudShosho ShareenNo ratings yet
- Connective SDocument1 pageConnective SKaneki KenNo ratings yet
- Types of Sentences: Miss Sania SajjadDocument17 pagesTypes of Sentences: Miss Sania SajjadAhmed Raza TareenNo ratings yet
- Conjunction SDocument18 pagesConjunction SLyka DarvinNo ratings yet
- Coordination, Correlation, and Subordination: Coordinating ConjunctionsDocument3 pagesCoordination, Correlation, and Subordination: Coordinating ConjunctionsLidia StefNo ratings yet
- ConjuctionsDocument2 pagesConjuctionsUREÑA SALAS GUADALUPE ABIGAILNo ratings yet
- Adjectives and AdverbsDocument3 pagesAdjectives and AdverbsAleNo ratings yet
- Common Sentence ErrorsDocument4 pagesCommon Sentence ErrorsrishigivingawayNo ratings yet
- Ued 102 Cornell Lecture NotesDocument2 pagesUed 102 Cornell Lecture NotesAfaf HusniyahNo ratings yet
- Group 10 Conjunction: Name: Riezka Amalia 2151020261 Riska Anggraini 2151020266 Safira Latifa 2151020273Document15 pagesGroup 10 Conjunction: Name: Riezka Amalia 2151020261 Riska Anggraini 2151020266 Safira Latifa 2151020273Rahma Septiana putriNo ratings yet
- English Assignment 2Document8 pagesEnglish Assignment 2Zeeshan KhanNo ratings yet
- Co-Ordinating ConjuctionDocument8 pagesCo-Ordinating Conjuctionsheikhmahbub67No ratings yet
- Define Correlating ConjunctionDocument23 pagesDefine Correlating ConjunctionRemebhel Marie MendozaNo ratings yet
- Parts of SpeechDocument44 pagesParts of SpeechdelvinNo ratings yet
- Subordination: Subordination, Coordination, and PredicationDocument13 pagesSubordination: Subordination, Coordination, and PredicationKrishly RomanosNo ratings yet
- Phrase, Clause and Types of SentencesDocument8 pagesPhrase, Clause and Types of SentencesJorge Alberto Solórzano NavasNo ratings yet
- Basic Punctuation Rules Basic Punctuation Rules: CommasDocument4 pagesBasic Punctuation Rules Basic Punctuation Rules: CommasLuigi OliNo ratings yet
- Aguirre Ronald Jonh M.Document33 pagesAguirre Ronald Jonh M.MELCHOR RUFONNo ratings yet
- Language Study GuideDocument4 pagesLanguage Study Guidekimka2007No ratings yet
- Types of Sentences 1Document5 pagesTypes of Sentences 1Babar HussainNo ratings yet
- Conjunction SDocument2 pagesConjunction Ssubtitle kurdiNo ratings yet
- Compound Sentence Group 4: Candra Arsyawan Evi Oktaviani Firman Rizky Ananda Yona NadiaDocument15 pagesCompound Sentence Group 4: Candra Arsyawan Evi Oktaviani Firman Rizky Ananda Yona NadiaCandra ArsyawanNo ratings yet
- Conjunctions Lesson Plan For Grade 4Document20 pagesConjunctions Lesson Plan For Grade 4prateek93153No ratings yet
- Helen's Work. Do Not Delete !!Document6 pagesHelen's Work. Do Not Delete !!helen_huang123No ratings yet
- Online Lecture Series: CSS, PMS, NTS, STS, Ots, Pts PPSC, SPSC, and All One Paper TestsDocument5 pagesOnline Lecture Series: CSS, PMS, NTS, STS, Ots, Pts PPSC, SPSC, and All One Paper TestsHajra bibiNo ratings yet
- RPT in EnglishDocument29 pagesRPT in EnglishJanila LopezNo ratings yet
- Passive VoiceDocument8 pagesPassive VoiceboskovdeNo ratings yet
- b2 Use of English Part 4 1Document53 pagesb2 Use of English Part 4 1martvseaNo ratings yet
- Lesson Notes 6Document195 pagesLesson Notes 6Cami Barn StjarnannaNo ratings yet
- AdverbulDocument18 pagesAdverbultamasraduNo ratings yet
- B1-1 (Nivel Cuatro)Document29 pagesB1-1 (Nivel Cuatro)Jorge A. BuitragoNo ratings yet
- Offering SomethingDocument11 pagesOffering Somethingputri rahayuNo ratings yet
- Practice With Adjective ClausesDocument7 pagesPractice With Adjective ClausesEmiliaNo ratings yet
- Examen Ingles 3 Modulo 1Document16 pagesExamen Ingles 3 Modulo 1luisNo ratings yet
- Verbs: Be,: Polyfunctional Have DODocument4 pagesVerbs: Be,: Polyfunctional Have DOAnnaNo ratings yet
- Causative VerbsDocument6 pagesCausative Verbsajit_ceoNo ratings yet
- ENGLISH OdtDocument17 pagesENGLISH Odtteresitas2011No ratings yet
- AdjectivesDocument3 pagesAdjectivesMeor SyazwanNo ratings yet
- Basic Sentence Stucture Pantang MenyerahDocument30 pagesBasic Sentence Stucture Pantang MenyerahGembleng SeretNo ratings yet
- English 10 Third QuarterDocument28 pagesEnglish 10 Third QuarterEHdz D. JameraNo ratings yet
- PrepositionDocument2 pagesPrepositionHannah Denise BatallangNo ratings yet
- Once Word Nerd Worksheet 3 February 23 2024Document1 pageOnce Word Nerd Worksheet 3 February 23 2024abantlea7No ratings yet
- Summary Morphology Chapter 4Document10 pagesSummary Morphology Chapter 4Maydinda Ayu PuspitasariNo ratings yet
- Kelompok 1 Diskusi 2-1-2Document10 pagesKelompok 1 Diskusi 2-1-2MuhamMad IrfanNo ratings yet
- New Pronouncing Di 01 Vel RichDocument714 pagesNew Pronouncing Di 01 Vel Richsingadishivu28No ratings yet
- Adjective Clauses in Complex SentencesDocument7 pagesAdjective Clauses in Complex Sentenceswildanum mukhalladahNo ratings yet
- Tabla de 200 Verbos ConjugadaDocument11 pagesTabla de 200 Verbos ConjugadaRamos Teodoro MiguelNo ratings yet
- Social Case Malayalam 05Document2 pagesSocial Case Malayalam 05Vinesh PvNo ratings yet
- Upper Intermediate - Unit 1 - Gerunds and InfinitivesDocument12 pagesUpper Intermediate - Unit 1 - Gerunds and InfinitivesAngie JacomeNo ratings yet
- Project 1 Unit 2 TestDocument13 pagesProject 1 Unit 2 Testkatalin szaboNo ratings yet
- Relative ClausesDocument3 pagesRelative ClausesJoana MamaniNo ratings yet
- Revised Tos To Be Followed in Developing The Pre Test in Mother TongueDocument6 pagesRevised Tos To Be Followed in Developing The Pre Test in Mother TongueJayleen Coy Sabling LadyongNo ratings yet
- Upsc Cds E: Study Material For EnglishDocument6 pagesUpsc Cds E: Study Material For EnglishShivamNo ratings yet
- ENG Answer Key.Document5 pagesENG Answer Key.Thalat Mohd0% (1)
- Repaso Grammar 2o BachDocument45 pagesRepaso Grammar 2o BachMar EscobarNo ratings yet
- 50 Verbos IrregularesDocument2 pages50 Verbos IrregularesViki PérezNo ratings yet